FIN Exam 2: Abdominal Exam
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Sequence for abdominal exam
Inspection
Auscultation
Percussion
Palpation
Why is auscultation done before percussion and palpation when performing an abdominal exam?
Percussion/palpating could make the internal structures jostled around/move and stimulate GI movement before being able to assess base GI sounds (e.g., stimulate peristalsis)
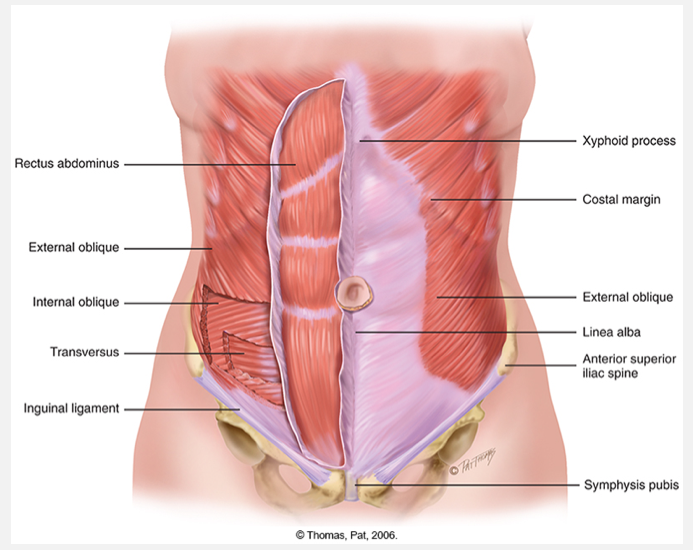
Musculature of abdomen
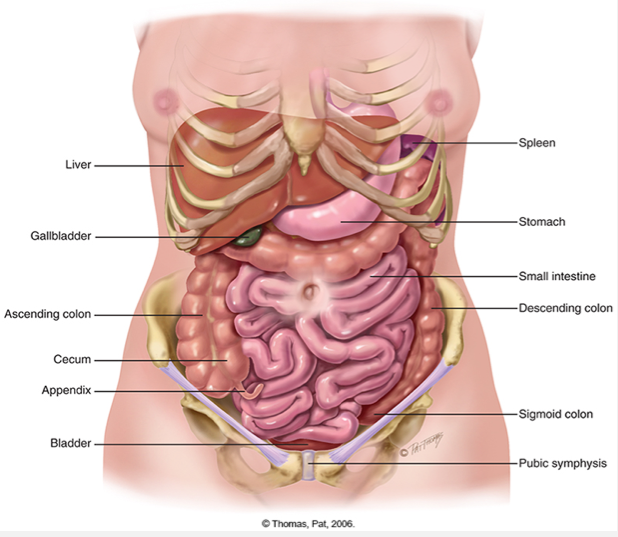
Organs of the GI tract
Preparation for an abdominal exam (5 steps)
Ask whether the patient needs to void (if so let them go before exam)
Place patient in supine position with knees slightly flexed (pillow under knees for comfort)
Examiner should stand on patient’s right side
Raise bed to a comfortable working position
Expose abdominal area
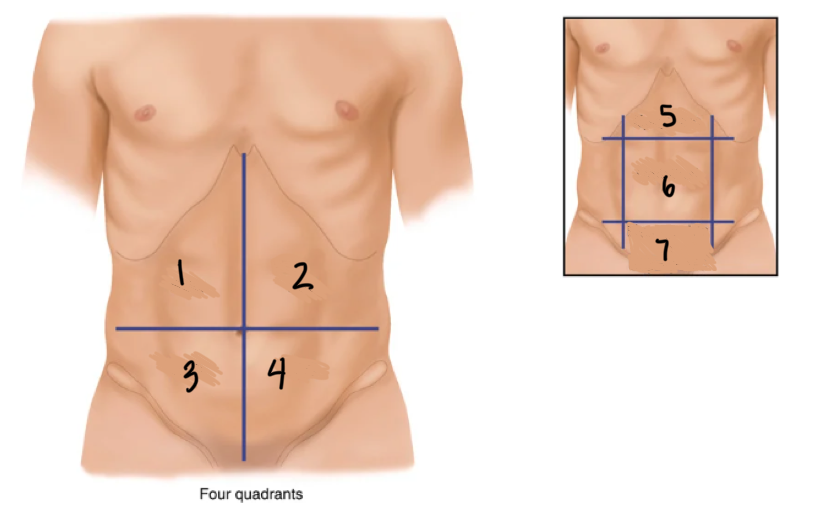
Label the parts of the abdomen
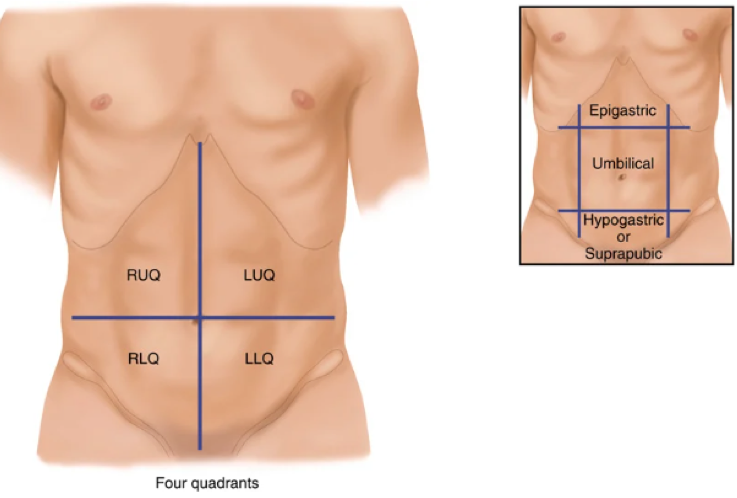
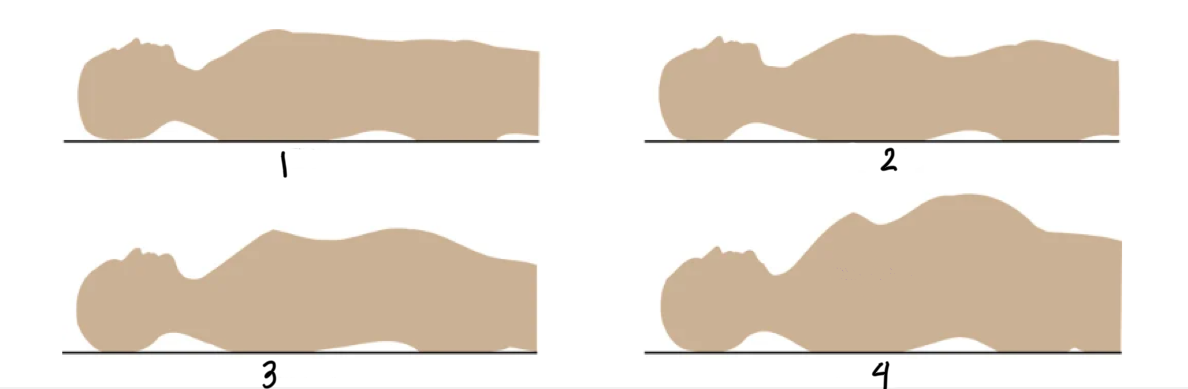
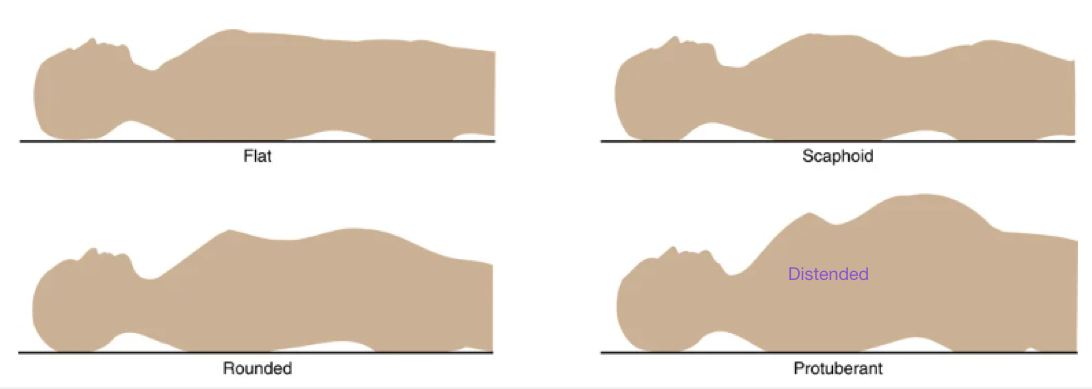
Label the contours, and what should you observe
How to auscultate for bowel sounds
Use diaphragm of stethoscope
Begin in RLQ and proceed through each quadrant in clockwise direction
To note: presence, character, and frequency of bowel sounds
Borborygmus
a rumbling or gurgling noise made by the movement of fluid and gas in the intestines
normal GI sounds
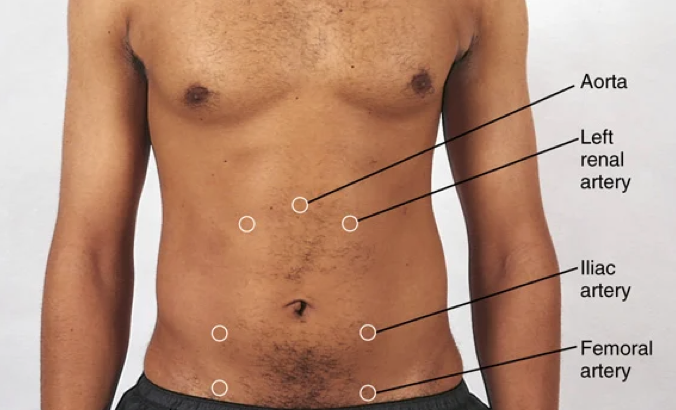
How to auscultate for bruits in abdomen
