AP Micro Monster Vocab (GRAPHS INCLUDED)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Absolute advantage
The ability of an individual or group to carry out a particular economic activity more efficiently than another individual or group.
Accounting profit
The difference between total revenue and explicit costs.
Allocative efficiency
A state of the economy in which production represents consumer preferences; resources are allocated in a way that maximizes total benefit.
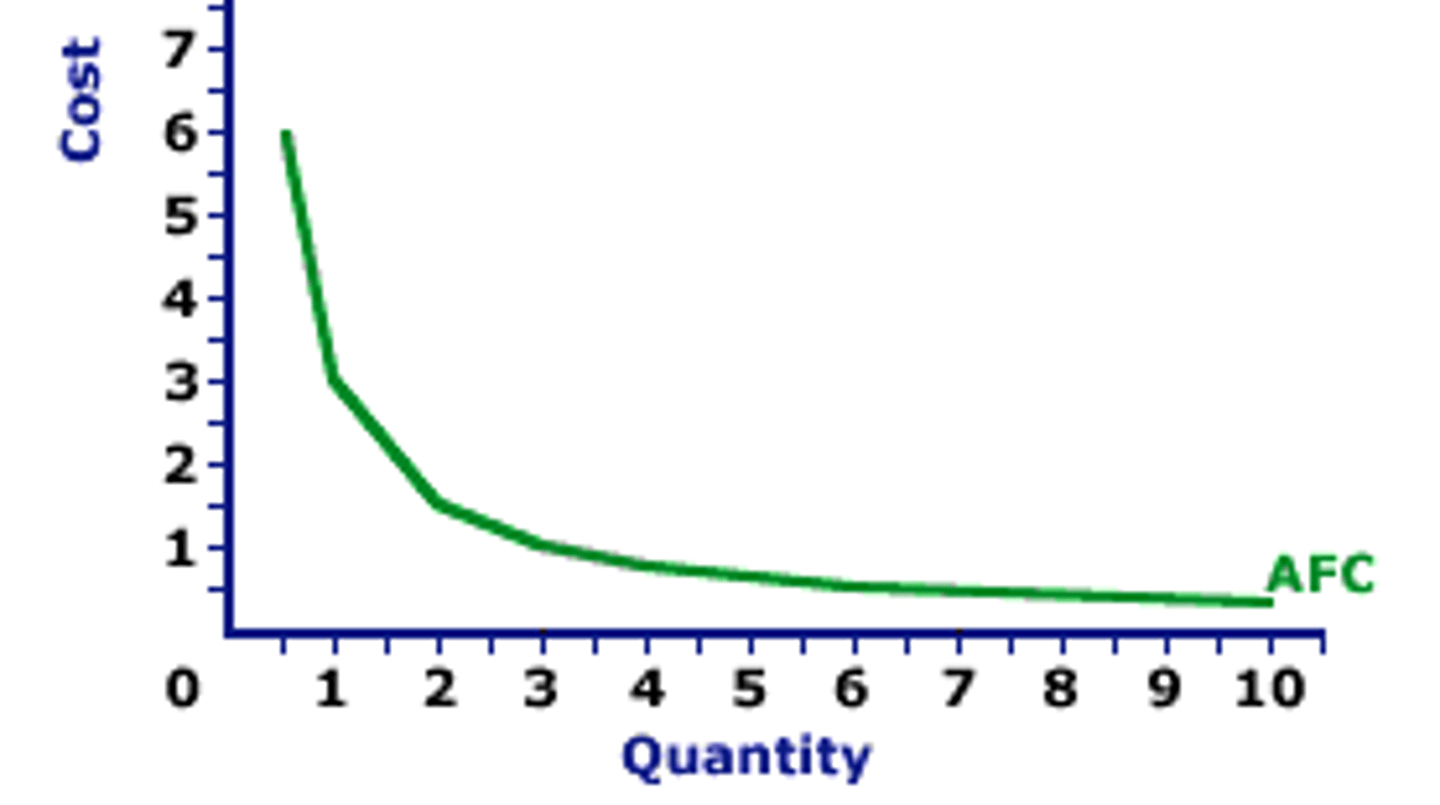
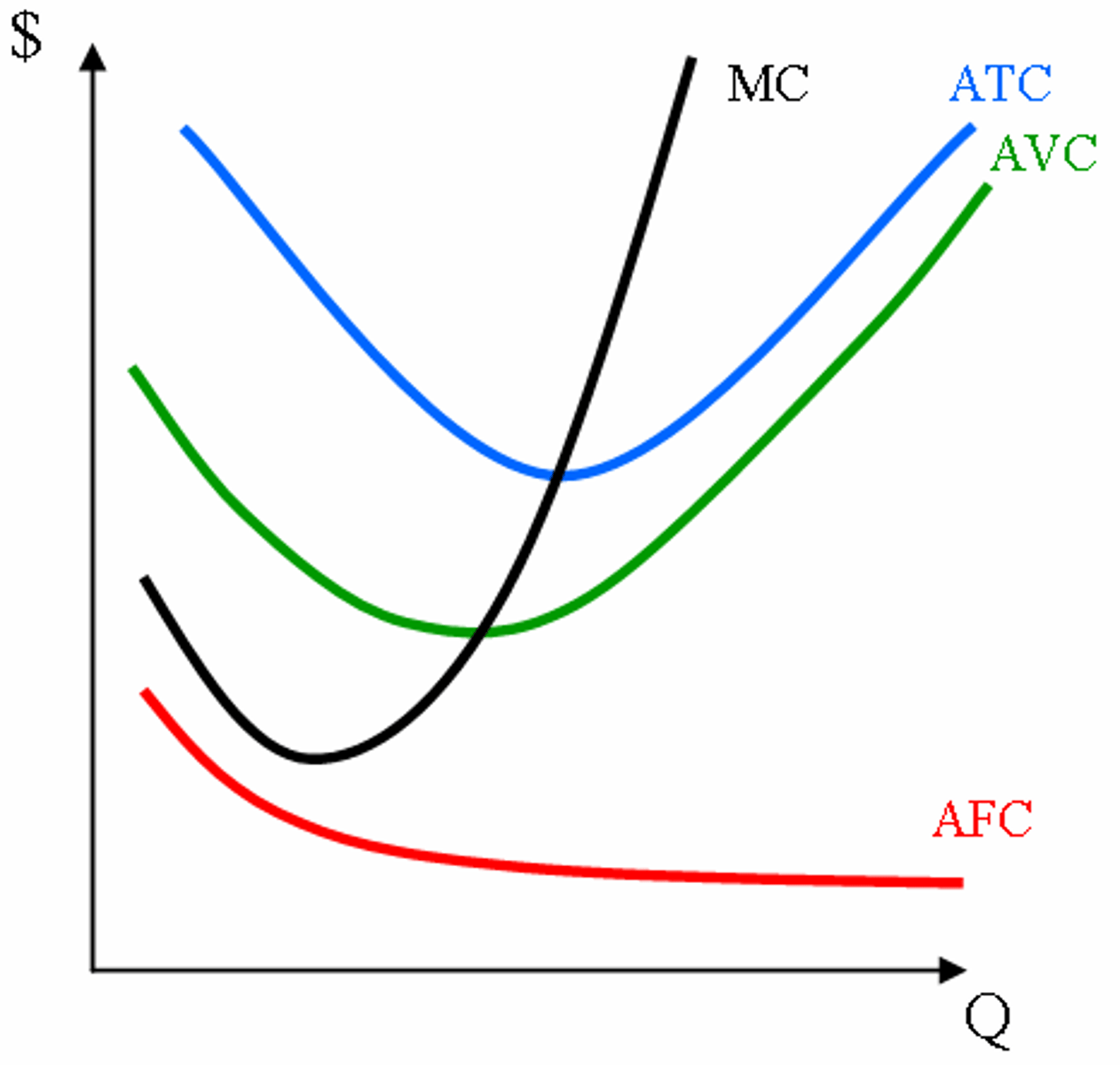
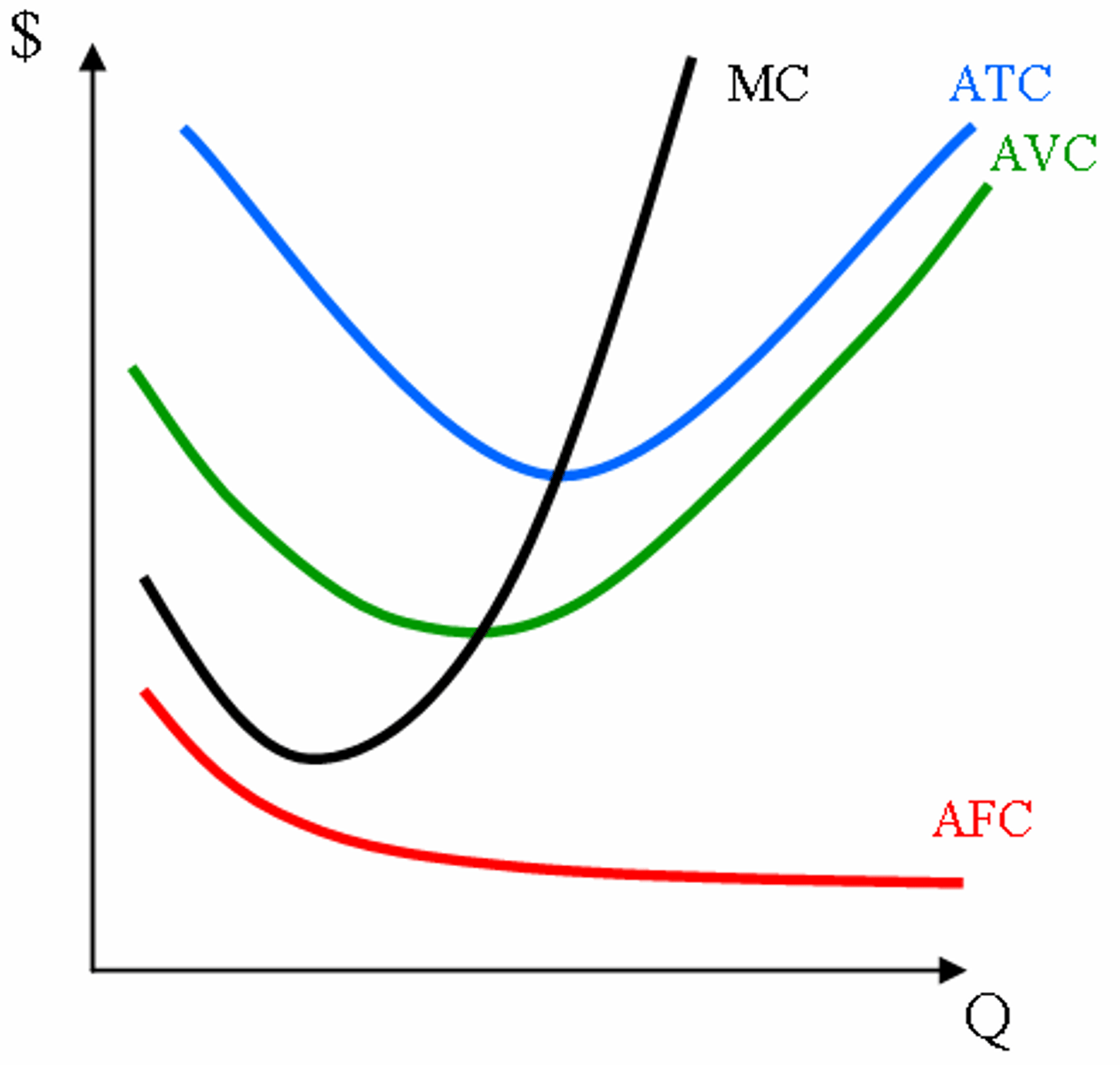
Average fixed cost (AFC)
Total fixed costs divided by the quantity of output produced.
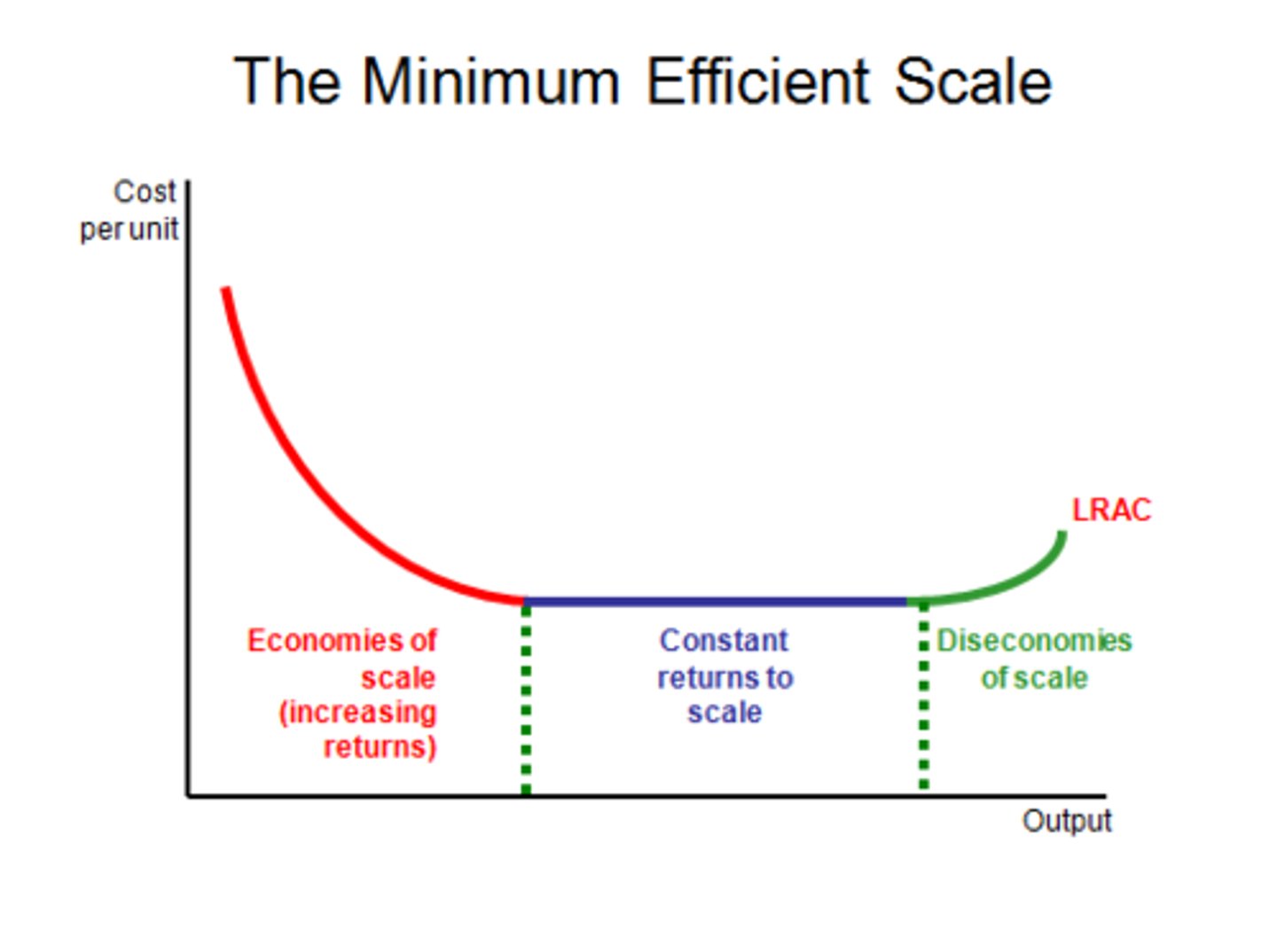
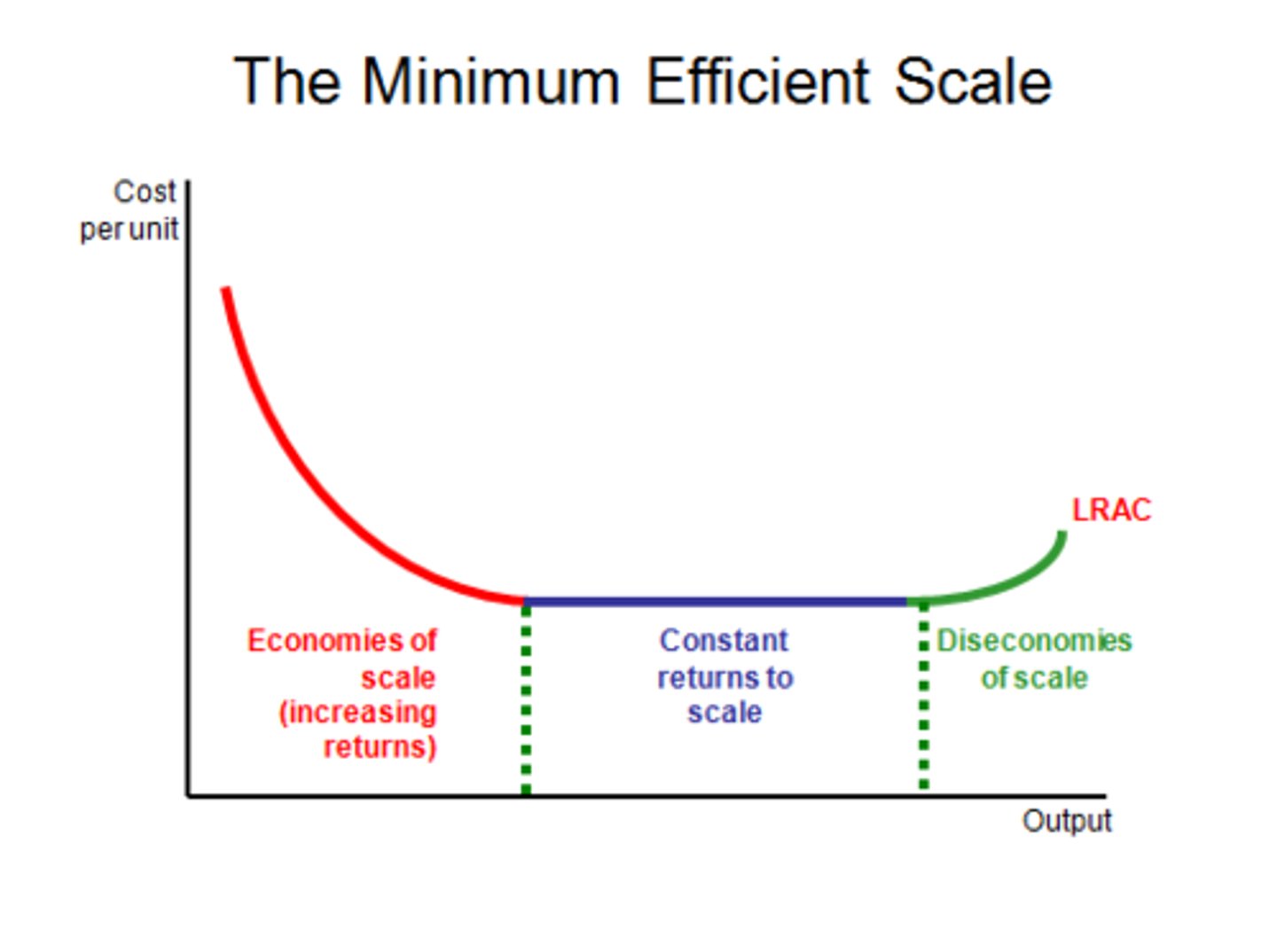
Diseconomies of scale
The phenomenon where, as a company or organization grows, the costs per unit increase.
