Bio307 - Ch. 19 - Kidneys
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:58 AM on 11/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
Urine
dynamically controlled fluid that has a a concentration changed depending on the body's water retention needs
2
New cards
Ureter
smooth muscle tube carrying urine, connects kidneys to the urinary bladder
3
New cards
Urinary Bladder
triangular shaped hollow organ in the lower abdomen, held by ligaments to other organs and pelvic bones
walls relax/expand to store urine
walls flatten and contract to empty urine through the urethra
walls relax/expand to store urine
walls flatten and contract to empty urine through the urethra
4
New cards
Urethra
allows urine to pass outside of the body
brain signals for the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder
sphincter muscles relax, allows urine to exit bladder through the urethra
brain signals for the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder
sphincter muscles relax, allows urine to exit bladder through the urethra
5
New cards
Renal
refers to anything dealing with kidney function
renal arteries branch off of the abdomen, supply blood to the kidney
renal veins carry blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava
renal arteries branch off of the abdomen, supply blood to the kidney
renal veins carry blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava
6
New cards
Cortex
outside layer or covering of many body organs, so the renal cortex is the outer layer of the kidney
7
New cards
Medulla
inner part of the kidney, visible in a cross section
8
New cards
Nephron
the functional unit of the kidney, a microscopic tubule which makes up an outer cortex and an inner medulla
9
New cards
Glomerulus
ball-like network, a capillary bed where blood flows from the afferent arteriole
10
New cards
Filtrate
a filtered fluid that passes into the lumen of the nephron
Filtration: movement of the fluid from blood into the lumen of the nephron
Filtration: movement of the fluid from blood into the lumen of the nephron
11
New cards
(Glomerular) Filtration
the first step in making urine, kidney filters excess fluid and waste products out of the blood into urine collecting tubules of the kidney
12
New cards
(Tubular) Reabsorption
movement of filtered materials from the tubule to the blood
13
New cards
(Tubular) Secretion
movement of selected molecules from blood to tubules
14
New cards
Excretion
separation or throwing off of waste product from cells to tissues of a plant or animal
15
New cards
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
volume of fluid (GFR) that filters into Bowman's capsule per unit time
16
New cards
(Renal) Clearance
excretion rate / concentration of substance in plasma
