Energy - Forces Doing Work
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:24 PM on 6/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
8\.1 Can you describe the changes involved in the way energy is stored when systems change?
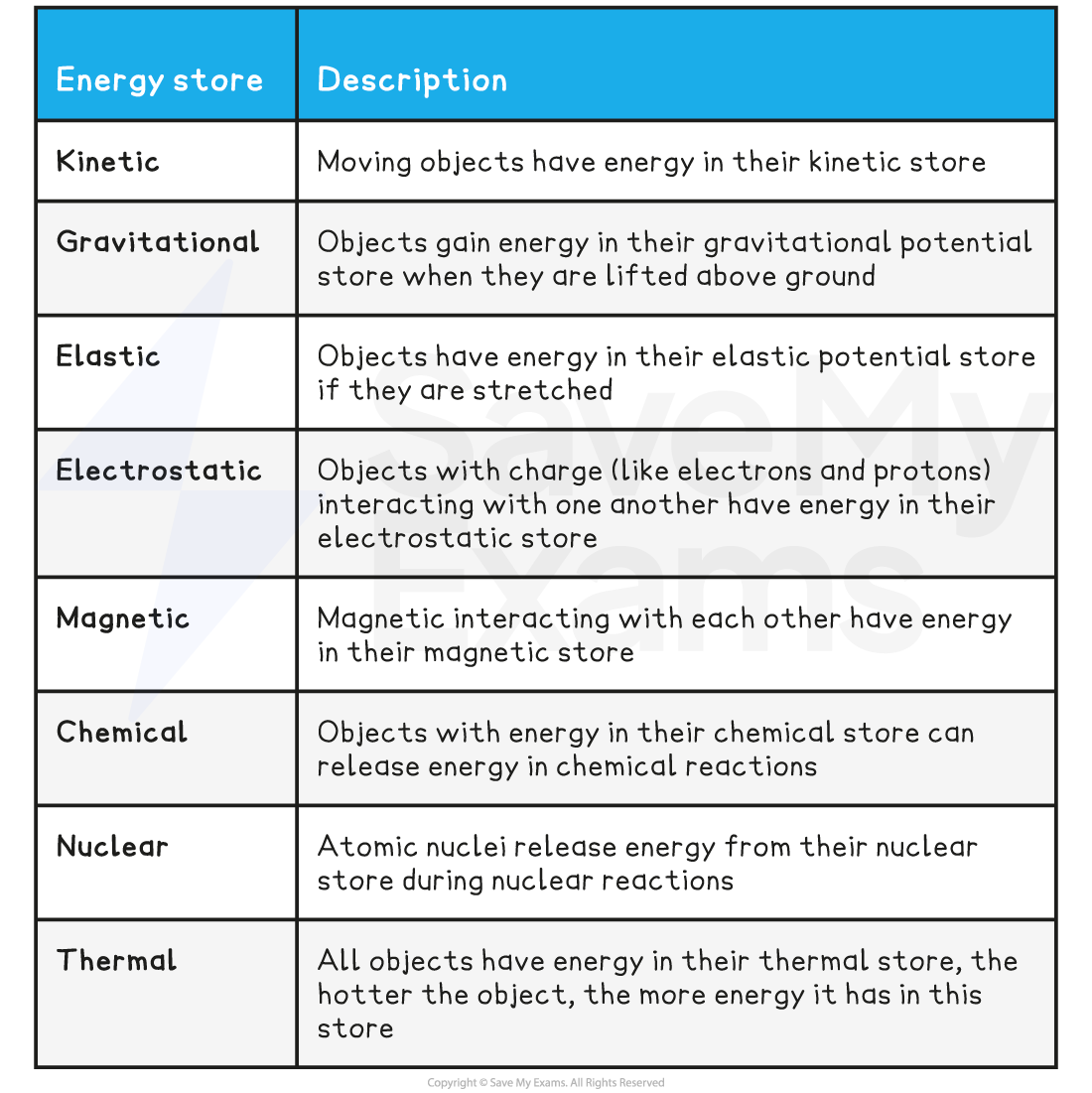
Energy is transferred between stores via transfer pathways
* mechanically - when a force acts on an object
* electrically - a current moving through a potential difference
* by heating - energy transferred from a hotter object to a cooler one
* by radiation - energy transferred by electromagnetic waves
* mechanically - when a force acts on an object
* electrically - a current moving through a potential difference
* by heating - energy transferred from a hotter object to a cooler one
* by radiation - energy transferred by electromagnetic waves
2
New cards
8\.2 Can you draw and interpret diagrams to represent energy transfers?
