AES 104 terms
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For AES 104 with Professor Vivian Brasfield at UAH
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
Anthropogenic climate change
human-caused climate change
The Atmosphere
A mixture of gas, liquid and solid particles, and falling precipitation
Weather
The state of the atmosphere at a given place and time, short term phenomena
Meteorology
Study of the atmosphere and the processes that cause weather
Climate
The average condition of the atmosphere (such as temp or precipitation) over a long period of time. Long term patterns.
Climatology
Long-term study of the atmosphere and processes that cause climate
Minimum climatology study period
30 years
Precipitation
All forms of moisture falling to the surface of the Earth (rain, snow, sleet, etc.)
Temperature
How warm or cool the air is outside
Climographs
A graph that often shows precipitation, temperature, and time of year for a specific location
atmospheric composition
Nitrogen 78%
Oxygen 21%
Carbon dioxide 0.035%
Argon 0.9%
Other gases
Atmospheric Pressure
pressure=force/area
Density
Mass (kg) per unit volume (m^3)
Standard atmospheric pressure at sea level
1013.25 millibars (mb)
1013.25 hectoPascals (hPa)
29.92 inches of Mercury (in of Hg)
Temperature (science-y)
Measure of average kinetic energy of individual molecules in matter
Conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius
F= 9/5(C)+32
Conversion between Kelvin and Celcius
K=C+273.15
Layers of the atmosphere
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere/Exosphere
What causes Planetary/Global winds?
well defined pressure patterns on Earth define global wind patterns
Zonal Winds
Winds that move in an east-west direction
Meridional Winds
winds that move in a north-south direction
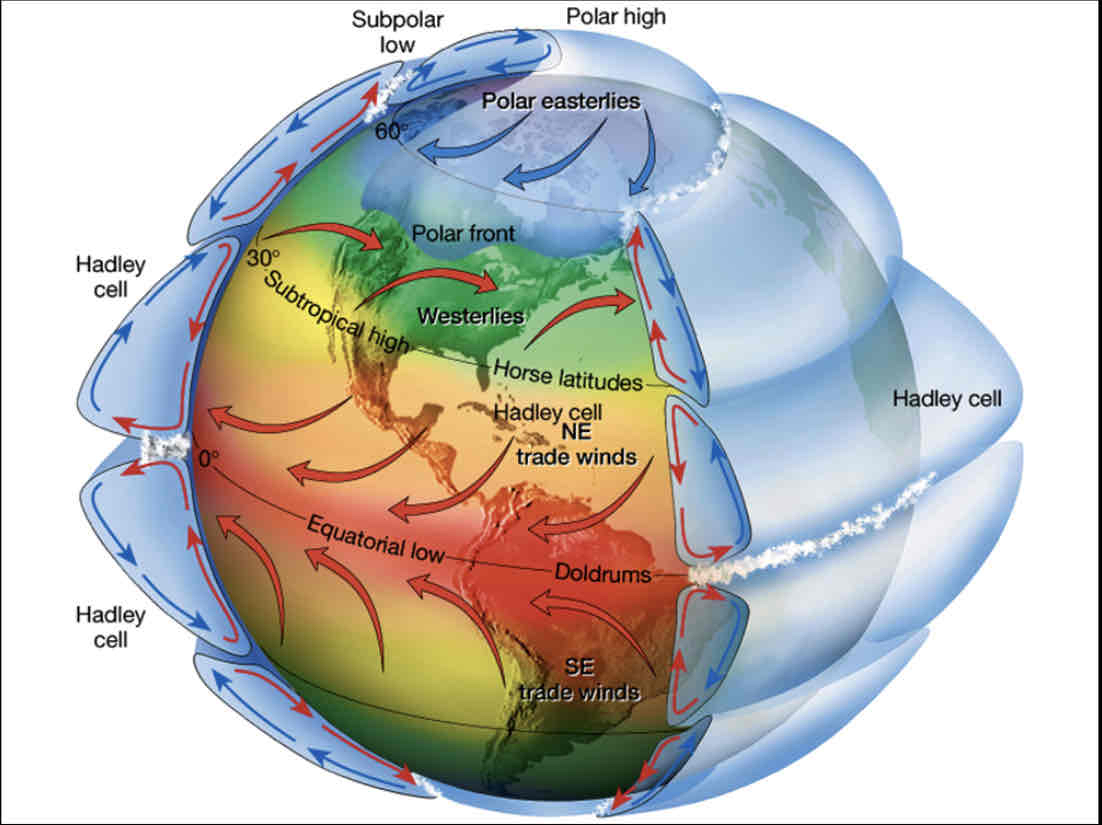
Single cell model
A wind movement model by George Hadley, that explains wind patterns with Hadley Cells
Thermally-direct circulation
circulation of air from expansion and contraction caused by changes in temperature
Three cell model
A more accurate, but still idealized model of wind movement that divides hemispheres into a Hadley Cell, a Ferrel Cell, and a Polar Cell
Thermally Indirect Circulation
movement of air that is driven dynamically, with friction, like gears turning
Easterlies
Winds blowing from the east
Westerlies/Prevailing Westerlies
winds blowing from the west
ITCZ
Intertropical Convergence Zone, a low pressure band around the Equator
Horse Lattitudes
the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator
Trade winds
easterlies
Doldrums
an Equatorial region of the Atlantic with calms, sudden storms, and light unpredictable winds. Where the trades of the Northern and Southern hemispheres collide.