17
New cards
Micturition
act of urinating, which is a spinal reflex subject to conscious and unconscious control
18
New cards
Major Functions of the Kidney
1: Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure
2: Regulation of osmolarity
3: Ion balance maintained
4: Homeostatic regulation of pH
5: Excretion of waste
6: Produce hormones
2: Regulation of osmolarity
3: Ion balance maintained
4: Homeostatic regulation of pH
5: Excretion of waste
6: Produce hormones
19
New cards
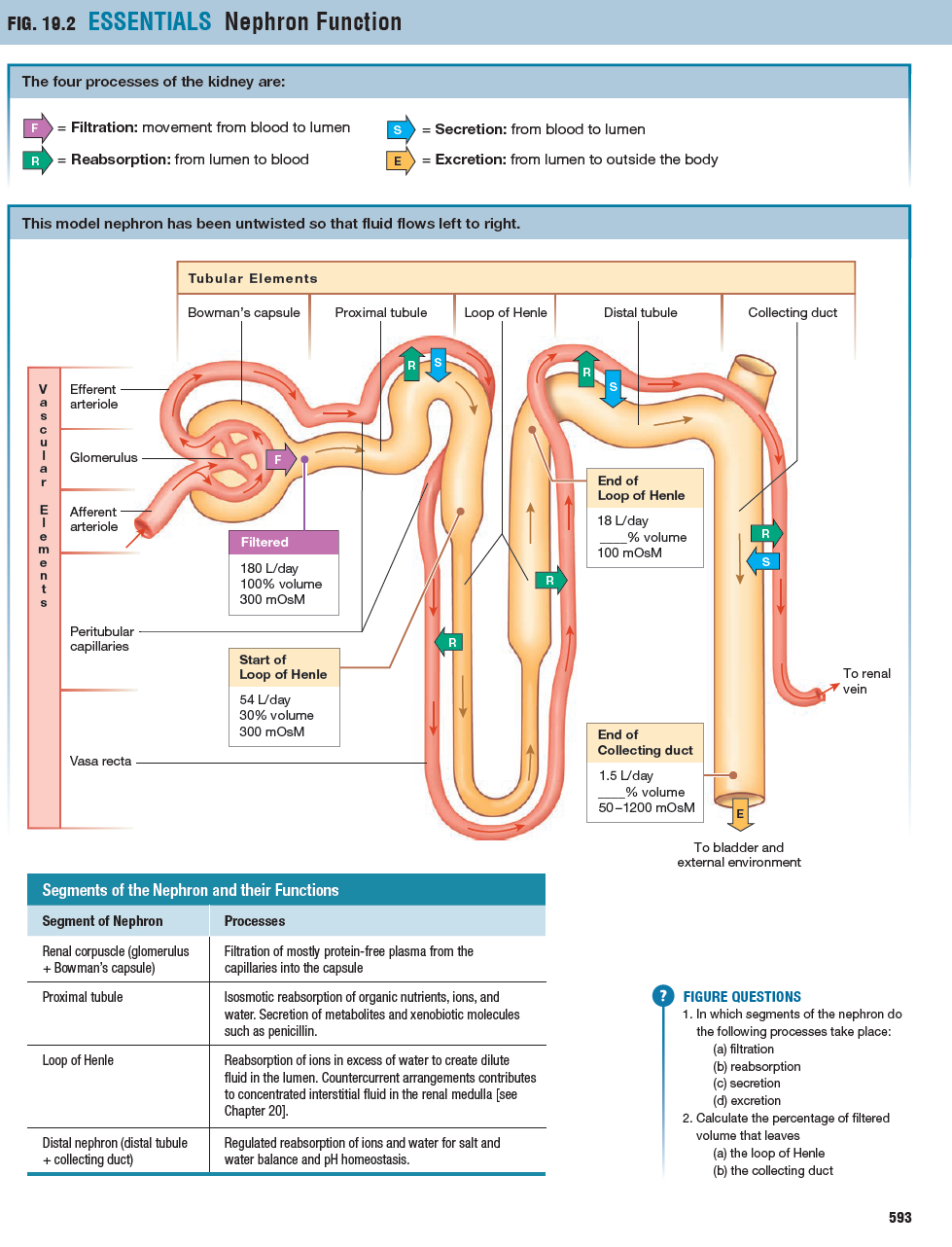
"Story" of Filtrate through the major sections of the nephron
1) Glomerulus/Bowman's Capsule: protein-free plasma flows from capillaries to the capsule
2) Proximal Tubule: Unregulated isosmotic reabsorption of nutrients (ex: glucose, amino acids), ions, water
3) Loop on Henle: Ions are reabsorbed
(Descending Limb): permeable to water
(Ascending Limb): permeable to ions
4) Distal nephron (distal tubule + collecting duct): regulated reabsorption of ions and water for salt water balance and pH homeostasis
2) Proximal Tubule: Unregulated isosmotic reabsorption of nutrients (ex: glucose, amino acids), ions, water
3) Loop on Henle: Ions are reabsorbed
(Descending Limb): permeable to water
(Ascending Limb): permeable to ions
4) Distal nephron (distal tubule + collecting duct): regulated reabsorption of ions and water for salt water balance and pH homeostasis