Economic costs
The total costs of production, including both explicit and implicit costs.
Economic profit
Total revenue minus total costs, including both explicit and implicit costs.
Economies of scale
The cost advantages that a business obtains due to the scale of operation, with cost per unit of output generally decreasing with increasing scale.
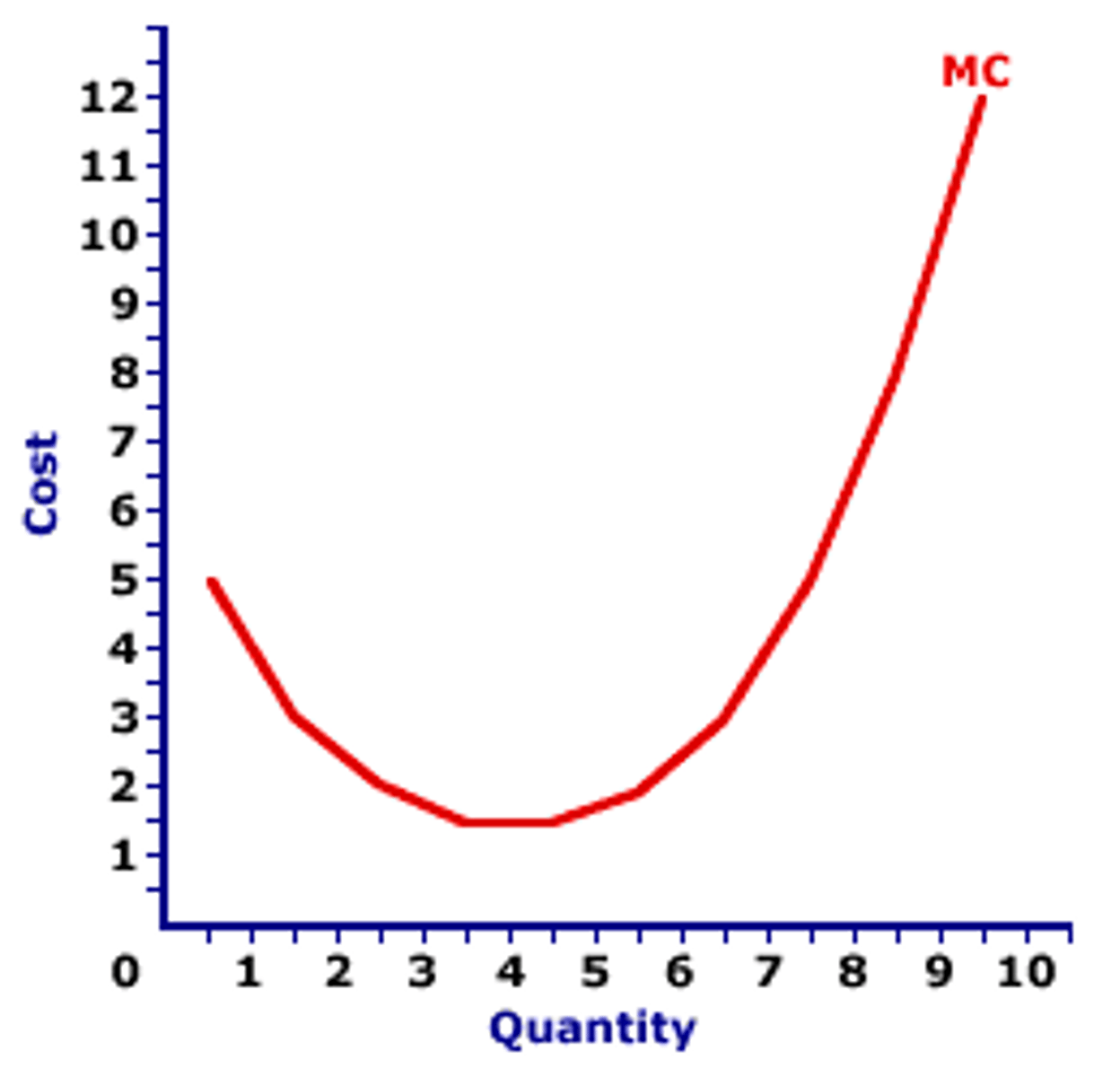
Marginal cost (MC)
The increase in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit of a product.
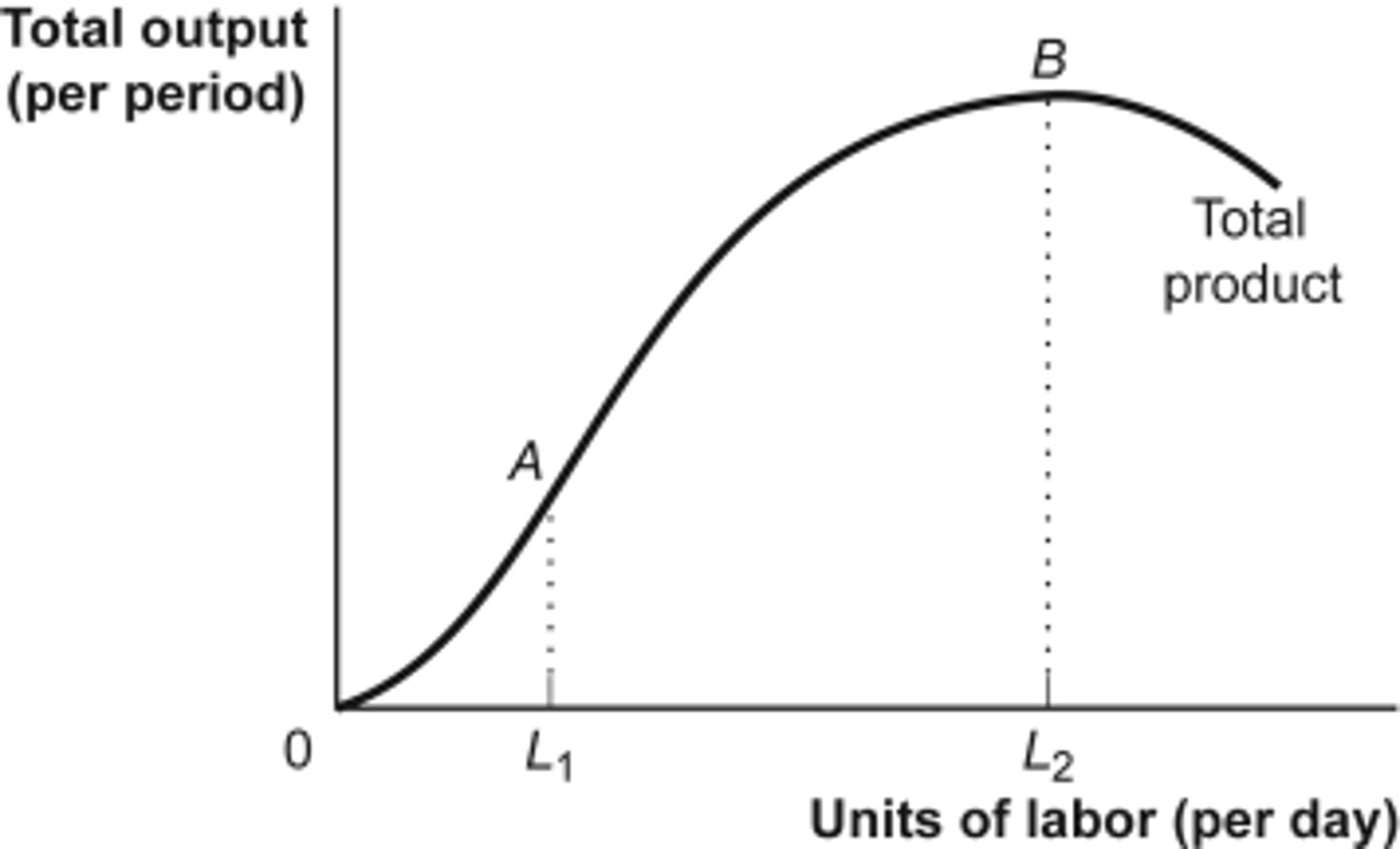
Marginal product (MPL) of labor
The additional output that is produced by adding one more unit of labor.
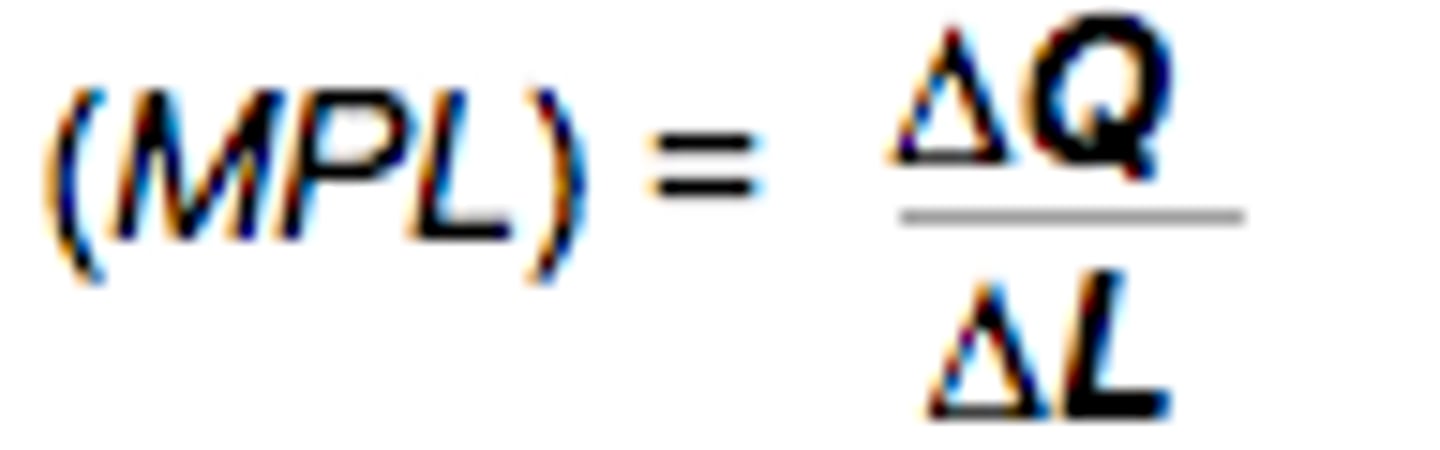
Marginal resource cost (MRC)
The additional cost incurred from hiring one more unit of a resource.

Marginal revenue product of labor (MRP)
The additional revenue generated from employing one more unit of labor.
