dental management of patients with medical conditions (imp)
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
conditons that are considered as immune compromise
end stage kidney disease
end stage liver disease.
malignancies
untreated or end stage HIV infection
malnutrition
rheumatoid arthritis
psoriasis
inflammatory bowel
lupus
vasculitidies
organ transplant
does immuno compromised conditions require surgical antibiotic prophylaxis? (true/false)
true
what modifications does a pt with stroke need in their denture and which prosthesis should be considered in these patients?
1) thickened flange
2) implant borne prosthesis
(the patient should be healthy and should be able to maintain good oral hygiene)
what are the precautions in case of an epileptic patients
1) assess stability of their condition ( how frequently seizures occur and what triggers them )
2) consider the use of mouth prop to prevent the patient from biting the operators fingers or instruments if a generalized seizure occurs
antiepileptic drugs causing gingival enlargement
phenytoin
sodium valproate
carbamezepine
barbiturates
clinical features of trigeminal neuralgia
paroxysmal attacks of facial or frontal pain (few seconds - 2 minutes)
usually in morning
between paroxysms pt is usually asymptomatic
no neurological deficit
attacks are STEROTYPED in particular patient
pain (has 4 characteristics)
1) distribution along trigeminal nerve / branches
2) sudden intense sharp superficial stabbing /burning in quality
3) pain intensity (severe)
4) precipitation from trigger areas by daily activites (eating talking washing face shavig cleaning teeth)
which dental pain is very similar to trigeminal neuralgia
pulpitis
what shouldyou do if a patient with trigeminal neuralgia pain comes to your clinic ?
REFER the patient for MEDICAL ASSESSMENT
patients with unstable trigeminal neuralgia dental tretment can exacerbate the pain evenif done in a different area of the mouth
treating the AREA AFFECTED with LA Block can help reduce the degree of exacerbation
diagnostic test of trigeminal neuralgia
exclusion by
1) history
2) examination (nneurological assessment of cranialnerves)
3) investigations :- MRI (exclude space occupying demylinating disease)
4) Blood test to exclude infections and systemic vasculitis
ONLY THEN IDIOPATHIC TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA AS A DIAGNOSIS CAN BE USED
MANAGEMENT OF TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA
SYMPTOMATIC
reigonal local anaesthetic injection
DEFINITIVE

drugs that cause dry mouth
antidepressants
antipsychotics
psycho stimulants
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI)
SEROTONIN AND NONADRENALINE REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SNRI)
DRUGS THAT CAN CAUSE BRUXISM
amfetamines
antipsychotics
if a psychotropic drug is causing an oral issue what do you do?
CONSULT a medical practitioner
ORAL CONDITIONS THAT CAN HAPPEN IN A PATIENT TAKING ILLICIT DRUGS
dry mouth
dental caries (cariogenic diet +lack of oral hygiene )
oral candidiasis and other oral infections
oral cancer intake of drugs through smoking)
bruxism , jaw clenching and resultant tooth damage (amfetamines and cocaine)
AT RISK OF DEVELOPING BENZODIAZEPINE DEPENDENCE
INSTRUCTIONS / PRECAUTIONS FOR ASTHAMATIC PATIENTS AND PATIENTS WITH COPD
bring their relieve inhaler and spacer to dental appointments.
SEVERE ASTHAMA increased risk from sedation and general anesthesia ( should be undertaken in ahospital with anaesthetist present )
rinse their mouth and throat with water after inhalation ( at risk for oral candidiasis secondary to use of inhaled corticosteroids )
patients are sometimes prescribed systemic corticosteroids (delay elective dental treatmet until the course is completed)
DO NOT PLACE PATIENTS WITH COPD IN A HORIZONTALPOSITION
NSAIDS that cabn be prescribed for asthamatic patients
NSAIDS that are contra indicated
COX 2 selective NSAIDS (CELECOXIB )
dont cause bronchospasm can be given in NSAID exacerbated respiratory disease
Non selective NSAID ( ASPIRIN , IBUPROFEN , NAPROXEN ) CAUSE BRONCHOSPASM AND ARE CONTRAINDICATED
FULL FORM OF COPD
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
what is contraindicated in some patients with COPD
supplemental oxygen according to COPD action plan
placing them in horizontal position
Is snoring SIGN of OSA ( obstructive sleep apnoea)?