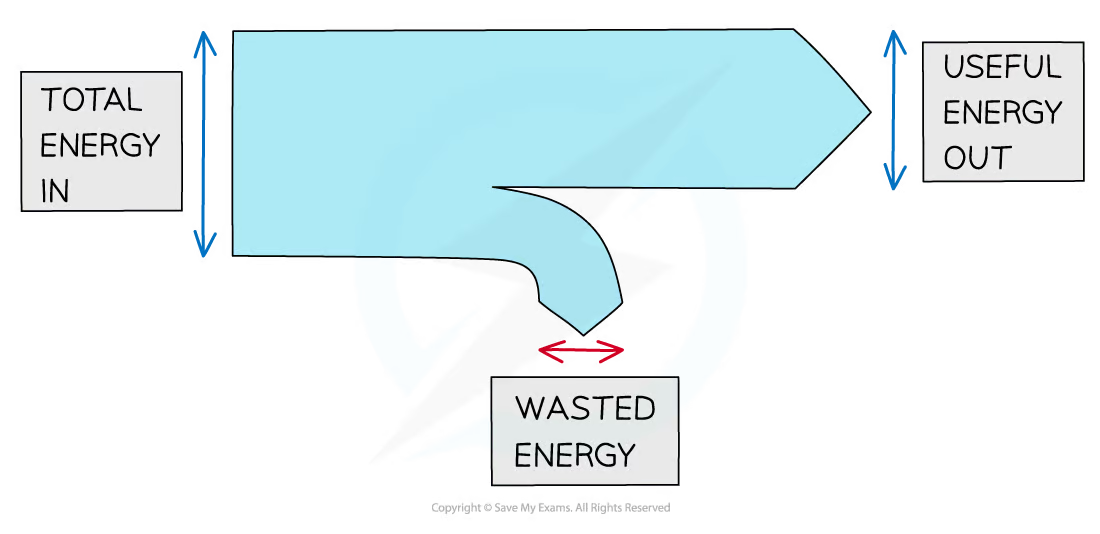
The arrow in a Sankey diagram represents the transfer of energy:
* the end of the arrow pointing to the right represents the energy that is transferred usefully to the desired store (the **useful energy output**)
* the end that points down represents the **wasted energy**
* the width of each arrow is proportional to the amount of energy going to each store
* the end of the arrow pointing to the right represents the energy that is transferred usefully to the desired store (the **useful energy output**)
* the end that points down represents the **wasted energy**
* the width of each arrow is proportional to the amount of energy going to each store
3
New cards
8\.3 When is there no net change to the total energy in a system?
When there are energy transfers in a closed system
4
New cards
8\.4 What are the different ways that the energy of a system can be changed through work done by forces?
Work is done when energy is transferred from one store to another
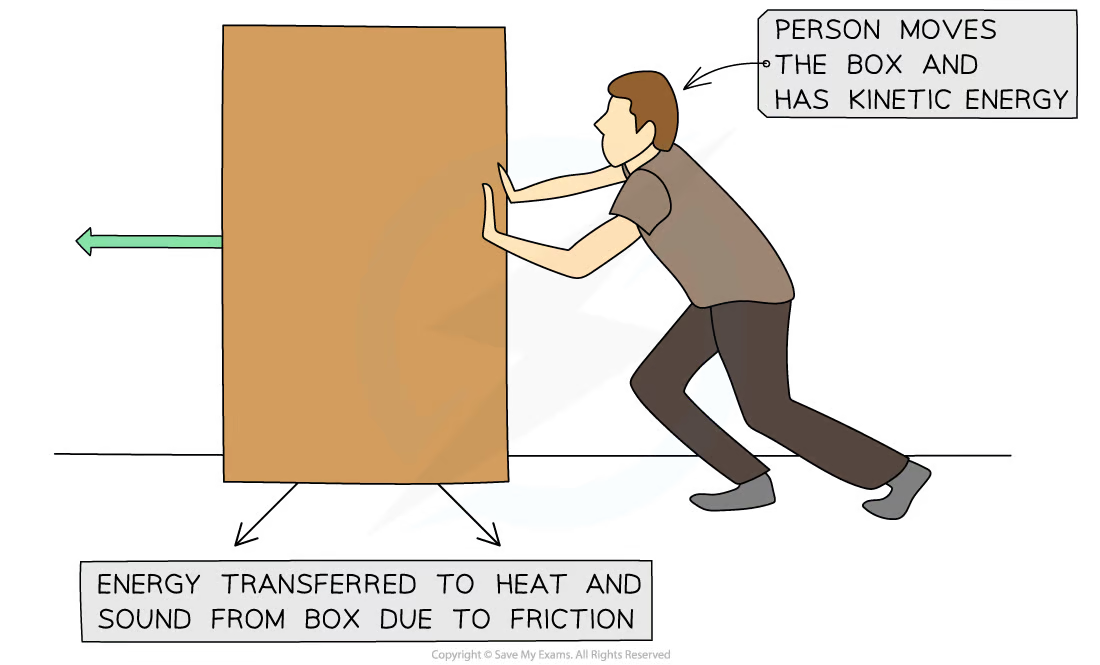
e.g. a person pushing a box across the floor
* if the system is defined as the man and the box, energy is transferred **mechanically** from the **kinetic** **store** of the person to the **kinetic** **store** of the box
* if the system is defined as the box and the floor, energy is transferred **by heating** from the **kinetic store** of the box to the **thermal store** of the floor (due to friction) and **by heating** to the **thermal** store of the surroundings as the sound waves transfer energy away from the system and cause the air particles to vibrate