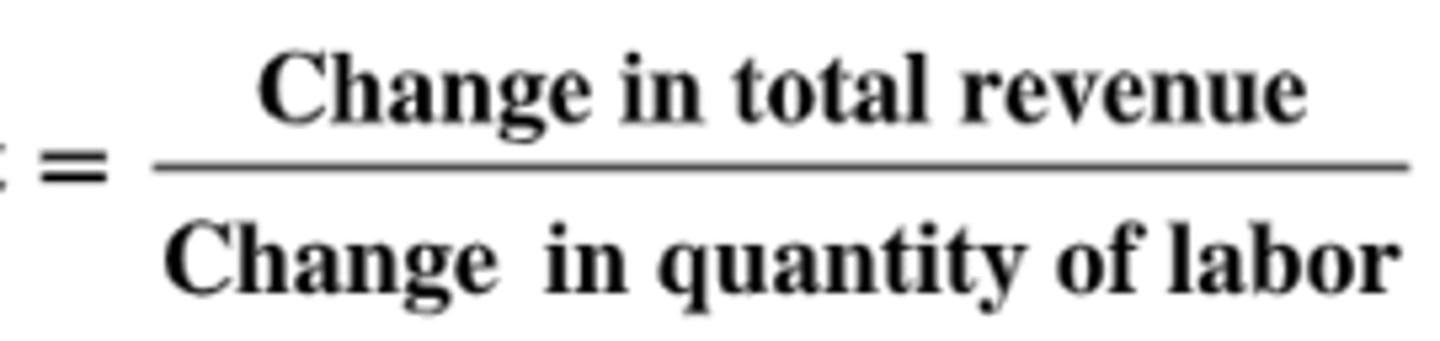
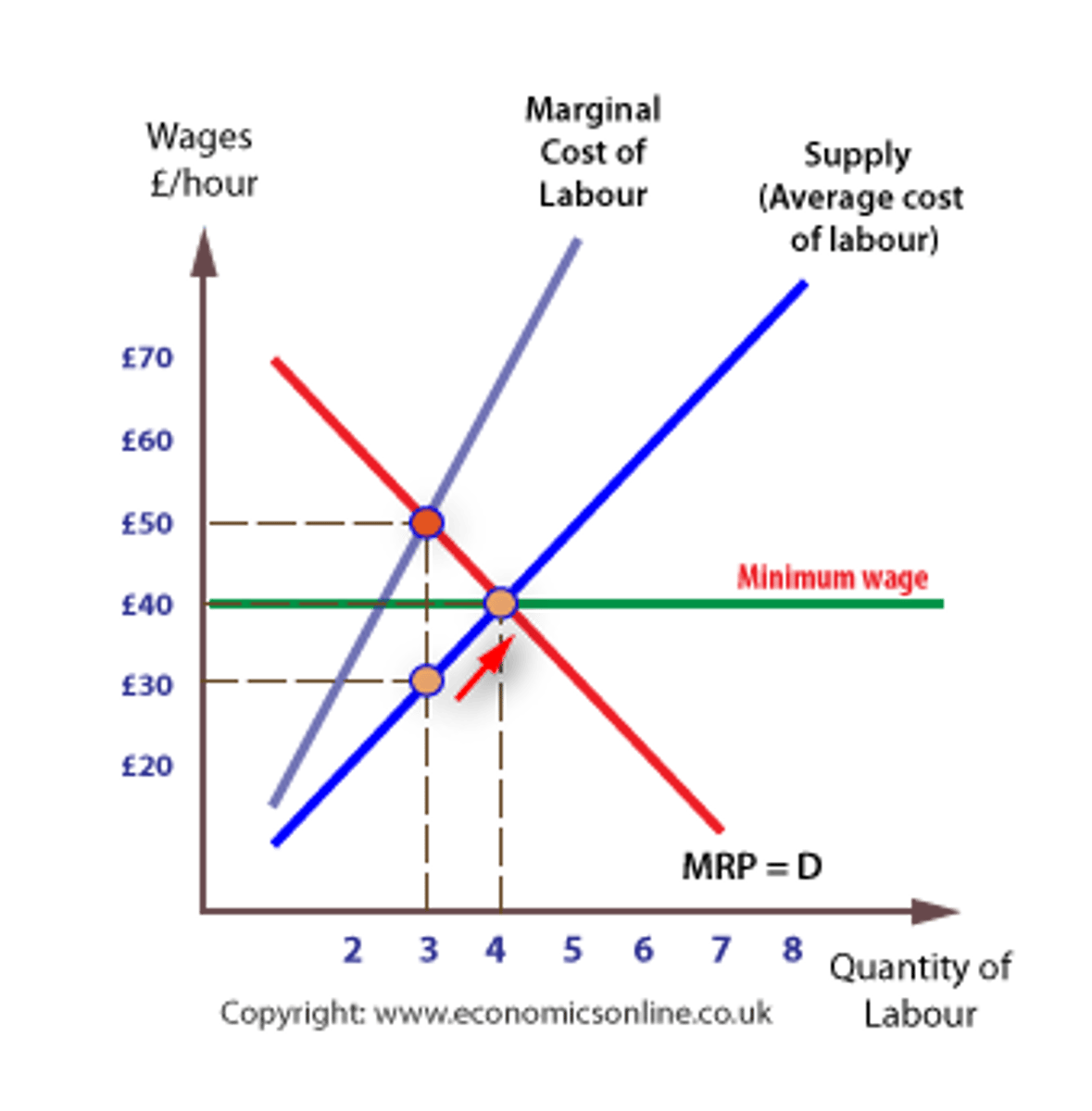
Price floor
A minimum price set by the government for a particular good or service.
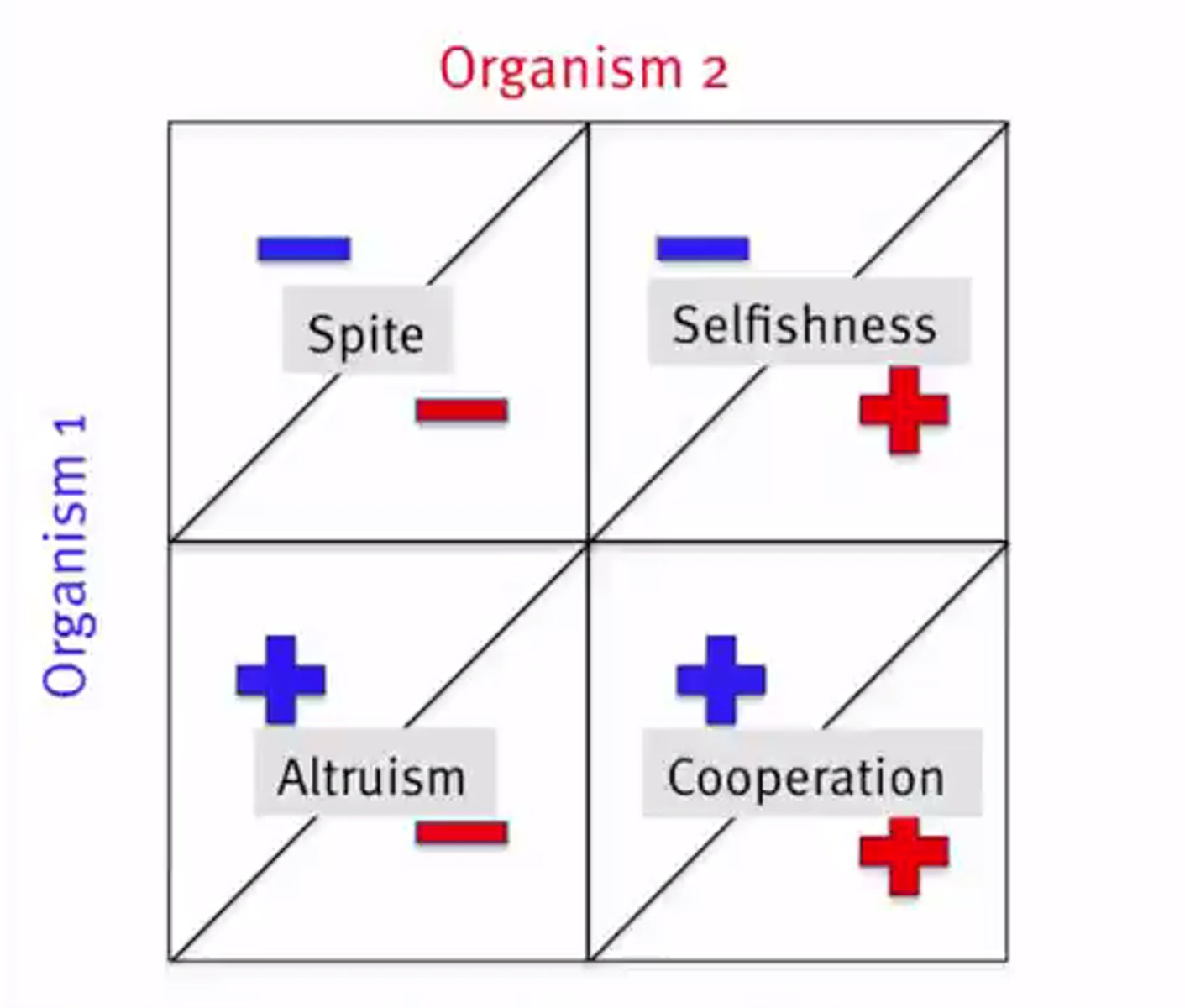
Prisoners' dilemma
A situation in game theory where two individuals acting in their own self-interest do not produce the optimal outcome.
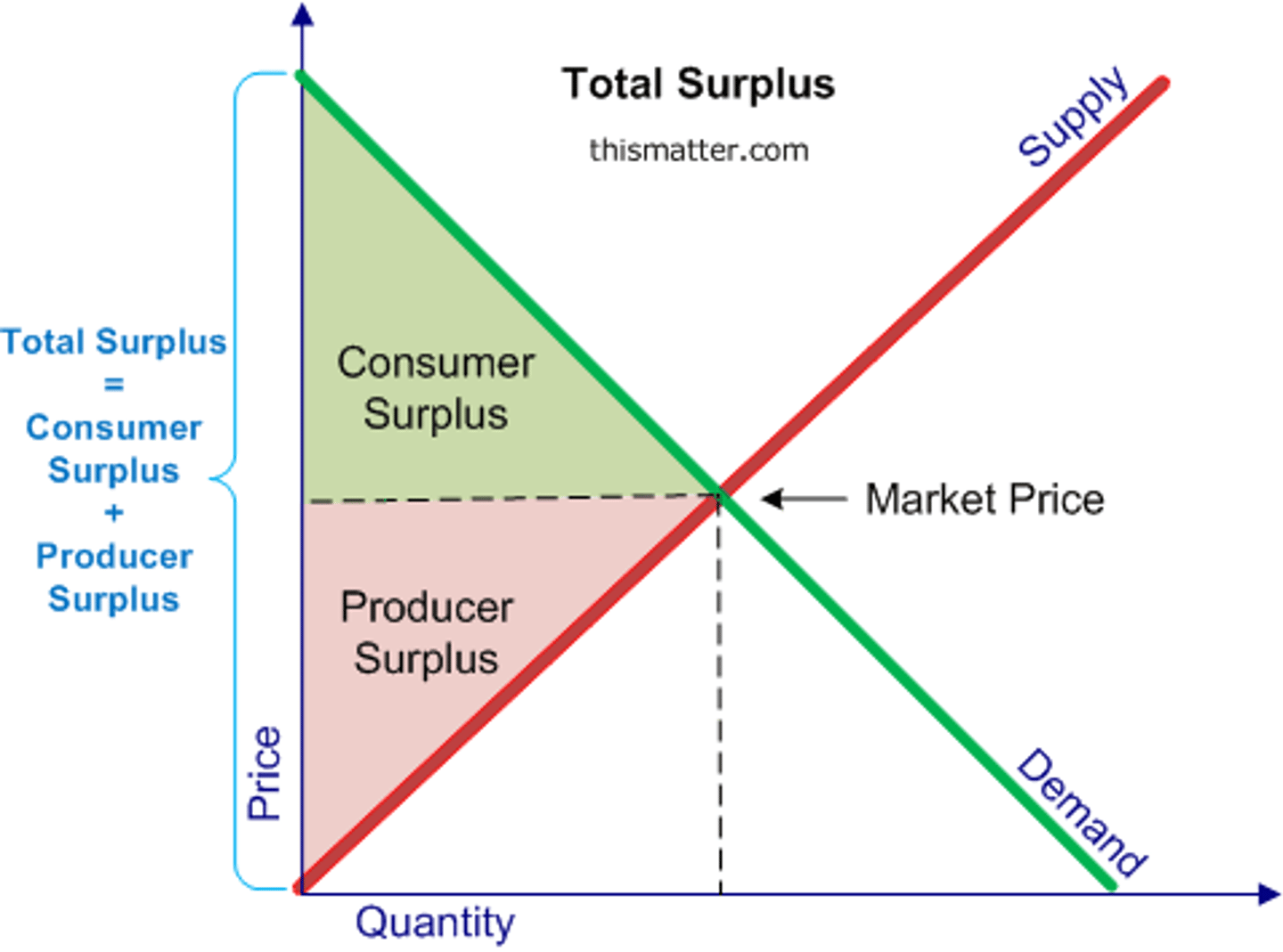
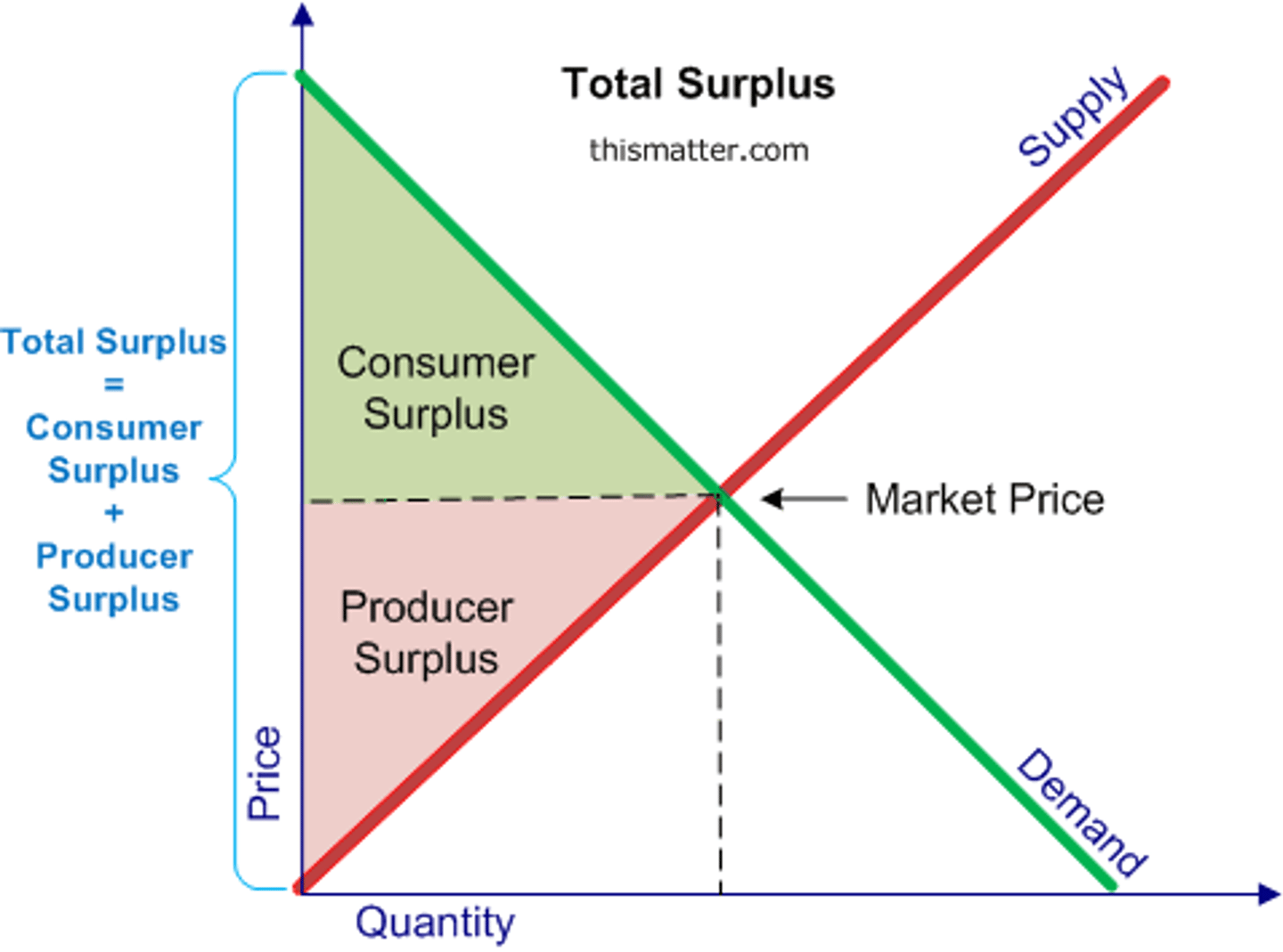
Producer surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good or service versus what they actually receive.