maybe ( needs a sleep laboratory investigation )
use of oral devices to treat snoring without medical examination is appropriate (TRUE/ FALSE)
FALSE ( if OSA is suspected always refer the patient for a medical examination )
in cases of OSA what sedation will you give the patient
pts with OSA have a increased risk of respiratory arrest from sedation and general anaesthesia and these procedures should be undertaken in ahospital under the care of an anaesthetist
what diagnosis is important in case of OSA
facial skeltal retrusion / RETROGNATHIA
construction of MANDIBULAR ADVANCEMENT SPLINTS ( MUST BE DONE in a MULTIDISCIPLINARY TEAM with a SPECIALIST RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN )
SLEEP APNOEA
sleep related breathing disorder that involves a decrease / complete halt in airflow despite an ongoing effort to breathe ( muscle relax during sleep causing soft tissue in the back of throat to collapse and block upper airway)
HYPPNEAS
partial reduction in breathing
APNEAS and its mechanism
complete pauses in breathing ( 10-30 secs or some may go 1-2 minutes or longer )
leads to oxygen dropping to less than 40%
brain responds to lack of oxygen by alerting the body causing a breif arousal from sleep
CLINICAL FEATURE OF SLEEP APNOEA
Snores loudly and frequently with periods of silence when airflow is reduced / blocked
choking/snorting/gasping sounds when airway reopens
RISK FACTORS OF OSA
overweight (BMI 25-29.9)
Obese (BMI 30 and above )
CHILDREN with large tonsils and adenoid
Family member with OSA
ACROMEGALY AND HYPOTHYROIDISM
SMOKERS
large neck sizes ( 17 inch and above men
16 nch and above women )
middle age and older men and postmenapausal women
ethnic minorities
abnormalities of bone and soft tissue
DOWNS SYNDROME
abnormal morhphology rhinitis
nocturnal nasal congestion
EFFECTS OF OSA
fluctuating o2 levels
Increased heart rate
chronic elevation in daytime bp
increased risk of stroke
higher death rate due to heart disease
impaired glucose tolerance due to insulin resistance
impaired concentration
mood changes
increased risk of accidents (improper sleep )
disturbed sleep of partner
what is AHI
APNOEA HYPONEA INDEX
Types of OSA
MILD (AHI 5-15)
involuntary sleep during activities that require mild attention
eg WATCHING TV/READING
MODERATE (AHI 15-30)
involuntary sleepiness during activities that require some attention
eg MEETINGS/PRESENTATIONS
SEVERE (AHI>30)
involuntary sleepiniess during activities that require more attention
EG TALKING/DRIVING
TREATMENT FOR OSA
1)CPAP( CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE )
2)ORAL APPLIANCE (LOOKS LIKE SPORTS MOUTHGUARD MAINTAIN OPEN /UNOBSTRUCTED AIRWAY )
3)SURGERY ( WHEN THERE IS OBVIOUS ANATOMY DEFORMITY BUT AFTER NON INVASIVE TREATMENT LIKE CPAP AND ORAL APPLIANCE HAS FAILED )
eg UVULOPALATOPHARYNGOPLASTY
ADENO TONSILLECTOMY
