3.3 Respiration
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
4 stages of respiration
Glycolysis
Link reaction
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
3 stages of glycolysis
1. A glucose molecule is phosphorylated by the addition of two phosphate groups, using two molecules of ATP, making hexose bisphosphate
2. Hexose bisphosphate is split into two triose phosphate molecules
3. The triose phosphate molecules are dehydrogenated, oxidising them to pyruvate. The hydrogen atoms are transferred to NAD. These steps release enough energy to synthesise 4 ATP molecules
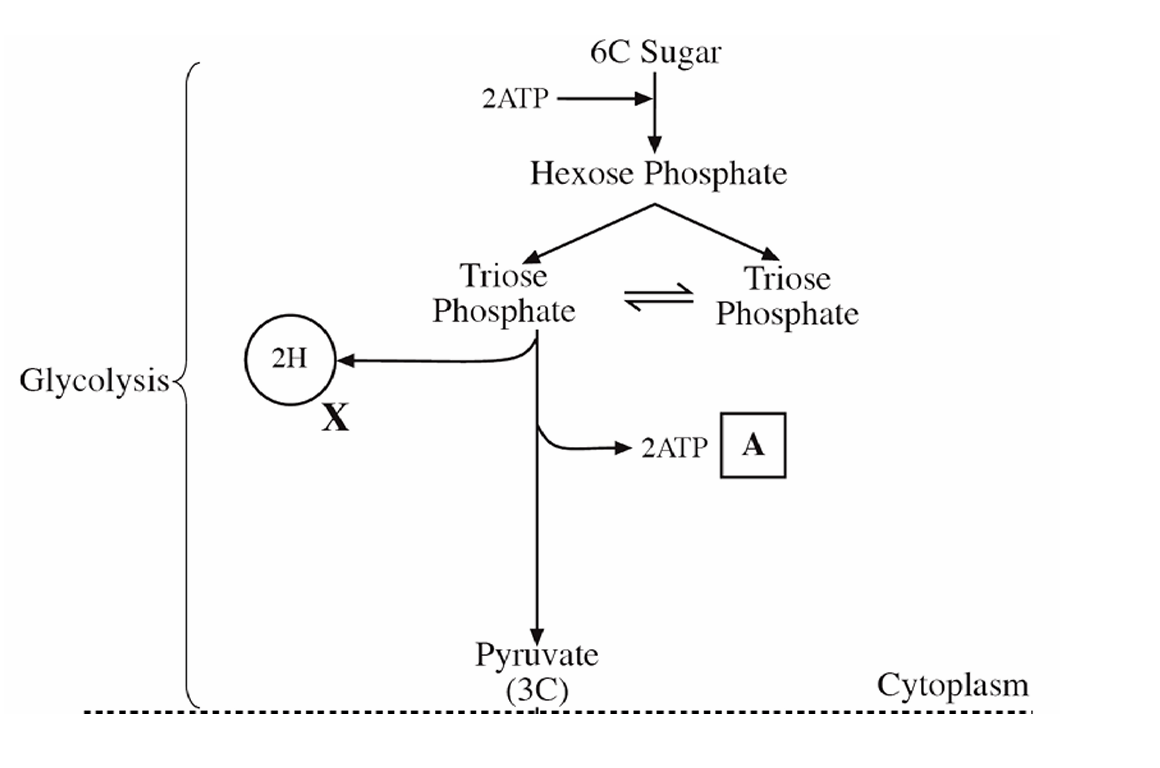
What does glycolysis produce
A net yield of 2 ATP produced by substrate level phosphorylation
2 molecules of reduced NAD
2 pyruvates
Full name for NAD
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Where does glycolysis occur
Cytosol/ cytoplasm
Does glycolysis require oxygen
no
Describe phosphorylated glucose
more reactive so less activation energy is required for the enzyme controlled reactions
More polar than glucose and therefore less likely to diffuse out of the cell
Why does glycolysis occur in the cytoplasm
Because glucose cannot pass through the mitochondrial membranes and enzymes for the breakdown of glucose are not present in the mitochondria
Where does the link reaction take place
Matrix of mitochondria
How is pyruvate transported to the matrix of the mitochondria
Diffusion
Describe the 3 stages of the link reaction
Pyruvate diffuses from the cytoplasm into the matrix
Pyruvate is dehydrogenated and decarboxylated
2 carbon acetate group combines with coenzyme A which makes acetyl coenzyme A
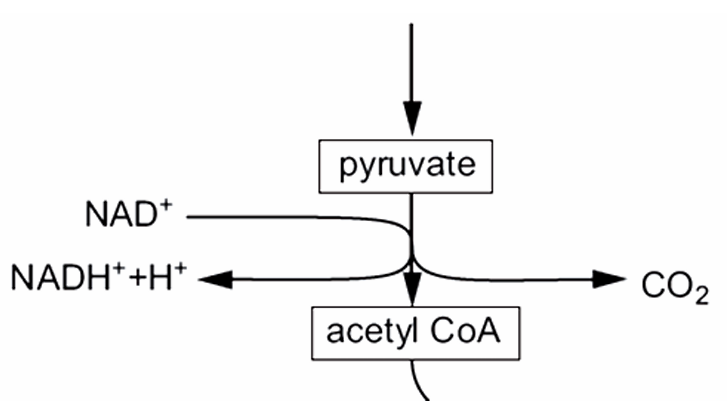
Define dehydrogenation
The removal of one or more hydrogen atoms from a molecule
Define decarboxylation
The removal of a carboxyl group from a molecule releasing carbon dioxide
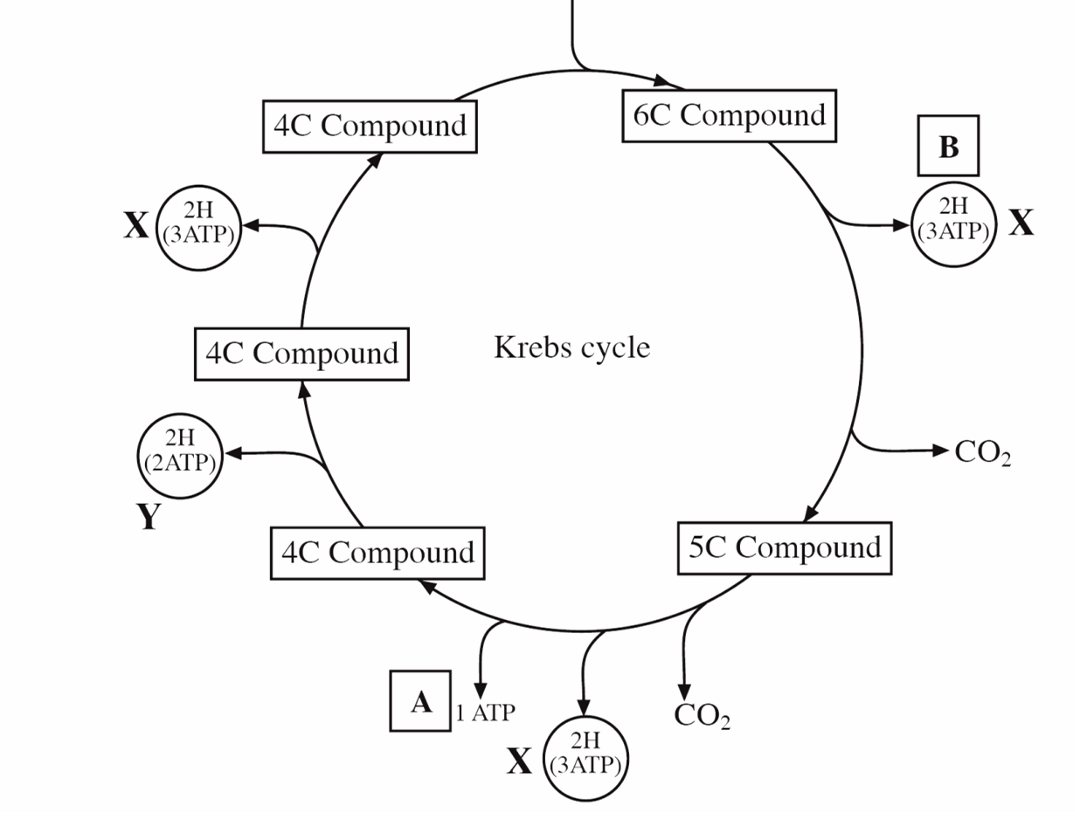
State what each turn of the krebs cycle produces
1 ATP produced by substrate level phosphorylation
3 NADH
1 FADH
2 molecules of carbon dioxide
State the full name of FAD