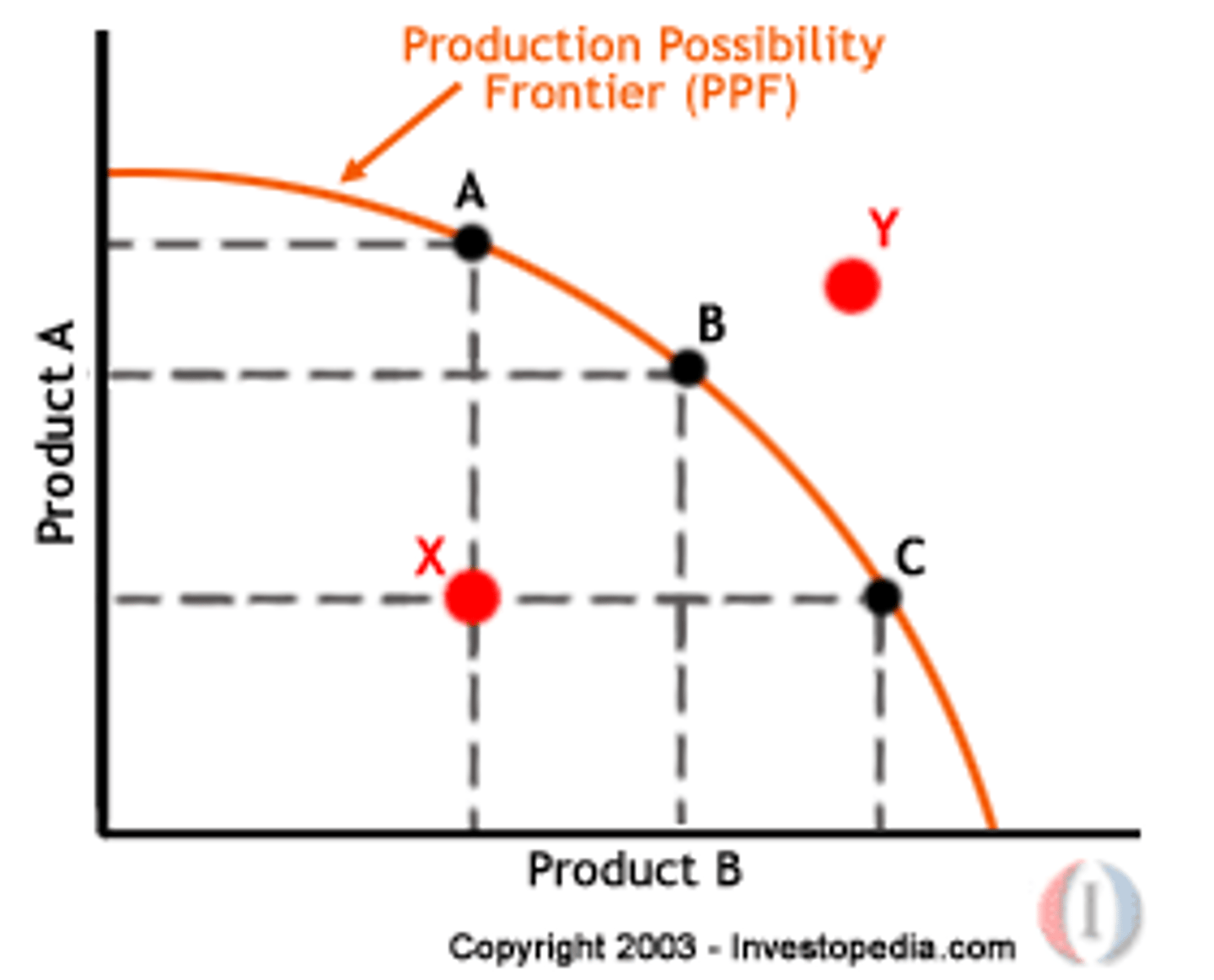
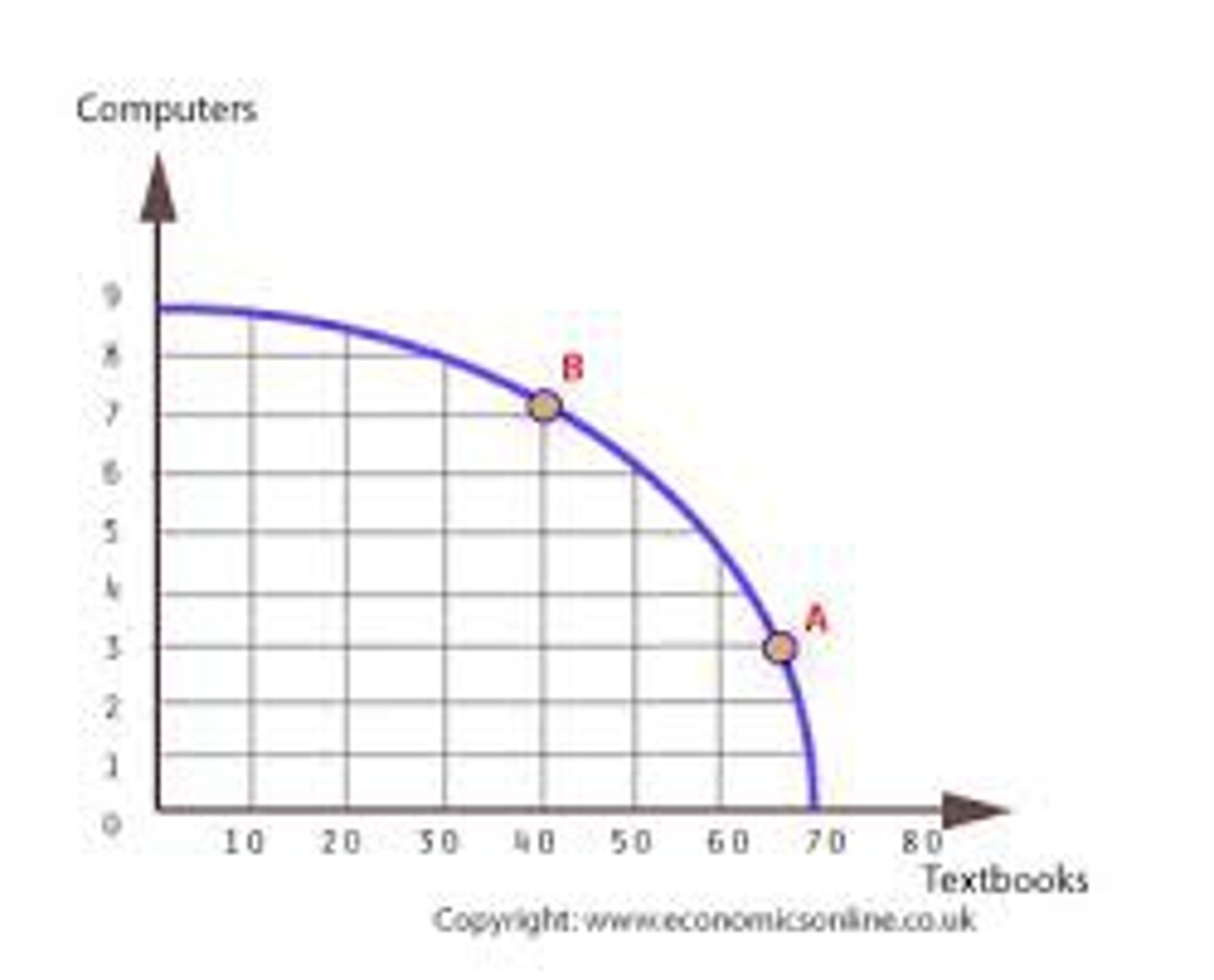
Production possibilities frontier (PPF)
A curve depicting the maximum feasible amounts of two goods that a business can produce with available resources.
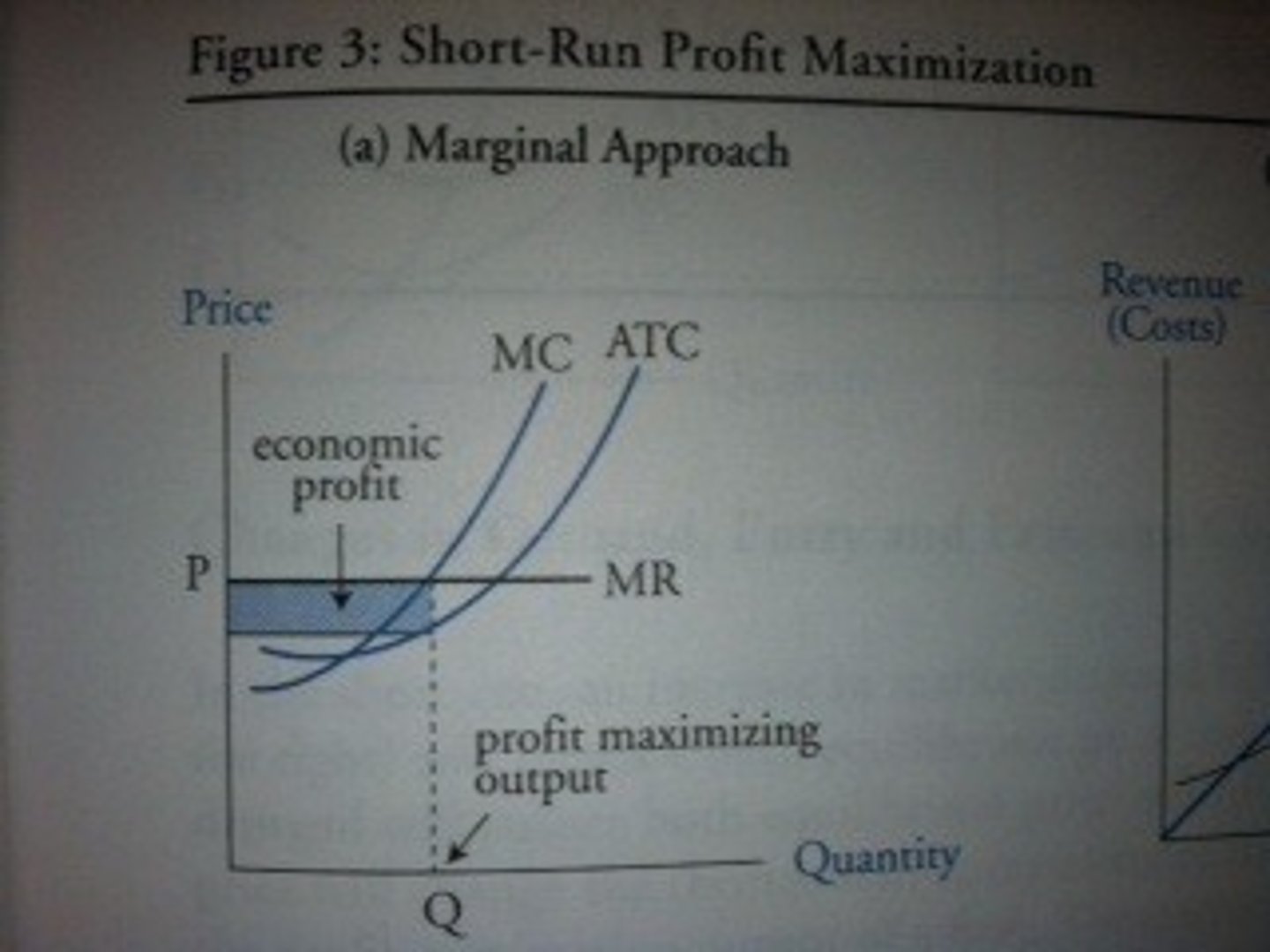
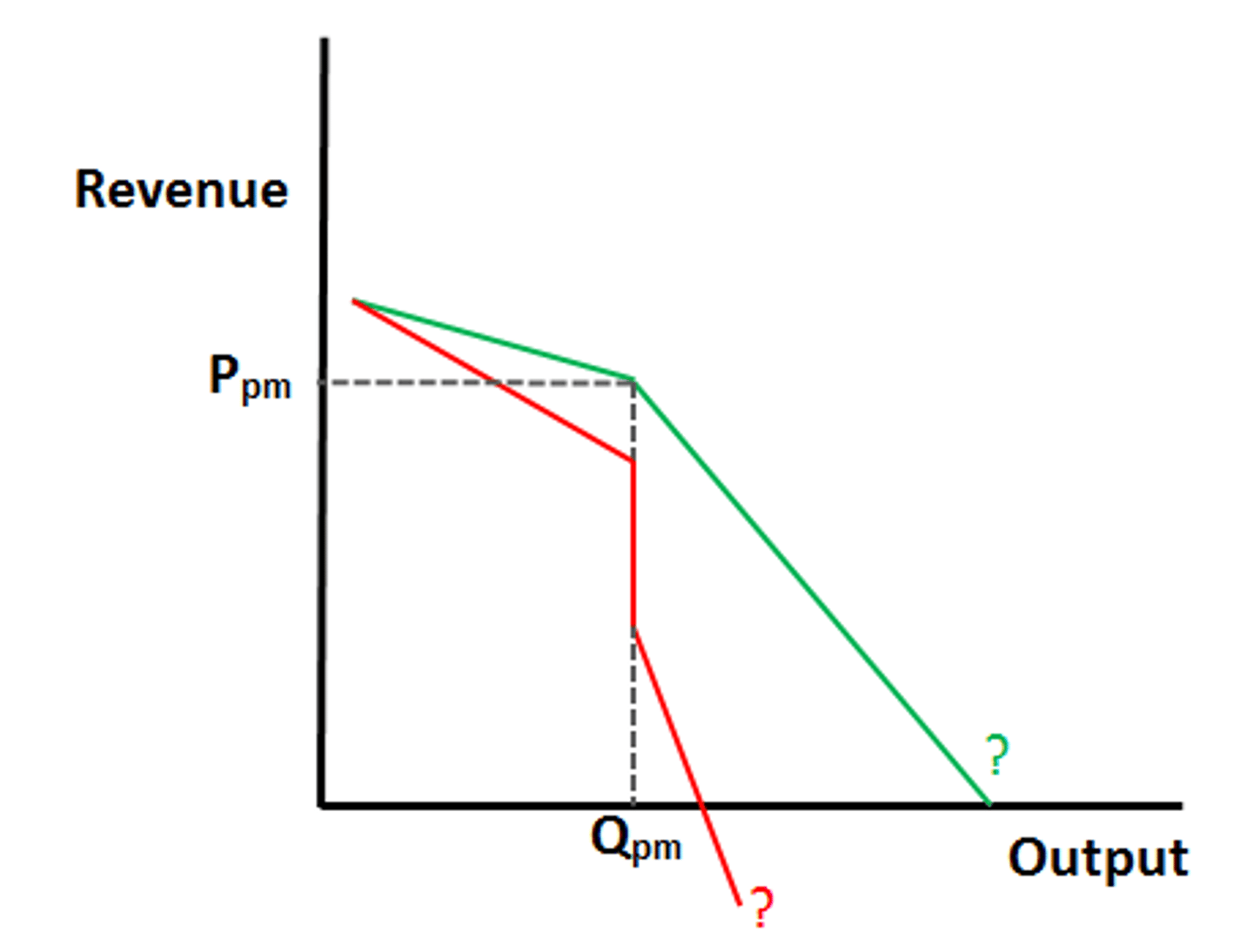
Profit maximizing
The level of output at which a firm's marginal cost equals its marginal revenue.
Average total cost (ATC)
Total costs divided by the quantity of output produced.
Explicit costs
Direct, out-of-pocket payments for expenses.

Free rider
An individual who benefits from resources, goods, or services without paying for them.
Game theory
The study of mathematical models of strategic interaction among rational decision-makers.
Human capital
The economic value of a worker's experience and skills.
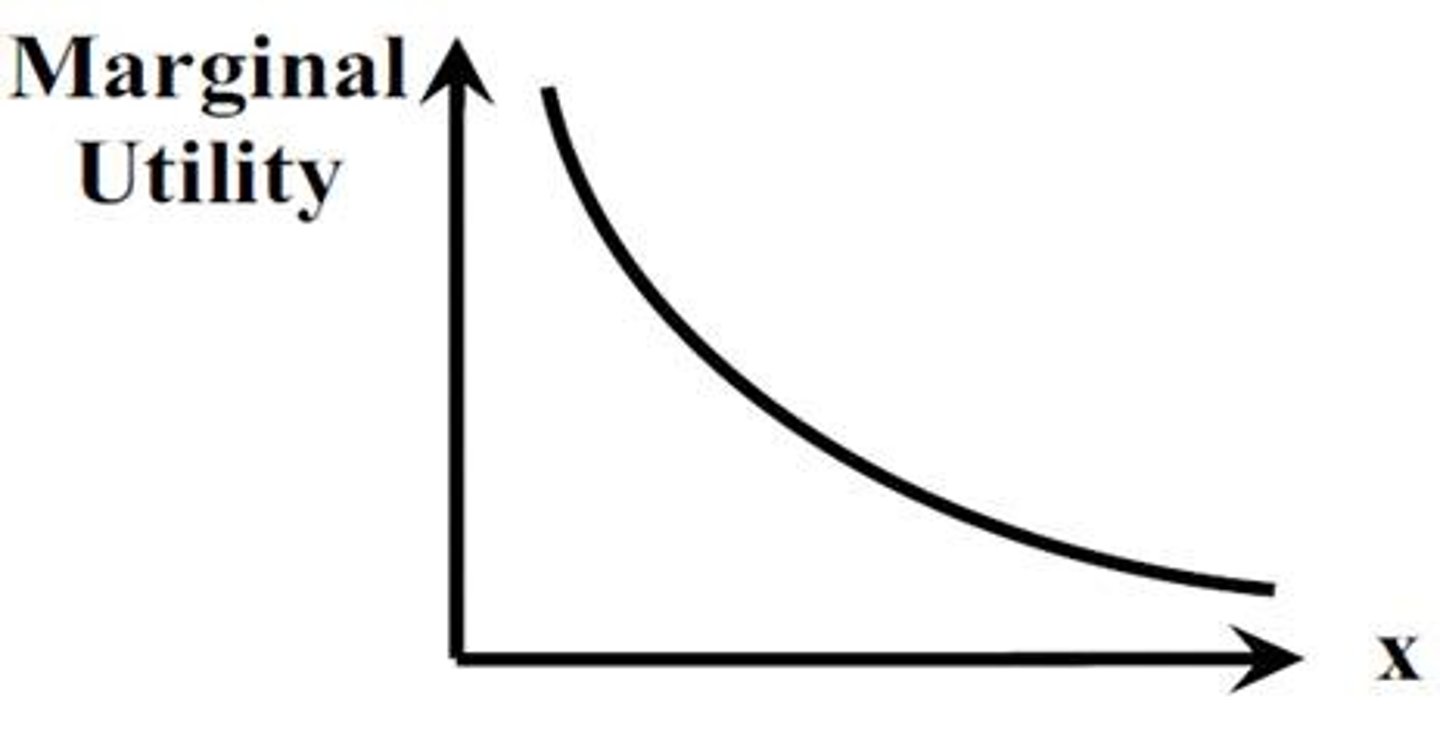
Marginal utility
The additional satisfaction or benefit received from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Market failure
A situation in which the allocation of goods and services is not efficient.