4) BEHAVIORAL CHANGES (WEIGHT LOSS , CHANGING FROM BACK TO SIDE SLEEPING )
5)OTC (over the counter ) REMEDIES
EXTERNAL NASAL DILATOR STRIPS
INTERNAL NASAL DILATOR
LUBRICANT SPRAYS
6)POSITION THERAPY
STAY OFF BACK AND RAISE HEAD
LIFESTYLE INDICATIONS of osa
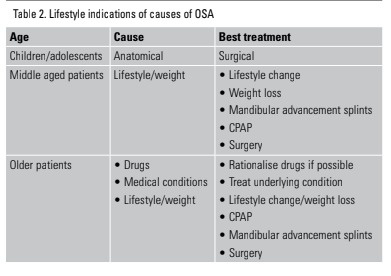
management in middle aged people with osa
caution about alcohol intake (<7 drinks )
antismoking advice
avoidance of sleep deprivation
initiation of nasal steroids
positional therapy
weightloss program
refer for sleeptherapy if symptoms persist after lifestyle management
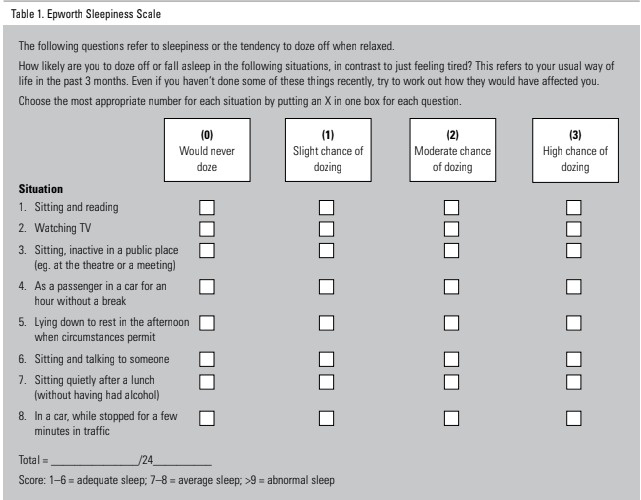
epworth sleepiness scale
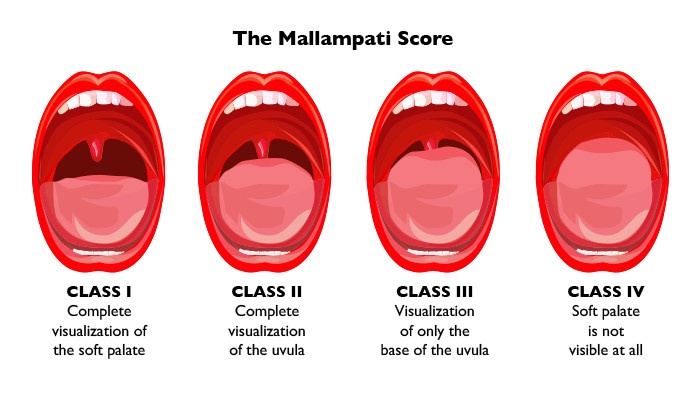
mallampati score
oral anticoagulant drugs
apixaban
dabigatran
rivaroxaban
warfarin
injectable anticoagulant drugs
enoxaparin
heparin
(PRESCRIBED FOR A SMALL DURATION )
antiplatelet drugs (P2Y12 INHIBITORS )
aspirin
clopidogrel
prasugrel
dipyridamole
ticagrelor
INR
international normalised ratio indicates the extent of anticoagulation in patients taking warfarin (inhibits production of vit K dependant coagulation factors)
in dental practice the consequences of a thromboembolic event are usually more significant thant the consequences of bleeding (true/false)
true
non vitamin k antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs)
dabigatran (direct thrombin inhibitors)
apixaban /rivaroxaban (factor Xa inhibitors)
PATIENT RELLATED FACTORS THAT INCREASE THE RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING
ELEVATED BP
ABNORMAL LIVER/KIDNEY FUNCTION
PRIOR STROKE
HISTORY OF BLEEDING ESP WITH A SIMILAR PROCEDUE
PRE EXISTING BLEEDING DISORDER
POOR ANTICOAGULANT CONTROL(INR)
OLDER AGE OR FRAILITY
OTHER DRUGS THAT PREDISPOSE TO BLEEDING (NB1) INCLUDING NSAIDS (NON PRESCRIBED / LOW DOSE ASPIRIN )
HAZARDOUS ALCOHOL CONSUMPTON
ORAL AND DENTAL PROCEDURES UNLIKELY TO CAUSE PROLONGED BLEEDING
examination and diagnostic procedures (eg periodontal examination /impressions)
restorative treatments (restorations and rootcanal therapy)
orthodontic treatment
oral and dental procedures that are likely to cause prolonged bleeding (lower risk of prolonged bleeding )
extraction of small number of teeth (1to 3) that are NOT ADJACENT
periodontal procedures (9subgingival debridement )
incision and drainage of swellings
limited or small soft tissue biopsies
oral and dental procedures likely to cause prolonged bleeding (high risk of prolongrd bleeding )
extraction of a large number of teeth (4 or more )
extraction of adjacent teeth that creates large wound
mucoperiosteal flap (surgical extractions , implant placement periapical surgery , periodontal surgery )
extensive soft tissue biopsy
hard tissue biopsy
local haemostatic measures in patient taking anti thrombotic drugs
apply pressure to wounds
minimise tissue trauma
place cellulose and collagen
place sutures to enclose wounds.