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Describe the 4 stages of Krebs cycle
Acetyl coenzyme A enters the Krebs cycle by combining with a 4-carbon acid to form citric acid. Coenzyme A is regenerated
Citric acid is dehydrogenated and decarboxylated to make a 5-carbon acid
The 5-carbon acid is dehydrogenated and decarboxylated to regenerate the 4-carbon acid
The 4-carbon acid can combine with more acetyl coenzyme A to repeat the cycle
How many water molecules are used in reactions in the Krebs cycle
3
Where does the krebs cycle occur
matrix
Where is the electron transport chain located
cristae of the inner mitochondrial membranes
Describe the steps of the passage of electrons in the electron transport chain
NADH donates the electrons of the hydrogen atoms to the first of a series of electron carriers in the ETC
Electrons provide energy for the proton pump and protons from the hydrogen atoms are pumped into the inter membrane space
The electrons pass along the chain of carrier molecules providing energy for each of 3 proton pumps in turn
The electrons combine with protons and oxygen to form water
Describe the steps of the passage of protons in the electron transport chain
The inner membrane is impermeable to protons and so the protons accumulate in the inter membrane space.
The concentration of protons in the inter membrane space becomes higher than in the matrix so a gradient of concentration and charge is set up and maintained by the proton pumps
The enzyme ATP synthetase is associated with each channel. Protons diffuse back through these channels and as they do so their electrical potential energy produces ATP.
Protons combine with electrons and oxygen to form oxygen
Where is ATP synthetase located
Stalked particles on the cristae
What process produces ATP in the ETC
Oxidative phosphorylation
Define chemiosmosis
The flow of protons down an electrochemical gradient through ATP synthetase coupled with the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate ion
NAD and FAD are electron carriers. Define electron carrier
A molecule required by an enzyme in order to function