Regressive tax
A tax that takes a larger percentage from low-income earners than from high-income earners.
Progressive tax
A tax that takes a larger percentage from high-income earners than from low-income earners.
Proportional tax
A tax that takes the same percentage from every taxpayer, regardless of income level.
Average variable cost (AVC)
Total variable costs divided by the quantity of output produced.
Ceteris paribus
A Latin phrase meaning 'all other things being equal'.
Circular flow
A model that illustrates how money and goods flow through the economy.
Comparative advantage
The ability of an individual or group to carry out a particular economic activity at a lower opportunity cost than another.
Complementary goods
Goods that are often consumed together, where the demand for one increases the demand for the other. Cross Price <0
Consumer surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus what they actually pay.
Cross-price elasticity of demand
A measure of how the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good.
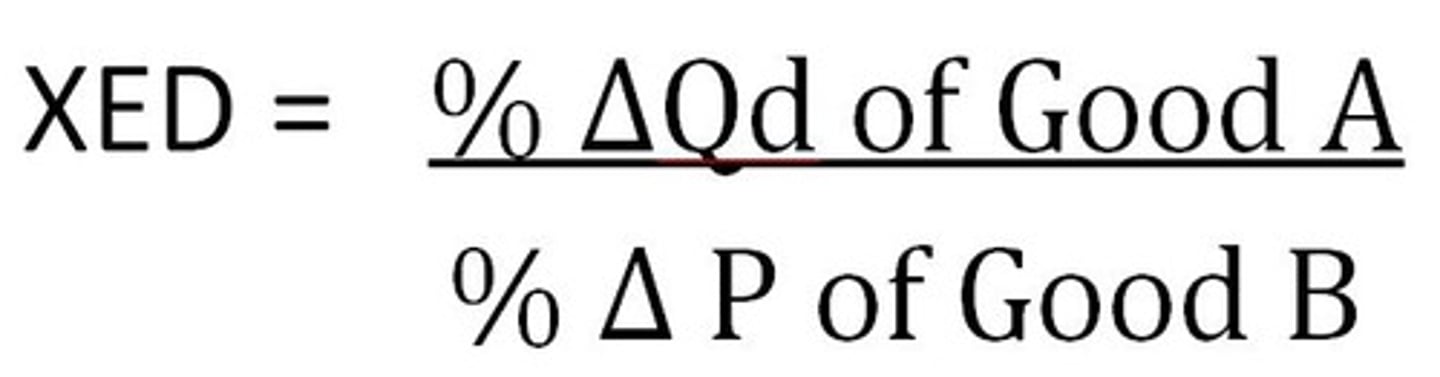
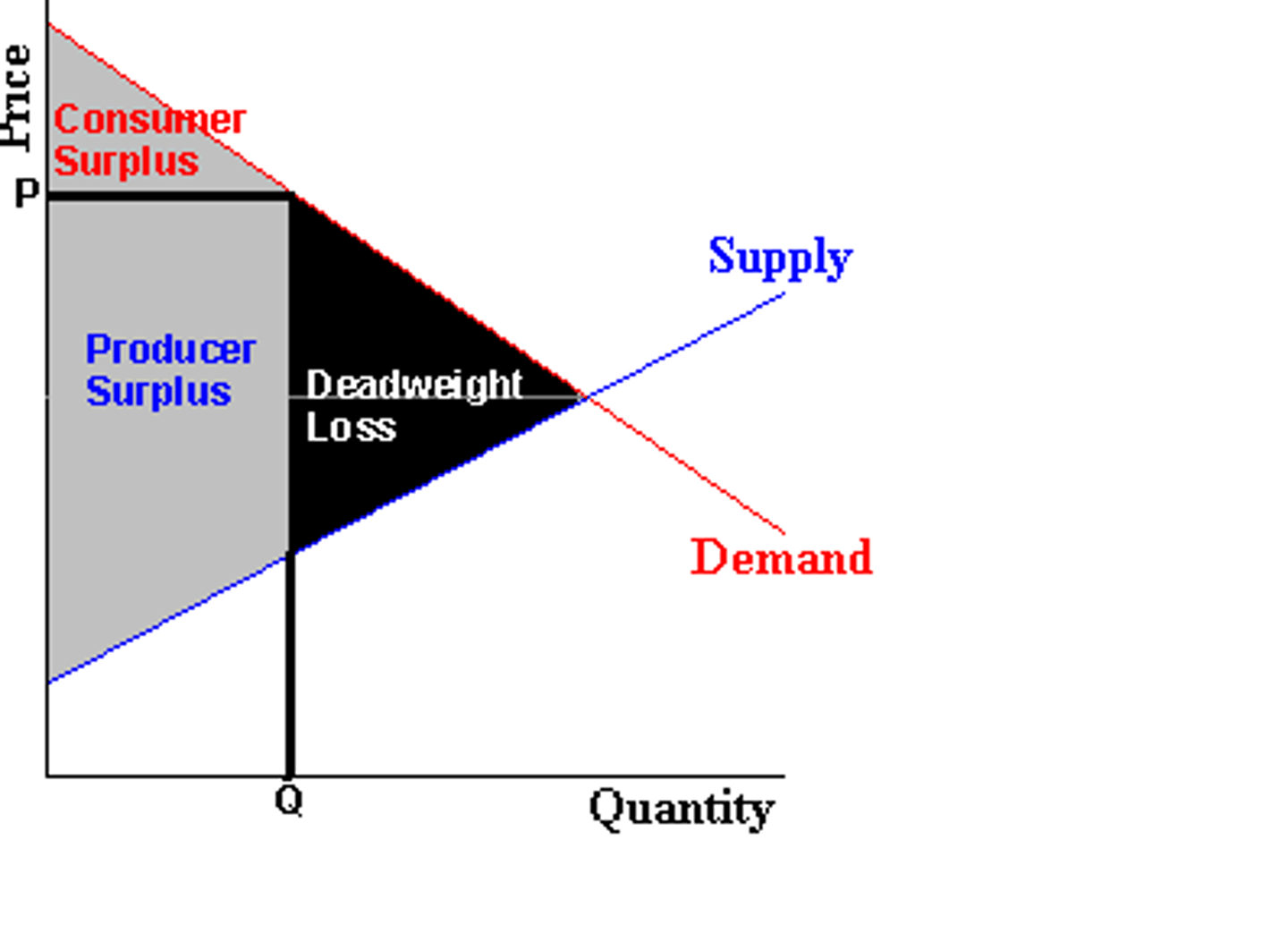
Deadweight loss
The loss of economic efficiency that occurs when the equilibrium outcome is not achievable or not achieved.
Derived demand
The demand for a factor of production or resource that results from the demand for the goods and services produced.
Determinants of demand
Factors that cause the demand curve to shift, including consumer preferences, income, and prices of related goods.
Determinants of supply
Factors that cause the supply curve to shift, including production costs, technology, and number of sellers.
Implicit costs
Costs that represent the opportunity cost of using resources owned by the firm.

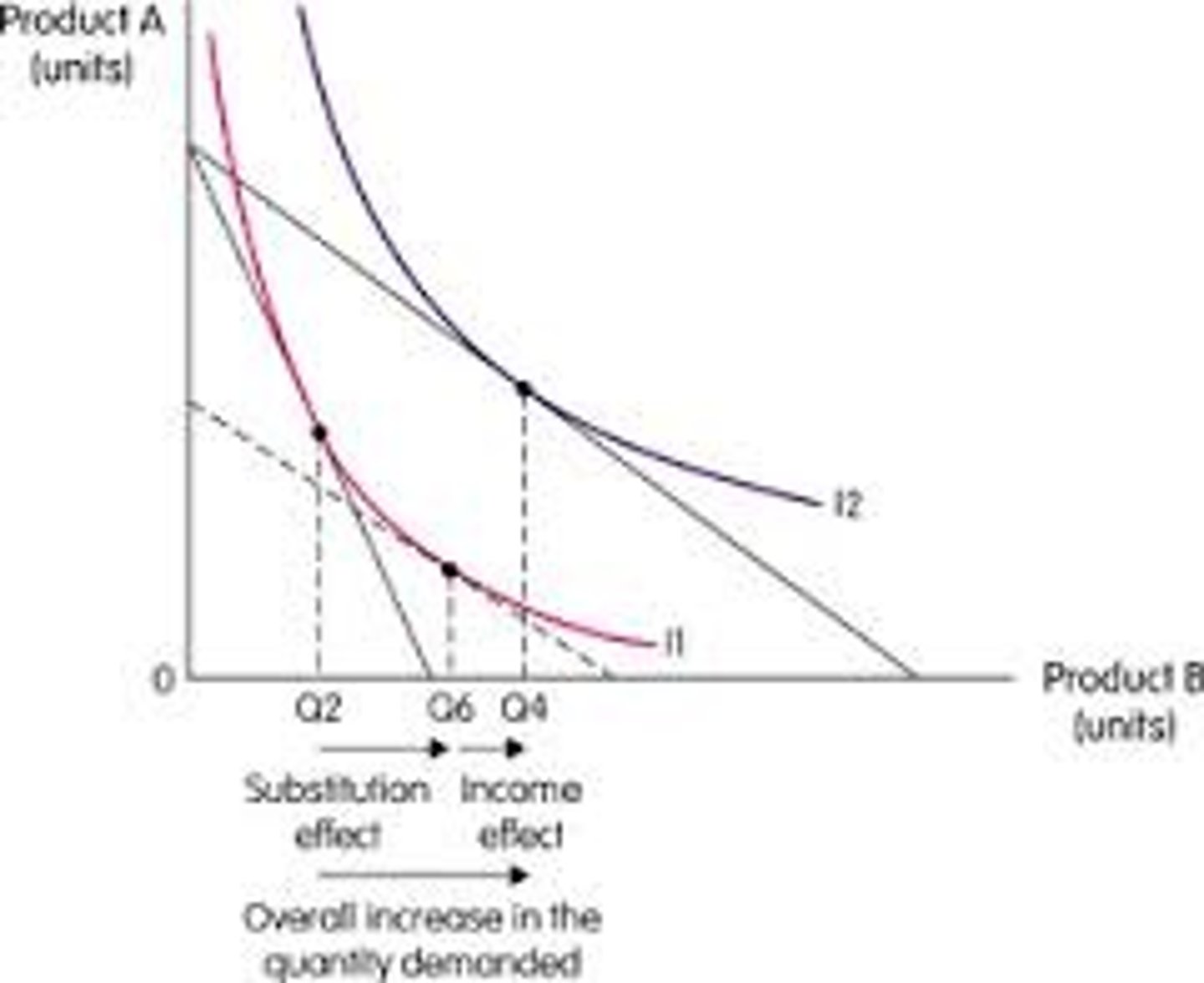
Income effect
The change in consumption resulting from a change in real income.
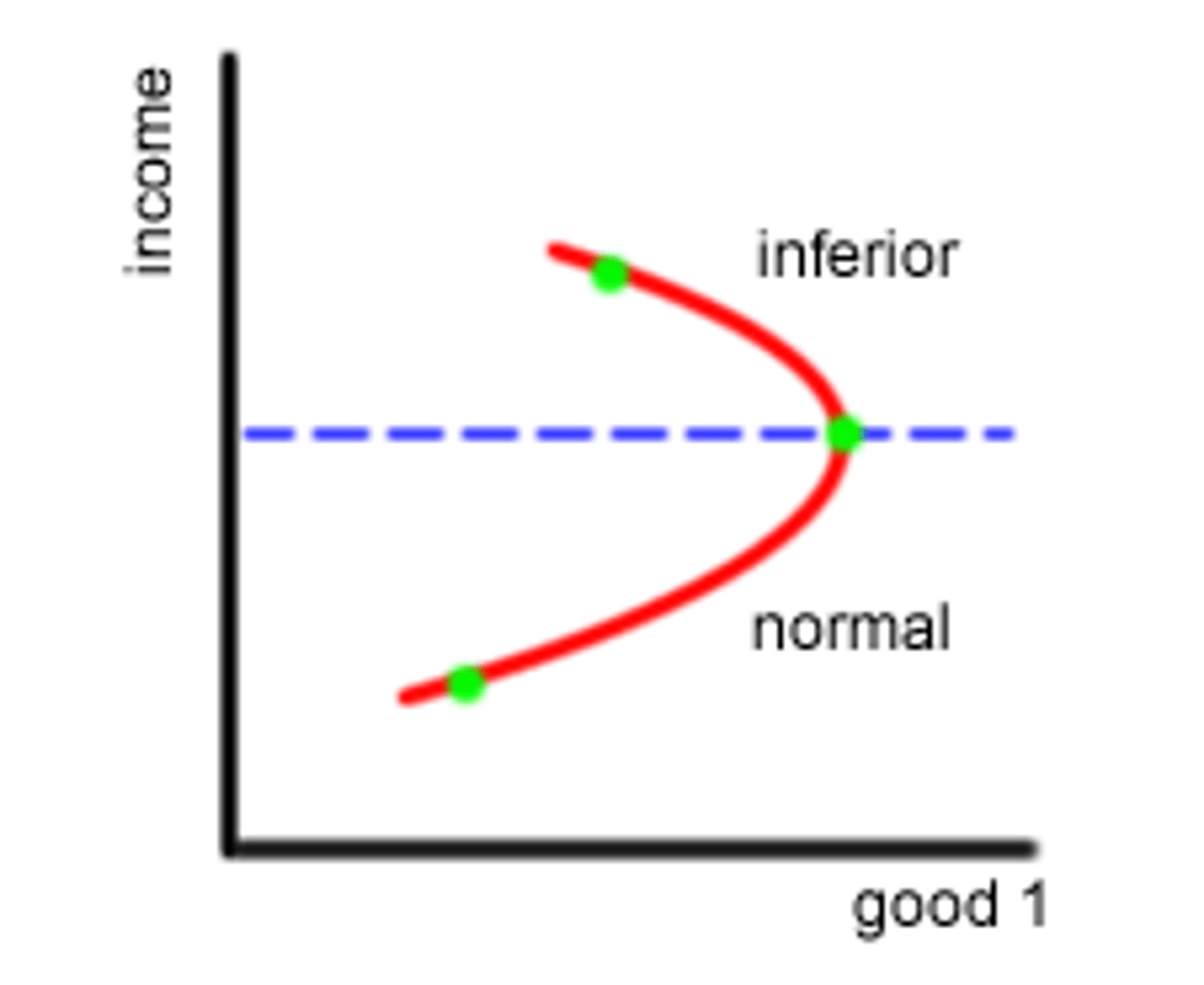
Inferior goods
Goods for which demand increases as consumer income decreases.
