psych202 ch3
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Why do psychological researchers study genetics?
to better understand the biological basis that contributes to certain behaviors
Theory of evolution by natural selection
Charles Darwin proposes that organisms best suited for their environment will survive and reproduce, and those that are poorly suited will die off
Genetic variation
difference between individuals and contributes to a species' adaptation to its environment
Evolutionary psychology
focuses on how universal patterns of cognition and behavior have evolved over time
Behavioral geneticists
study how individual differences arise through interaction of genes and the environment (twin and adoption studies are a large focus)
Chromosomes
long strings of genetic material known as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
DNA
helix-shaped molecule made of nucleotide base pairs
Genes
sequences of DNA that control a number of traits, or visible characters
Traits
i.e. eye color, hair color
Alleles
a specific version of a gene; a gene may have multiple variations
Genotype
genetic makeup of the individual
Phenotype
individual's inherited physical characteristics - a combination of genetic and environmental influences
Dominant allele
variation of a gene that will result in a dominant phenotype, even in presence of other alleles (BB or Bb)
Recessive allele
variation of a gene that will result in a recessive phenotype only in the presence of two copies (bb)
Heterozygous
a combination of alleles for a given trait
Homozygous
two of the same allele
Mutation
a sudden, permanent change in a gene that can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect
Polygenic
traits that involve more than one gene
Range of reaction
our genes set the boundaries within which we can operate, and our environment interacts with genes to determine where in that range we will fall
(genes set limits on potential and the environment determines how much of that potential is achieved)
Genetic environmental correlation
genes influence environment, and our environment influences the expression of our genes; not only do the two interact, but they influence one another bidirectionally
Epigenetics
looks beyond the genotype itself and studies how genotype is expressed in different ways
(how one genotype can lead to many different phenotypes)
Epigenetic example
identical twins - develop from the same fertilized egg that splits, so genetic material is exactly the same; even with identical genes, there remains a large amount of variability in how gene expression unfolds through life
fraternal twins - develop from two different eggs fertilized by different sperm, so genetic material varies the same as it does with non-twin siblings