Polar Easterlies
the dry, cold winds that blow around the high-pressure of the polar highs at the North and South poles.
Polar Front
the weather front boundary between the polar and ferrel cell around 60 degrees lattitude. At this boundary a sharp temp gradient occurs between the two air masses.
Polar Vortex
a large region of cold, rotating air. They encircle both of Earth’s poles.
Subtropical Jet
air converging between Hadley and Ferrel cells
Polar Jet
air converging between Polar and Ferrel cells
Semi Permanent Pressure Cells
pressure cell that may fluctuate seasonally and may be thermal or dynamic
Air Pressure
Force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weight of air above the surface.
980mb
Anything below this pressure is a Low Pressure system.
Isobars
Lines of Equal pressure.
Pressure gradient
depict the rate of change in pressure over a distance.
Pressure gradient force
the force exerted by air flowing from high pressure to low pressure areas.
Coriolis Force
deflection of large non-tethered objects cause by the rotation of the Earth
Coriolis Deflection In Northern Hemisphere
Westerly flow deflects to South, Easterly flow deflects to the North
Coriolis Deflection In Southern Hemisphere
Westerly flow deflects to North, Easterly flow deflects to South
Upper Air Flow
Air flow about 2 km above surface
Geostrophic wind
The wind resulting from the balance of Coriolis Force and PGF
Centripetal Acceleration
For a circular path at uniform speed, centripetal acceleration is the radially inward-directed acceleration of something
Cyclonic Flow
Circular flow around a low-pressure center. In NH, flow is counter-clockwise.
Anti-cyclonic Flow
Circular flow around a high-pressure center. In NH, flow is clockwise.
Trough axis
Has rising air ahead, sinking air behind, and winds slower than geostrophic
Ridge Axis
Has sinking air ahead, rising air behind, has winds faster than geostrophic
Wind direction
the direction the wind is flowing from
Azimuth
the degree of the angle the wind is blowing from
Wind vanes
tool that indicates wind direction
Anemometers
tool that can record wind speed
Aerovanes
tool that can measure wind speed and direction
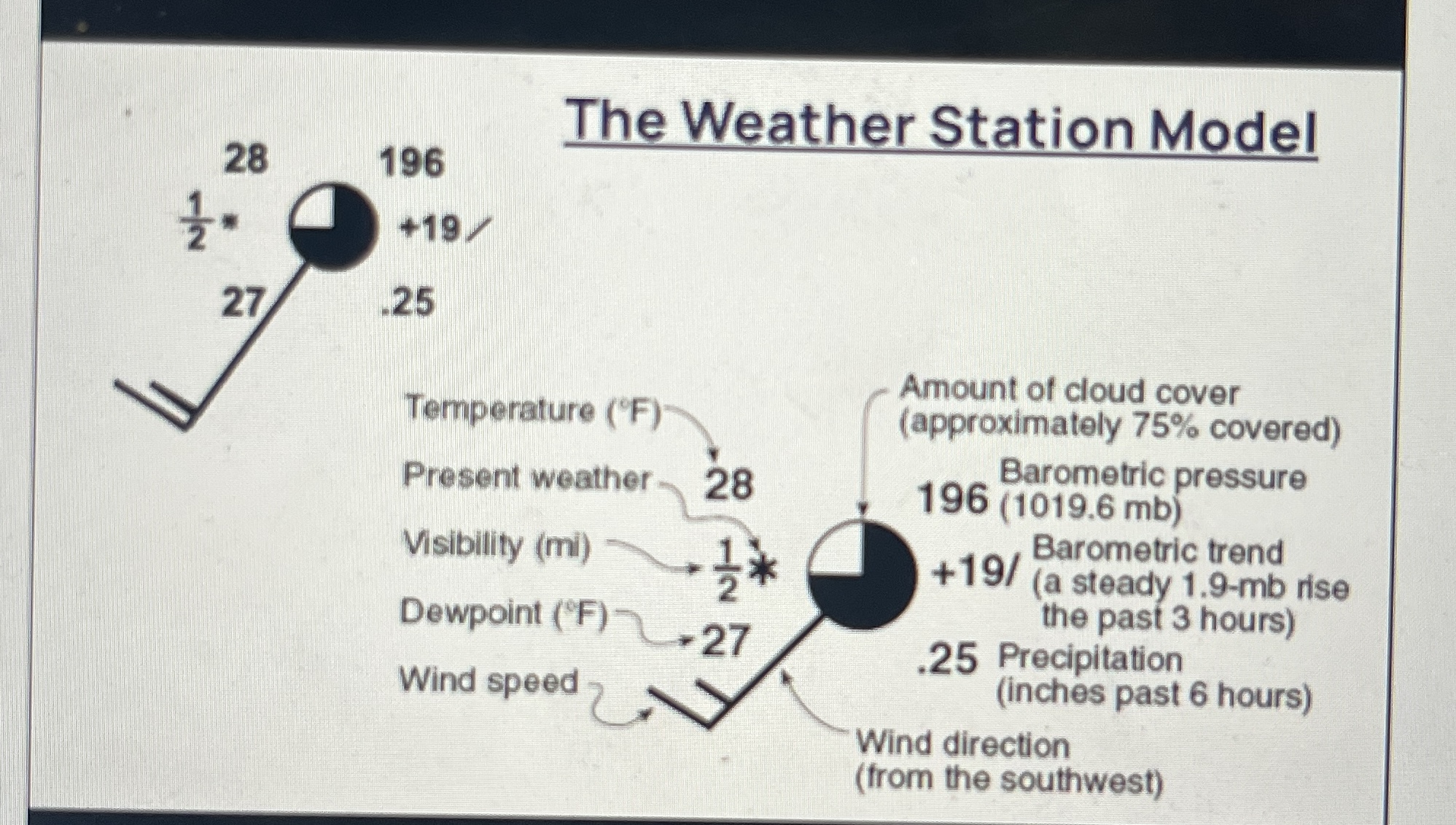
The Weather Station Model
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Conduction
Heat transfer between things that are touching molecules, most effective in solid materials
Convection
Transfer of energy by mixing a fluid or gas
Radiation
Transfer of radiation that requires no physical medium (can occur in empty space)
Radiation Quality
the wavelength of radiation
Radiation Quantity
Refers to amount of energy being transferred, associated with wave amplitude
amplitude
wave height
Electromagnetic Spectrum (EM)
Wavelength of radiation categorized into a few individual “bands” along the electromagnetic spectrum
shortwave radiation
Wavelengths less than 4 microns, also called visible radiation
longwave radiation
Wavelengths longer than 4 microns, also considered infrared
Earth/Terrestrial radiation
Radiation emitted by the surface of the earth