e.g. a person pushing a box across the floor
* if the system is defined as the man and the box, energy is transferred **mechanically** from the **kinetic** **store** of the person to the **kinetic** **store** of the box
* if the system is defined as the box and the floor, energy is transferred **by heating** from the **kinetic store** of the box to the **thermal store** of the floor (due to friction) and **by heating** to the **thermal** store of the surroundings as the sound waves transfer energy away from the system and cause the air particles to vibrate
5
New cards
8\.4 What are the different ways that the energy of a system can be changed in electrical equipment?
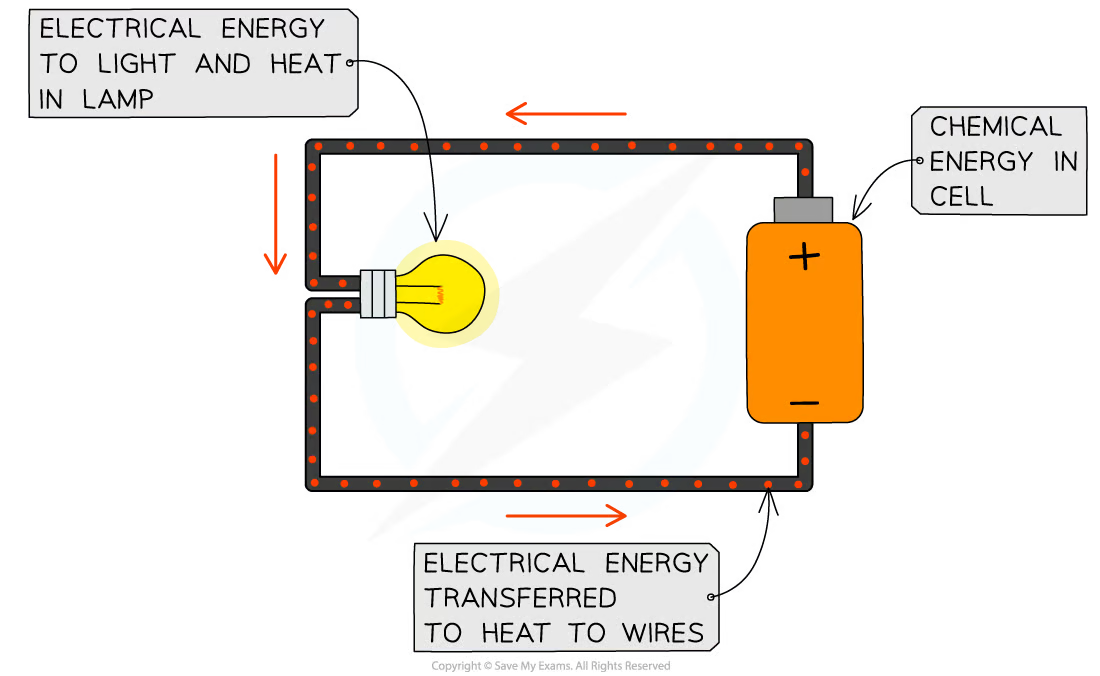
* a current flows when there is a potential difference applied to the circuit, provided by the power supply or a cell
* energy is transferred **electrically** from the power supply to the components in the circuit (this is the **electrical work done** by the power supply when a current flows)
* energy from the **chemical** **store** of the cell is transferred **electrically** to the **thermal** **store** of the lamp as the filament heats up
* energy is transferred from the **thermal store** of the lamp **by heating** and **by radiation** (light) to the **thermal** **store** of the surroundings