20
New cards
Generally, what categories of substances are typically completely reabsorbed from the kidney and which are selectively reabsorbed, depending on need:
Energy molecules are COMPLETELY reabsorbed (dont want to pee out ur glucose)
Na+ and H2O as needed
Glucose, amino acids are completely reabsorbed
Na+ and H2O as needed
Glucose, amino acids are completely reabsorbed
21
New cards
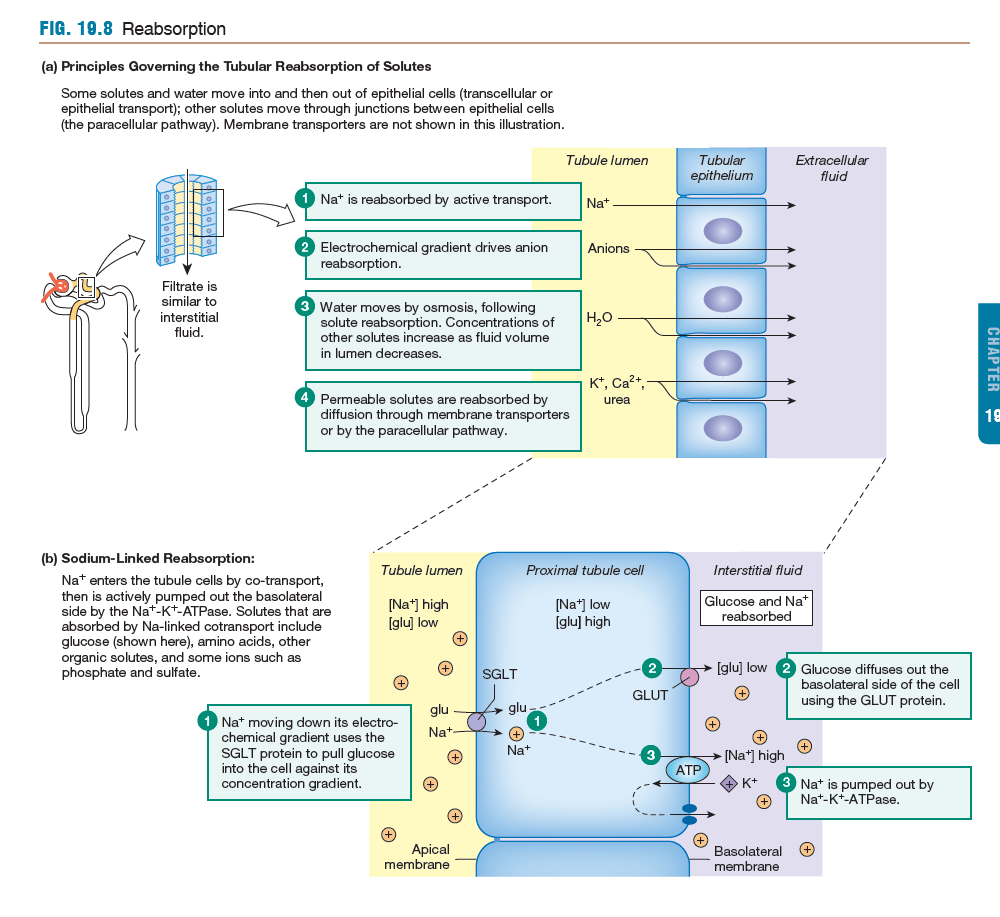
Mechanism of Tubular Reabsorption
a) draw/explain major mechanisms by which Na+, Cl-, water, glucose reabsorbed
b) why a change in one parameter affects another
(how does having fewer Na+/K+ pumps affect water reabsorption)
a) draw/explain major mechanisms by which Na+, Cl-, water, glucose reabsorbed
b) why a change in one parameter affects another
(how does having fewer Na+/K+ pumps affect water reabsorption)
a) SGLT (cotransport) of glucose/Na+
(sodium-linked reabsorption pathway)
b) Na+/K+ primary active transport pump impacts Na+/Glucose, secondary active transport pathway affected
having less transporters slows diffusion due to a smaller gradient (piggybacking)
(sodium-linked reabsorption pathway)
b) Na+/K+ primary active transport pump impacts Na+/Glucose, secondary active transport pathway affected
having less transporters slows diffusion due to a smaller gradient (piggybacking)
22
New cards