Income Elasticity < 0
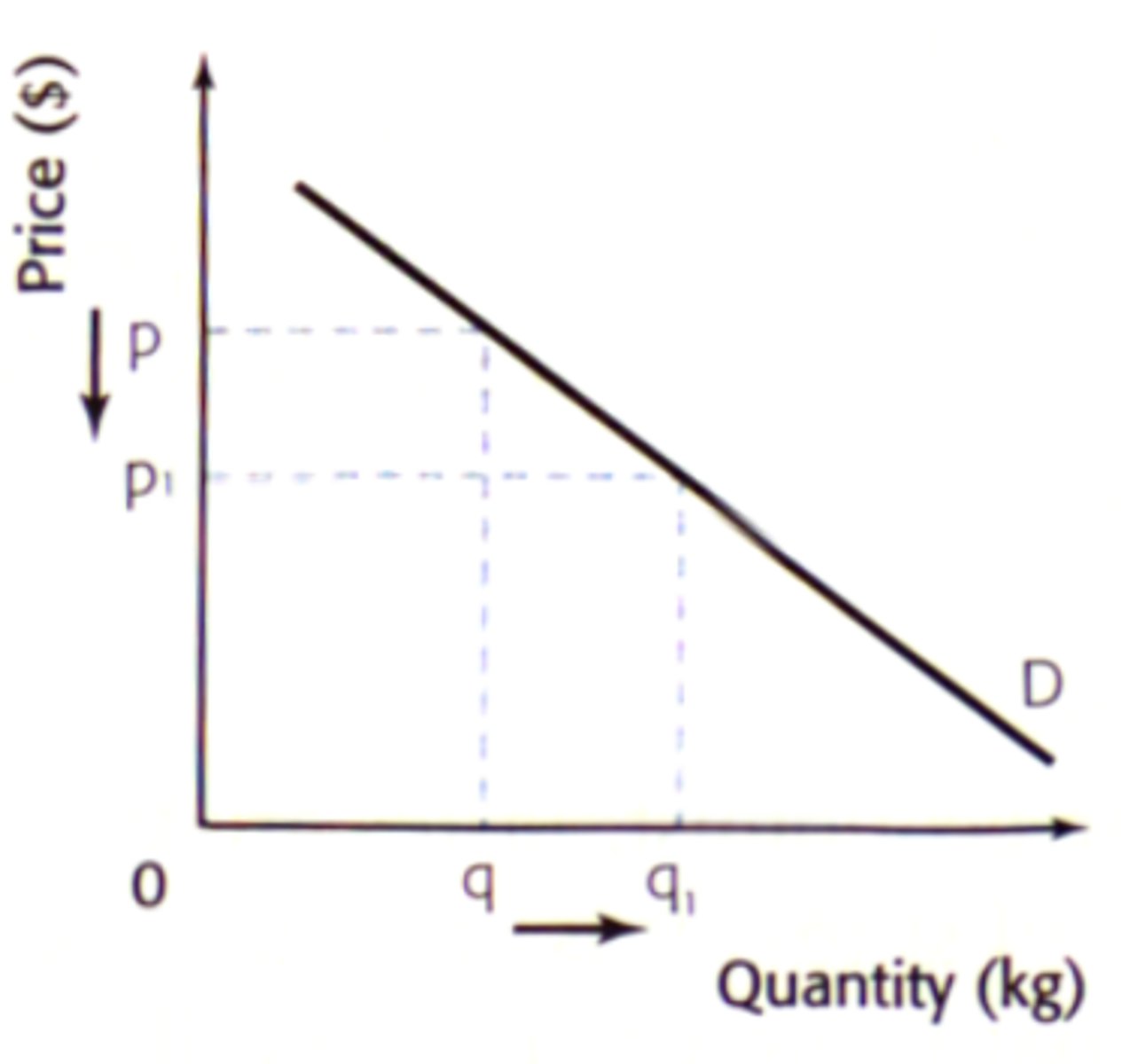
Law of demand
The principle that, all else being equal, an increase in the price of a good will decrease the quantity demanded.
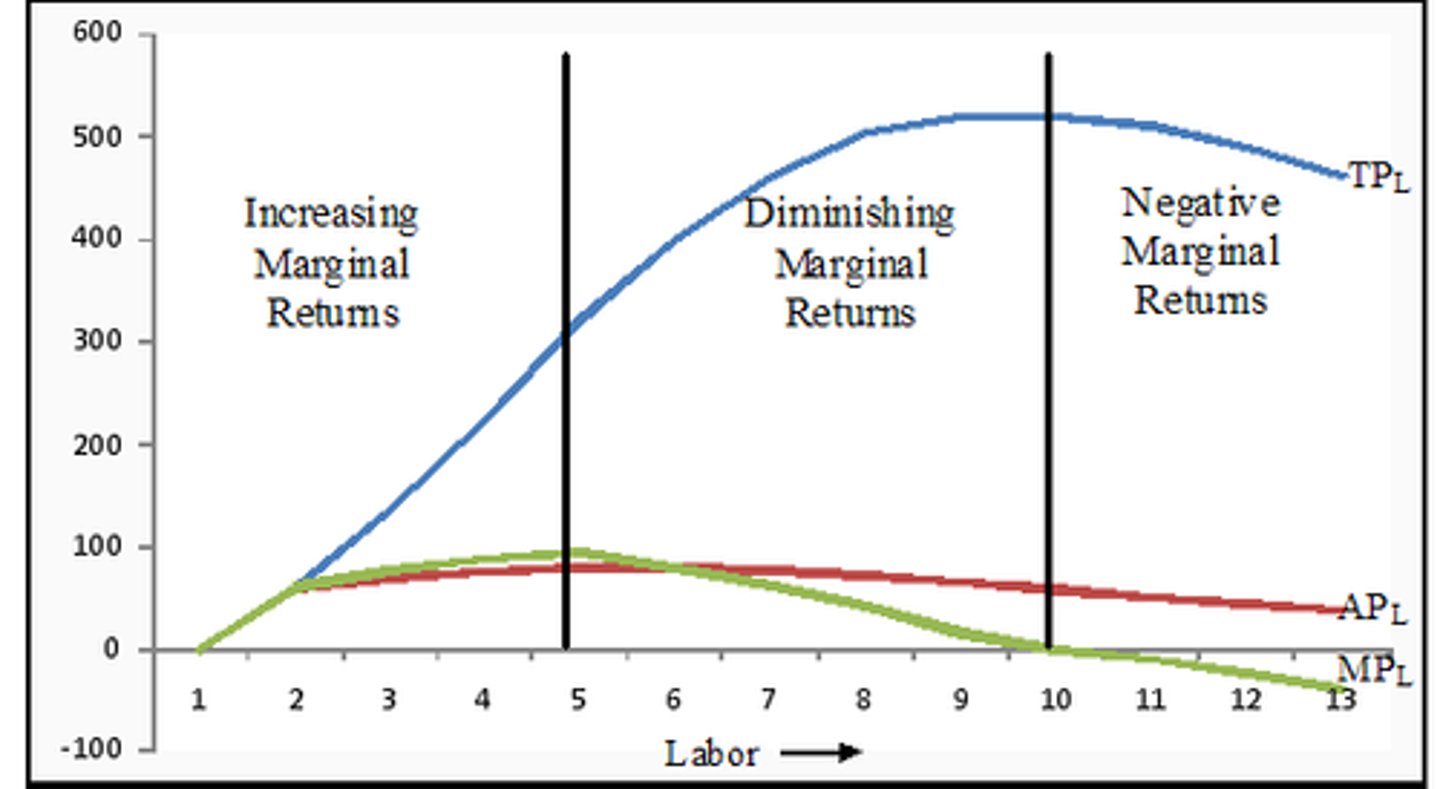
Law of diminishing marginal returns
The principle that as more units of a variable resource are added to a fixed resource, the additional output produced will eventually decrease.
Law of diminishing marginal utility
The principle that as a person consumes more units of a good, the additional satisfaction gained from each additional unit will eventually decrease.
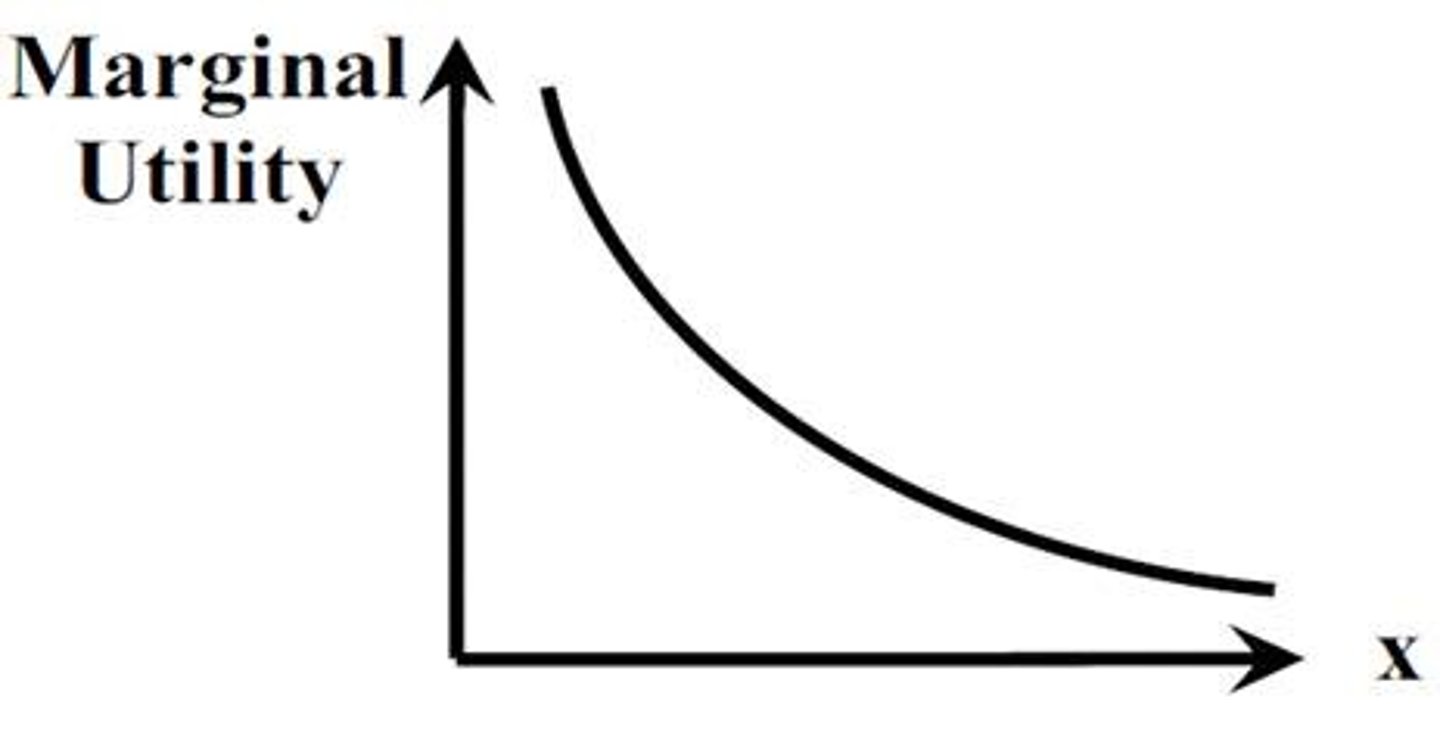
Law of increasing costs
The principle that as production increases, the opportunity cost of producing additional units also increases.
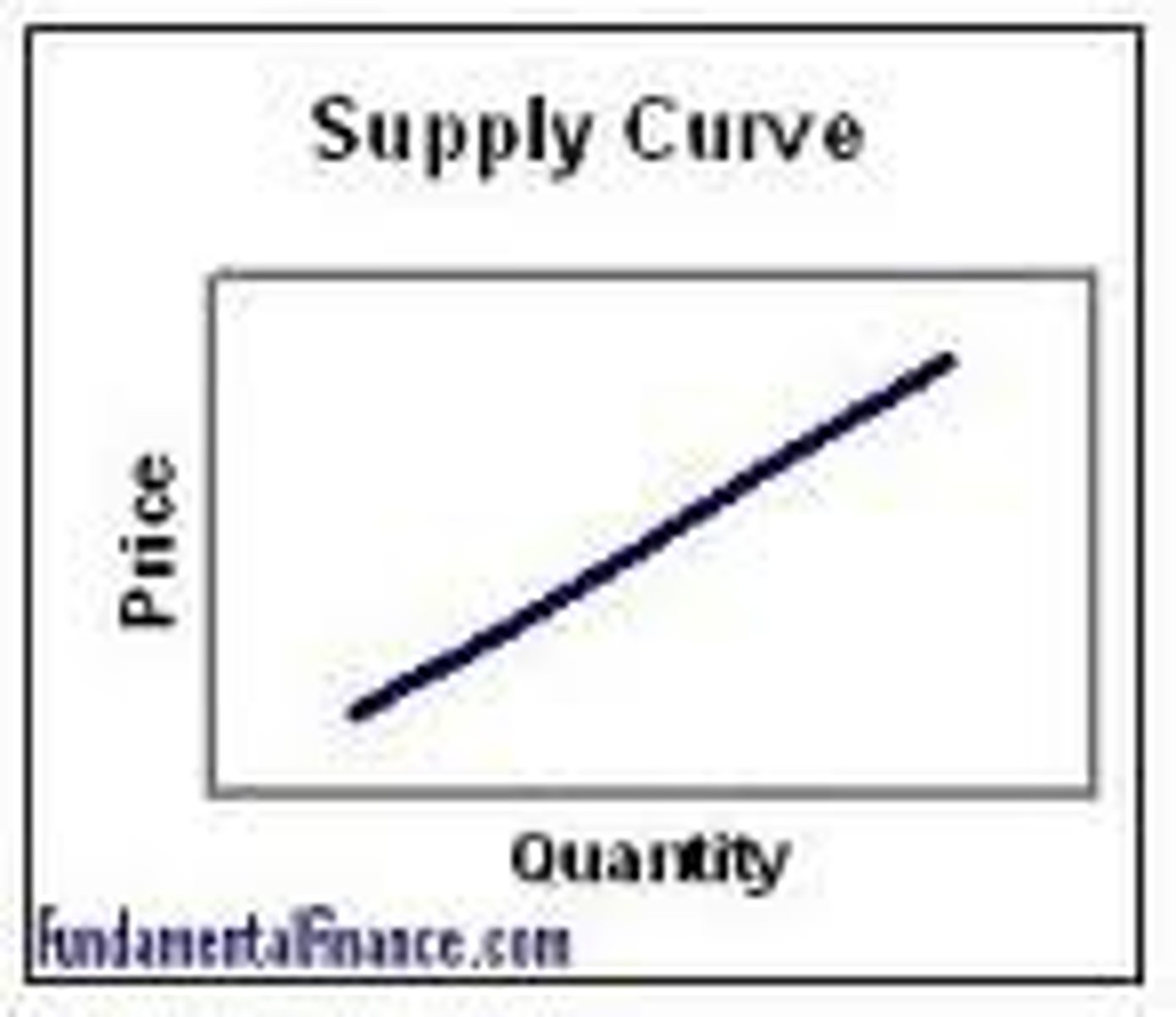
Law of supply
The principle that, all else being equal, an increase in the price of a good will increase the quantity supplied.
