U1: Atomic Structures and Properties
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Atomic Mass Unit (AMU or U)
Measures mass at an atomic scale, because atoms are super small.
Protons and Neutron’s Effect on Atomic Mass
Protons and Neutrons weigh way more than electrons, approximately 1 amu (or u), so you can use the number of protons and neutrons in an element to find its atomic mass.
Isotope
Different version of an element with same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Atomic Number
The number assigned to an element on the periodic table, equal to the number of protons found in an atom of that element.
Avogadro’s Constant
6.02214076 × 1023. Often abreviated to 6.022 × 1023.
Mole
6.022 × 1023. of something, a unit of measurement.
Imagine it like saying a dozen of something. If you have a dozen Hydrogen atoms, you have 12 hydrogen atoms. If you have a ____ of hydrogen atoms, you have 6.022 × 1023 hydrogen atoms.
If 1 atom weighs 6.94 u, then:
6.022 × 10²³ atoms of lithium (1 mole of lithium) will weigh 6.94 grams
Isotope
A different version of an element with the same # of protons but a different number of neutrons.
Mass Spectrometry
A process that takes a certain element and shows the abundance of each of that elements isotopes in nature.
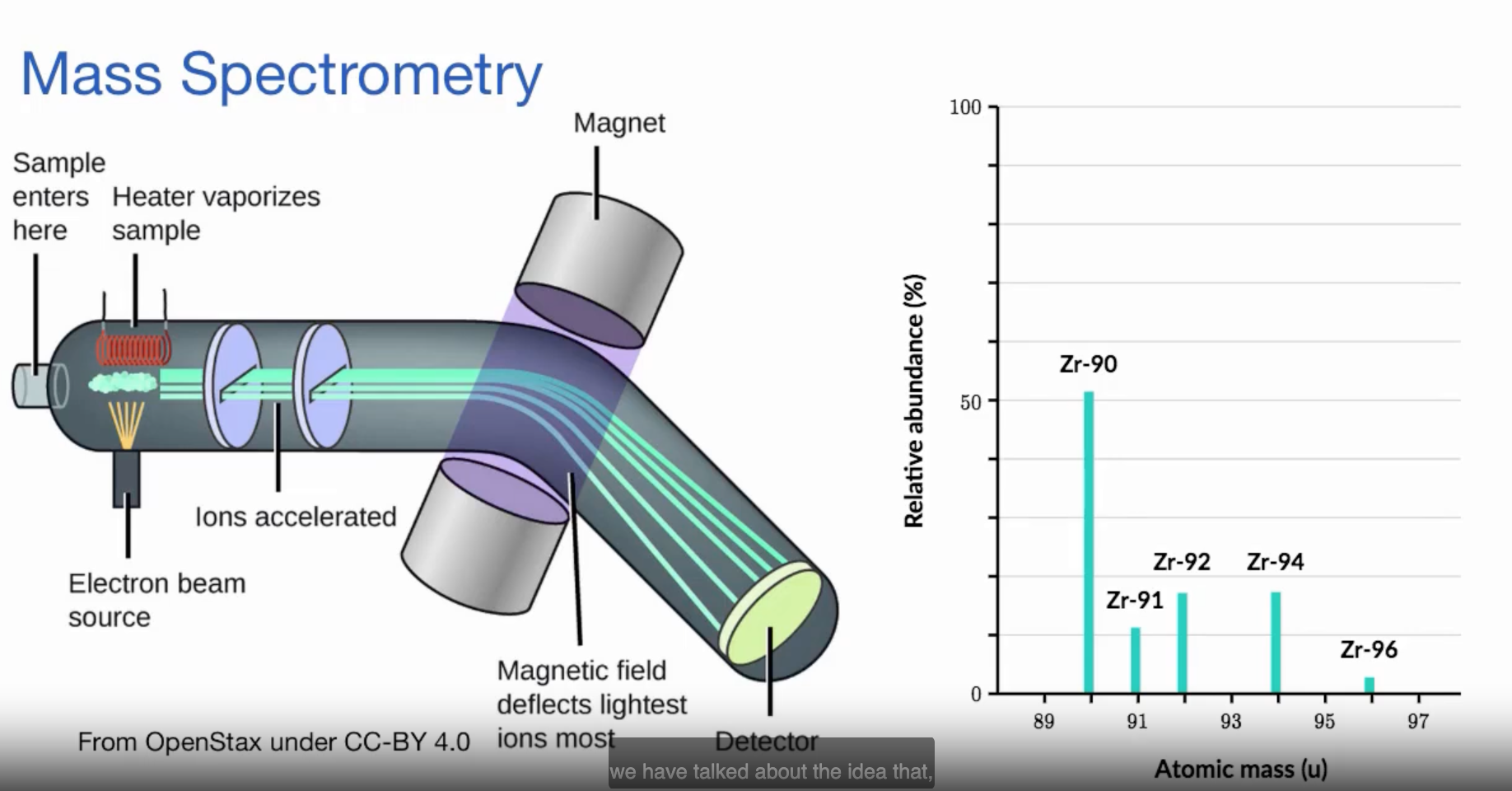
Relative Abundance
The percentage of that isotope found in a naturally occuring sample of its element.
Subatomic Particles
The parts making up an atom. They include protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Mass Number
The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom of a given element.
Atomic Mass
The mass of an isotope in u, often close to the mass number because the mass of neutrons and protons are close to 1 u, and the mass of electrons is neglible.

Average Atomic Mass
An average of of the atomic masses of all isotopes of an element weighted based on each isotope’s relative abundance.