consider usng tranexamic acid 4.8% mouthwash as an adjunctive measure for patient taking WARFARIN ( NO EVIDENCE FOR TRANXENAMIC ACID IN PTS TAKING NOACs)
10ml rinsed in mouth for 2 minutes then spit 4 times daily for 2 days
ADVICE PATIENTS TO SEEK URGENT MEDICAL ATTENTION TWITH PATIENT RELATED BLEEDING RISK FACTORS FOR PROCEDURES WITH A HIGHER RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING
ARRANGE A REVIEW DENTAL APPOINTMENT FOR 2 DAYS AFTER THE PROCEDURE
consider specialist referral for patients with patient related bleeding risk factors for procedures with a higher risk of prolonged bleeding (true/false)
TRUE
PARACETAMOL is the preffered analgesic for POSTOPERATIVE pain in patients taking anti thrombotic drugs (true/false)
TRUE (NSAIDs INCREASE THE RISK OF BLEEDING PATIENTS TAKING ANTITHROMBOTIC DRUGS )
ANTIPLATELET DRUGS
aspirin
clopidrogel
prasugrel
ticagrelor
dipyridamole
ANTICOAGULANTS
Apixaban
Dabigatran
Warfarin
Rivaroxaban
ANTIANGIOGENIC DRUGS
Sunitib
bevacizunib
ANTIRESORPTIVE DRUGS
biphosphonates
denusab (prolia)
denusab
PT IS ON TRIPLE ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY (2 ANTICOAGULANT +1 ANTIPLATELET)
FOR ANY ORAL AND DENTAL PROCEDURE REFER TO MEDICAL SPECIALIST FIRST FOR ADVICE
PT IS ON DOUBLE ANTIPLATELET ( OR )
PT IS ON SINGLE ANTICOAGULANT
CONSIDER SPECIALIST REFERAL BEFORE ANY THERAPY
1) PROCEDURES UNLIKELY TO CAUSE BLEEDING +PROCEDURES AT LOWER RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING
NO NEED FOR TEMPORARY PAUSE
2) PROCEDURES WITH LOWER RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING +PT HAS BLEEDING RELATED RISK FACTORS
AND
PROCEDURES WITH HIGHER RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING
CLINICAL ADVICE SHOULD BE TAKEN BEFORE PAUSING OR ALTERING MEDICATION
PT ON 1 ANTICOAGULANT AND ONE ANTIPLATELET
1) PROCEDURES UNLIKELY TO CAUSE PROLONGED BLEEDING
NO TEMPORARY INTERUPTION NEEDED
2) PROCEDURES WITH LOW RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING AND PROCEDURES WITH HIGH RISK OF PROLONGED BLEEDING
CONSULT CLINICIAN
PT ON WARFARIN
CHECK INR 24 HRS BEFORE PROCEDURE
INR 3.5 AND LESS PERFORM PROCEDURE
INR 3.5 AND MORE MEDICAL ASSESSMENT
PT ON SINGLE ANTIPLATELET THERAPY
1) PROCEDURES AT HIGHER RISK OF BLEEDING
MEDICAL REVIEW
2) PROCEDURES WITH LOW RISK OF BLEEDING
PROCEDURES UNLIKELY TO CAUSE BLEEDING
TEMP INTERUPTION NOT REQUIRED
PTS USING INJECTABLE ANTICOAGULANT
DELAY ELECTIVE PROCEDURES UNTIL AFTER ANTICOAGULANT USE
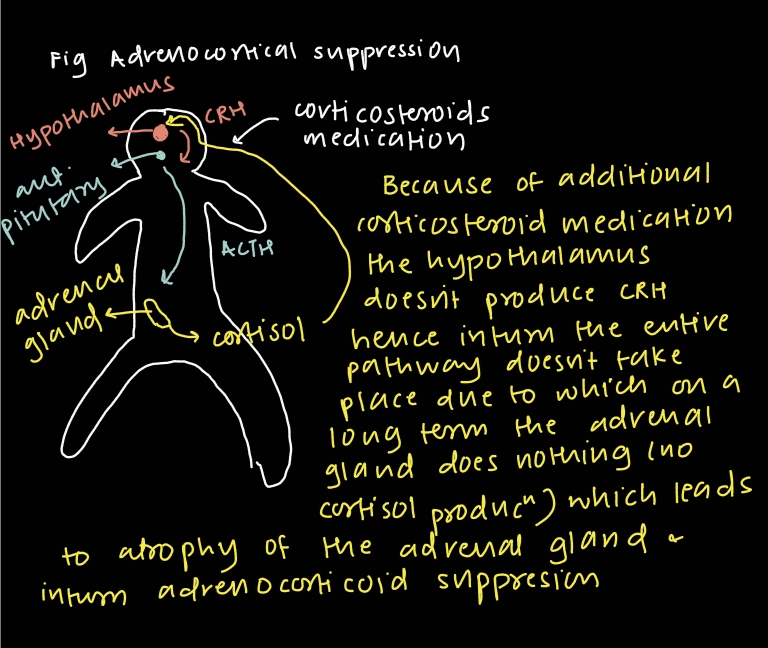
What dose of prednisolone will cause adrenocortical suppression?