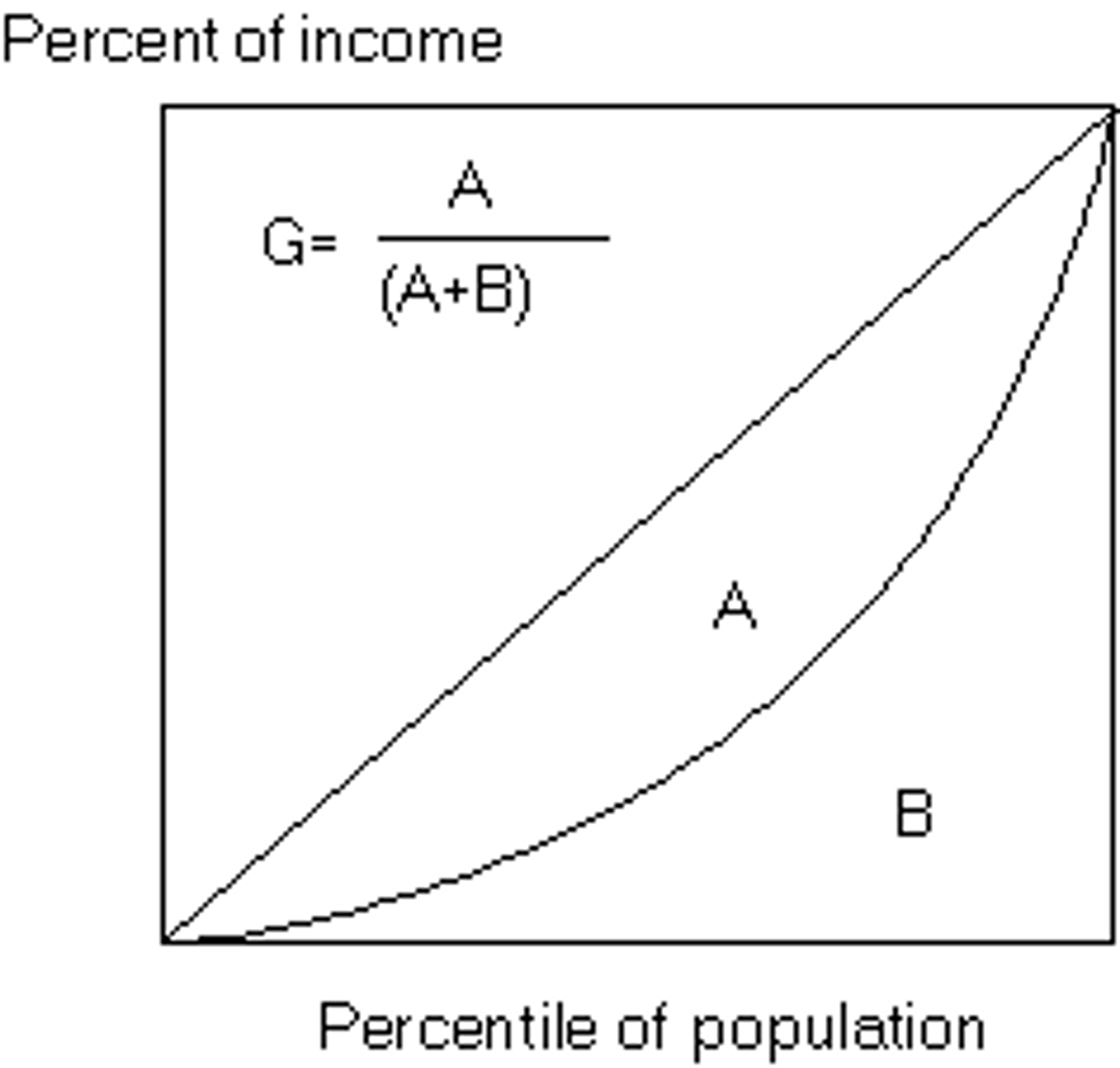
Lorenz curve - Gini ratio
A graphical representation of income distribution, showing the proportion of total income earned by cumulative percentages of the population.
Marginal benefit (MB)
The additional benefit received from consuming one more unit of a good or service.

Monopolistic competition
A market structure characterized by many firms selling products that are similar but not identical.
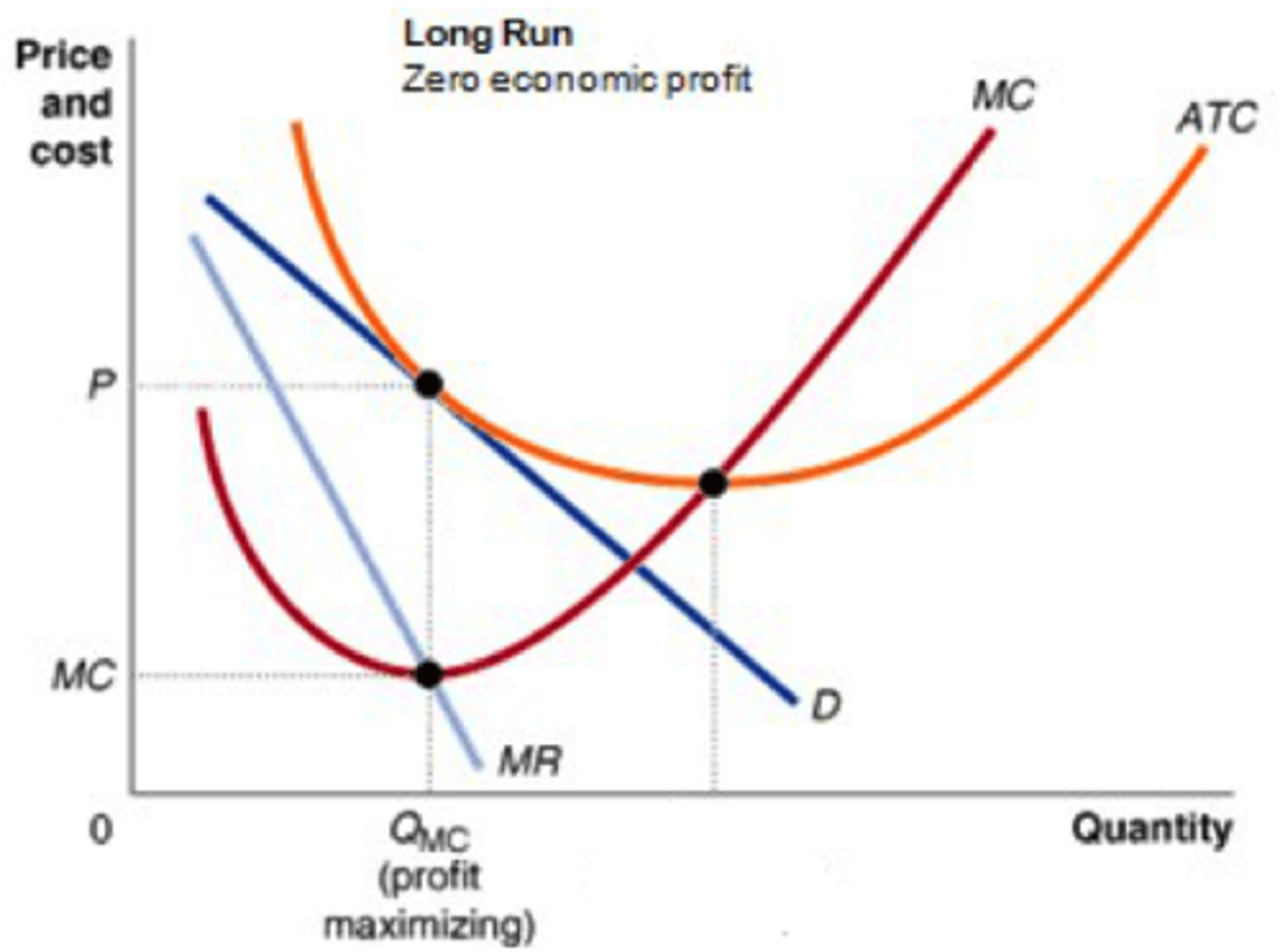
Monopoly
A market structure where a single seller controls the entire market for a product or service.
Monopsony
A market situation where there is only one buyer for a product or service.
Resources
Inputs used to produce goods and services.
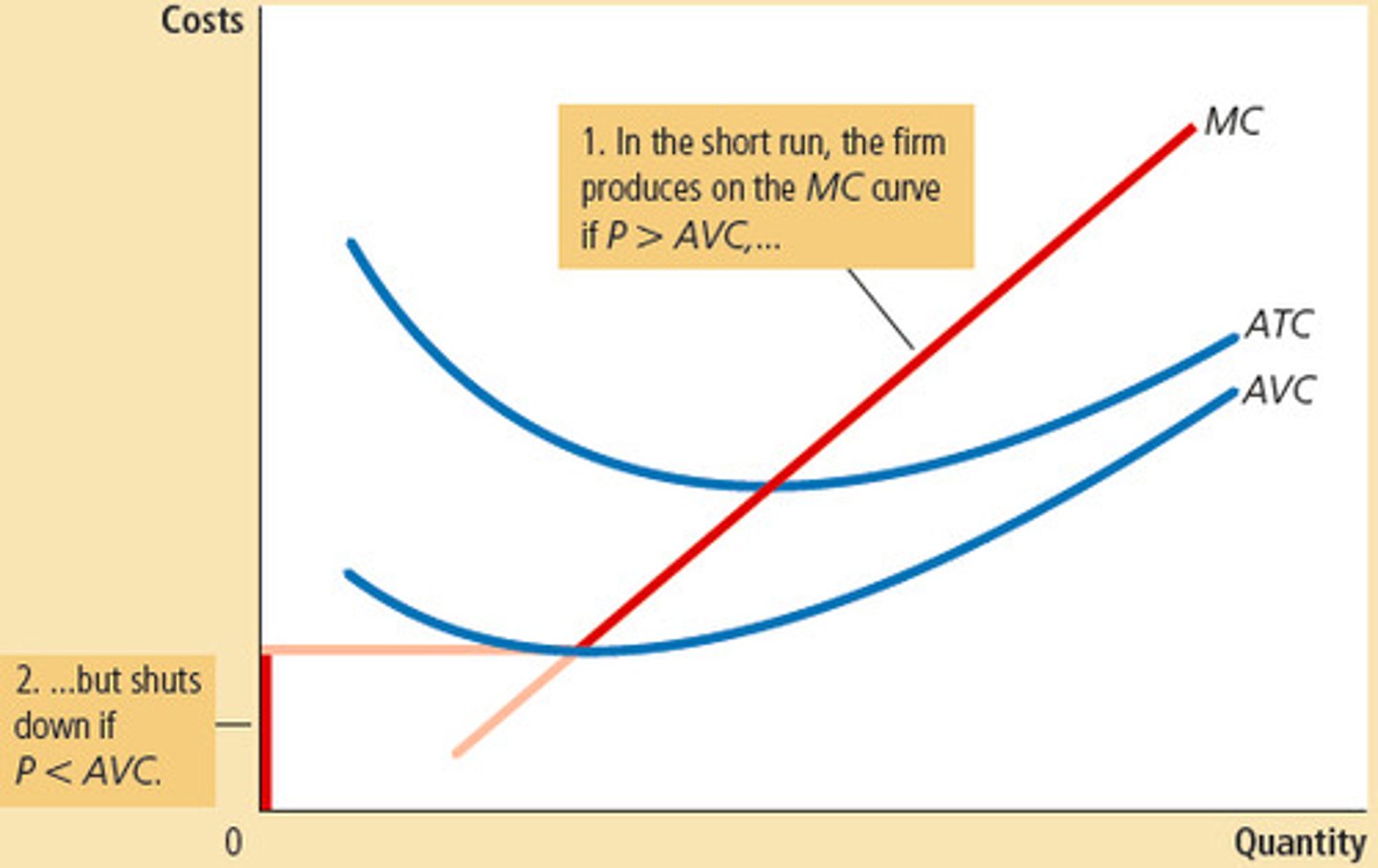
Short run
A period in which at least one input is fixed and cannot be changed.
Substitute goods
Goods that can be used in place of each other; an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in demand for the other.
Substitution effect
The change in quantity demanded of a good due to a change in its price relative to other goods.
Natural monopoly
A market structure where a single firm can supply the entire market at a lower cost than multiple firms.
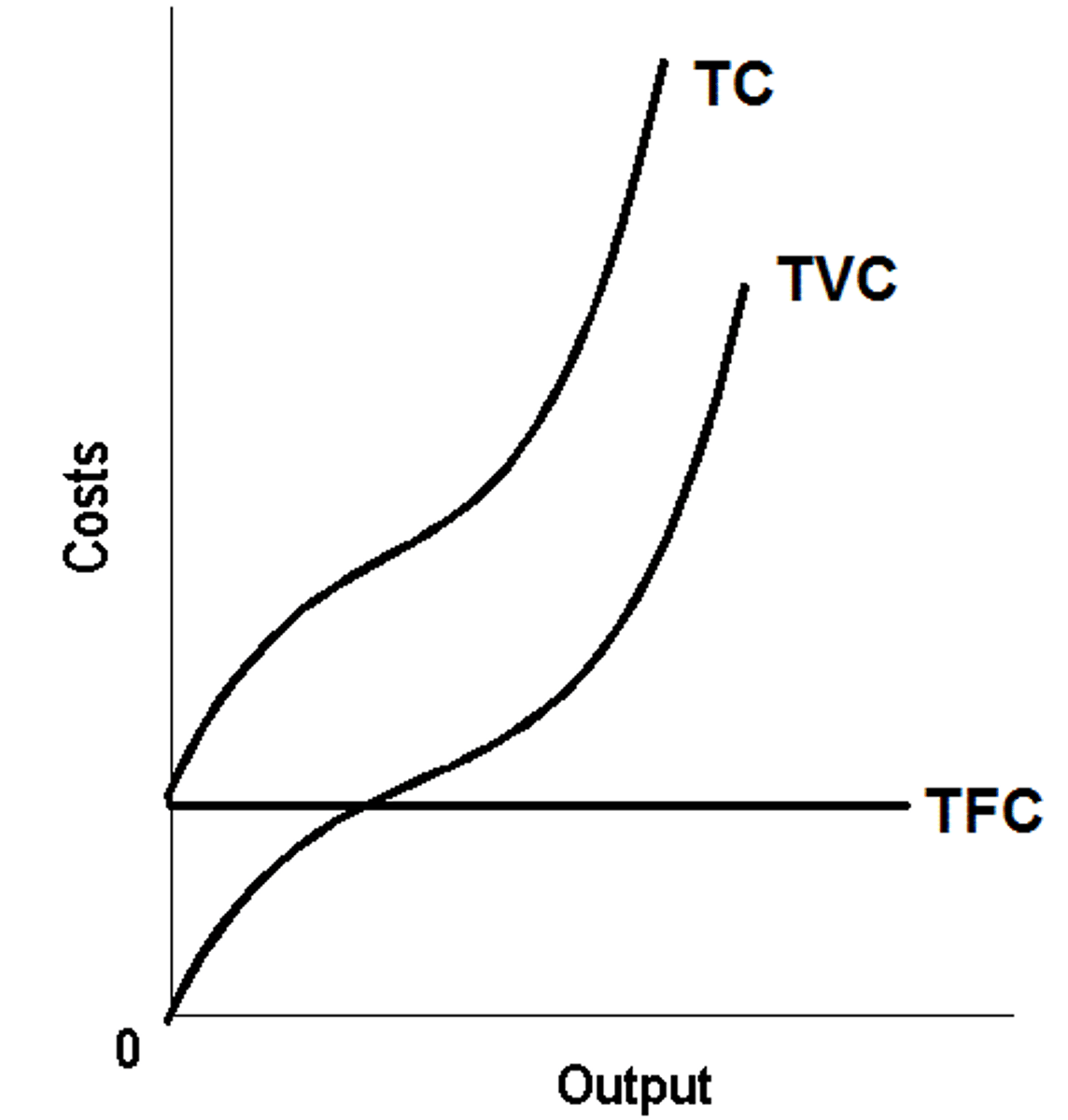
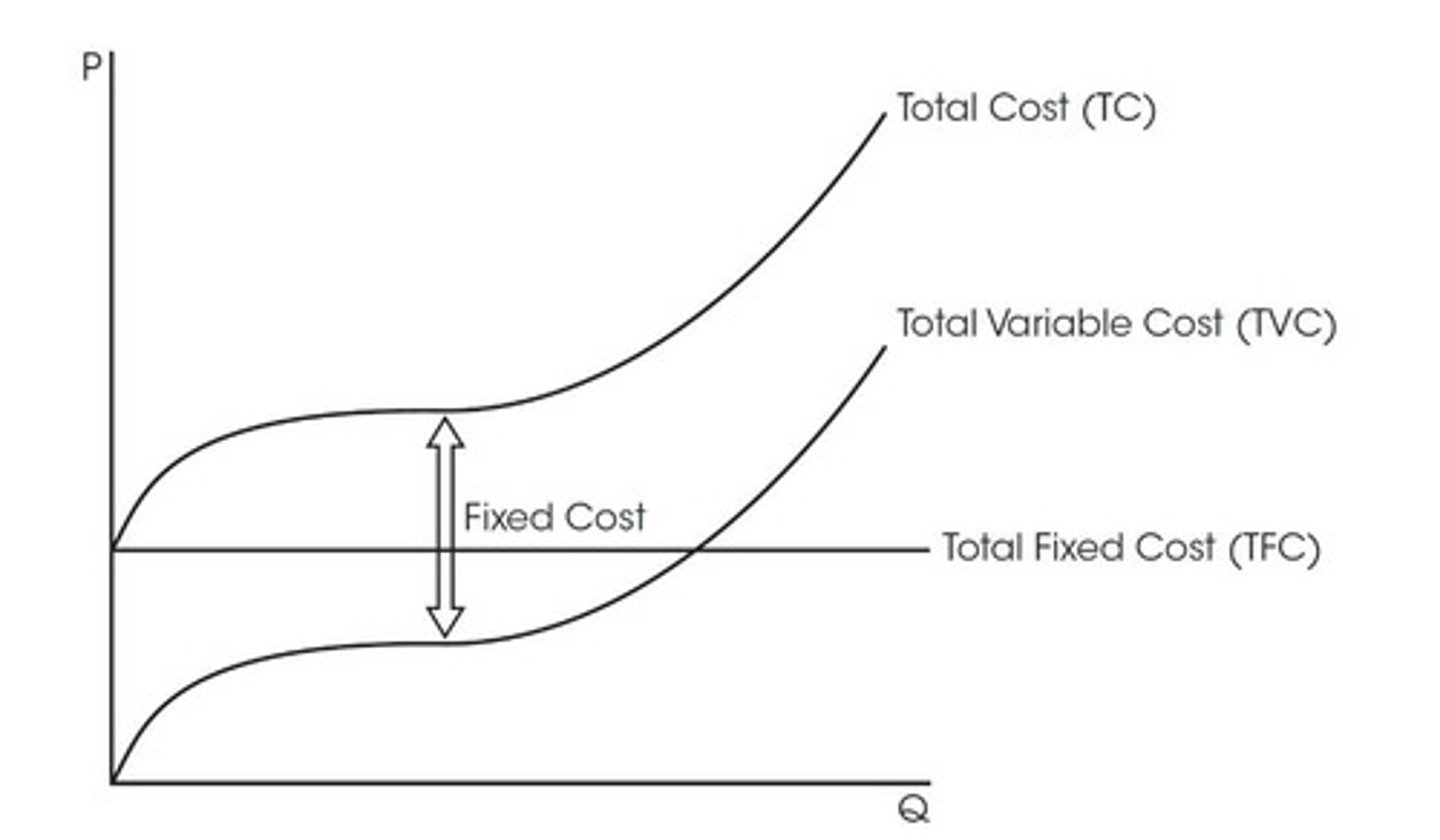
Total cost (TC)
The sum of fixed and variable costs incurred by a firm in the production of goods.