* energy is also transferred **by heating** to the **thermal store** of the wires (due to resistance)
* energy is transferred **electrically** from the power supply to the components in the circuit (this is the **electrical work done** by the power supply when a current flows)
* energy from the **chemical** **store** of the cell is transferred **electrically** to the **thermal** **store** of the lamp as the filament heats up
* energy is transferred from the **thermal store** of the lamp **by heating** and **by radiation** (light) to the **thermal** **store** of the surroundings
* energy is also transferred **by heating** to the **thermal store** of the wires (due to resistance)
6
New cards
8\.4 What are the different ways that the energy of a system can be changed in heating?
Energy transfers by heating increase the energy in the thermal store of the particles that make up that system, either raising the system's temperature or producing a change of state
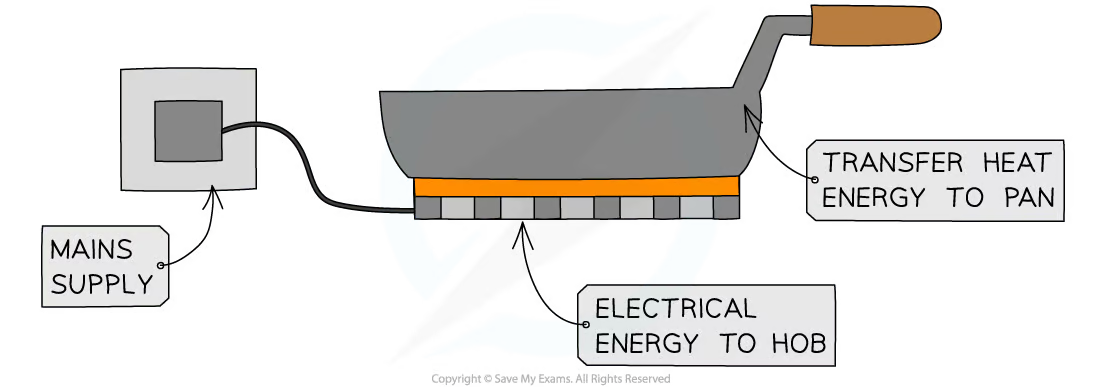
e.g. warming a pan on a hob
* energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the **thermal store** of the hob
* this is then transferred **by heating** to the **thermal store** of the pan
e.g. warming a pan on a hob
* energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the **thermal store** of the hob
* this is then transferred **by heating** to the **thermal store** of the pan
7
New cards
8\.5 Can you describe how to measure the work done by a force?