What are genes associated with?
Things such as temperament and a number of psych disorders; they affect our physical characteristics and behavioral characteristics
What are the two cell types of the nervous system?
glial cells and neurons
Glial cells
provide scaffolding on which the nervous system is built and provides insulation to neurons, transports nutrients and waste products, mediate immune responses
Neurons
information processors that are essential for all of the tasks of the nervous system
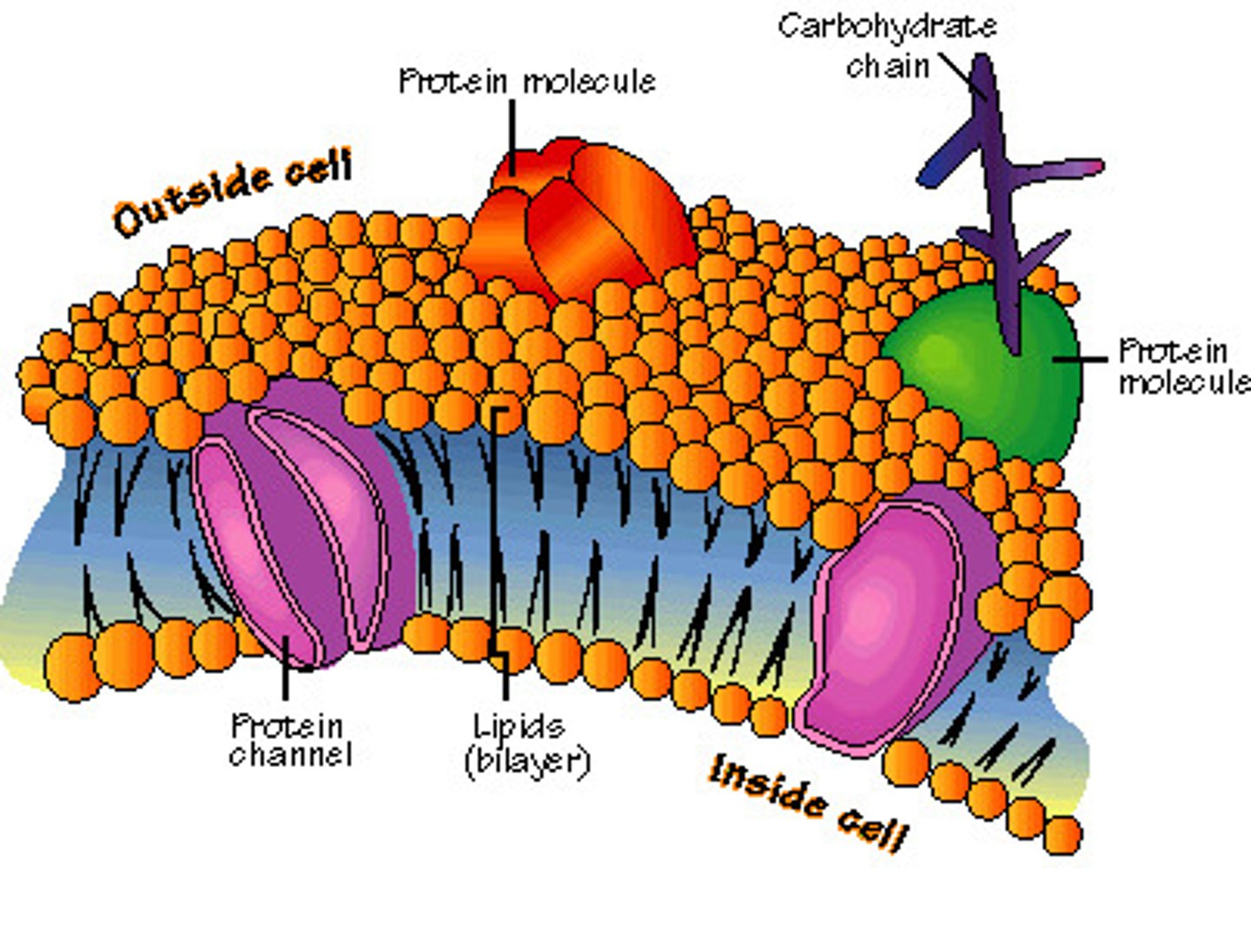
Cell membrane
semipermeable, allowing some smaller and not electrically charged molecules to pass through while larger, charged molecules cannot
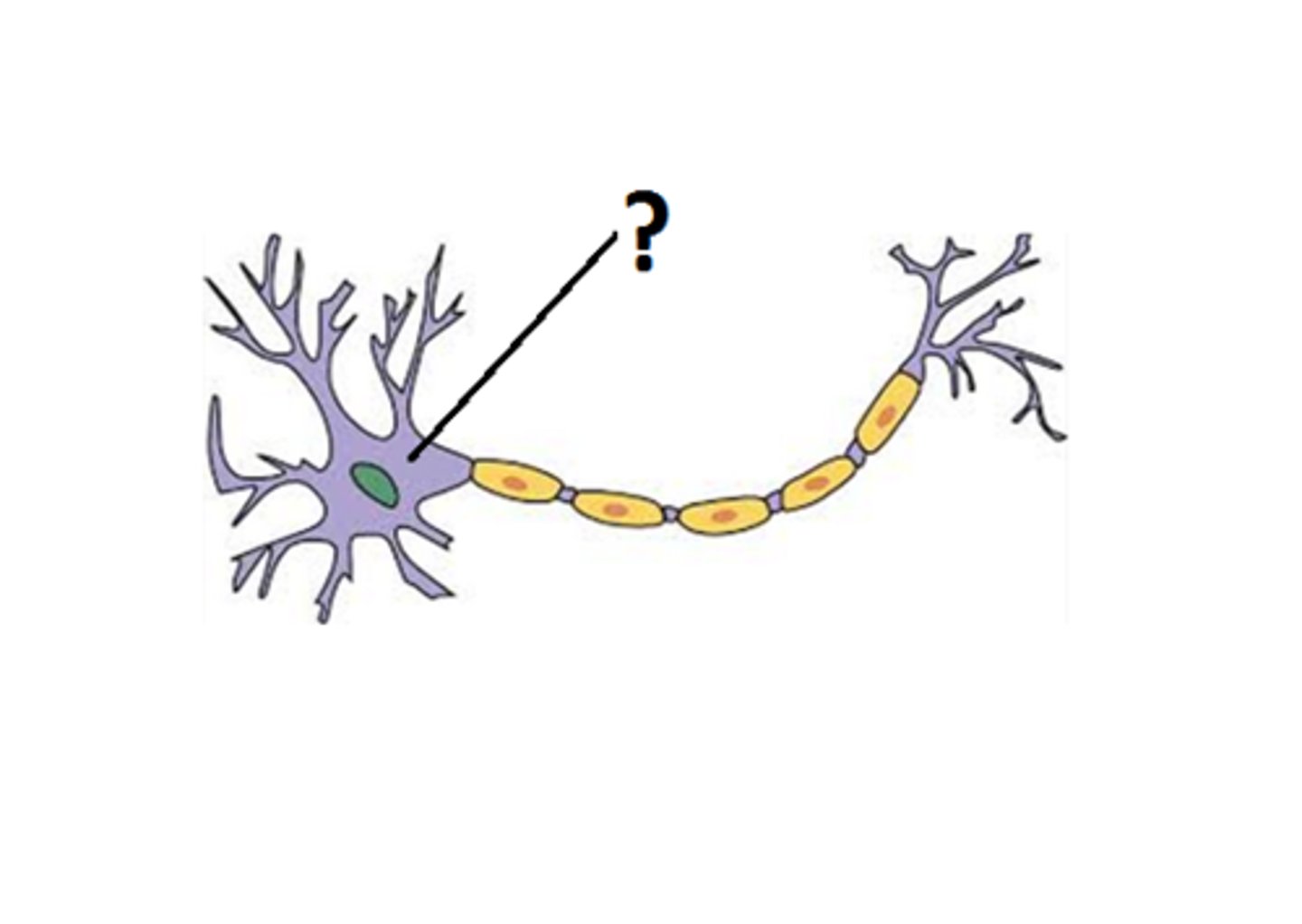
Soma
cell body of the neuron, where the nucleus is located; has branching extensions
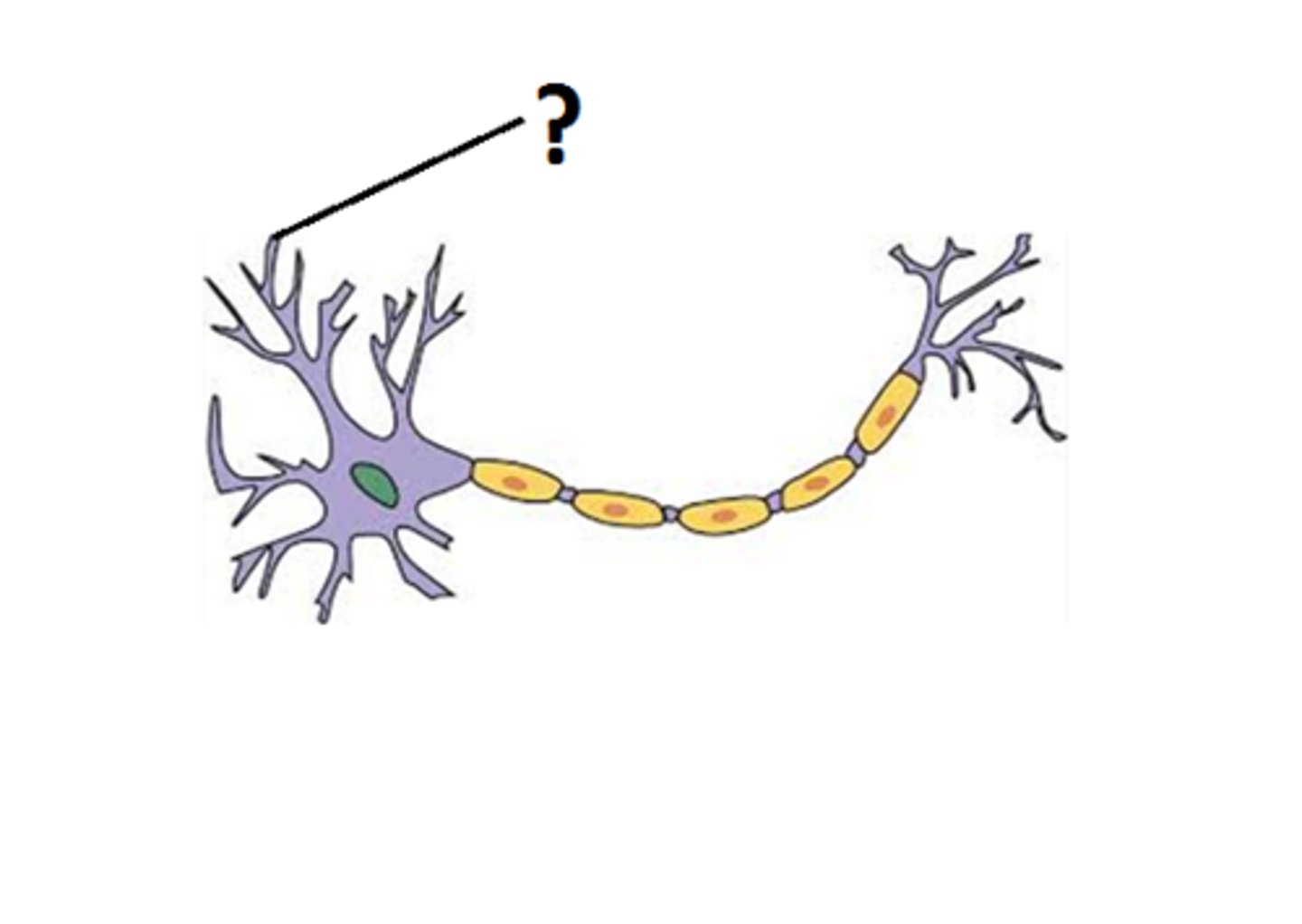
Dendrites
branching extensions of the soma; serve as input sites where signals are received from neurons
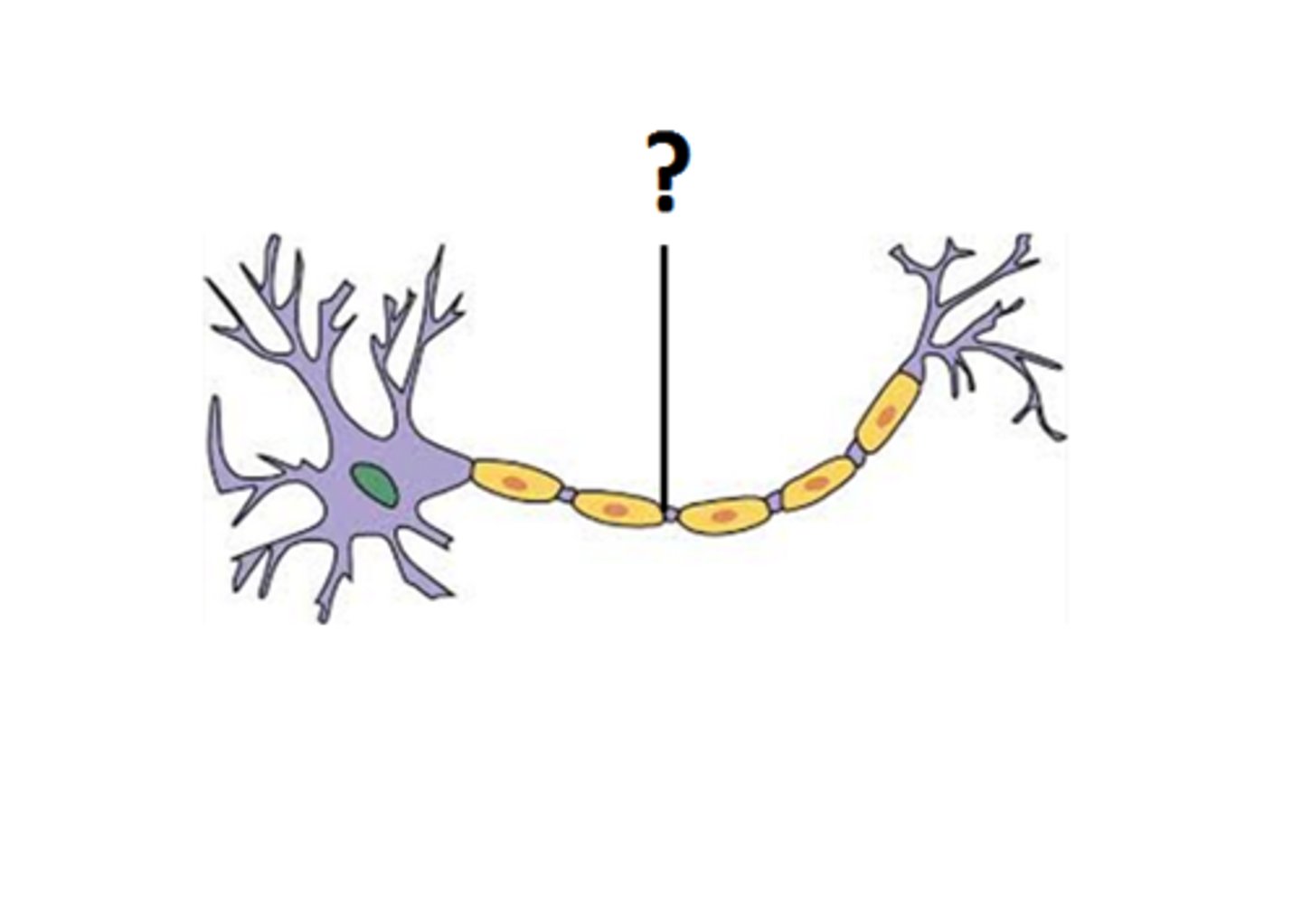
Axon
major extension of the neuron where electrical signals travel
Terminal buttons
the end of the axon that contains synaptic vesicles that house neurotransmitters
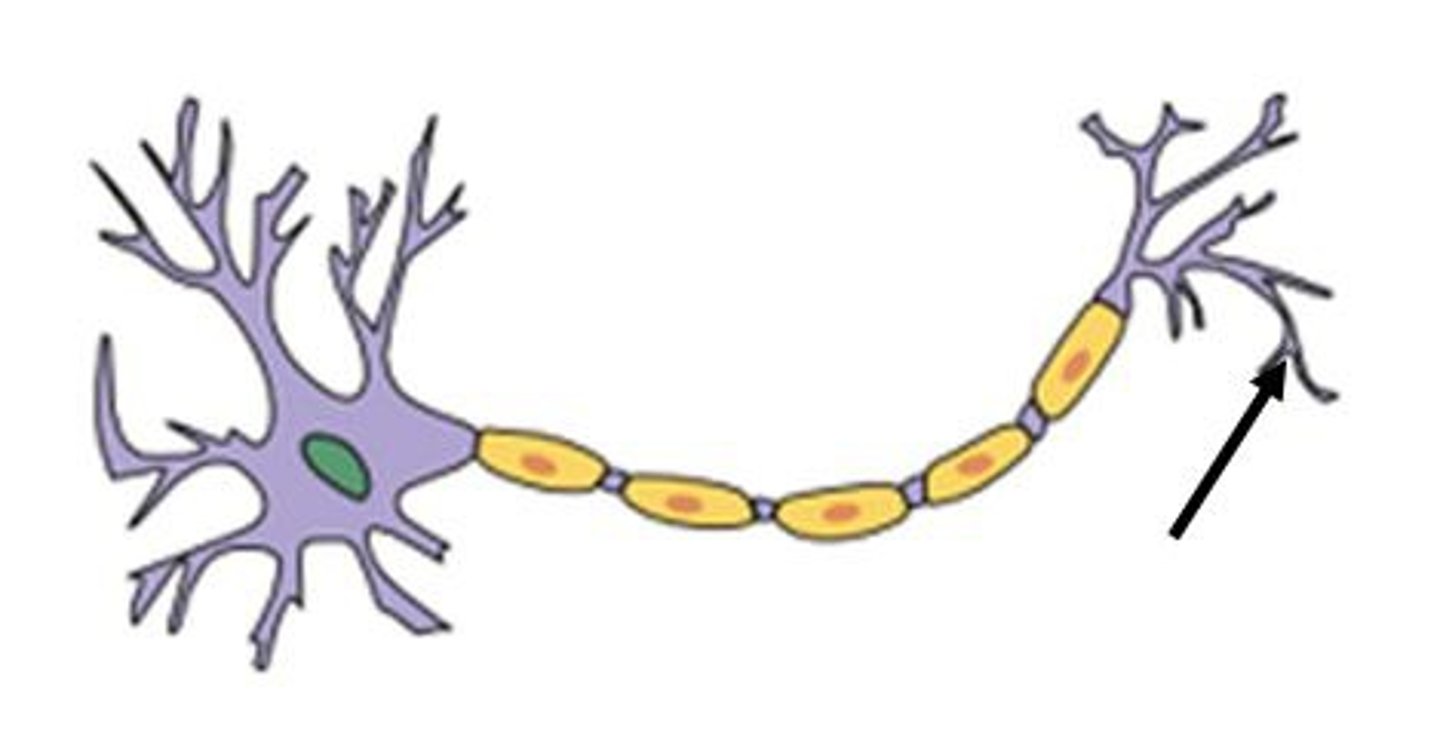
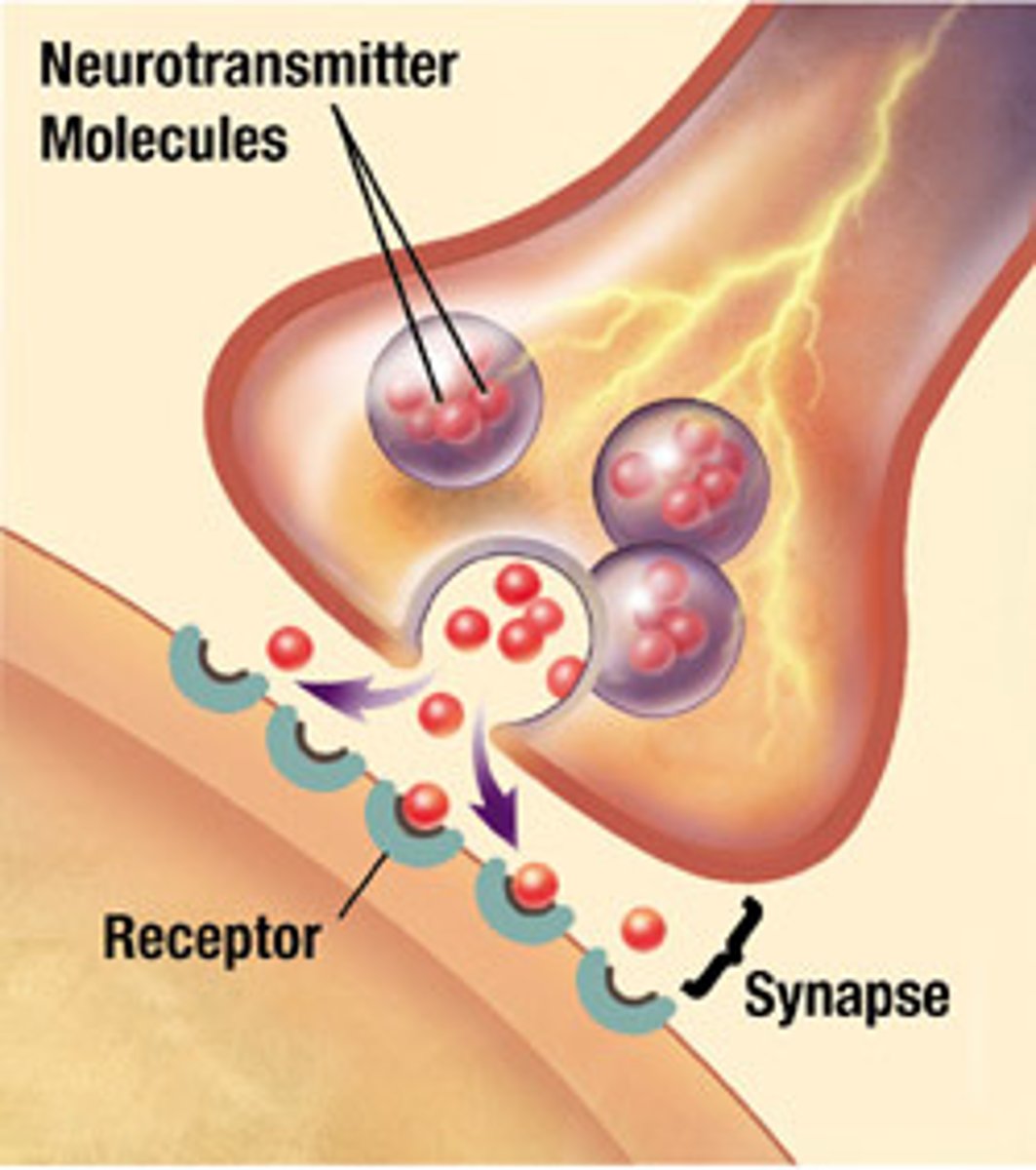
Neurotransmitters
the chemical messengers of the nervous system (i.e. dopamine, serotonin)
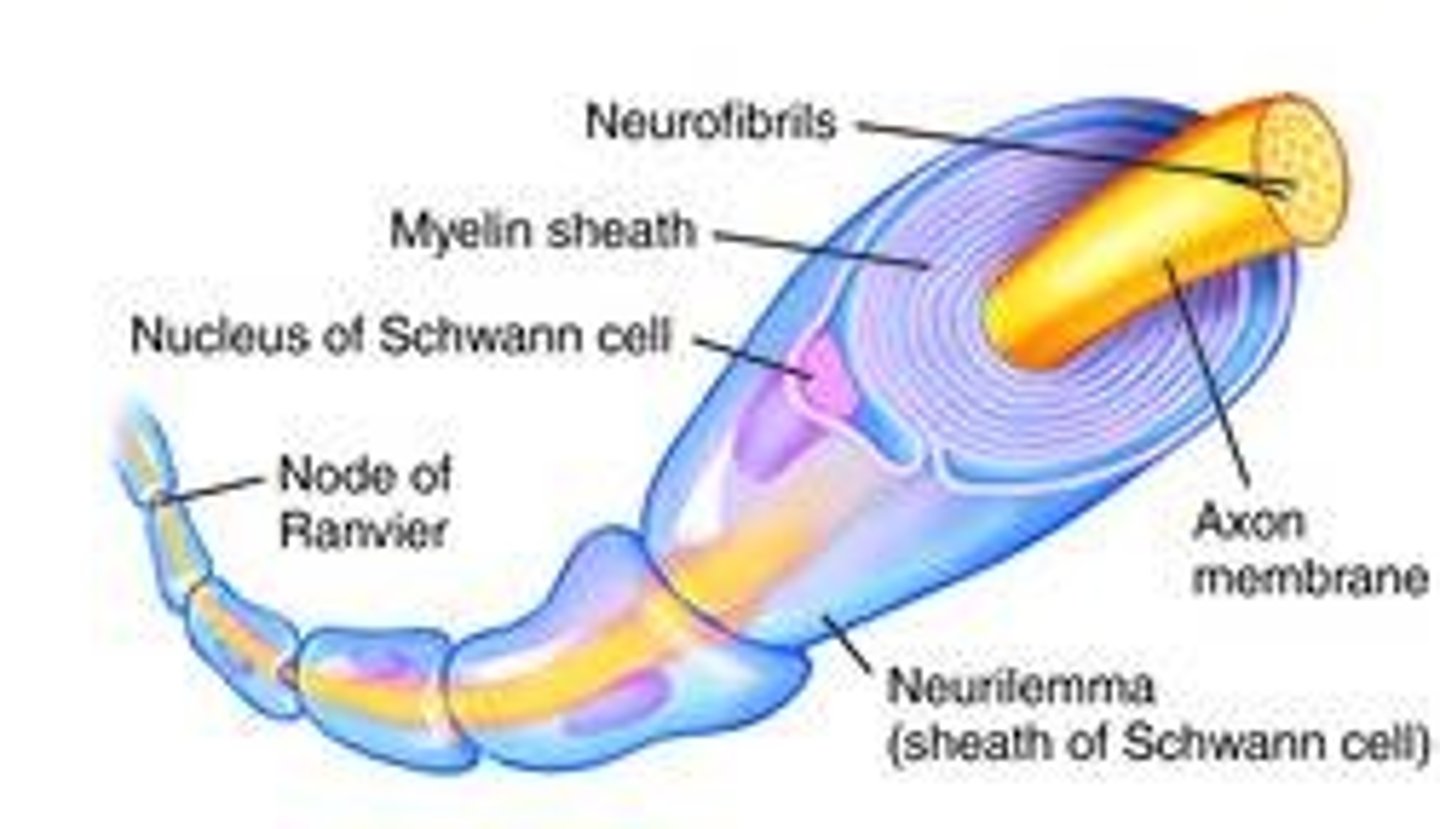
Myelin sheath
fatty substance made of glial cells that insulates the axon in segment and increases the speed of signal transmission
Synapse
small space between two neurons where communication occurs; neurotransmitters are released and travel across to bind with corresponding receptors of an adjacent neuron
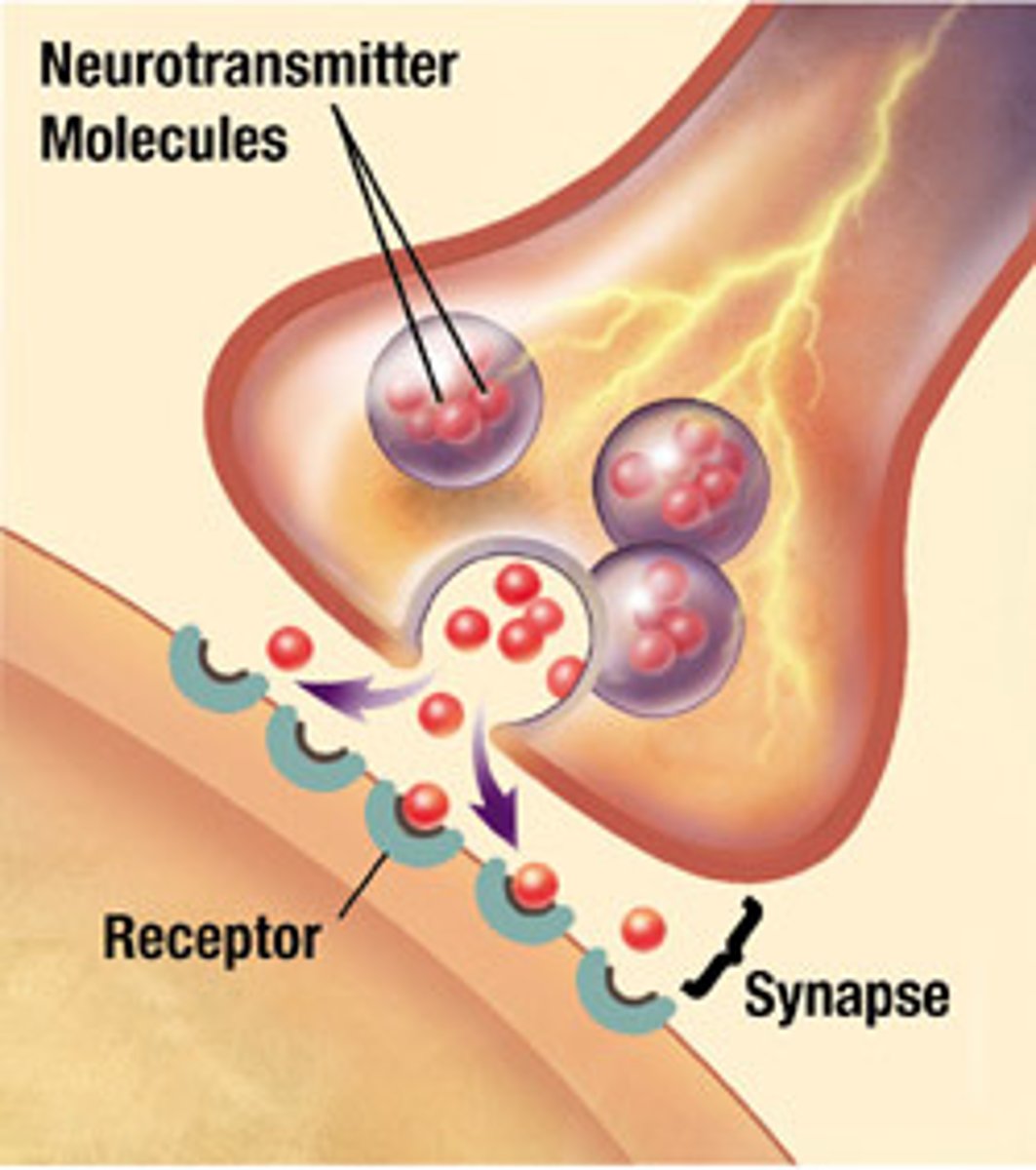
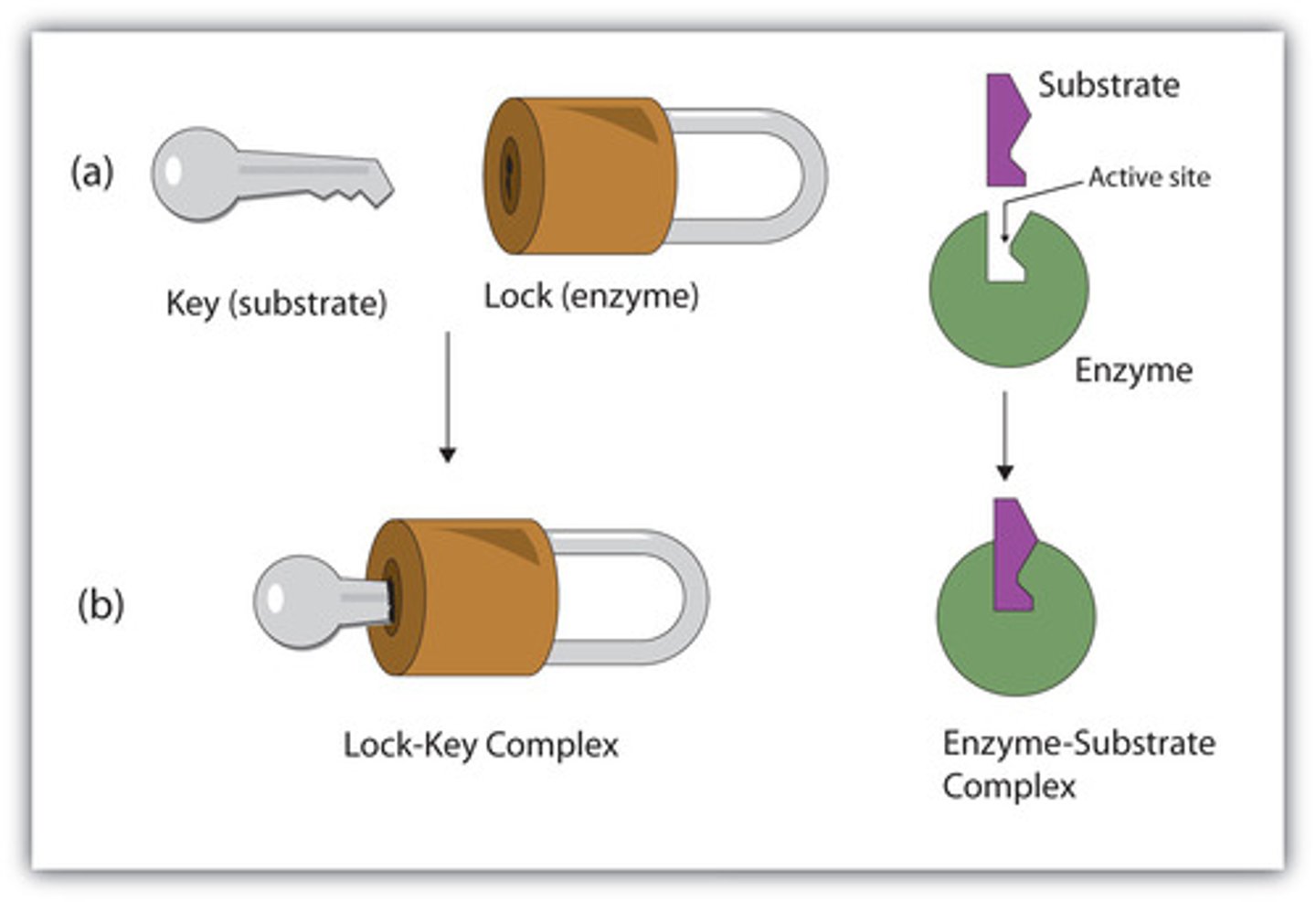
Receptors
proteins on cell surface where neurotransmitters attach, and their different shapes match different neurotransmitters
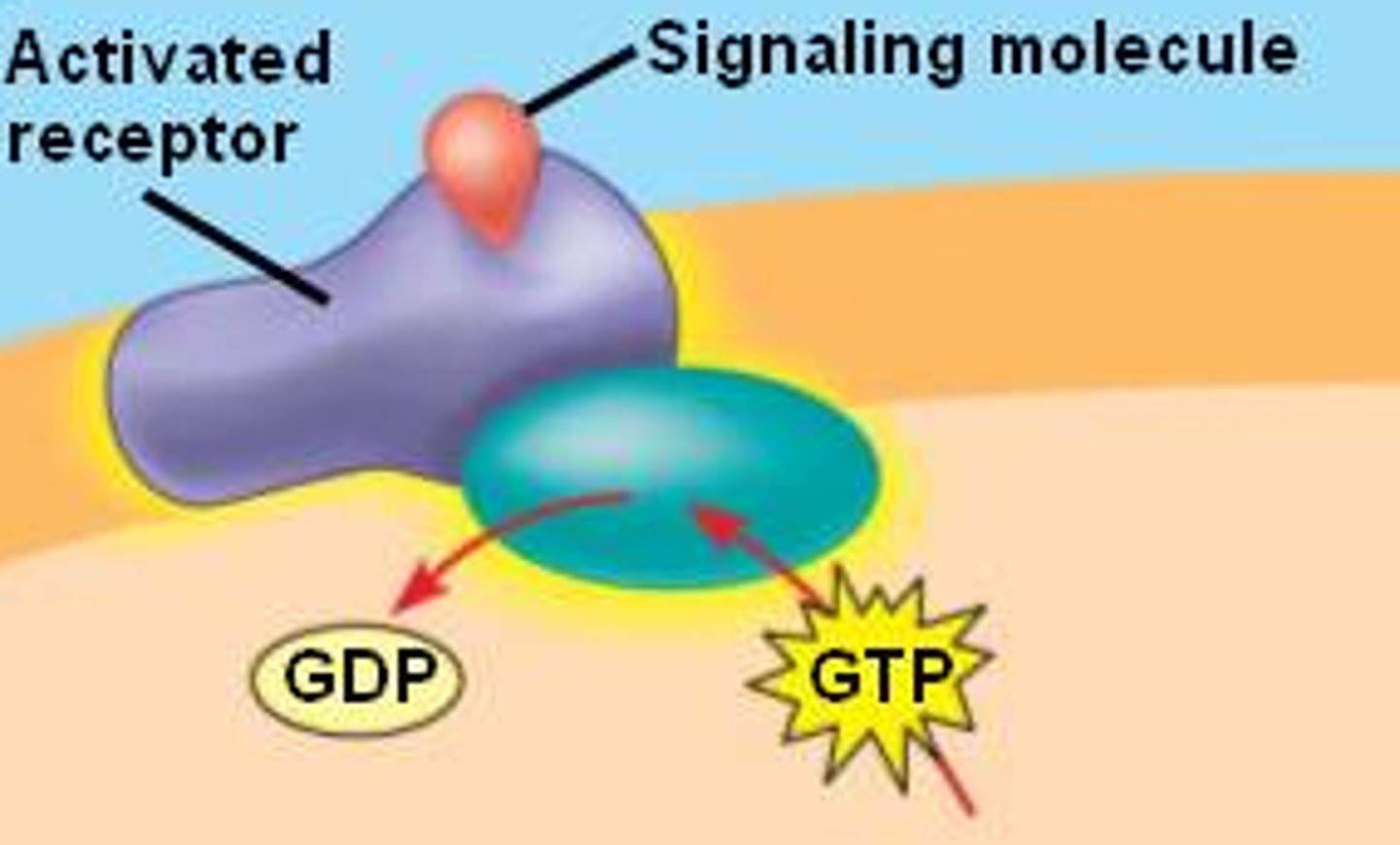
Lock-and-key relationship
relationship between neurotransmitters and the receptor, where connection is specific like a lock and key
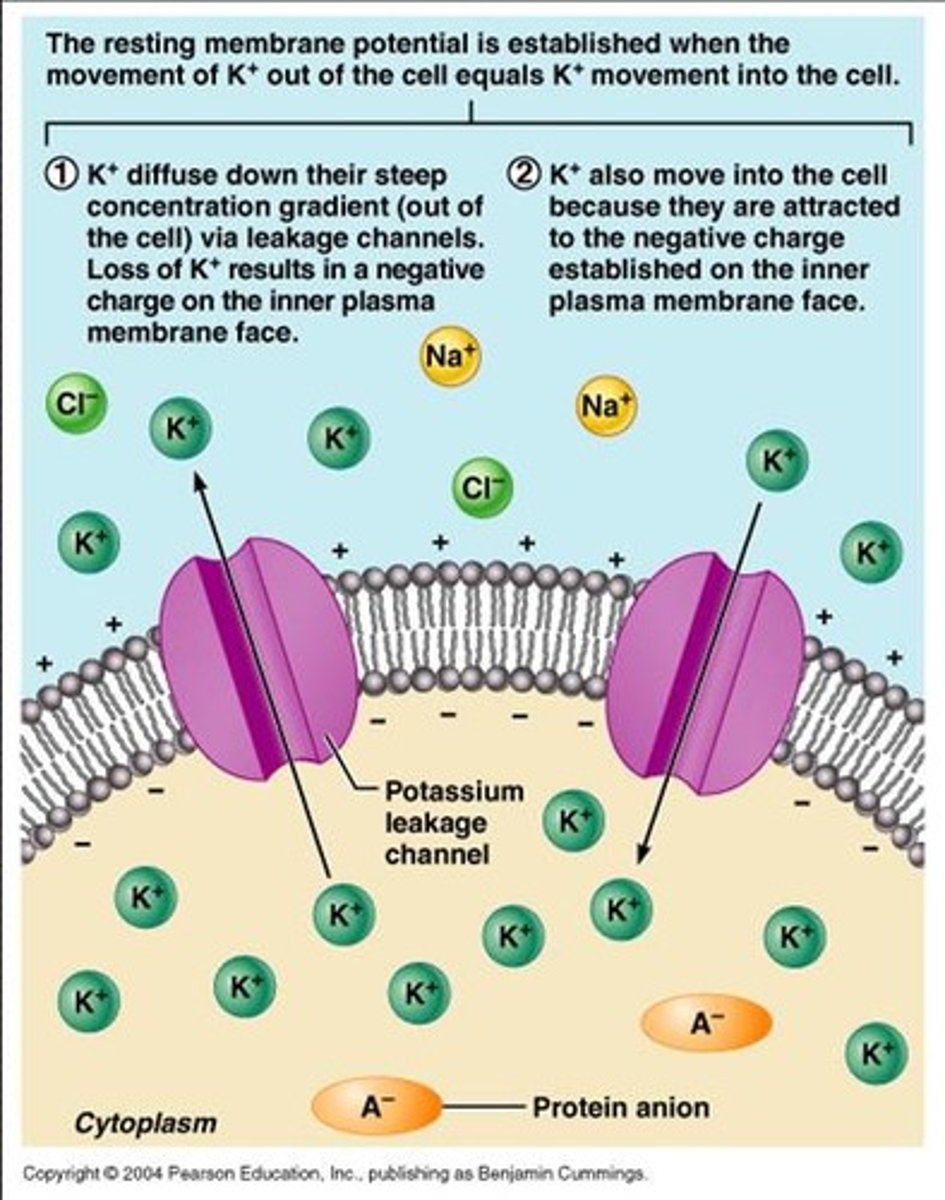
Why must the neuronal membrane keep the extracellular and intracellular fluid of the neuron separate?
the electrical signal passing through a neuron depends on these fluids being electrically different
Membrane potential
difference in charge across the membrane
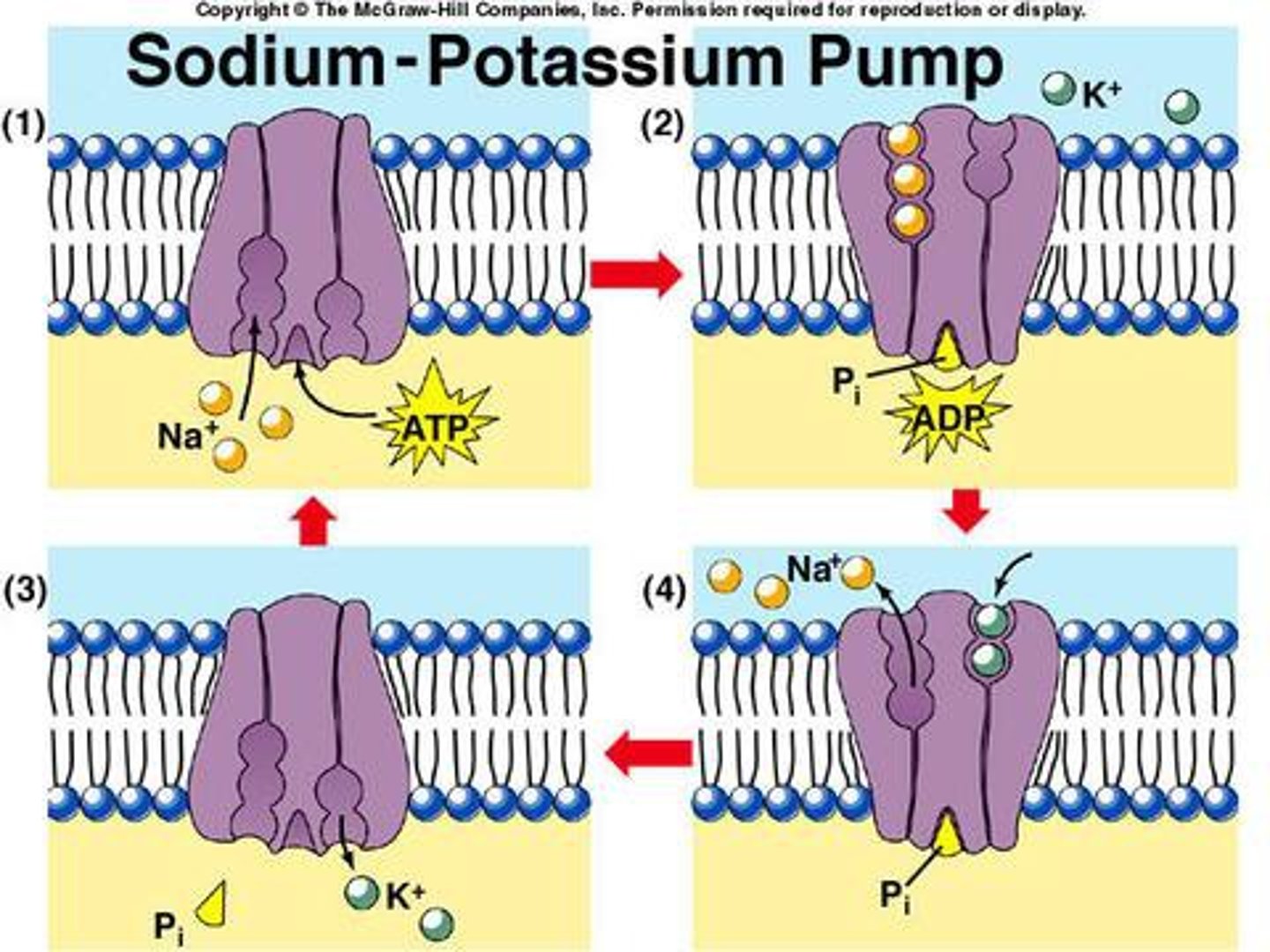
Resting potential
the relaxed state of a neuron between signals, where Na+ ions are in high concentration outside of the cell and K+ ions are in high concentration inside the cell;
The inside of the cell is slightly negatively charged compared to the outside, which provides an additional force on Na+ to move it into the cell
When do Na+ ions move into the cell?