Why is oxygen important in the ETC
Without oxygen NADH and FADH cannot by reoxidised and therefore made available to pick up more hydrogen atoms
How much ATP does NAD generate
3
How much ATP does FAD generate
2
How many turns of the kerbs cycle does glucose give
2
What is the total molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose respired
38
State the stage of respiration that can occur without respiration
glycolysis
How many proton pumps can NAD use
3
How many proton pumps can FAD use
2
Why can FAD only use 2 proton pumps
FAD passes the hydrogen atoms directly to the second proton pump
How many hydrogen atoms are needed to synthesise one ATP molecule
2
Describe lactic acid fermentation
Pyruvate is the hydrogen accepter and is reduced to lactate regenerating NAD
Describe alcoholic fermentation
Pyruvate is converted to carbon dioxide and to ethanal, a hydrogen accepter, by decarboxylase.
Ethanal is reduced to ethanol and NAD is regenerated
Is lactic acid fermentation reversible
yes
Is alcoholic fermentation reversible
no and it will accumulate in the cells and can rise to toxic concentrations
State the yield of ATP under anaerobic respiration
2 ATP by substrate level phosphorylation
What happens to triglycerides as a respiratory substrate
it is hydrolysed to glycerol and fatty acid chains
Glycerol is converted into triose phosphate
Fatty acid chains molecules are split into 2C fragments which enter the krebs cycle as acetyl coenzyme A
Gives the pros and cons of respiring fats
More carbon atoms so more carbon dioxide is produced. More carbon dioxide produced than could be removed quickly enough
More hydrogen atoms so more FAD and NAD are reduced so more ATP produced
More hydrogen atoms so more water is produced
What happens to proteins as a respiratory substrate
Proteins are hydrolysed into their constituent amino acids
When are proteins used as a respiratory substrate
starvation
What happens to amino acids as a respiratory substrate
The amino group is converted into urea
The residue is converted to acetyl CoA, pyruvate or some other Krebs cycle intermediate