* if a force acts **in the direction** that an object is moving, then the object will **gain energy** (usually in the form of kinetic energy)
* if the force acts in the **opposite direction** to the movement then the object will **lose energy** (usually as heat)
* if the force acts in the **opposite direction** to the movement then the object will **lose energy** (usually as heat)
8
New cards
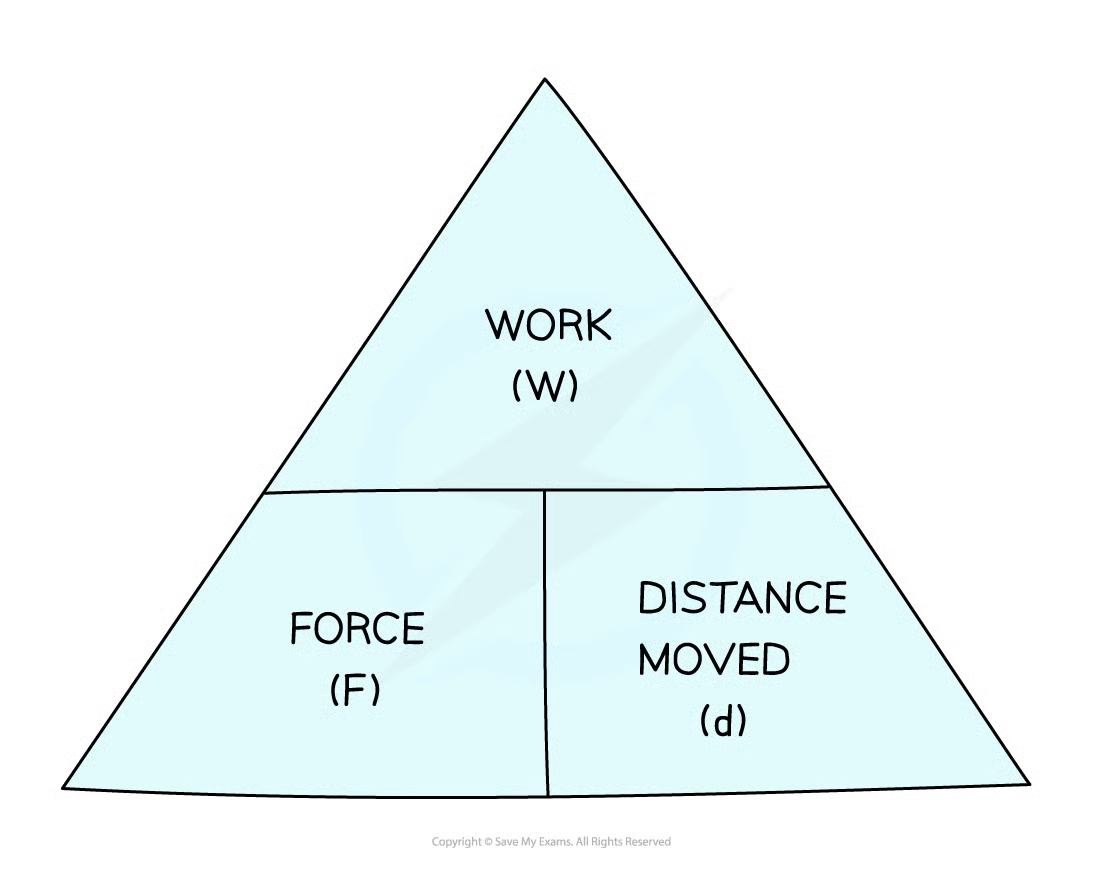
8\.6 What is the equation involving work done, force and distance moved in the direction of the force?
**Work done = force × distance moved in the direction of the force**
joule (J) = newton (N) × metre (m)
joule (J) = newton (N) × metre (m)
9
New cards
8\.7 Can you describe and calculate the changes in the energy involved when a system is changed by work done by forces?
Common forms of energy that work can be transferred to:
* **kinetic energy** - when speeding an object up
* **gravitational potential energy** - when raising an object higher
* **thermal energy** - in heating the object up
* **sound energy** - in producing noise