When a neuron receives a signal at the dendrites and small gates open, allowing Na+ ions to move in
Threshold of excitation
the level of charge in the cell necessary for a neuron to become active (approx. -55 mV)
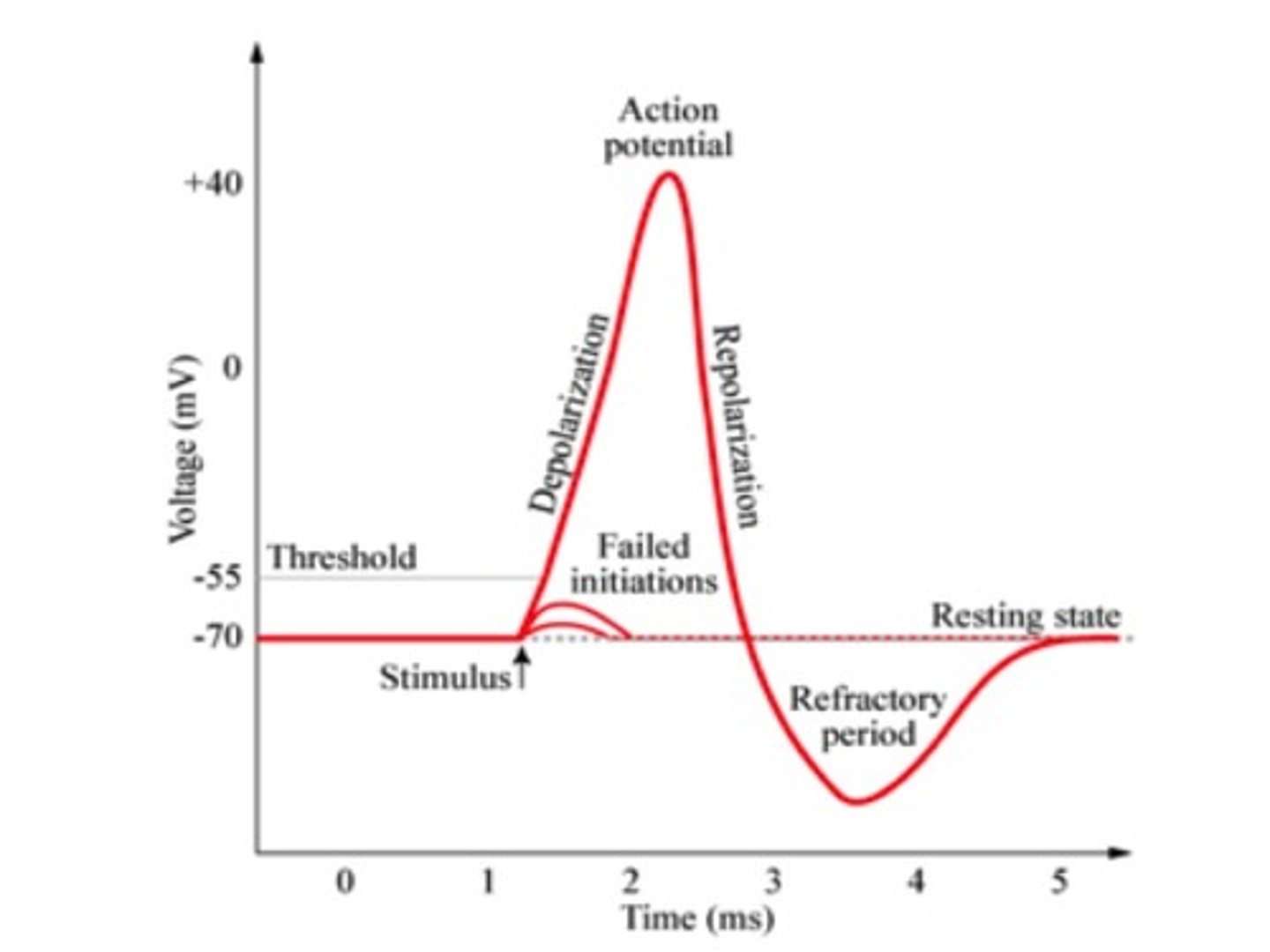
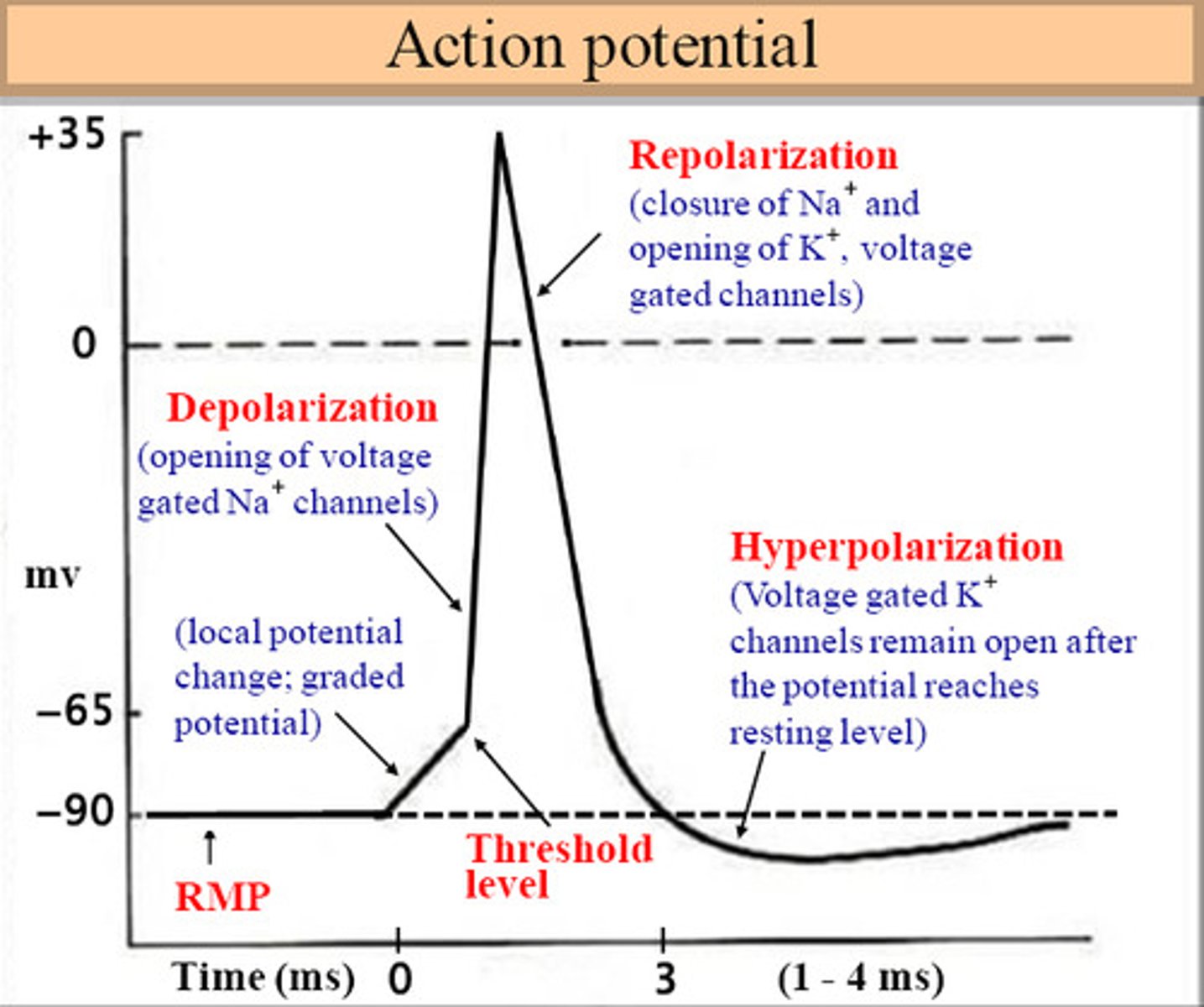
Action potential
an all-or-none phenomena where an electronic signal travels down a neuron like a wave
What happens during an action potential?
1) many pores open up, allowing an influx of Na+ ions to flood in; at peak action potential, or the most positive charge in the membrane, K+ pores open up and allow K+ ions to leave
2) as K+ ions leave the cell, the membrane repolarizes and becomes more negative
3) the cell membrane hyperpolarizes, becomes more negative than resting membrane potential
4) cell membrane returns to resting membrane potential (approx. 70mV)
What happens when an action potential reaches the terminal buttons?
synaptic vesicles release their neurotransmitters into the synapse; they travel across to bind to receptors on the dendrites of an adjacent neuron and the process repeats itself into a new neuron
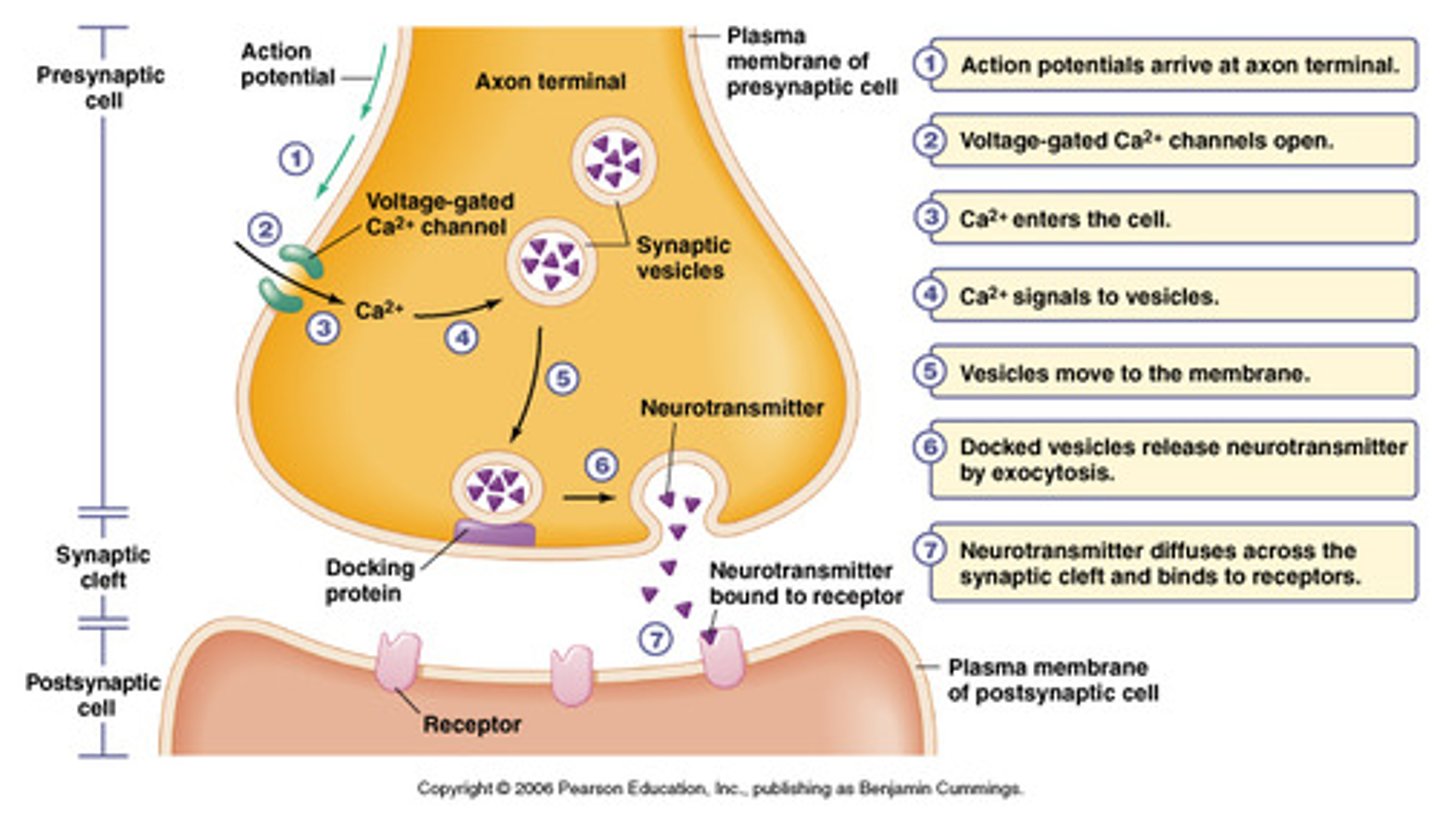
What are the two things that can happen to an unused neurotransmitter?
1) drift away and are broken down into inactive fragments
2) reabsorbed by reuptake
Reuptake
neurotransmitter pumped back into the neuron that released it in order to clear the synapse
Why is neuronal communication electrochemical?
1) the movement of an action potential down an axon is electrical
2) the movement of a neurotransmitter across a synapse is chemical
Biological perspective of psychology
psychological disorders are associated with an imblance in one or more neurotransmitter systems
Psychotropic medication
improve symptoms associated with psychological disorders, used to restore neurotransmitter balance
Psychoactive drug as an agonist
chemicals that mimic a neurotransmitter at the receptor site and thus strengthens its effects
Psychoactive drugs as an antagonist