Insolation
Incoming Solar Radiation
Atmospheric Influences on Insolation
Absorption, Reflection/scattering, Transmission
Absorption
Energy transfer to an absorber, which gains heat energy and warms. Once it warms, it will emit longwave radiation as heat.
Reflection and scattering
Energy redirected by objects without energy being absorbed via reflection.
Transmission
The percentage of energy transmitted through the atmosphere to the surface. Is dependent on the atmosphere’s ability to absorb, scatter, and reflect
Specular reflection
Radiation is reflected back as a beam of equal intensity
Diffuse reflection, or scattering
Radiation is reflected as dispersed energy in a larger number of weaker rays going in many directions
Albedo
the percentage of energy reflected by an object
Rayleigh Scattering
It involves gases smaller than the incoming solar radiation wavelength, and air molecules scatter radiation via diffuse reflection. Makes the sky blue.
Mie Scattering
Scattering by dust, haze, aerosols. It has forward scattering and is equally effective across the color spectrum.
Non-Selective Scattering
Happens when atmospheric particles are much larger than the wavelength of incoming radiation. All colors are scattered equally. makes clouds white.
Greenhouse Gases (GHG)
Gases that are efficient in absorbing infrared (IR) radiation
Free Convection
Mixing related to buoyancy. Warmer, less dense fluids and gases rise
Forced Convection
Mixing initiated by eddies and other disruptions. Smooth uniform flow, associated with higher wind speeds
sensible heat
temperature changing that we can physically sense.
specific heat
the amount of energy required to produce a temperature change per unit mass
laminar boundary layer
layer where the flow takes place in layers, i.e., each layer slides past the adjacent layers.
turbulent boundary layer
occurs when smooth laminar flow breaks down and transitions to flow with eddies.
Latent Heat
no felt/experience change in temperature. Energy required to change phase (solid, liquid, gas) of substance
Isoheights
Lines of same height
Isotherms
Lines of equal temperature
Altitude
the difference in sea level height
elevation
difference in height above ground level
Influences on Temperature
Lattitude, Altitude/Elevation, Atmospheric Circulations, Contrasts between Land/Water, Warm/cool ocean currents, and Local Conditions
advection
transport of something via wind
Continentality
the effect of inland location that favors greater temperature extremes
Warm currents
Currents that move poleward from the equator in the western portion of the ocean basin. Found near the east coasts of continents in mid-latitudes.
Cool currents
Currents that move toward the equator in the eastern portion of ocean basins. It causes moderate west coast temps in mid-latitudes.
Adiabatic
no heat exchange, no heat release
Dewpoint
The temperature at which condensation occurs
(depends on humidity). It is always equal to or less than the air Temperature
Relative humidity (RH)
How close the air is to being saturated.