Negative externality
A cost that affects a third party who did not choose to incur that cost.
Total fixed costs (TFC)
Costs that do not change with the level of output.
Normal profit
The minimum profit necessary for a company to remain competitive in the market.
Oligopoly
A market structure characterized by a small number of firms whose decisions are interdependent.
Total product of labor (TPL)
The total output produced by a given amount of labor.
Opportunity cost
The value of the next best alternative that is foregone when a choice is made.
Total revenue test
A method to determine the price elasticity of demand by observing changes in total revenue.
Total variable costs (TVC)
Costs that change with the level of output.
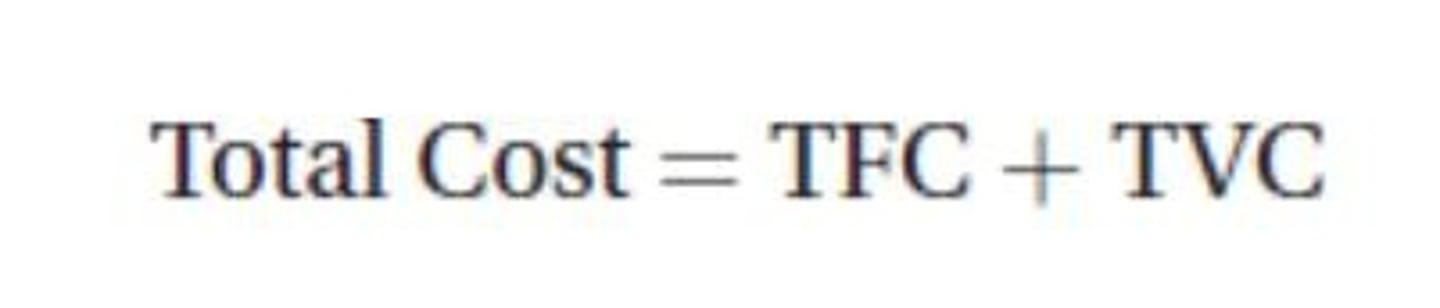
Utility maximizing rule
Consumers will maximize their utility when the last dollar spent on each good provides the same level of marginal utility.
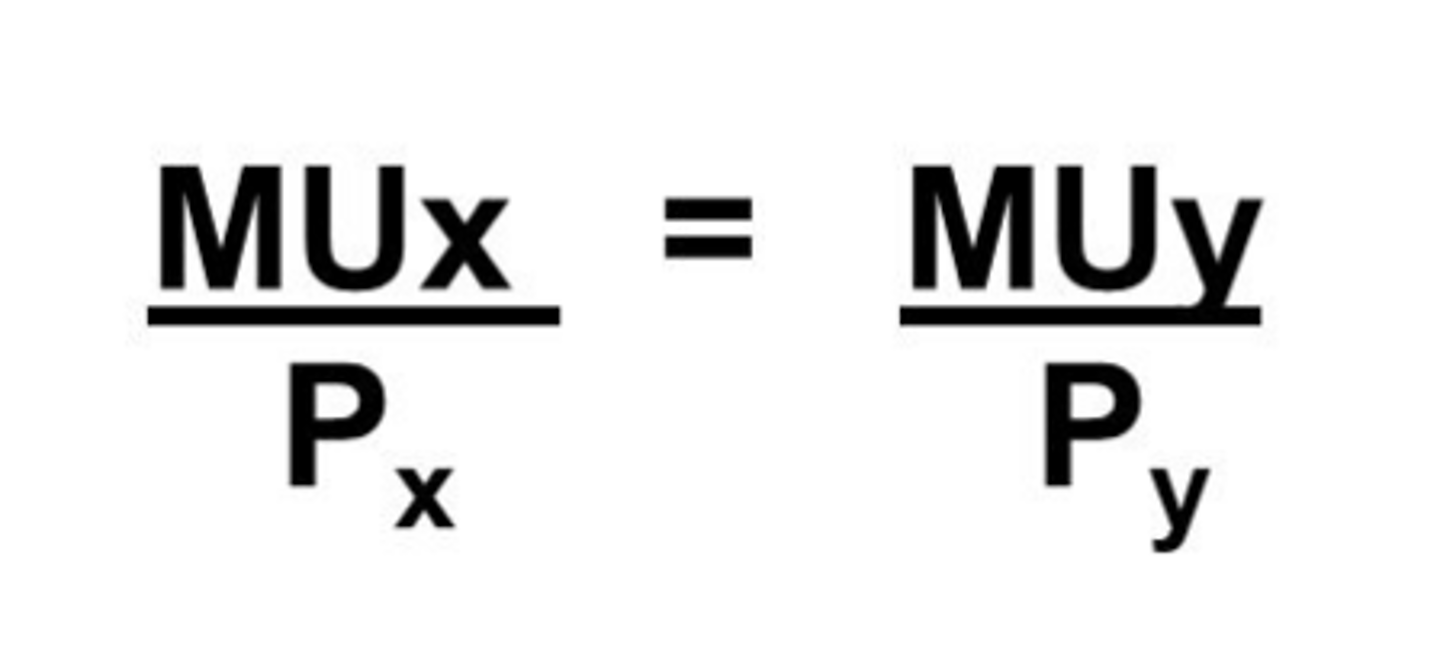
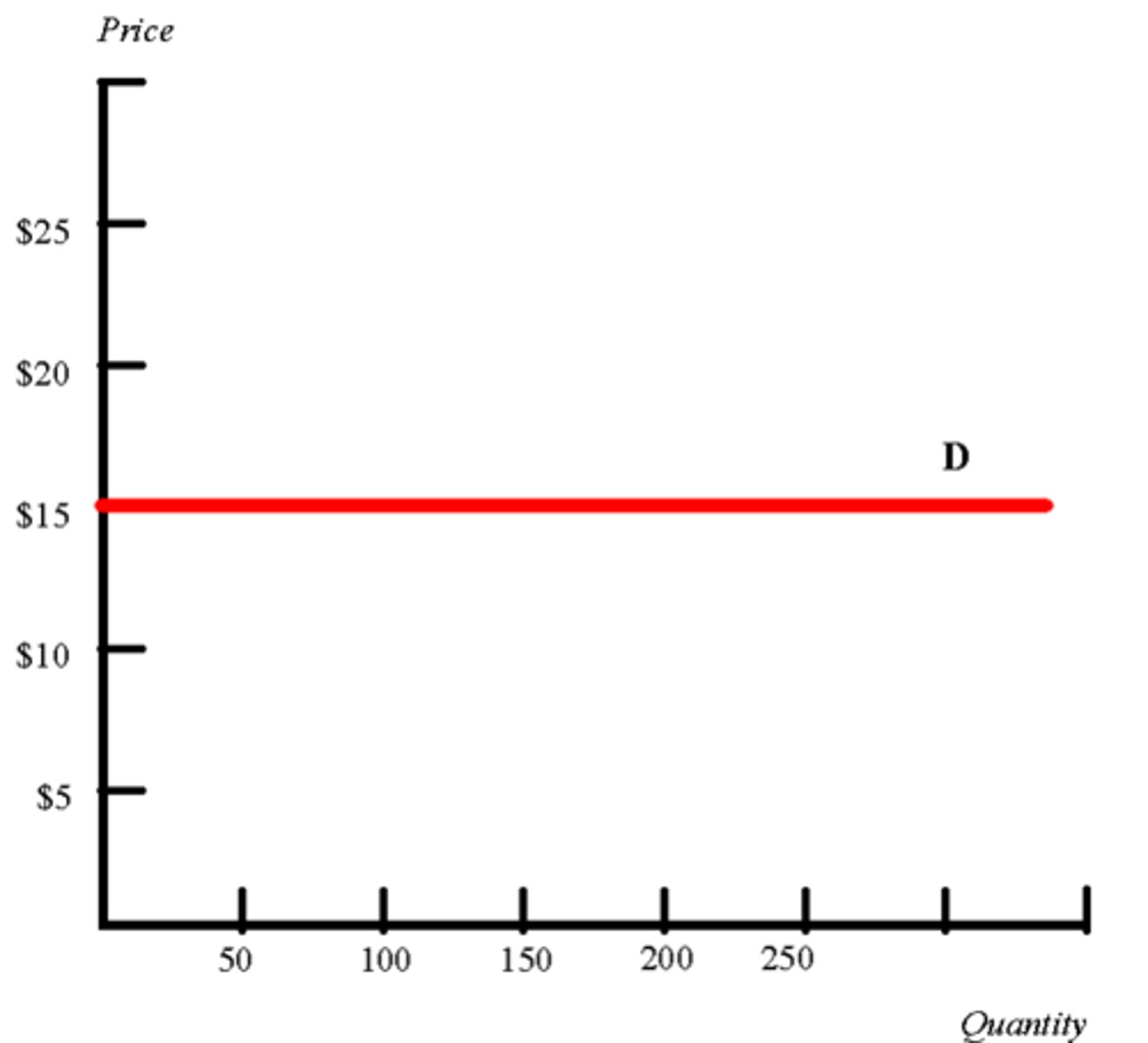
Perfectly elastic
A situation in which the quantity demanded changes infinitely with any change in price.
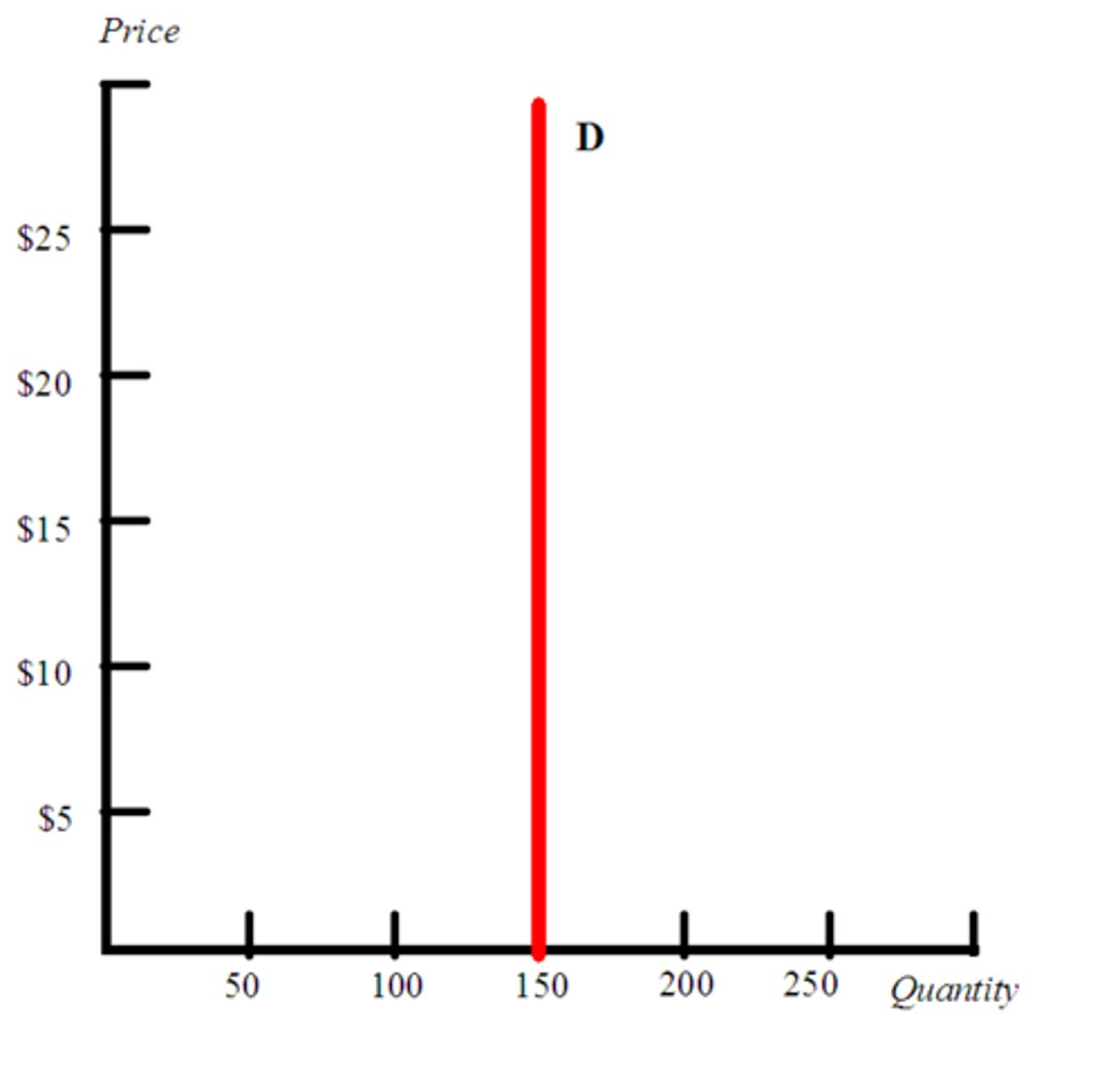
Perfectly inelastic
A situation in which the quantity demanded does not change regardless of price changes.
Positive externality
A benefit that affects a third party who did not choose to incur that benefit.
Price ceiling
A maximum price set by the government for a particular good or service.
Still learning (7)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!