blocks or impedes the normal activity of a neurotransmitter at the receptor
Reuptake inhibitors
prevent unused neurotransmitters from being transported back to the neuron, leaving more neurotransmitters in the synapse for a longer time, increasing its effects (agonist)
Depression and schizophrenia
associated with imbalance in one or more neurotransmitter systems
SSRIs
treatment for depression, prevent reuptake of serotonin to strengthen its effect and give it more time to interact with receptors on dendrites
Peripheral nervous system
connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body through a system of extending nerves
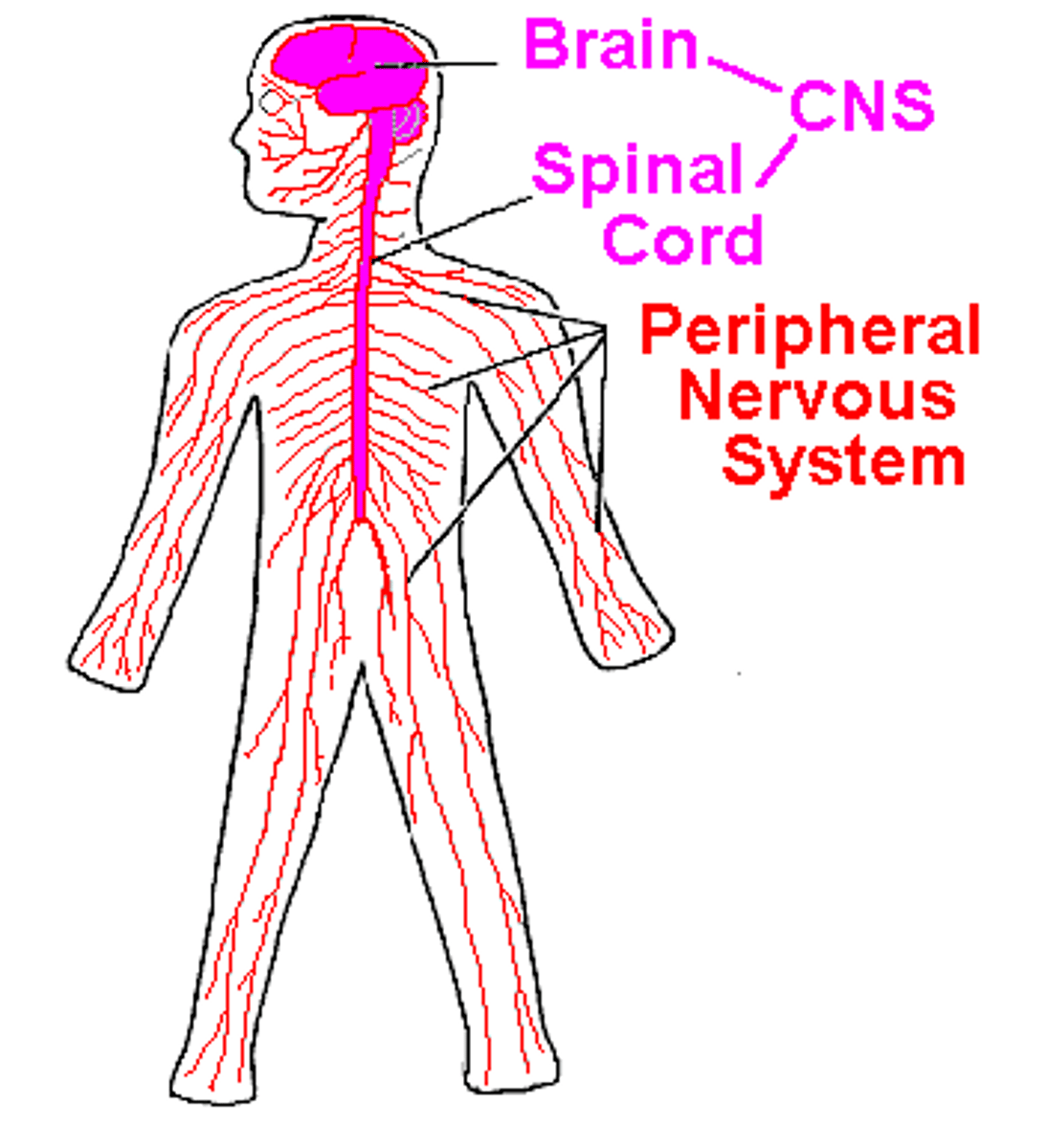
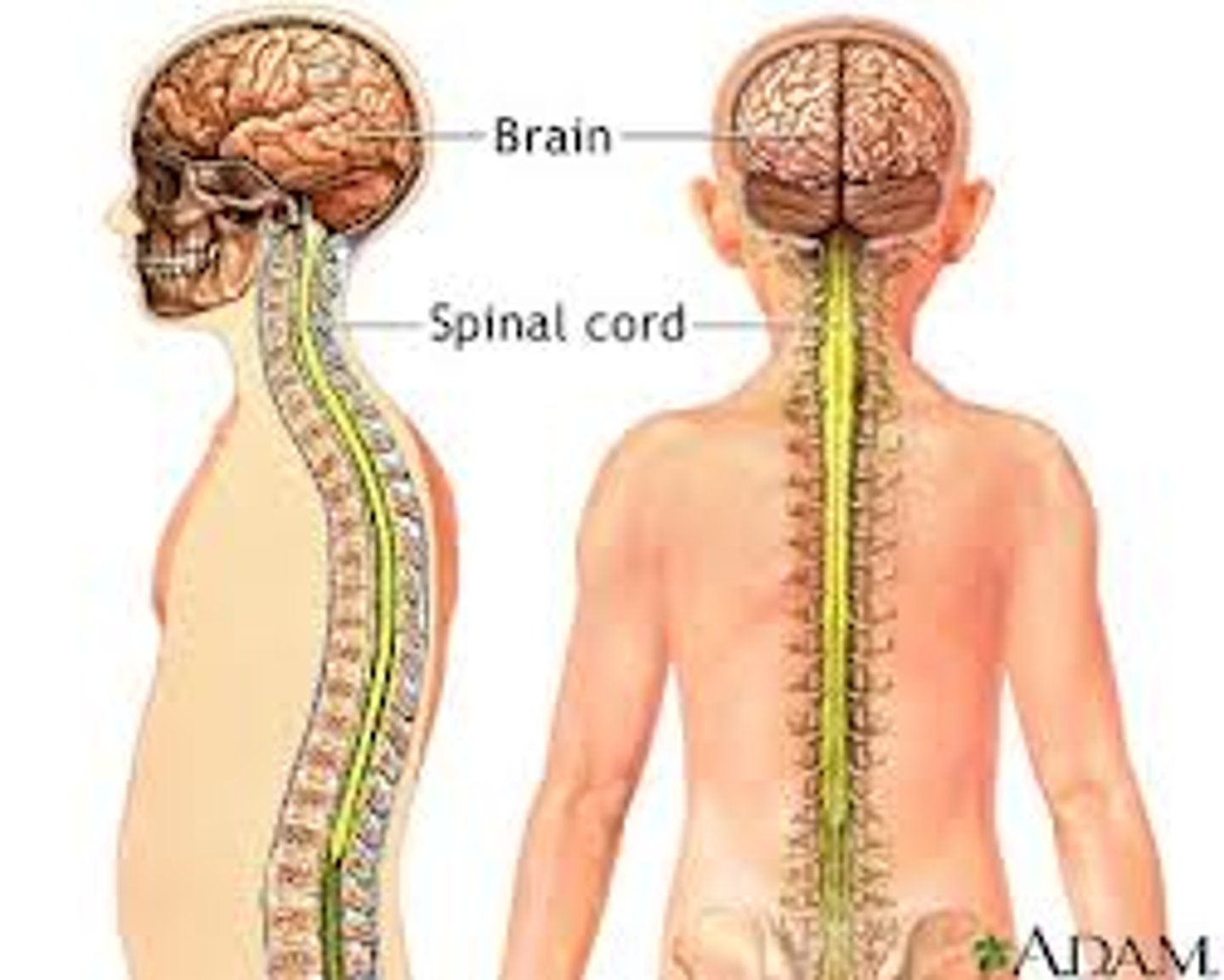
Central nervous system
the brain and spinal cord
Two subdivisions of the PNS
1) somatic nervous system
2) autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
(PNS) associated with activities traditionally thought of as conscious or voluntary
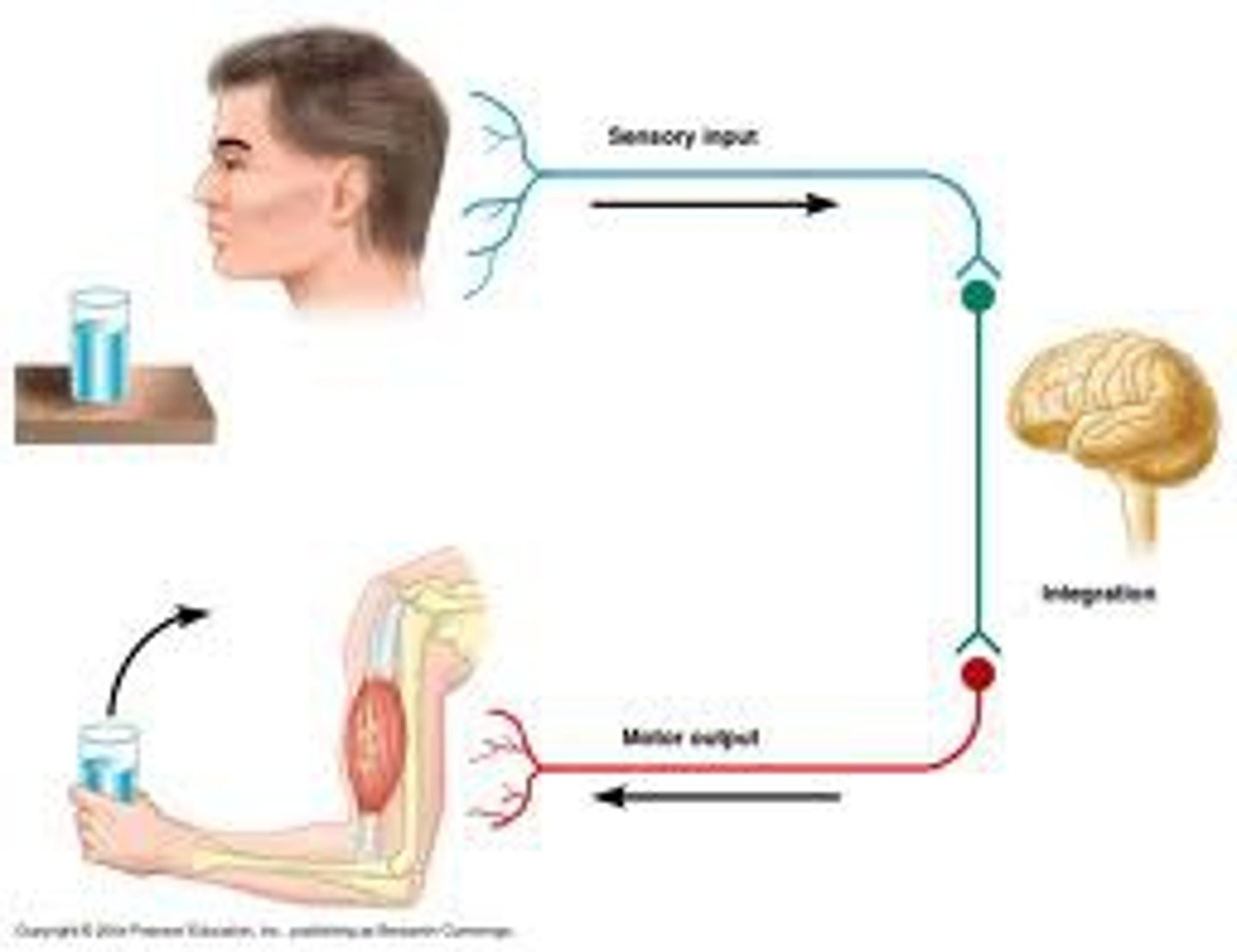
Motor neurons
carry instruction from CNS to the muscles - EFFERENT FIBERS
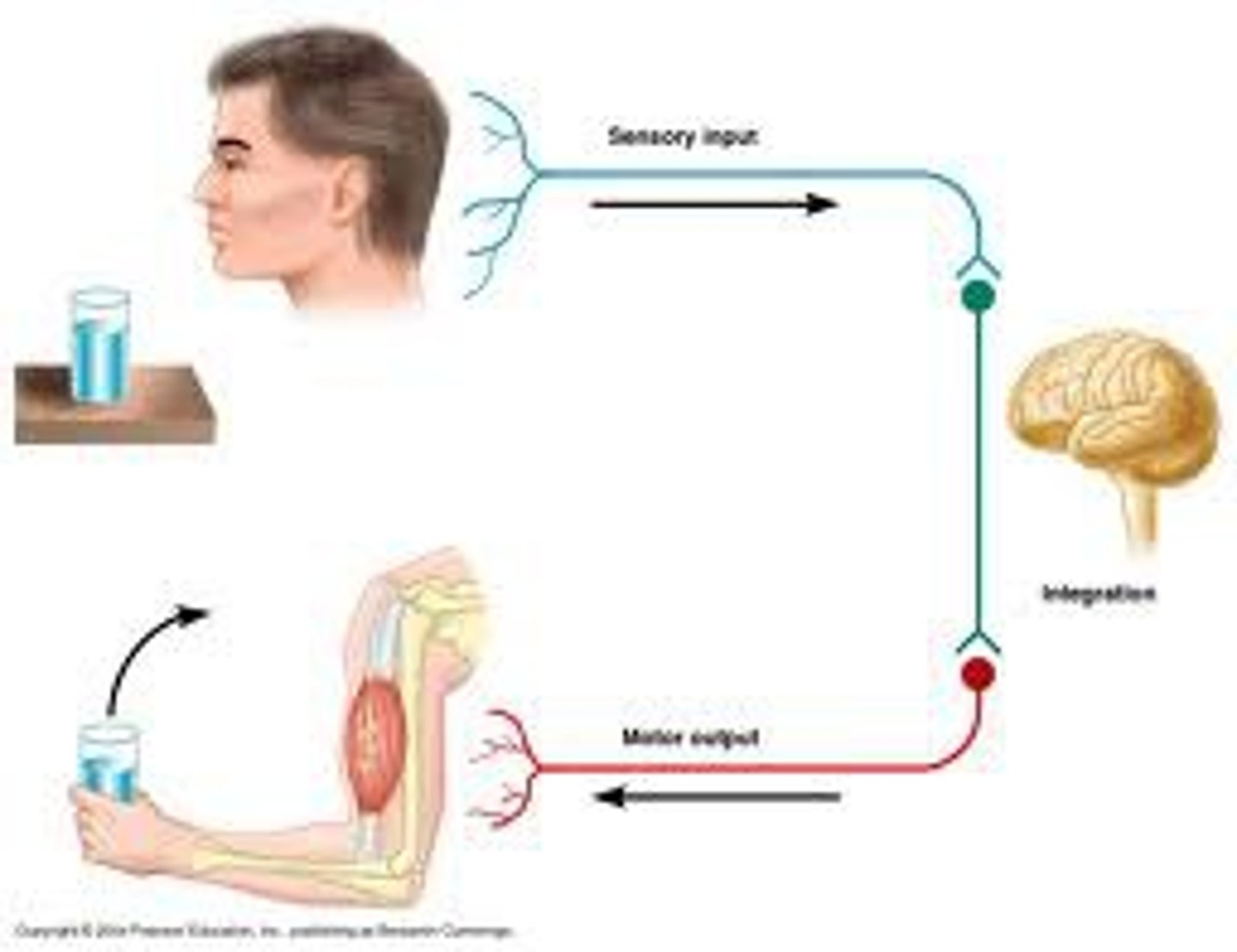
Sensory neurons
carries sensory information to the CNS - AFFERENT FIBERS
Autonomic nervous system
(PNS) controls our internal organs and glands, outside of the realm of voluntary control
Two subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system
1) sympathetic nervous system
2) parasympathetic nervous system
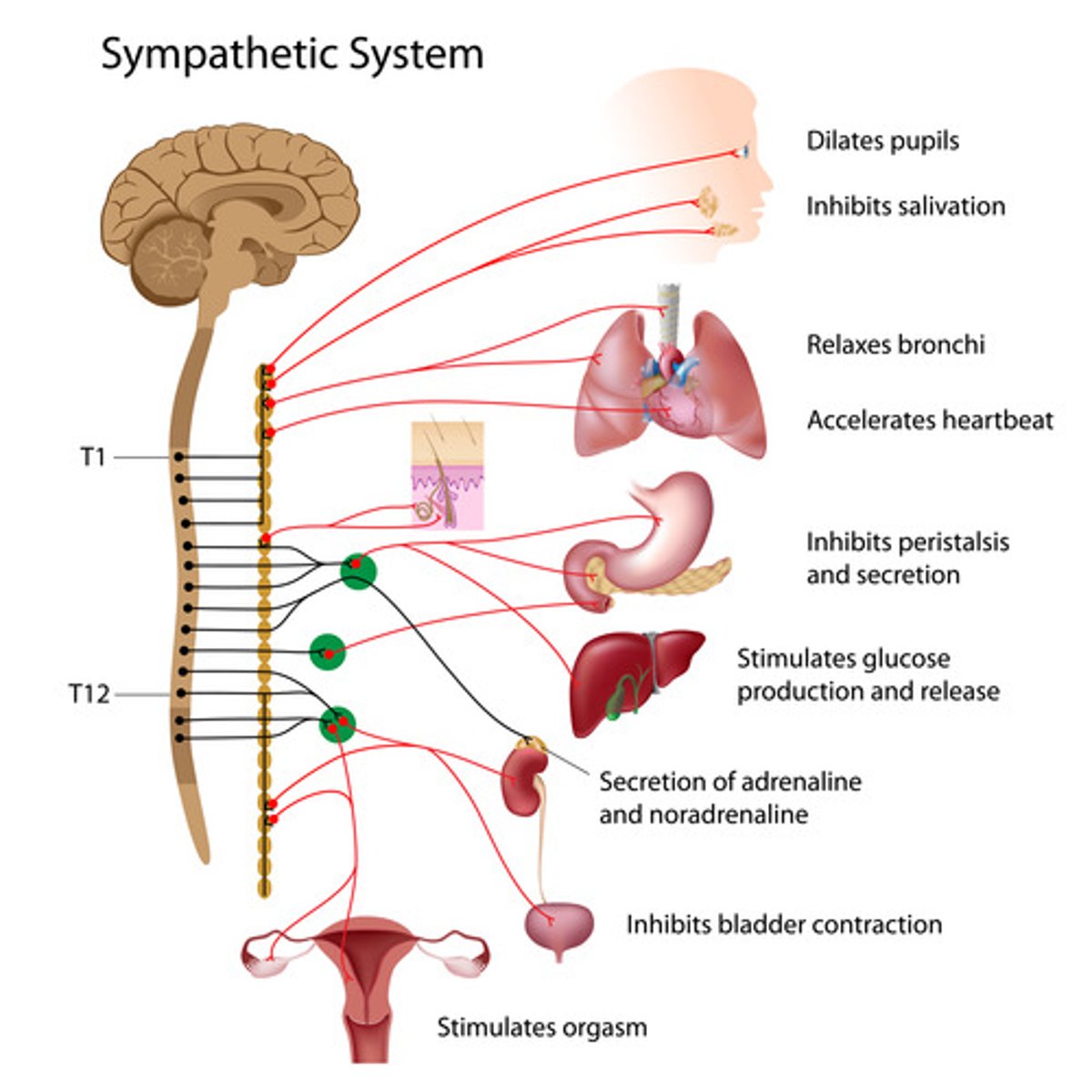
Sympathetic nervous system
preparing the body for stress-related activities
-dilate pupils, bronchi
-inhibit bladder, salivation, digestion
-increase heart rate, blood pressure, alertness
Parasympathetic nervous system
returning body to routine operations, relaxing the body
-constricts pupils, bronchi
-stimulate salivation, digestion, bladder
-decreased heart rate, blood pressure, alertness
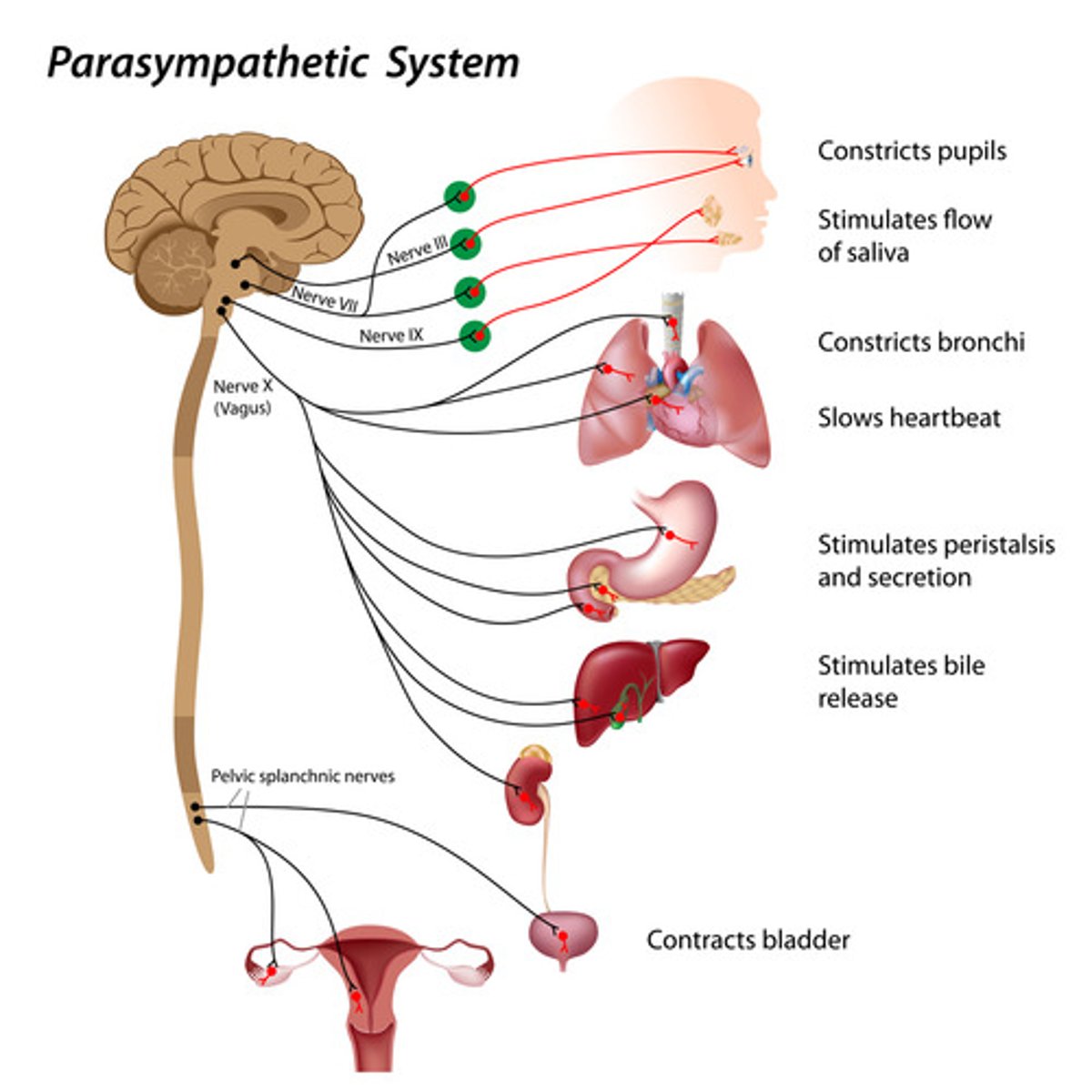
How do the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system work together?
