topic 5- forces
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
what’s a vector quantity?
have a magnitude and a direction
what type of quantity is force?
vector quantity
examples of vector quantities?
force
velocity
displacement
acceleration
momentum
what’s a definition of scalar quantities?
quantities with only magnitude and no direction
examples of scalar quantities?
speed
distance
mass
temperature
time
what is the definition of a force?
a push or pull on an object that is caused by it interacting with something
what can all forces either be? (2 things)
contact it non-contact forces
what is the unit of force?
newton (N)
what is a contact force?
when the two objects are physically touching
what are non-contact forces?
when the objects do not need to be touching for the force to act
what type of force is friction?
contact
what type of force is magnetic force?
non-contact
what type of force is gravitational force?
non-contact?
what type of force is air resistance?
contact
what type of force is electrostatic force?
non-contact?
tension in ropes?
contact
what is an interaction pair?
a pair of forces that are equal and opposite and act on two interacting objects
example of an interaction pair and why?
a chair exerts a force on the ground, whilst the ground pushes back at the chair with the same force (normal contact force). equal but opposite forces are felt by both the chair and the ground
what does the mass of an object tell us?
how much matter the object has in it
does The mass of an object depend on where the object is?
no
what is the weight of an object?
the force acting on it due to gravity
what is the unit of weight?
newton (N)
does the weight of an object depend on where the object is?
yes
what is the gravitational force at the surface of the earth? (gravitational field strength)
9.8N/kg
what is a definition of the gravitational field strength?
The gravitational field strength is a measure of the force of gravity in a particular location.
what is the weight of an object in relation to the mass of the object?
directly proportional
what can be used to determine an objects weight?
by using a calibrated spring-balance (also called a newton meter)
what is the centre of mass?
where the weight of an object can be considered to act at a single point
what is a resultant force?
The resultant force is a single force that has the same effect as all of the original forces acting together.
how do you work out the resultant force?
subtract the smaller force from the larger force
what are examples of the different forces that can act on an object? (diagram)
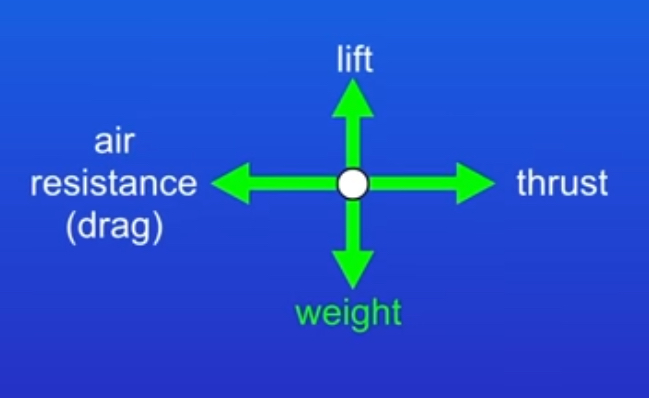
what does altitude mean?
height above the ground
what is work done?
when a force moves an object through a distance energy is transferred and work is done on the object

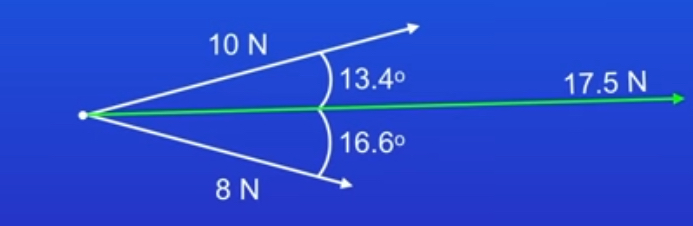
how would you answer this question?
make a scale (1N=1cm)
draw a point to represent the object
use a ruler to draw a 10cm long arrow to represent the 10N force
use a protractor to measure an angle of 30°
use a ruler do draw an 8cm arrow to represent the 8N force
now we need to create a parallelogram(copy the 8cm line and draw it at the head of the 10cm line)
join the parallelogram together
draw a line from the corners of the parallelogram
measure the length of the vector (line) and write it as newtons
what is an object in if the forces acting on it are balanced?
equilibrium
what is the unit for work done?
joules (J)
what is work done a measure of?
Energy transfer
5 examples of elastic materials?
slinky
rubber bands
rubber gloves
playground surface
tennis ball
What happens to elastic materials once we stretch them and then let go?
Elastic materials will always return to their original length or shape if we remove the forces acting on them
what must there be in order to change an object shape or length?
Have to apply more than one force
what would happen if we only applied one force to a stationary object?
The forces will no longer be balanced, so the object will just move in the direction of the applied force instead of changing shape
What happens when we stretch inelastic materials?
They do not return to their original length or shape when the forces are removed
what is an example of inelastic materials?
polymers
what do the scientists call it when they don’t return to their original shape and length after the forces have been removed?
inelastically deformed
what is the equation for the force needed to stretch an elastic material?
Force= spring constant x extension
what is the unit for spring constant?
N/m
what is the unit for extension?
metres
what are we using when we stretch or compress an elastic object?
using a force to do work
what is energy transferred to when work is done on an elastic object?
Causes energy to be transferred to the elastic potential energy store of the object
is the work done equal to the elastic potential energy in the object?
yes
how would you carry out the force and extension practical?
read the position of the pointer on the meter ruler(This is the unstretched length)
Hang a 1N weight on the spring
Read the new position of the pointer on the ruler
Continue adding one new weights to the spring and reading the points on the ruler
why is it important that the ruler is vertical?
because otherwise the readings would be inaccurate
how do you work the extension produced by adding each weight?
Subtract the length of the unstretched spring from each reading
what is the relationship between the extension and the weight in the spring practical?
They are directly proportional
what would a graph look like if we stretch the spring too much?
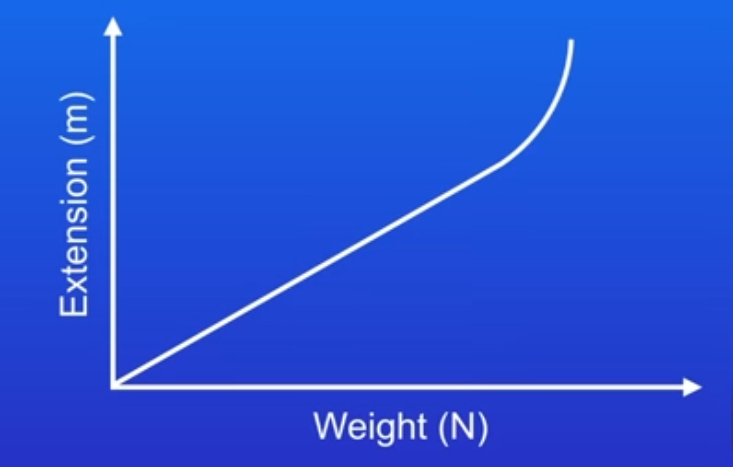
By overstretching the spring, what have we exceeded?
The limit of proportionality
what is the turning effect of a force called?
It’s moment
What is the equation to calculate the moment of a force?
moment of a force= force x distance
what is the unit for moment?
Nm
what must the distance be from the line of action when calculating the moment?
The distance has to be perpendicular From the line of action of the force to the pivot
why do levers make it easier for us to do work?
levers imvreaee the distance from the pivot at which the force is applied. since the moment= force x distance, this means less force is needed to get the same moment
what is hooked law?
The Force is directly proportional to the extension until the limit of proportionality
The ice hockey players were protective pads filled with foam. explain how these help reduce injury when collisions happen.
Increase the time taken to stop
So the rate of change of momentum decreases
reducing force/impact if force