Note locations of arteries in relation to umbilicus
Auscultate over the arteries using the bell of the stethoscope
If present, note locations, pitch, and timing of bruit
How to percuss abdomen
Percuss in all four quadrants using zig-zag pattern
Note predominant sound (tympani) and areas of dullness
Where will dullness be heard during percussion of the abdomen? (6)
Dense organs
Descending colon (if stool is present)
A full bladder
Adipose tissue
Fluid
Mass
How to perform light palpations on the abdomen
Perform light palpation in all four quadrants
Depress skin about 1 cm
Make a gentle rotary motion with fingers
Lift fingers and proceed to next location in clockwise direction
What should you assess for when doing light palpitations on the abdomen?
Muscle guarding
Rigidity
Tenderness
How to do deep palpations on the abdomen
Perform deep palpation in all four quadrants
Depress about 5-8 cm (2-3 inches)
Palpate all areas of abdomen
What should you assess for when doing deep palpitations on the abdomen?
Tenderness
Masses
Location
Consistency
Size of any organs
Normally palpable structures???
Rebound tenderness
characterized by pain that is felt upon the release of pressure rather than during the application of pressure to the abdomen
How to perform a rebound tenderness exam
Perform at end of exam
Hold hand perpendicular to abdomen
Push down slowly and deeply, then lift up quickly
There should be no pain on release of pressure
What does pain after deep palpation indicate?
Peritonitis or appendicitis