they operate in tandem to maintain body's homeostasis
Homeostasis
state of equilibrium in which biological conditions (i.e. body temp) are maintained at optimal levels
Spinal cord
considered the relay station because it routes messages t the brain while also having its own system of automatic processes, or relfexes
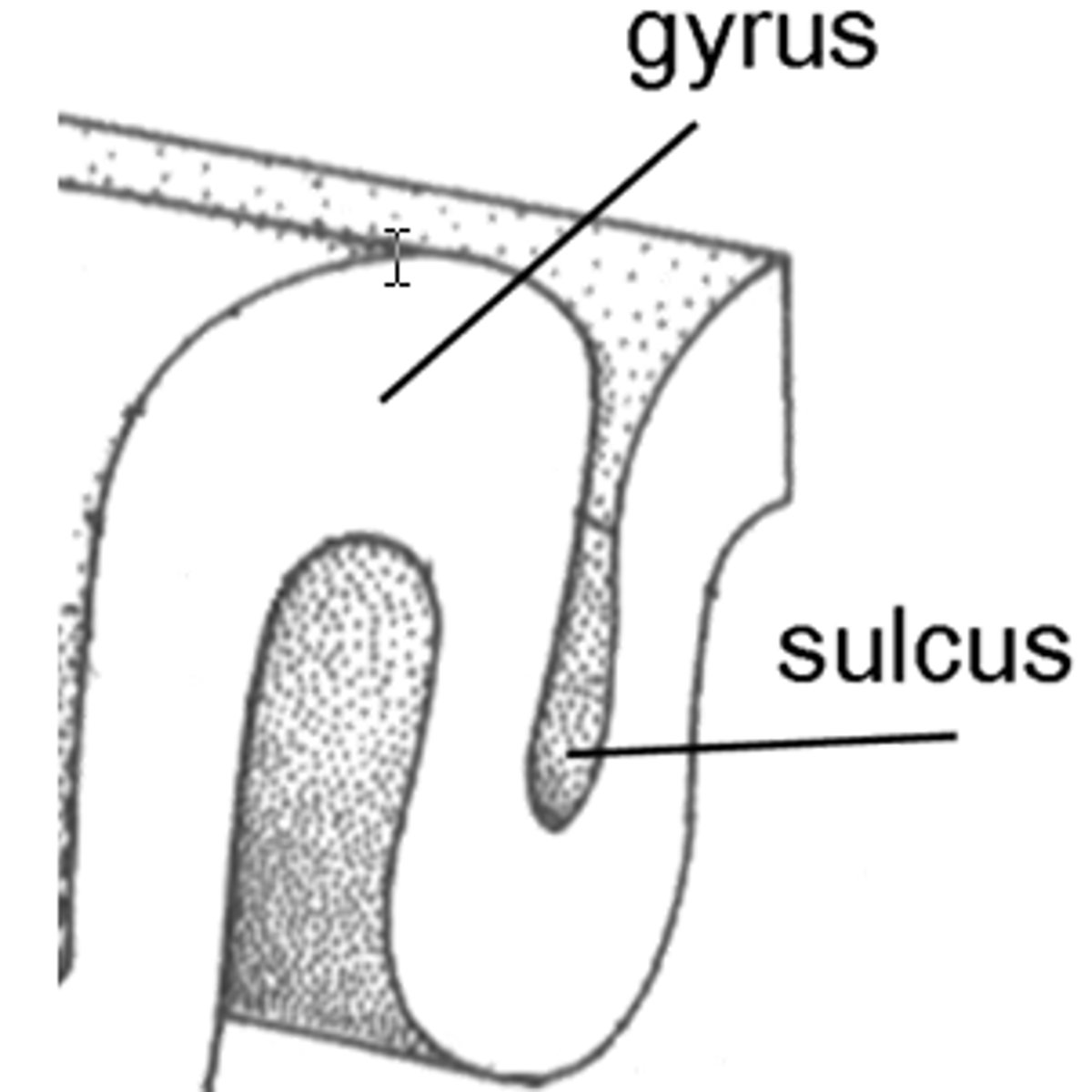
Cerebral cortex
the surface of the brain, very uneven and characterized by gyri and sulci
Gyri
bumps (mountains)
Sulci
grooves (valleys)
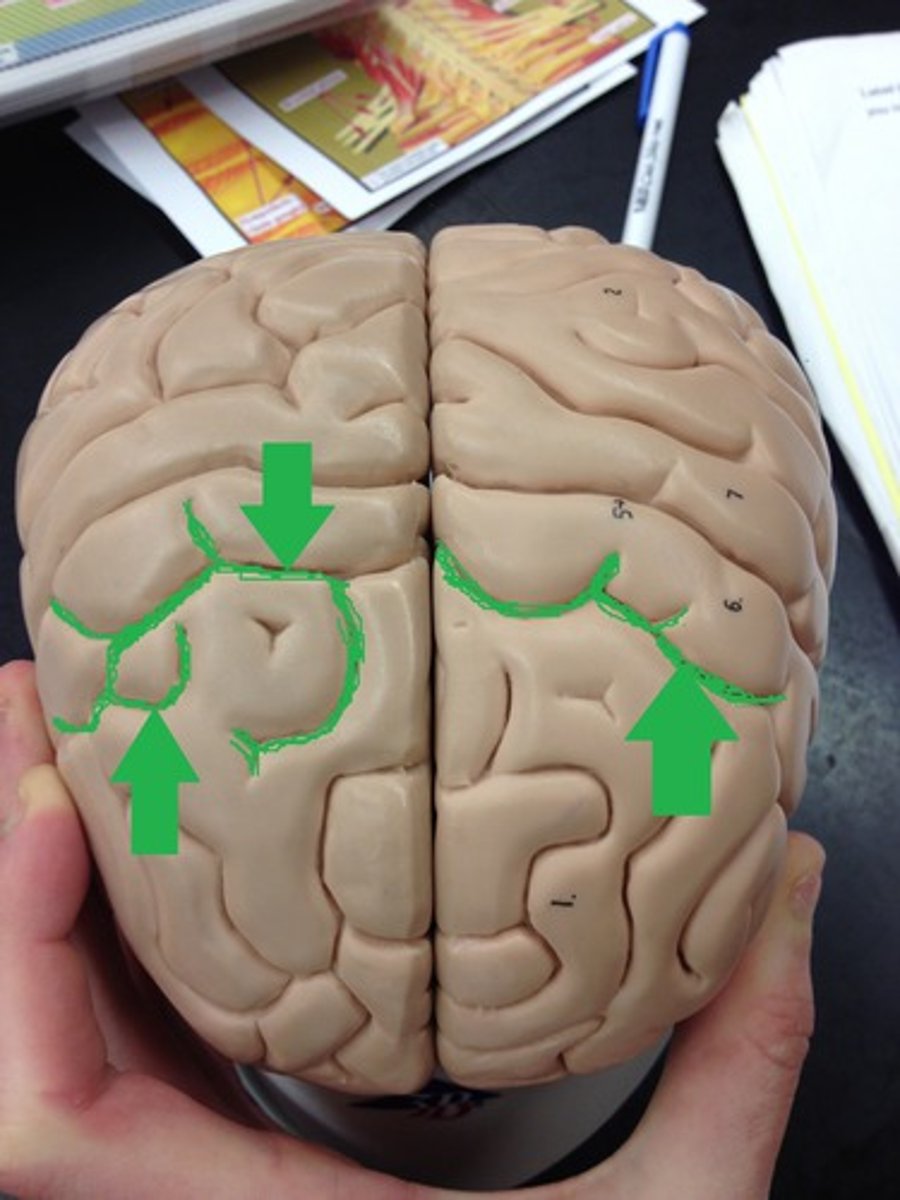
Gyri vs Sucli
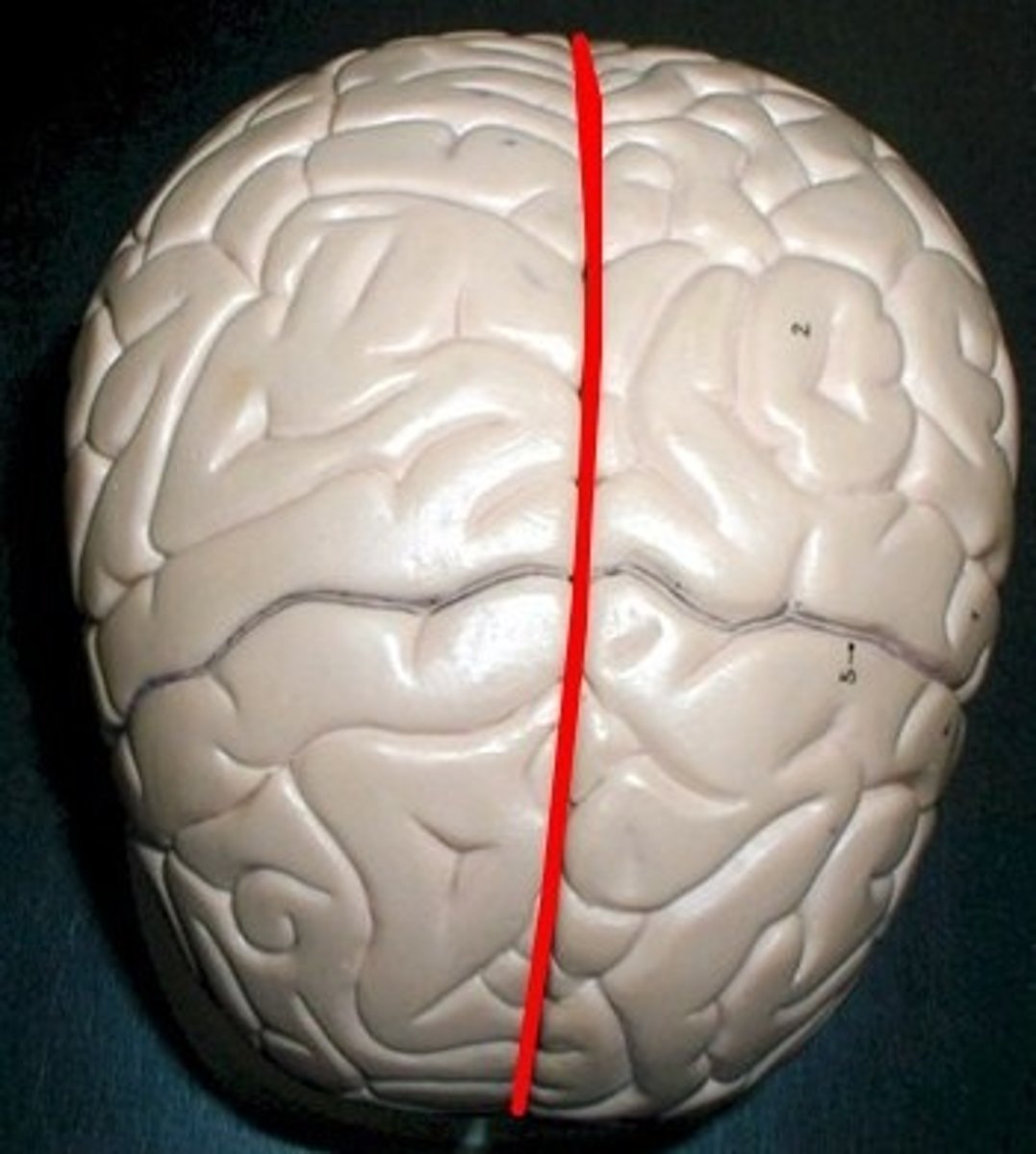
Longitudinal fissure
most prominent sulcus that separates brain into right and left hemisphere
Lateralization
specialization of function in each hemisphere, mainly in language ability
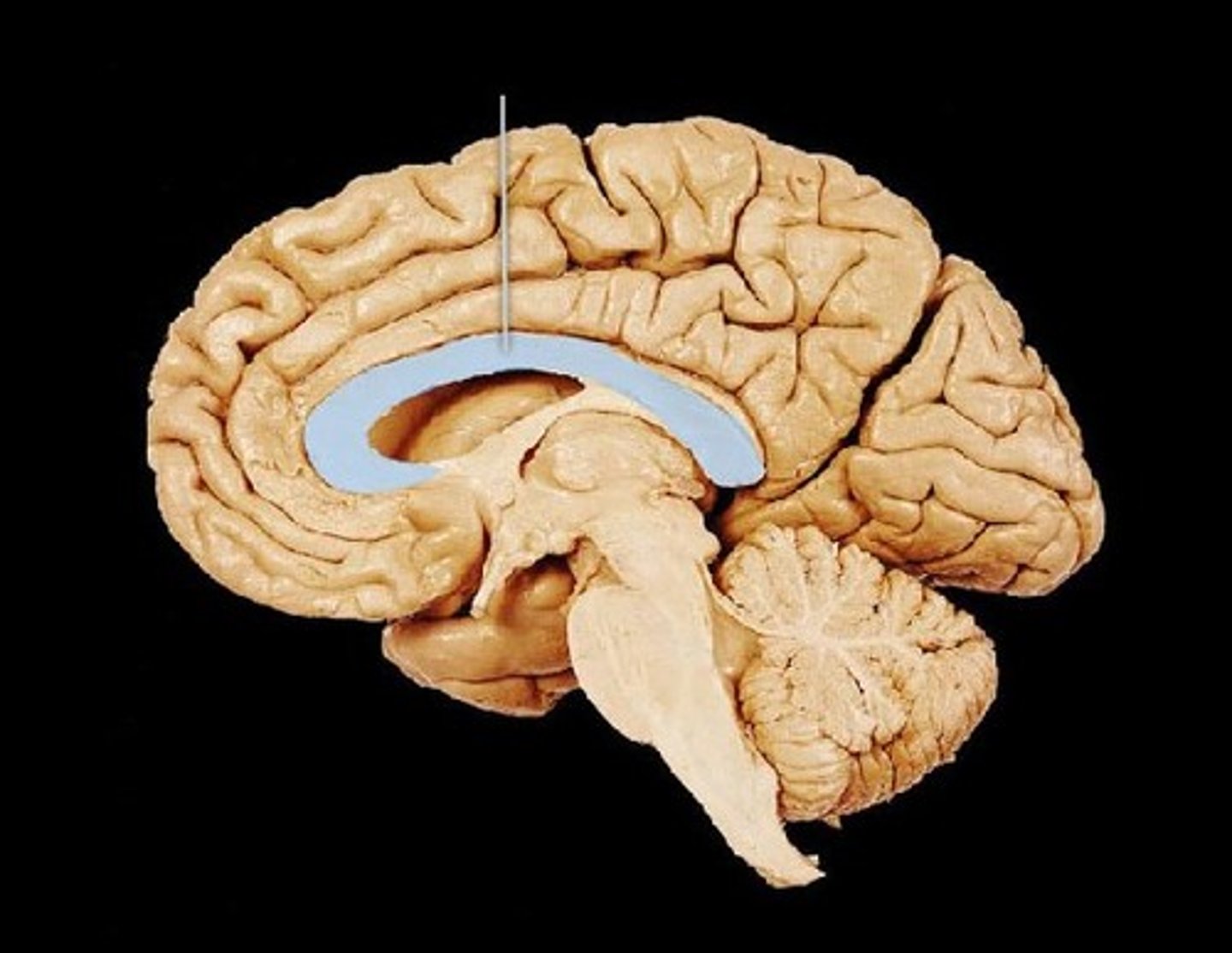
Corpus callosum
thick band of neural fibers connecting the hemispheres, allowing for communication and information processing
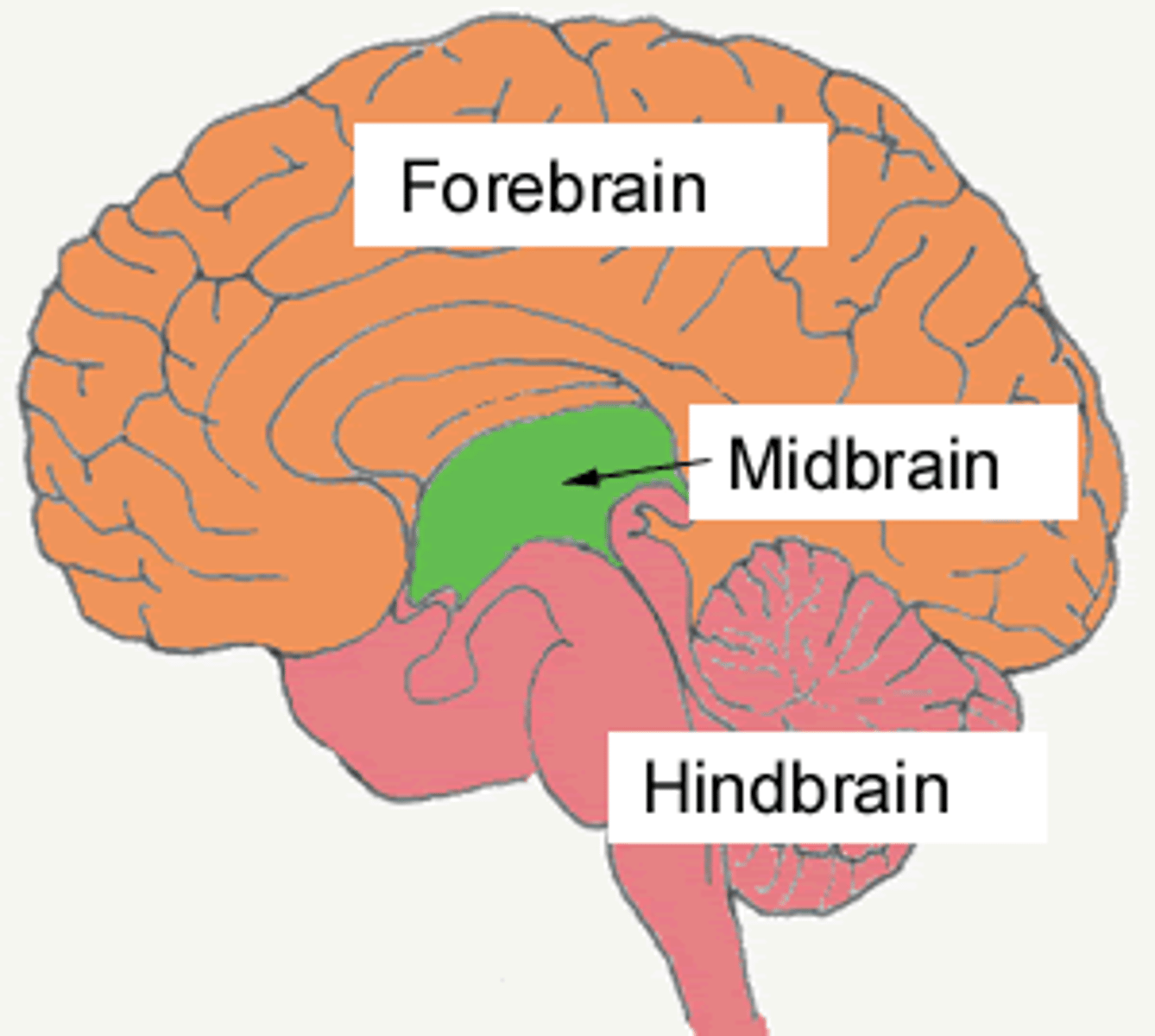
Forebrain
Largest part of the brain; consists of cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and limbic system
Forebrain - cerebral cortex