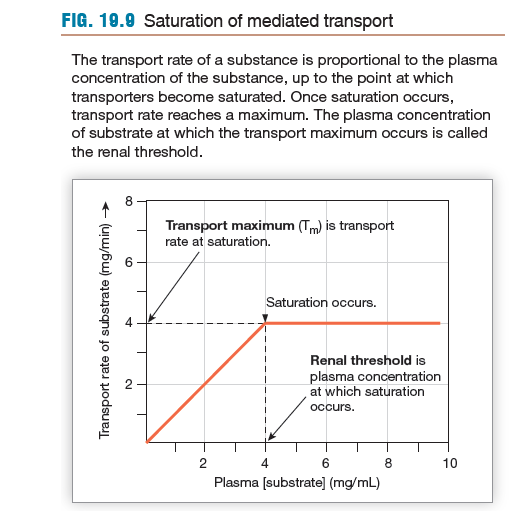
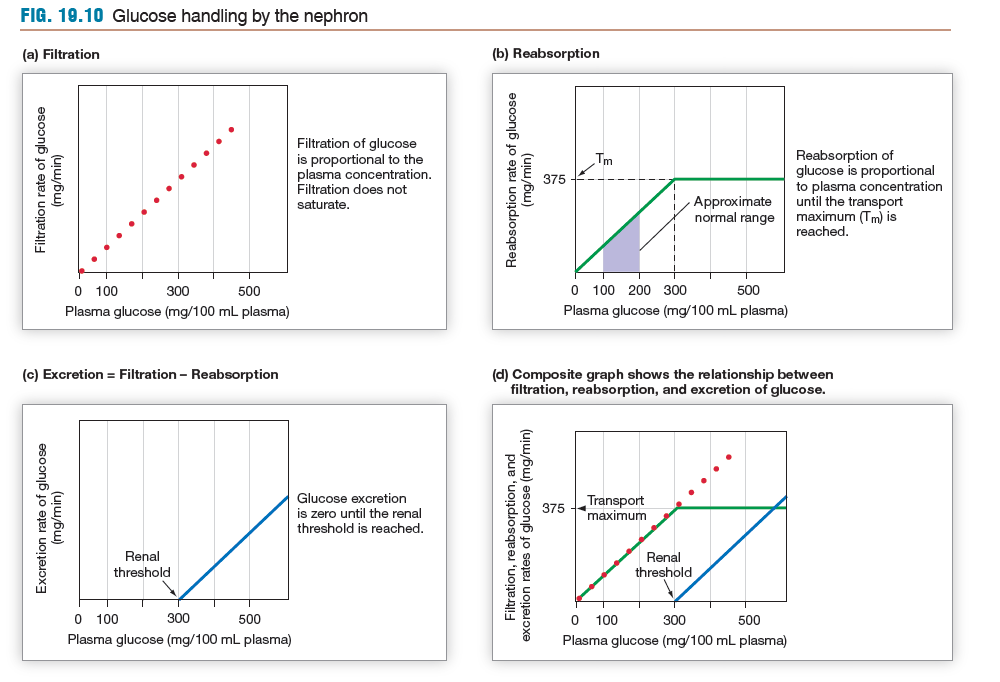
Recognize that saturation of transporters limits reabsorption:
explain the role of saturation in diabetes mellitus
explain the role of saturation in diabetes mellitus
glucose transporters reach a fully saturated state, not allowing any more substrate to be absorbed
(glucose concentration surpasses renal threshold so any extra is excreted)
(glucose concentration surpasses renal threshold so any extra is excreted)
23
New cards
Several substances that are commonly secreted into kidney tubule (tubular secretion)
penicillin
PAH (para-aminohippurate)
urea
PAH (para-aminohippurate)
urea
24
New cards
GFR remains relatively constant through normal changes in posture or through renal autoregulation
constriction of afferent restricts blood leading to glomerulus
constriction of efferent restricts blood from leaving the glomerulus
constriction of efferent restricts blood from leaving the glomerulus
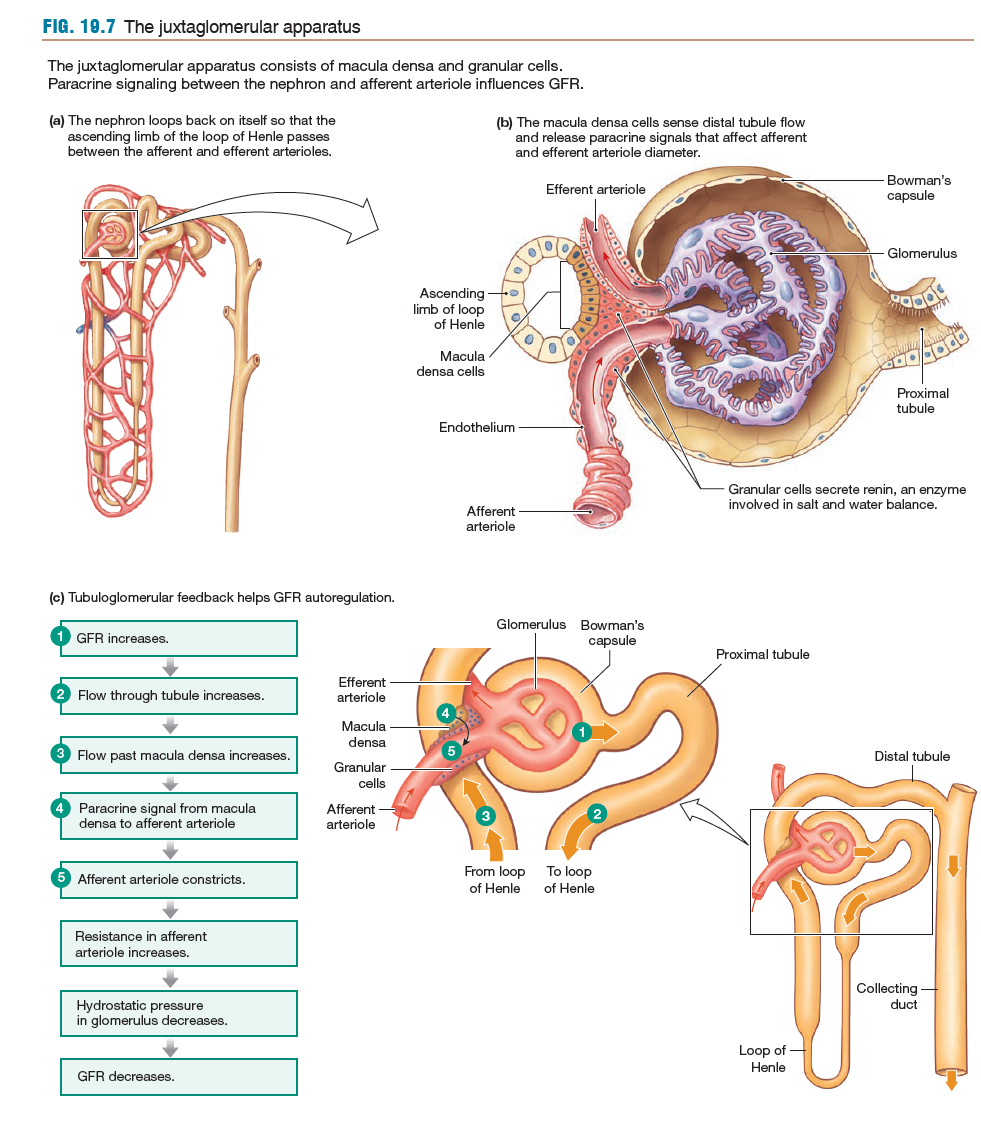
25
New cards
explain how knowing a substance's clearance compared to the GFR tells you whether its secreted or reabsorbed (net)
clearance rate = GFR - neither reabsorbed nor secreted
Clearance of X > GFR: net secretion of X
Clearance of X < GFR: net reabsorption of X
Clearance of X > GFR: net secretion of X
Clearance of X < GFR: net reabsorption of X