* **kinetic energy** - when speeding an object up
* **gravitational potential energy** - when raising an object higher
* **thermal energy** - in heating the object up
* **sound energy** - in producing noise
10
New cards
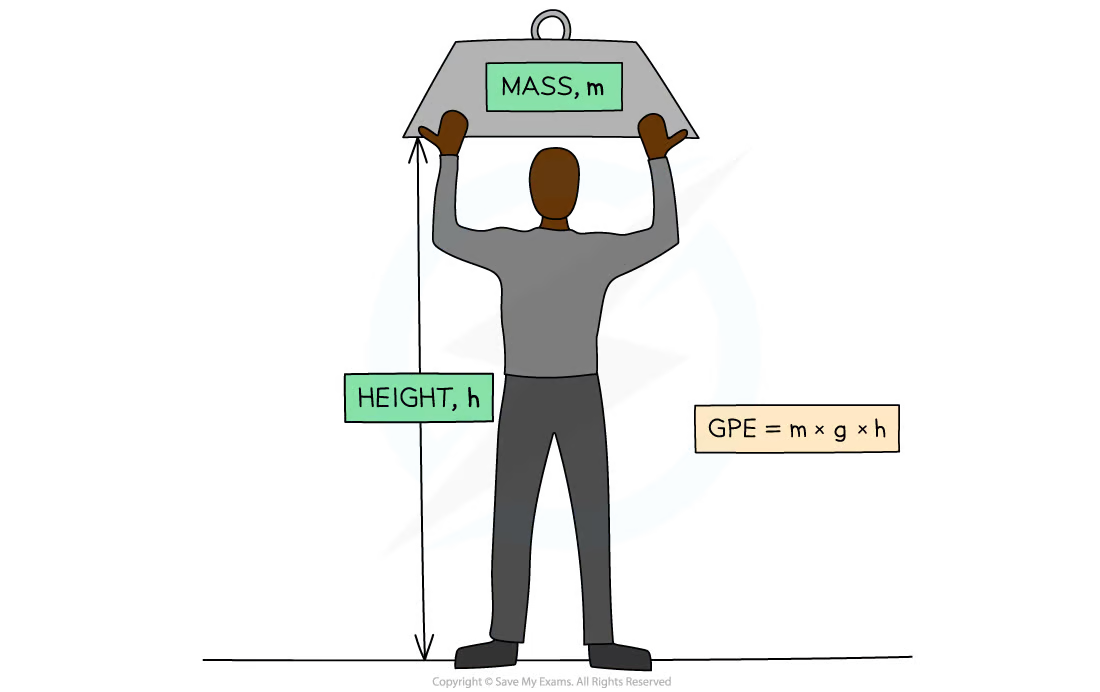
8\.8 What is the equation to calculate the change in gravitational potential energy when an object is raised above the ground?
**Δ Gravitation potential energy = mass × gravitational field strength × Δ vertical height**
joule (J) = kilogram (kg) × Newtons per kilogram (N/kg) × metre (m)
joule (J) = kilogram (kg) × Newtons per kilogram (N/kg) × metre (m)
11
New cards
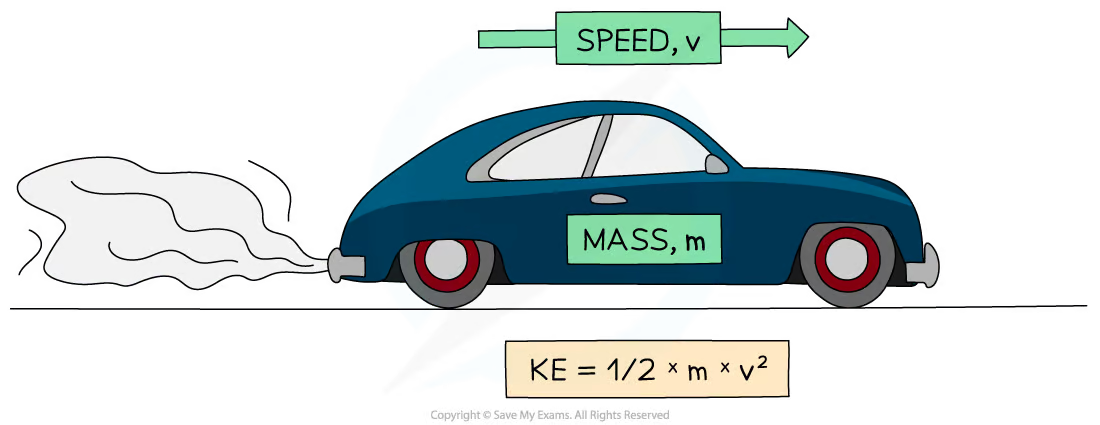
8\.9 What is the equation to calculate the amounts of energy associated with a moving object?
**Kinetic energy =½ × mass × velocity²**
joule (J) = ½ × kilogram (kg) × metres per second squared (m/s²)
joule (J) = ½ × kilogram (kg) × metres per second squared (m/s²)
12
New cards
8\.10 How is energy dissipated so that it is stored in less useful ways in all system changes?