higher-level processes such as consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory; divided into four different lobes
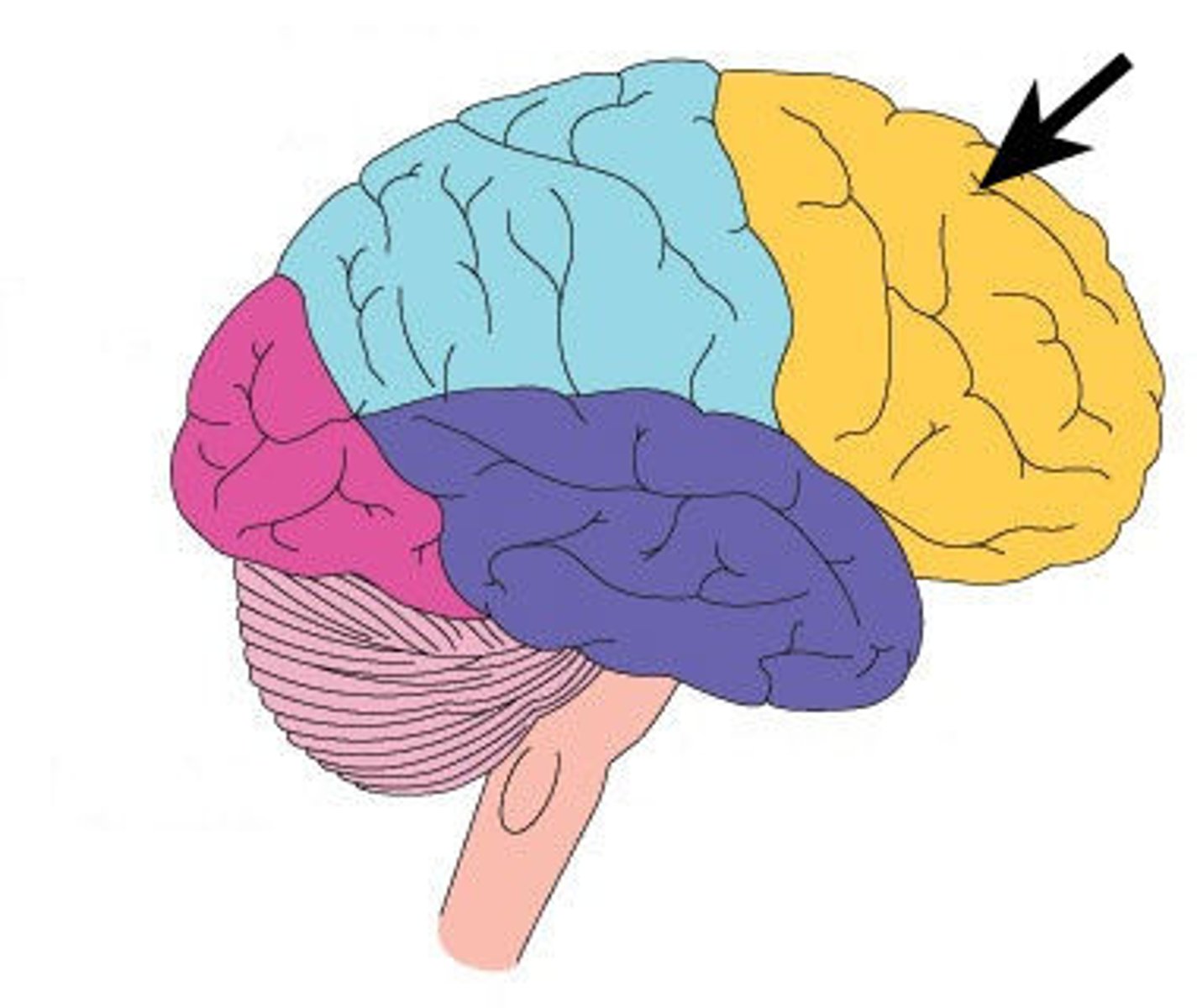
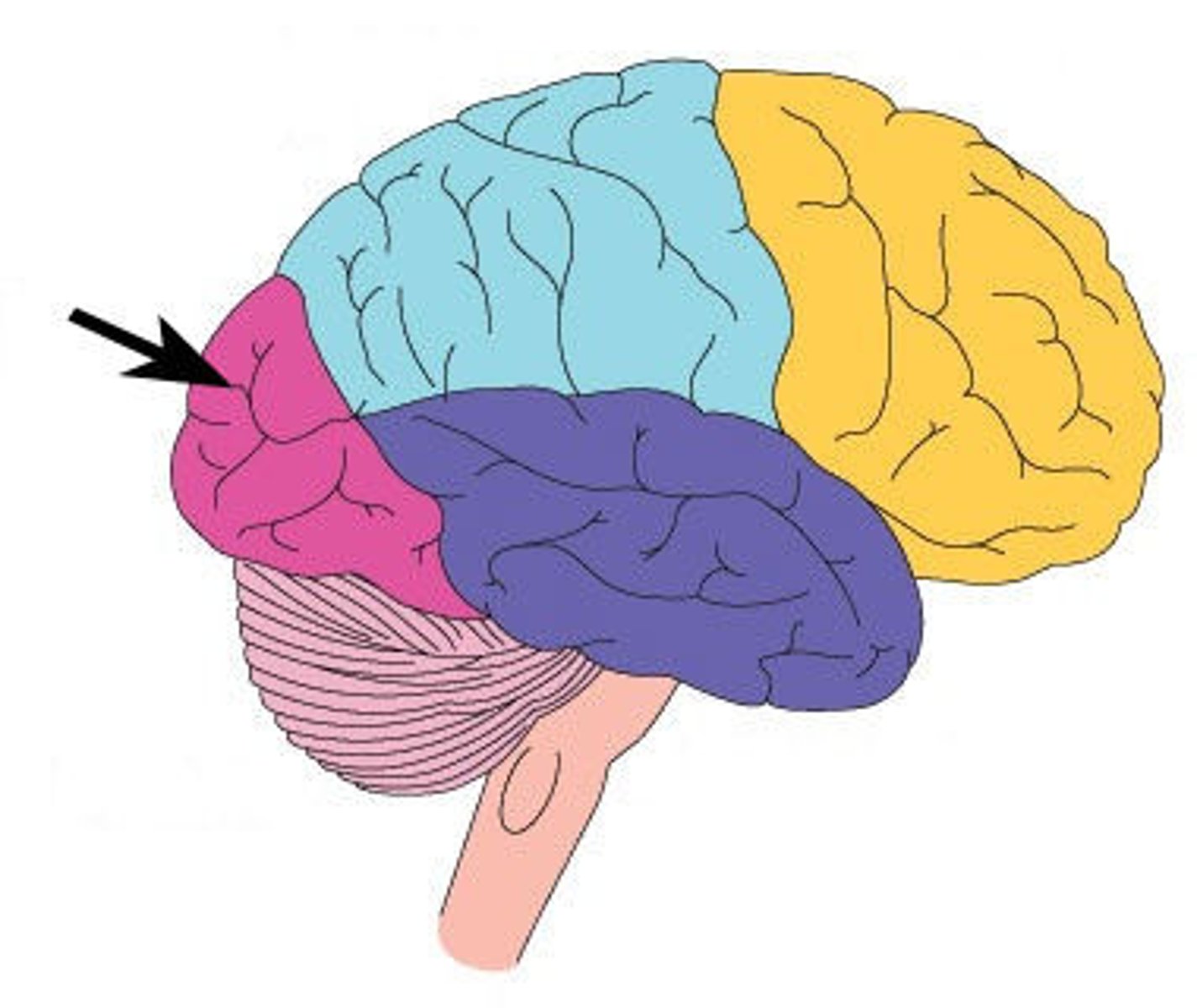
Frontal lobe
reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language
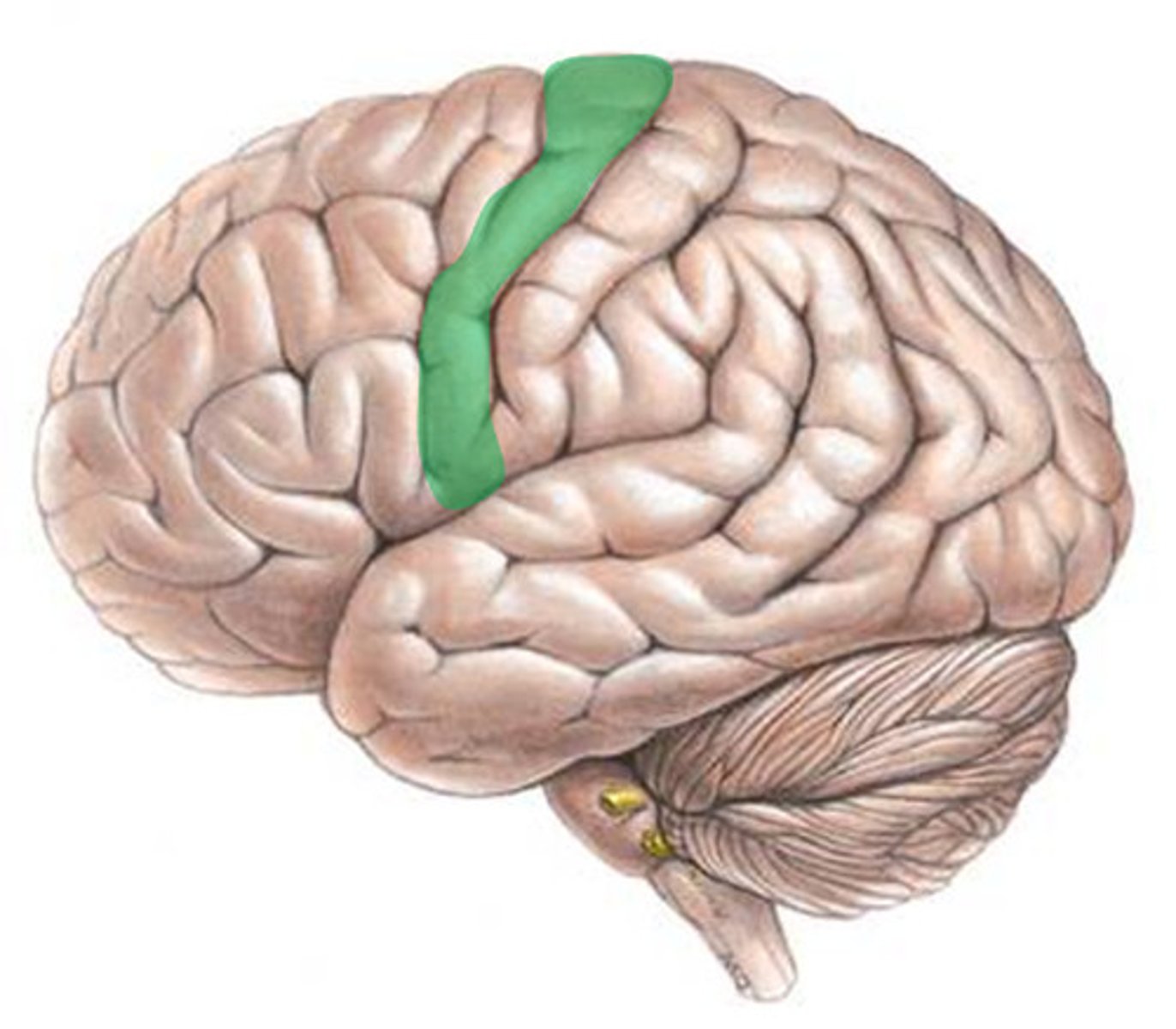
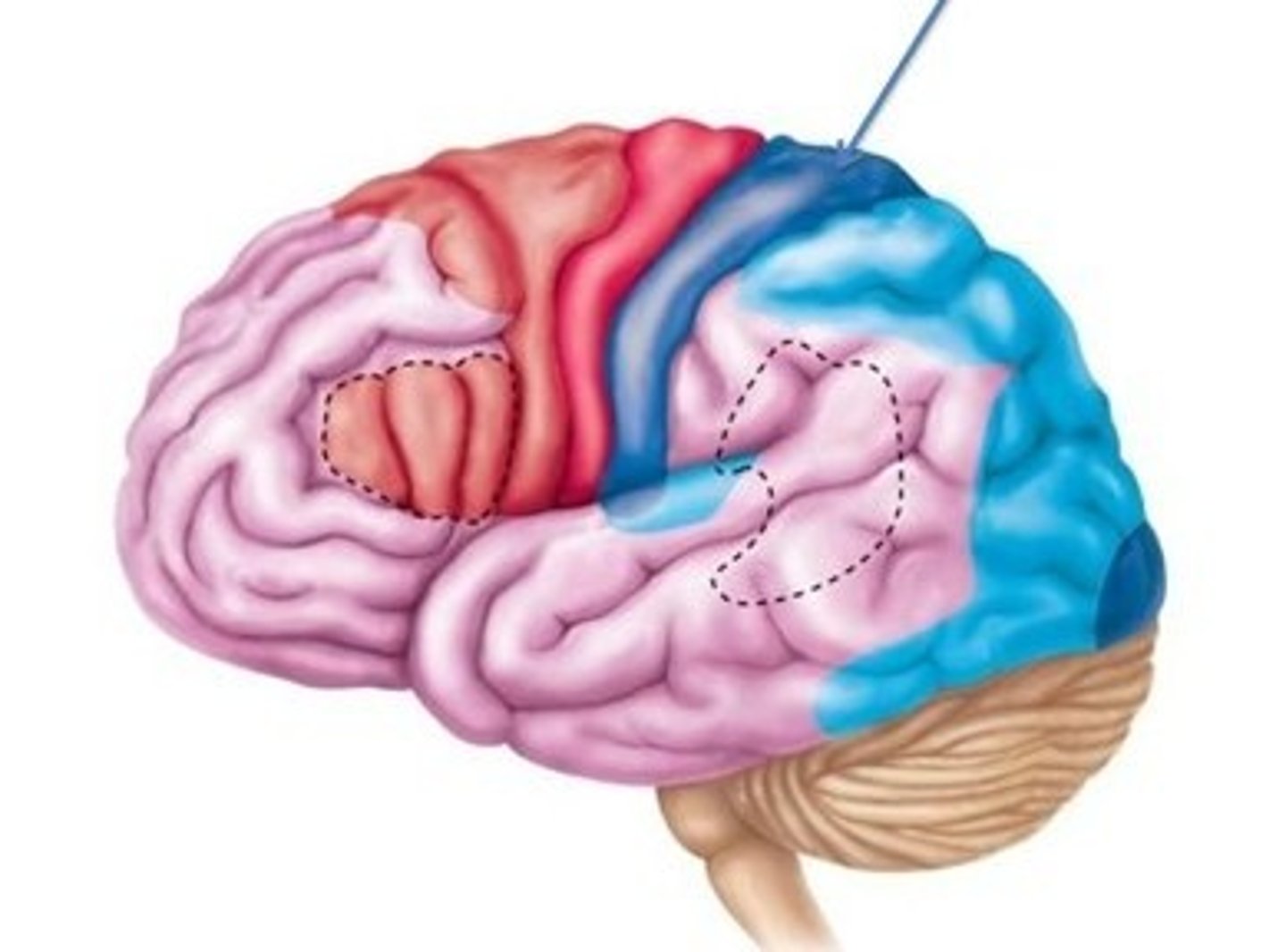
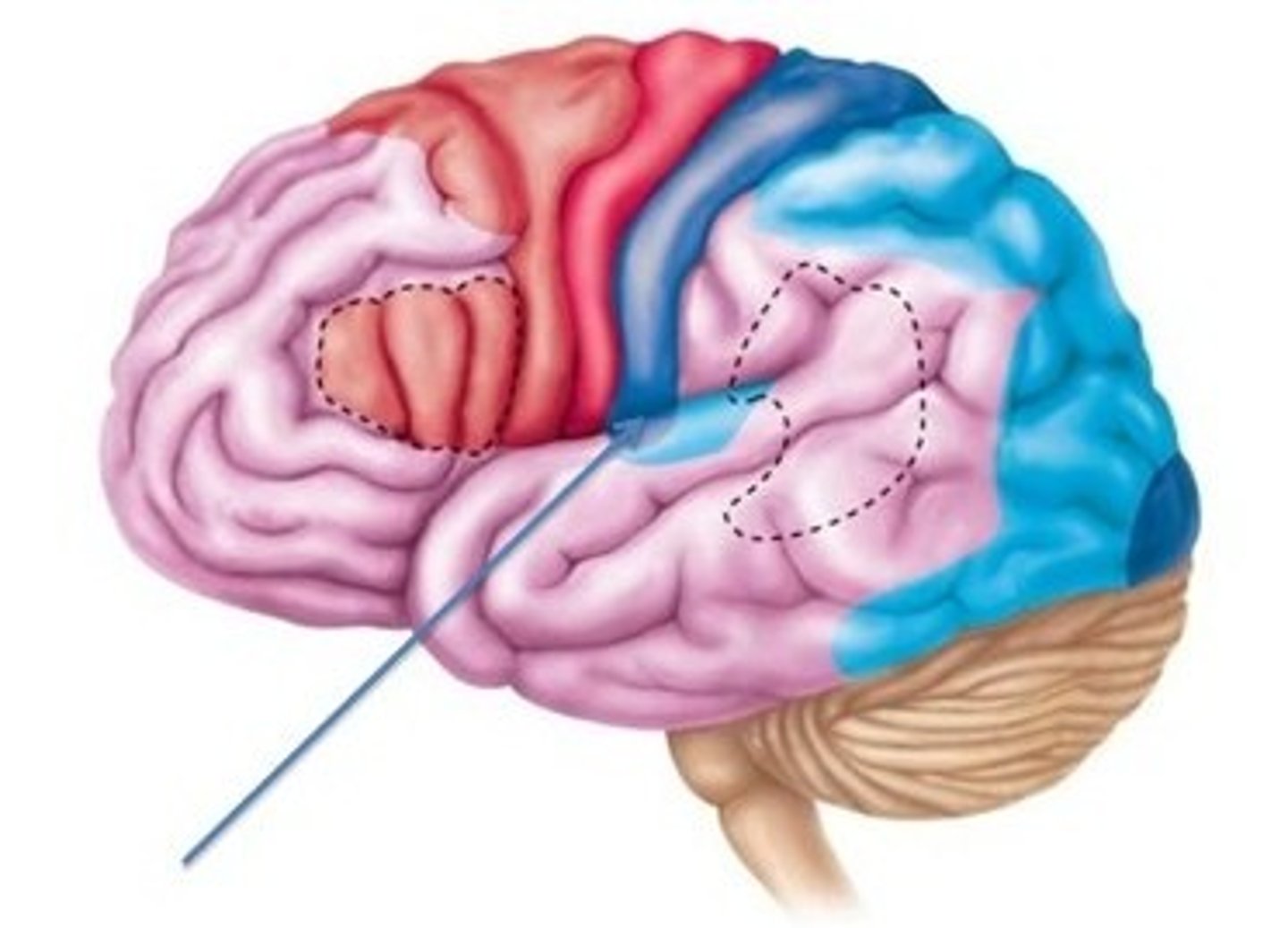
Motor cortex
frontal lobe; planning and coordinating movement
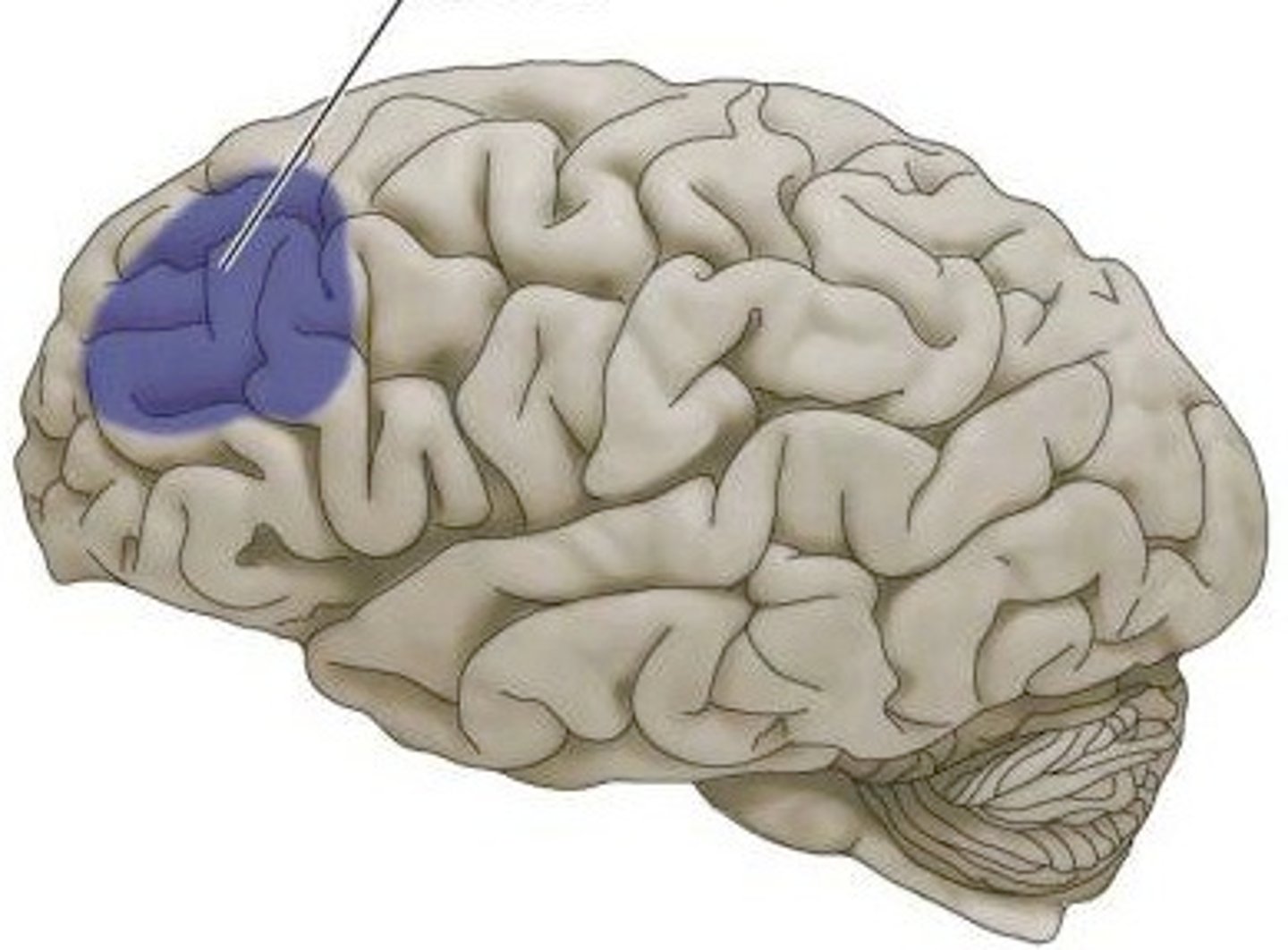
Prefrontal cortex
frontal lobe; higher-level cognitive functioning
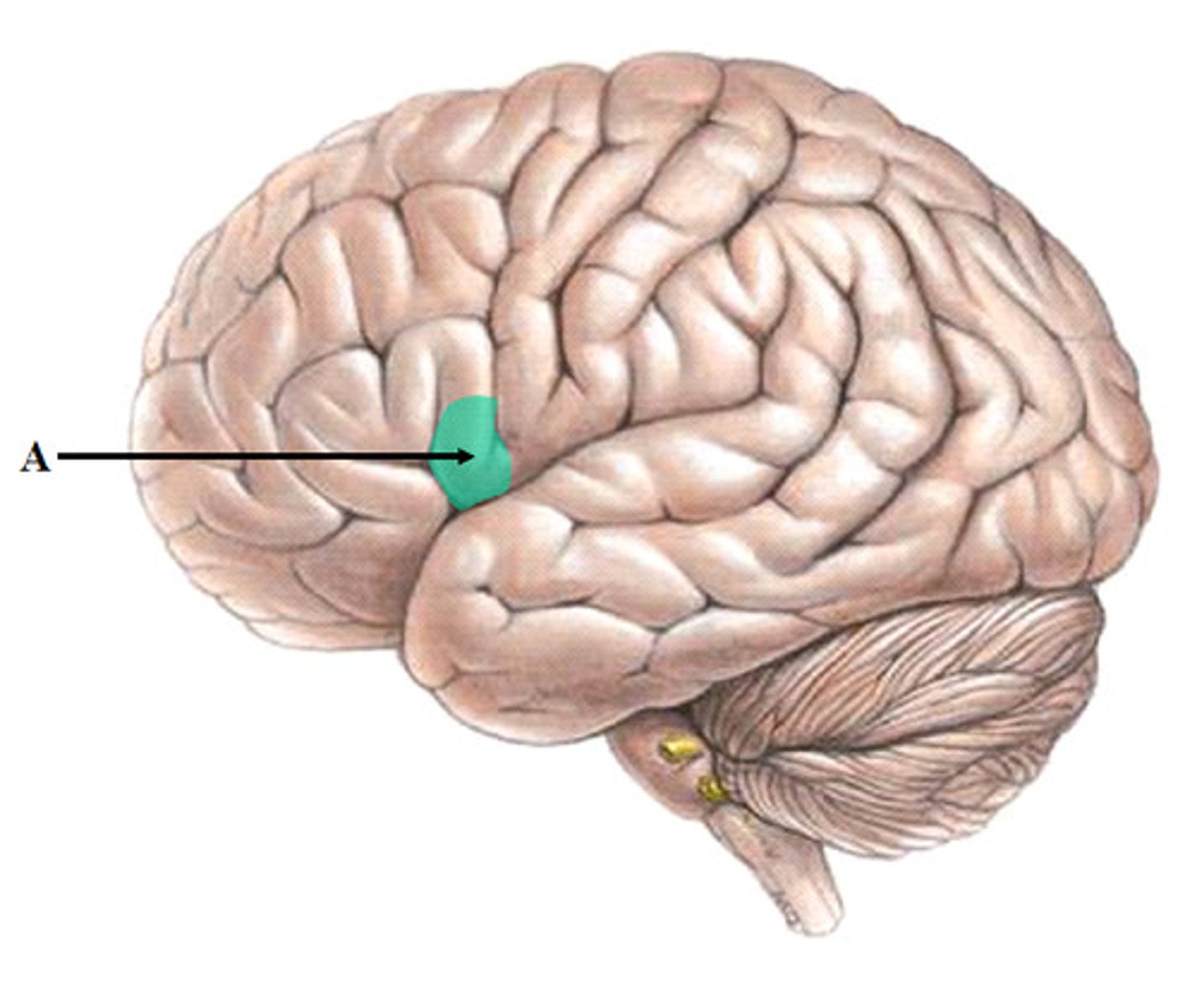
Broca's area
frontal lobe; language production
Parietal lobe
processing sensory information
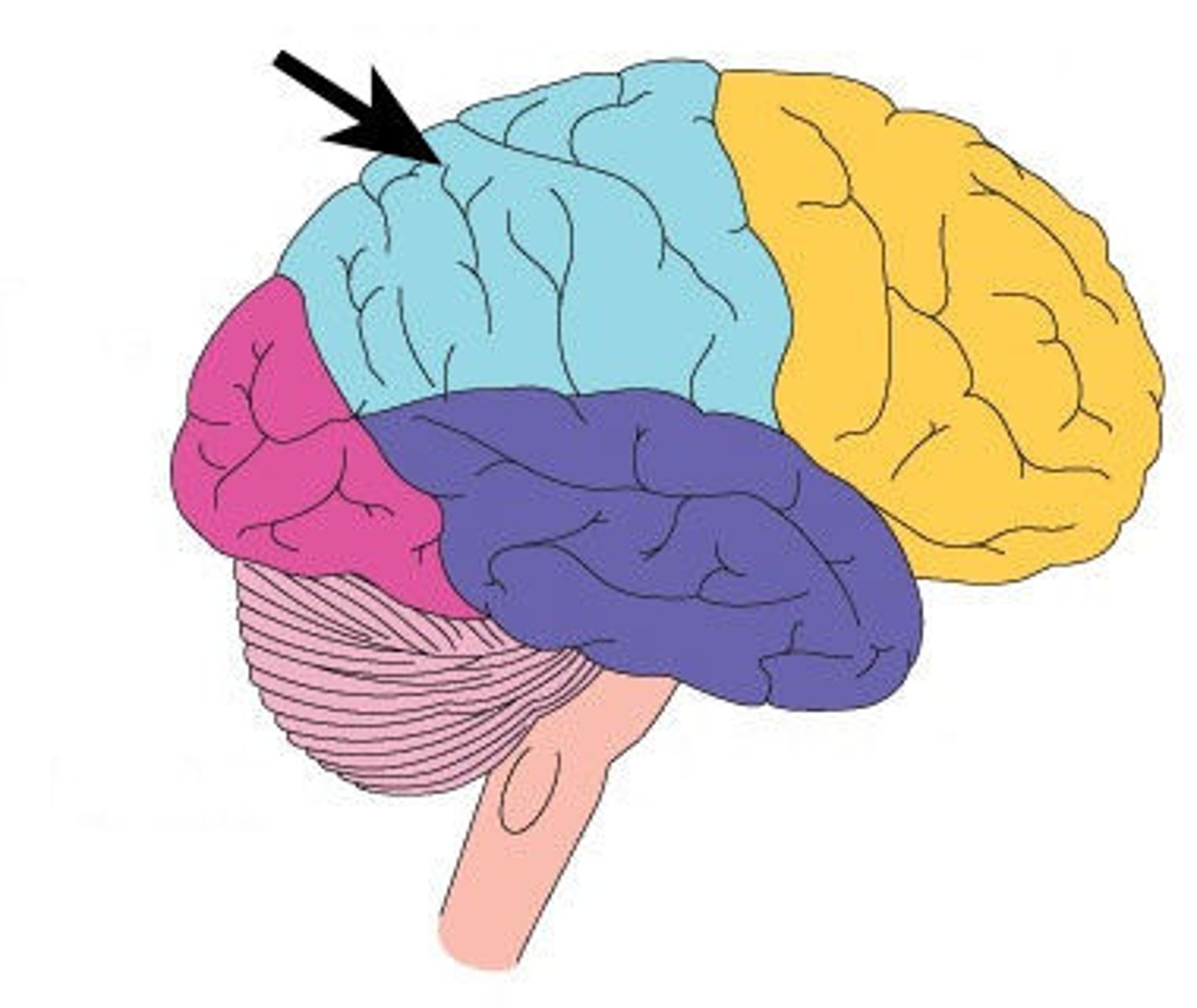
Somatosensory cortex
parietal lobe; processes sensory information across the body such as touch, temperature, pain
Temporal lobe
hearing, memory, emotion, some language
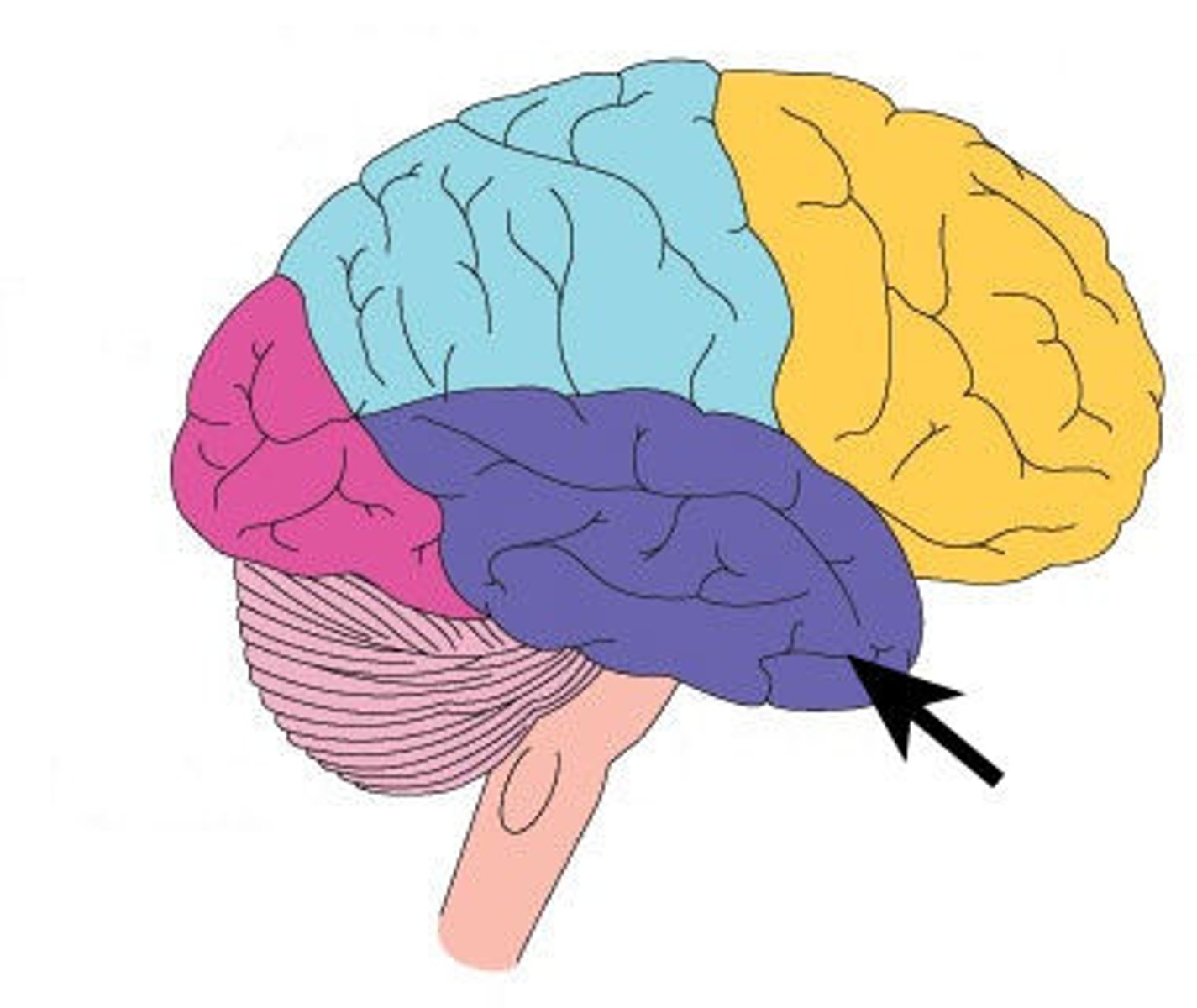
Auditory cortex
temporal lobe; processing auditory information
Wernicke's area
temporal lobe; speech comprehension
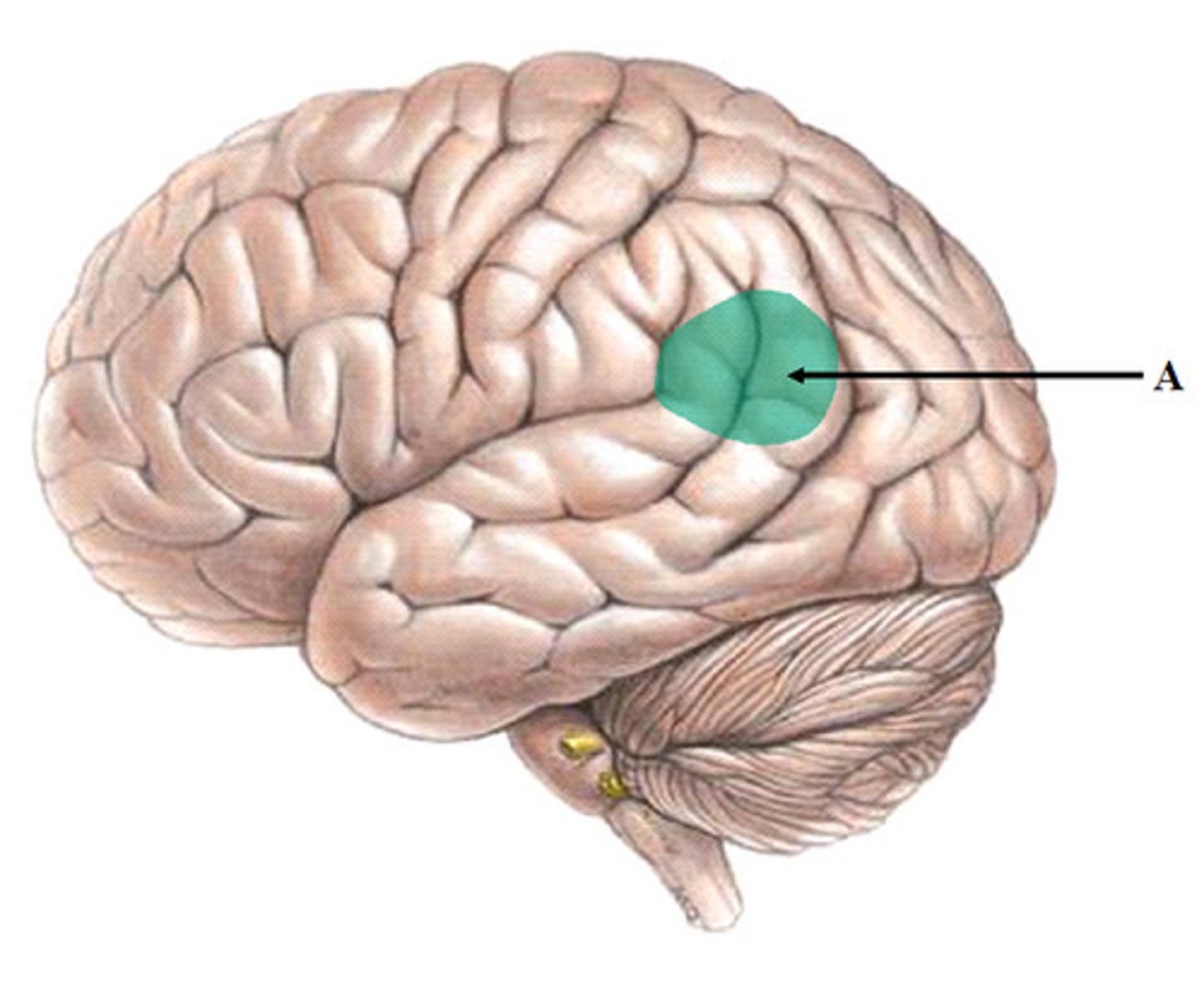
Occipital lobe