Oral prednisolone at the dose of 10 mg or more daily (equivalent dose of other corticosteroid ) for more than 3 WEEKS .
ADRENAL CRISIS
patients with adrenocorticoid suppression or adrenal insufficiency are at risk of glucocorticoid deficiency during periods of physiological stress (significant systemic illness or surgery ) since usual response of increased corticosteroid production doesnt happen leading to ADRENAL CRISIS / ACUTE ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY OR ADISONIAN CRISIS)
MANIFESTATIONS OF ADRENAL CRISIS
GASTROINTESTINAL SYMPTOMS
ACUTE CIRCULATORY FAILURE(HYPOTENSION / CONFUSION)
SEVERE WEAKNESS
LOW BP
DEHYDRATION
CONFUSION
POTENTIALLY LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS
PRECAUTIONS IN CASES FOR PTS ON CORTICOSTEROIDS
Perform dental treatment in the morning
ensure pt remains in the care of an responsible adult for rest of day and carer remains in contact for 2-3days
pts require an increased dose of corticosteroid (if required) for the procedure
when does the dose of steroid doesnt need to be increased?
in case of non invasive procedures like
dental check
Xrays
impressions
when do we need an increased dose in cases of adrenal crisis?
usually on the morning of the procedure and pt has an dosing strategy or an action plan in place (if not refer a specialist)
done in cases of invasive procedures lasting less than 1 hr
professional teeth cleaning
restorative treatment
tooth extraction
periodontal treatment
implant placement
when do we need to refer to a specialist in cases of adrenal crisis?
Invasive dental procedures longer than 1 hr
dental procedures requiring sedation , general anaesthesia or fasting
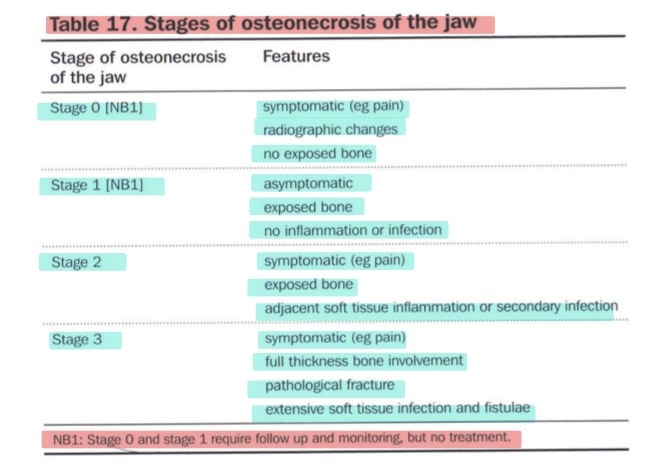
what is MRONJ?
Medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw
area of exposed bone in jaw persisting for more than 8 WEEKS in a patient currently or previously treated by antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drug WHO HAS NOT RECIEVED RADIATION THERAPY TO CRANIOFACIAL REIGON
EXACT MOA OF ADRENAL CRISIS
STAGES OF MRONJ
RISK ASSESSMENT OF MRONJ