**Useful energy** = the energy that is transferred to the place where it is wanted and in the form that it is needed
**Wasted energy** = the energy that is not useful for the intended purpose and is dissipated to the surroundings
In practice, most systems tend to be open systems
Unlike other forms of energy, **heat**, **light** and **sound** have a tendency to spread out into the surroundings
When they do so it becomes very difficult to "gather" the energy back together again
* as a result, the energy becomes **less useful**
* hence, whenever a process produces unwanted heat, light or sound, the energy that ends up in those forms is **wasted**
**Wasted energy** = the energy that is not useful for the intended purpose and is dissipated to the surroundings
In practice, most systems tend to be open systems
Unlike other forms of energy, **heat**, **light** and **sound** have a tendency to spread out into the surroundings
When they do so it becomes very difficult to "gather" the energy back together again
* as a result, the energy becomes **less useful**
* hence, whenever a process produces unwanted heat, light or sound, the energy that ends up in those forms is **wasted**
13
New cards
8\.11 When do mechanical processes become wasteful?
When they cause a rise in temperature so dissipating energy in heating the surroundings
14
New cards
8\.12 What is power?
The rate at which energy is transferred
15
New cards
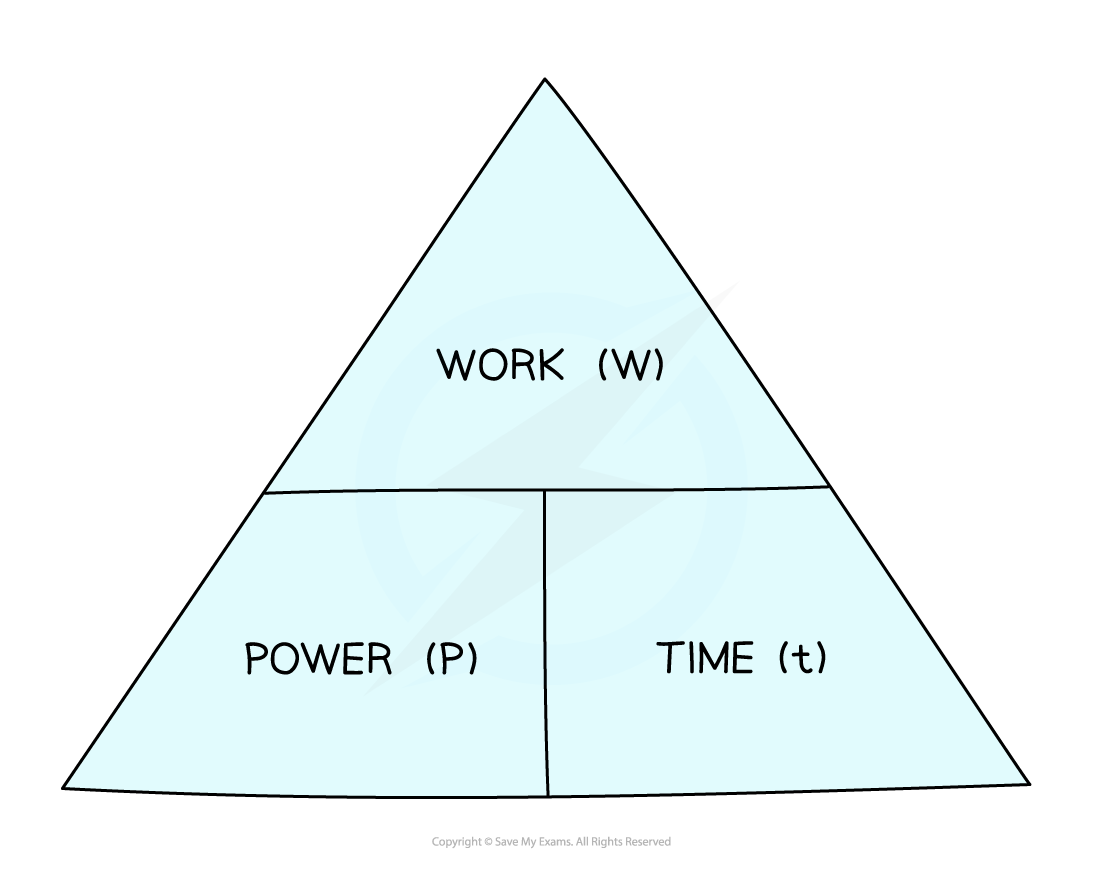
8\.13 What is the equation involving power, work done and time taken?
**Power = work done** **÷ time**
watt (W) = joule (J) ÷ second (s)
watt (W) = joule (J) ÷ second (s)
16
New cards
8\.14 What is one watt equal to?
One joule per second
17
New cards
8\.15 What is the equation for efficiency?
**Efficiency = (useful energy transferred by the device ÷ total energy transferred to the device) × 100%**