processing visual information
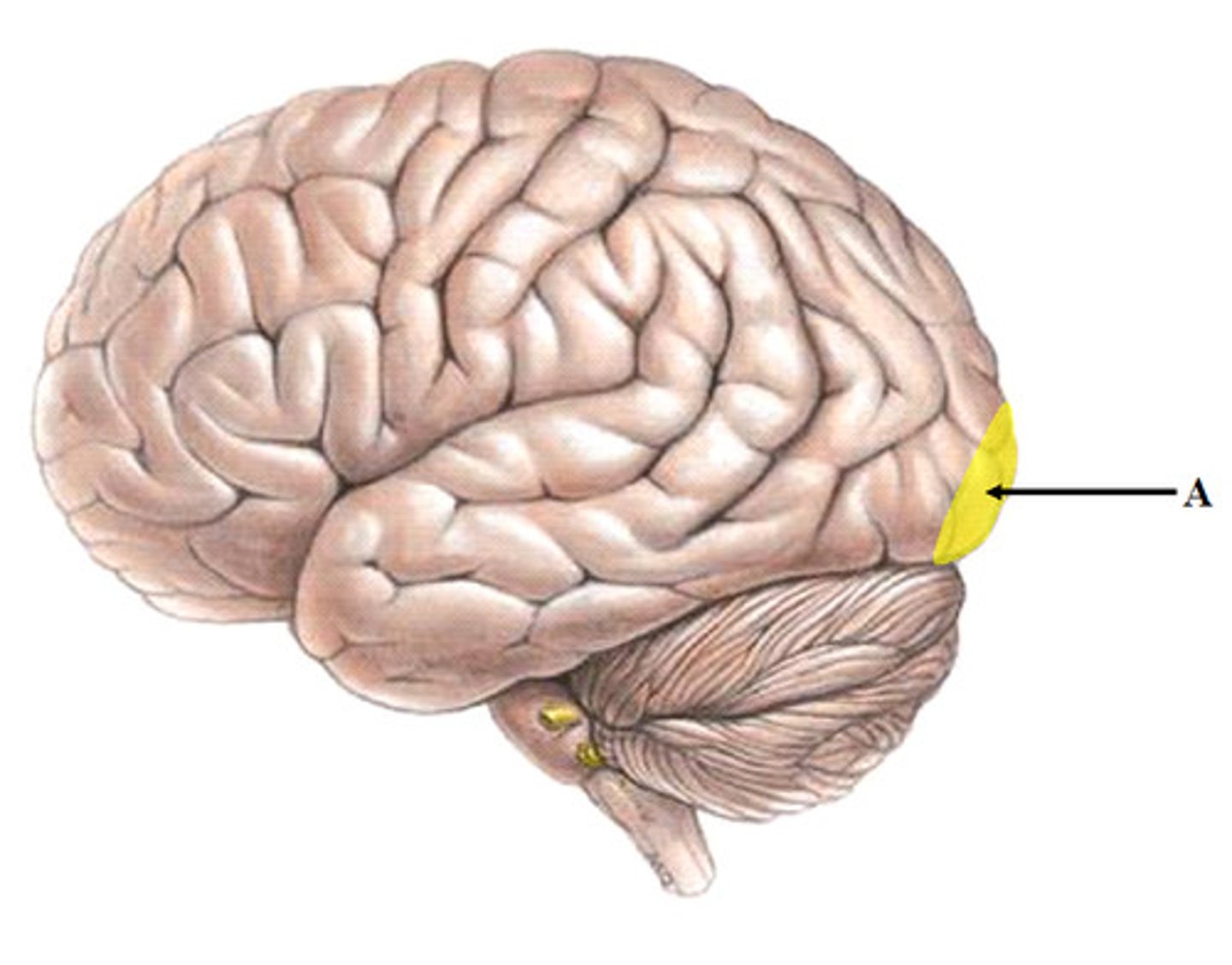
Primary visual cortex
occipital lobe; retinotopical interpretation of images
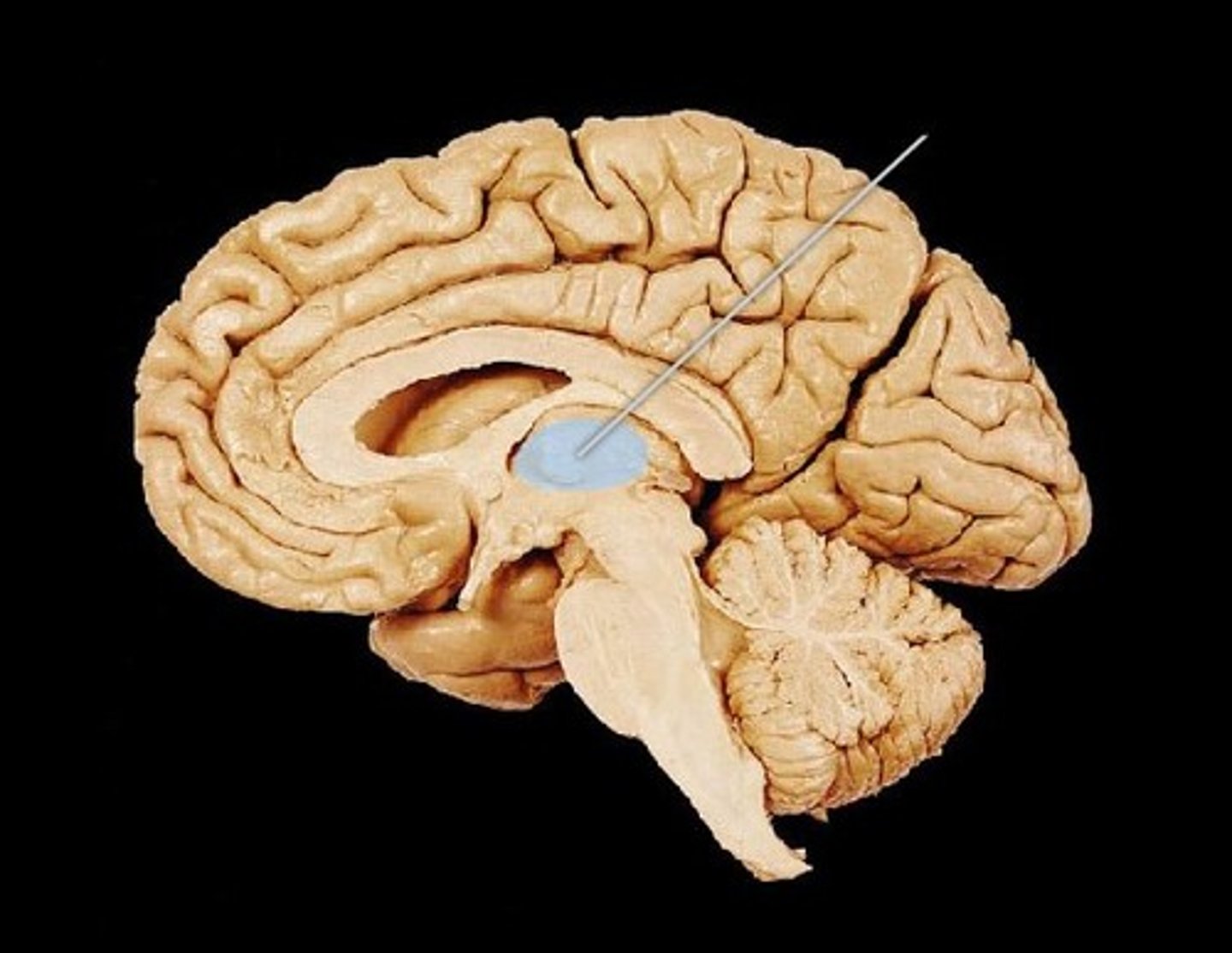
Thalamus
area of forebrain; sensory relay for the brain - all senses but smell!
Limbic system
area of forebrain; processing both emotion and memory; smell is directly related, so scents can evoke emotional responses; made up of hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus
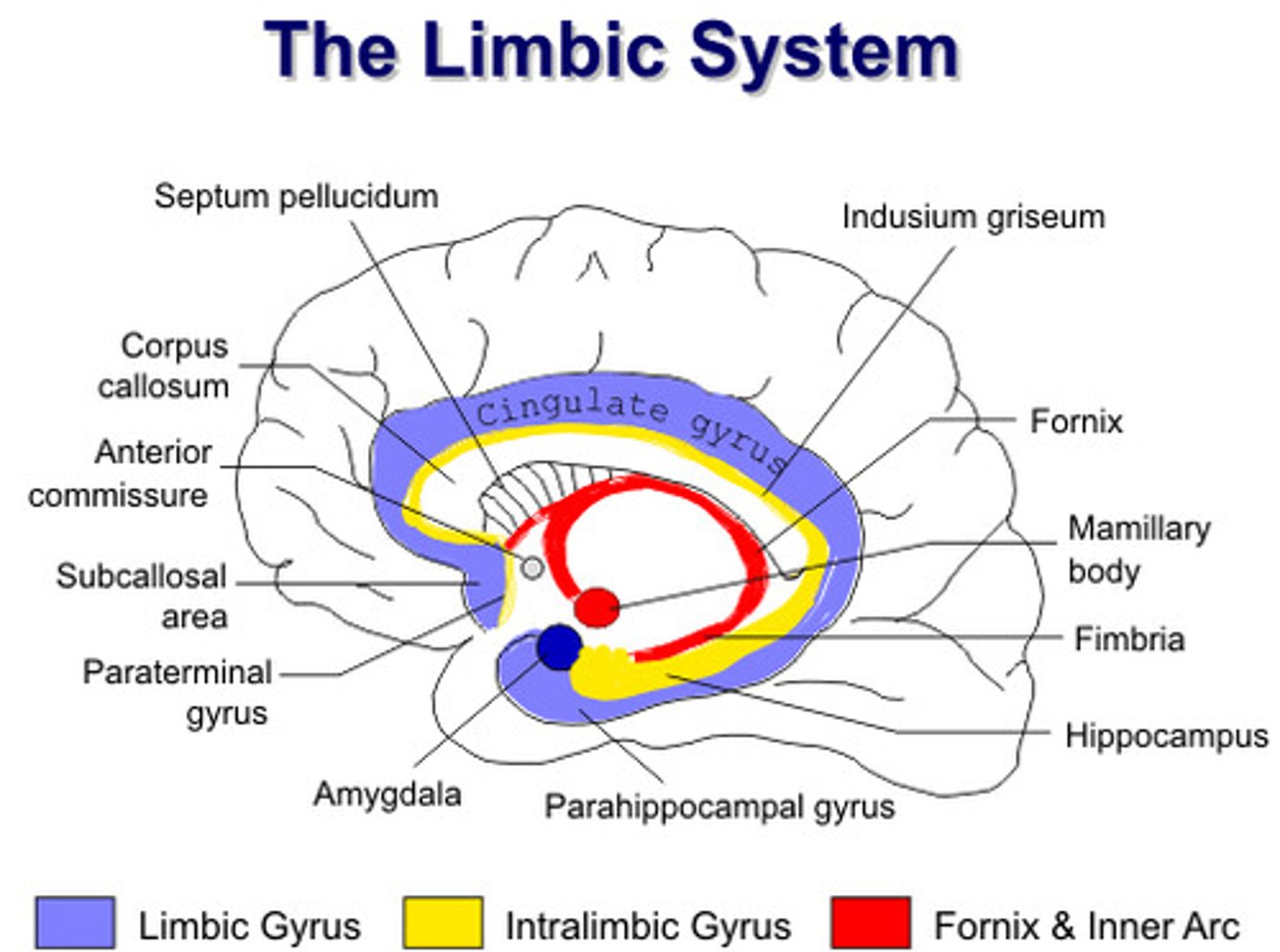
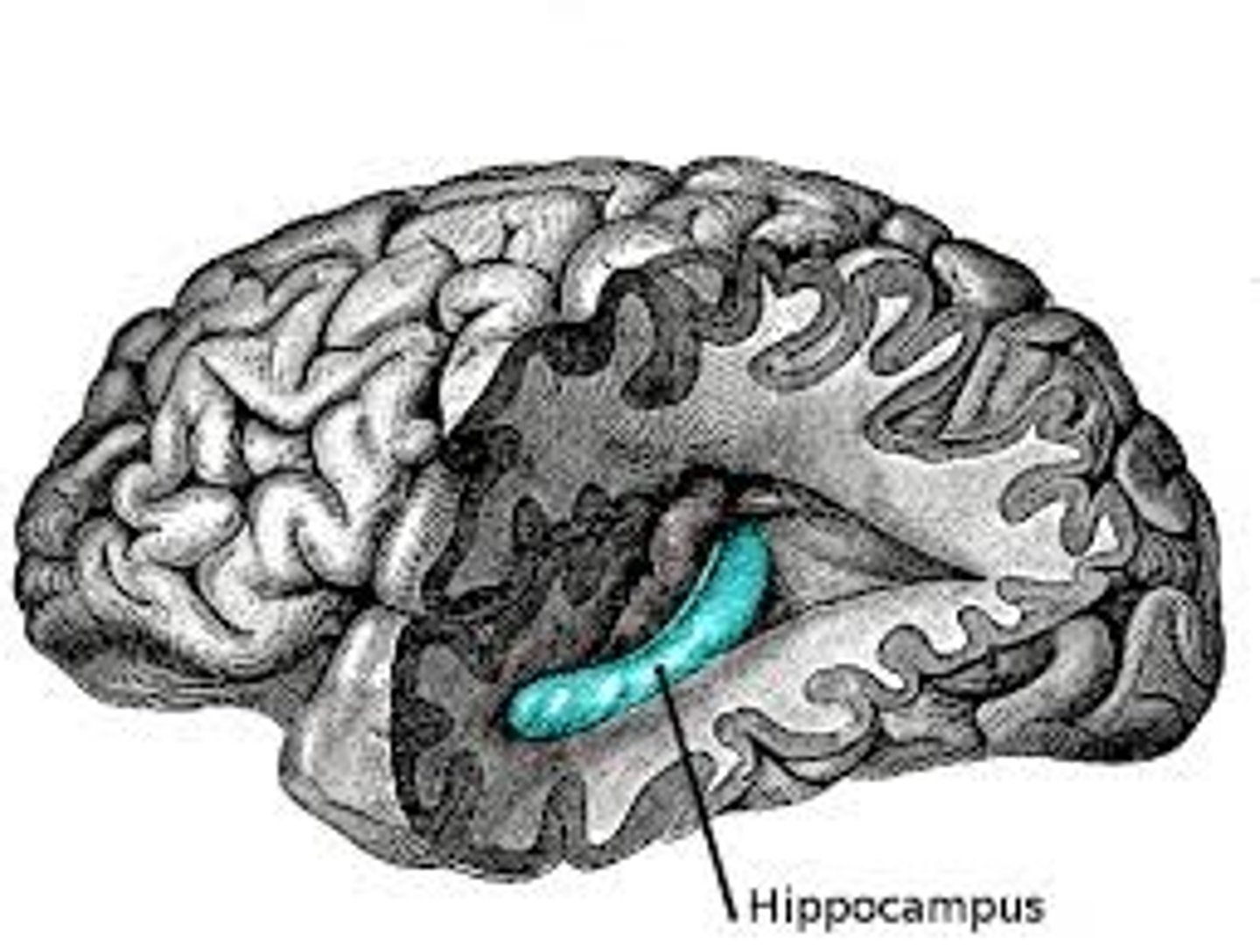
Hippocampus
limbic system component; learning and memory
Amygdala
limbic system component; emotion and emotional tie to memory
Hypotahlamus
limbic system component; regulates homeostatic processes such as body temp, BP, and interface between endocrine and nervous system that regulates sexual motivation and behavior
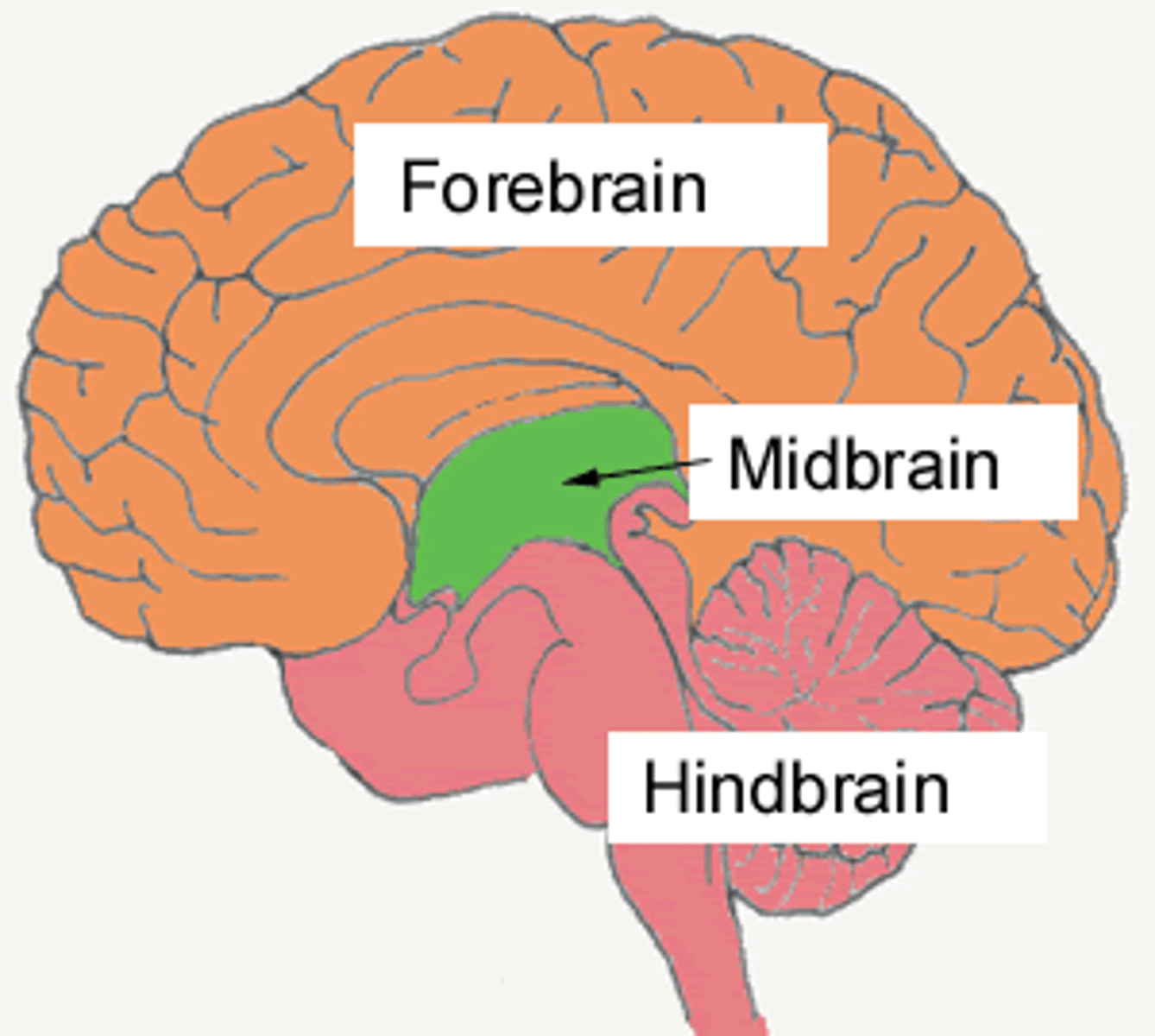
Midbrain
structures deep within the brain, between forebrain and hindbrain
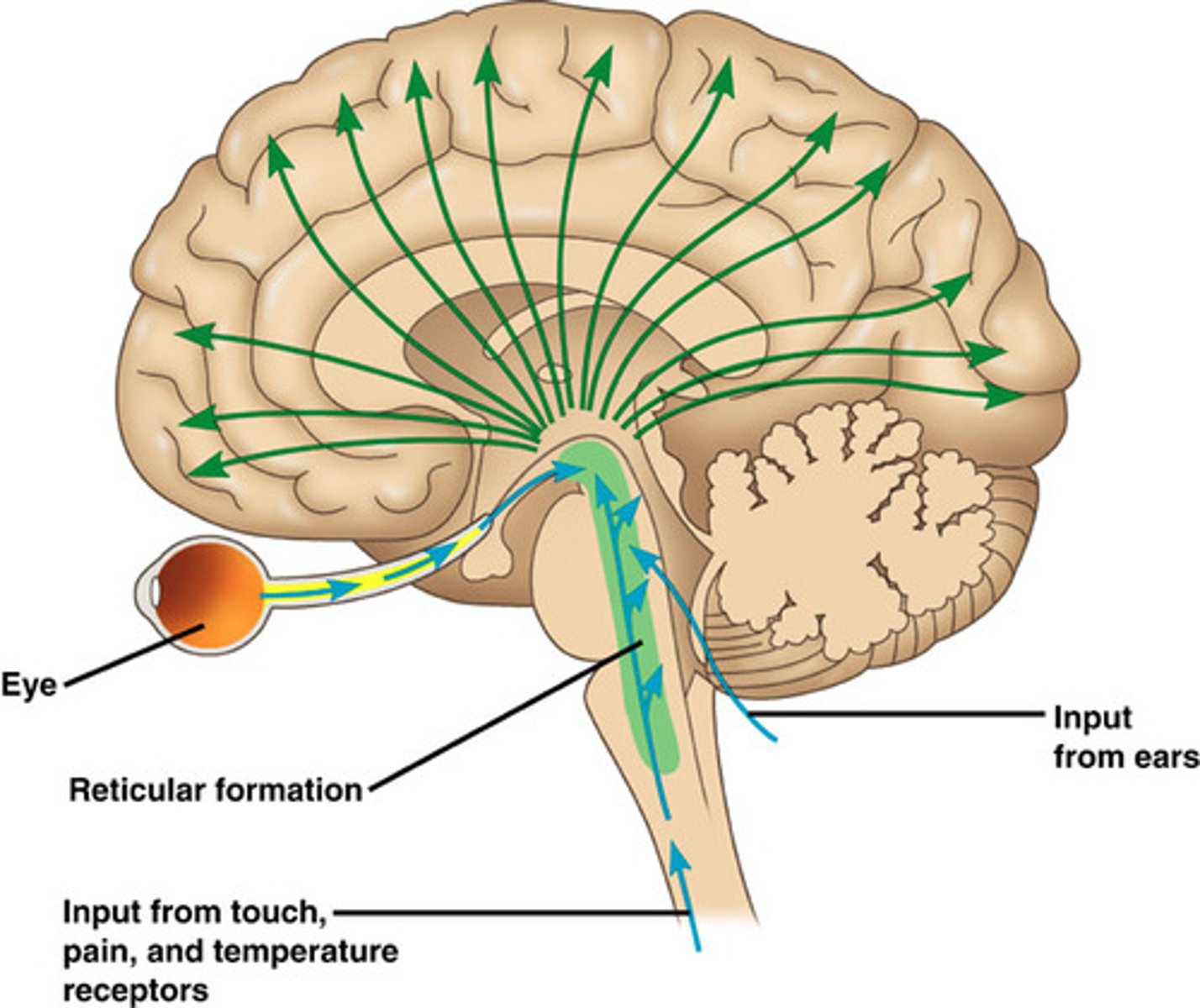
Reticular formation
midbrain component that extends up into forebrain and down into hindbrain; regulates sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor activity
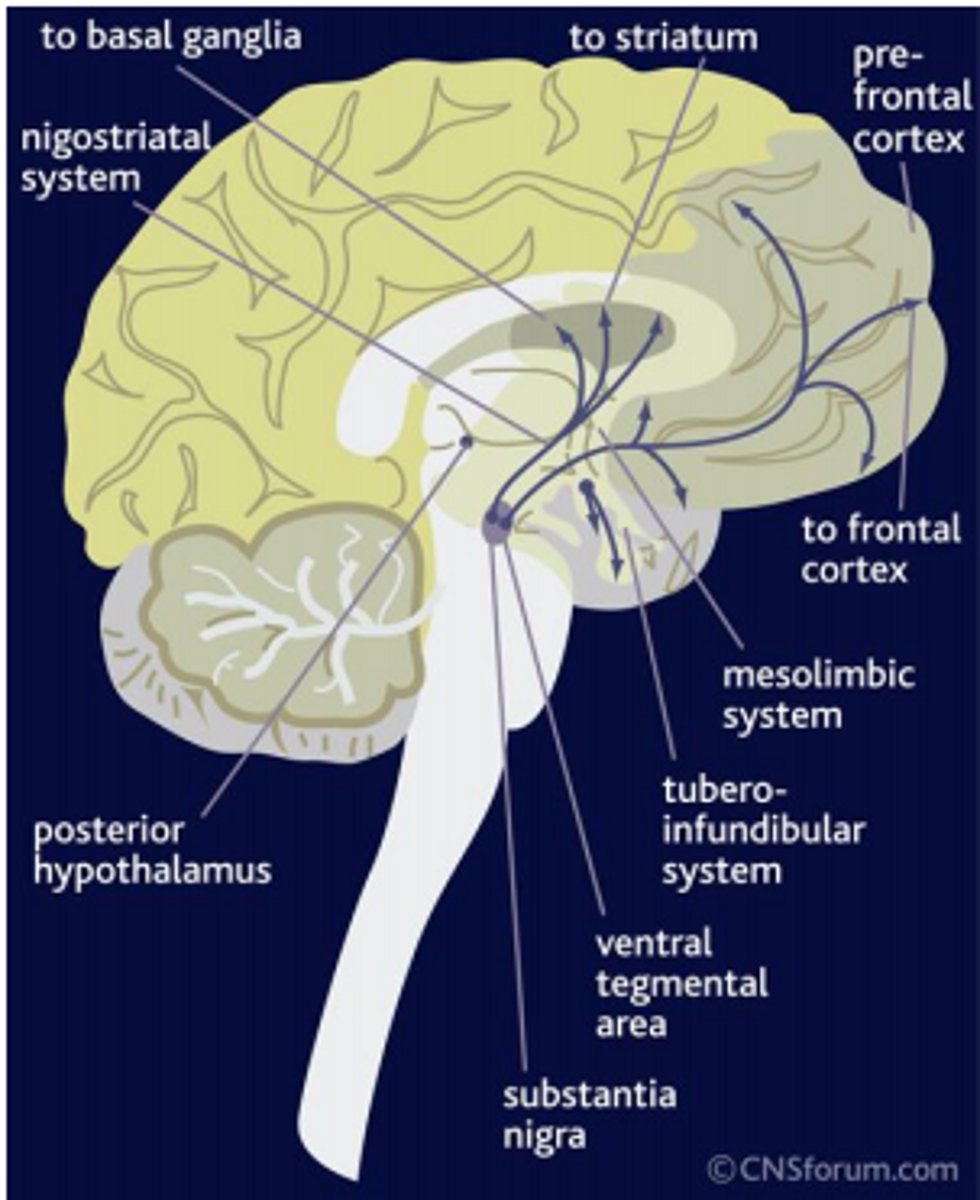
Substantia nigra/Ventral tegmental area (VTA)
midbrain component; contain cell bodies that produce dopamine and are critical for movement; also involved in mood, reward, and addiction
degeneration of these areas are involved in Parkinson's disease
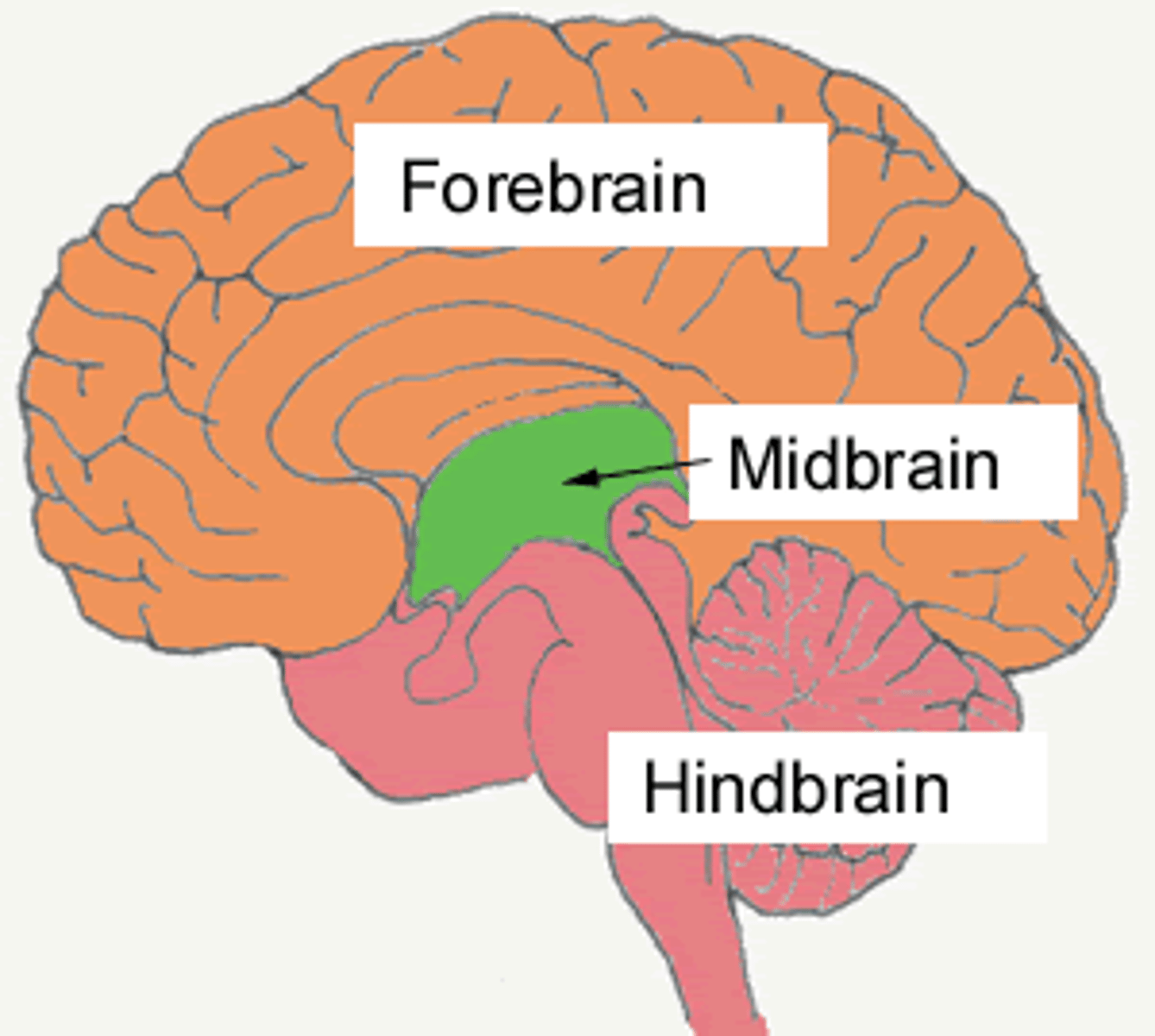
Hindbrain
located at back of head and appears like an extension of the spinal cord; made up of medulla, pons, and cerebellum
Medulla
controls automatic processes of autonomic nervous system (i.e. breathing, BP, heart rate)
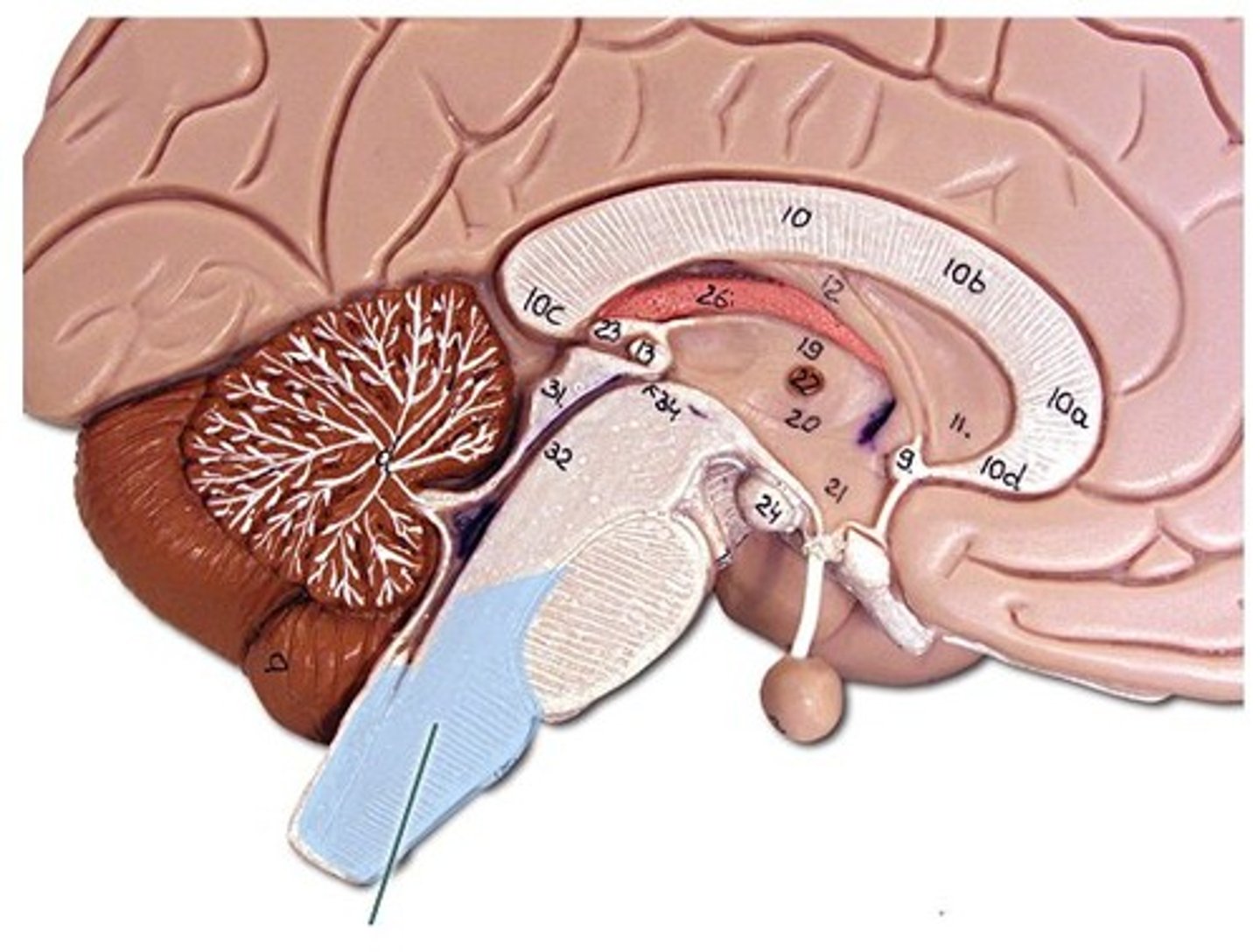
Pons
literally means "bridge"; serves to connect brain and spinal cord, and regulates brain activity during sleep
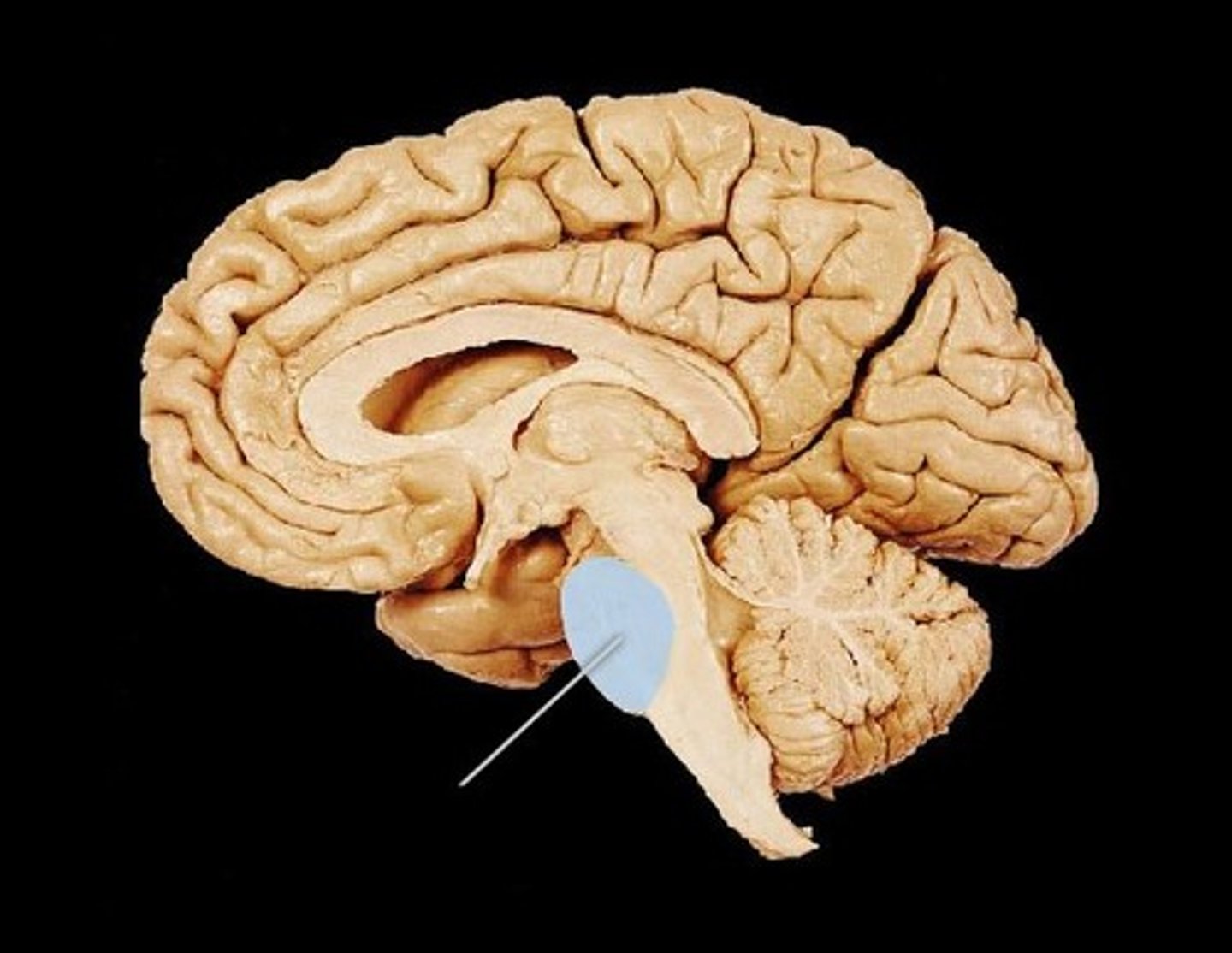
Cerebellum
receives messages from muscles, tendons, joints, and structures in ear to control balance, coordination, movement, motor skills; also thought to be important in processing memories
Brain imaging
provides insightful information about the function of different parts of the brain without needing an injured brain to study