6 Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic Drugs
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Polypeptide hormone produced by the pancreatic beta cell
Insulin
Insulin synthesis and release are modulated by the following:
Glucose
Amino acids, fatty acids, and ketone bodies also stimulate insulin release
Islets of Langerhans contains several cell types, other than beta cells that help modulate insulin secretion
a-adrenergic pathways inhibit secretion of insulin – the predominant inhibitory mechanism
B-adrenergic stimulation – increases insulin release
Elevated intracellular Ca2+ acts as an insulin secretagogue
Insulin binds to the extracellular domain of specific high-affinity receptors (with tyrosine kinase activity) on the surface of liver, muscle, and fat cells.
When insulin binds, specific tyrosine residues of the insulin receptor become phosphorylated which will lead to a signal transduction cascade.
Insulin
Actions of Insulin
Insulin promoted systemic cellular K+ uptake
Liver: inhibits glucose production
Muscle: Increase glycogen deposition
Classified by the timing of its action in the body, including the onset of action and duration of action
Insulin Preparation
used to treat all manifestations of hyperglycemia in both type 1 (insulin-dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus
Insulin Preparations
INsulin Preps AEs
hypoglycemia (symptoms include tachycardia, tremor, sweating, confusion, agitation, and in more severe cases, loss of consciousness or coma)
Hypokalemia, hypertrophy of the SC fat at the injection site, weight gain
Insulin Prep Table
Insulin Prep Table
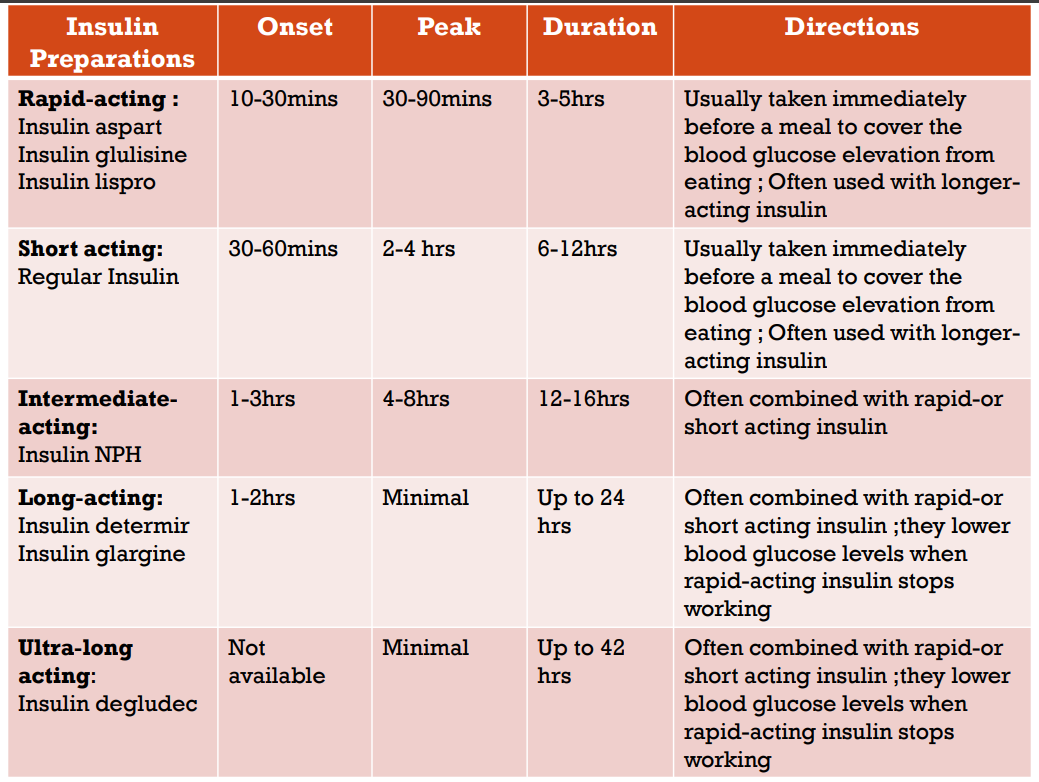
These agents are modified with different amino acid residues to make them more soluble, allowing them to rapidly dissociate into monomers
They are often injected minutes before a meal and provide better postprandial control of glucose levels than regular insulin
Rapid-acting
Regular crystalline insulin naturally self-associates into a hexameric molecule (6 insulin molecules) when injected SQ. before it is absorbed, it must dissociate to dimers and then to monomers
Short-acting
Insulin NPH (neutral protamine Hagedorn)
This insulin is modified with the addition of protamine, which prolongs the time required for absorption and increases the duration of action
Intermediate-acting
These agents were modified to mimic basal insulin secretion and have a steady release with no peak effect
Long-acting
Patients with type 2 DM may require higher doses of insulin, due to insulin resistance
Dosing considerations
This may occur in patients recently diagnosed with Type 1 DM
It occurs when beta cells in the pancreas can still secrete enough endogenous insulin to aid in blood glucose control, resulting in reduced exogenous insulin requirement
Honeymoon phase
Oftentimes with acute illness, there is an increase in cortisol, which causes an elevation in blood glucose
Patients with an acute illness may require higher insulin doses
Acute illness
Sulfonylureas
1st generation: Tolbutamide, chlorpropamide, tolazamide
2nd generation: Glyburide, glipizide, glimepiride
1st Gen Sulfonylureas
Tolbutamide, chlorpropamide, tolazamide
2nd Gen Sulfonylureas
Glyburide, glipizide, glimepiride
All are equally effective in lowering blood glucose
1st generation: Tolbutamide, chlorpropamide, tolazamide
2nd generation: Glyburide, glipizide, glimepiride
are prescribed more often ; they are more potent and have fewer adverse effects and drug interactions
2nd generation agents Sulfonylureas
Approved for the management of adults with Type 2 DM since they require functional pancreatic beta cells to produce their effect on blood glucose ; they cannot be used in patients with Type 1 DM
Sulfonylureas
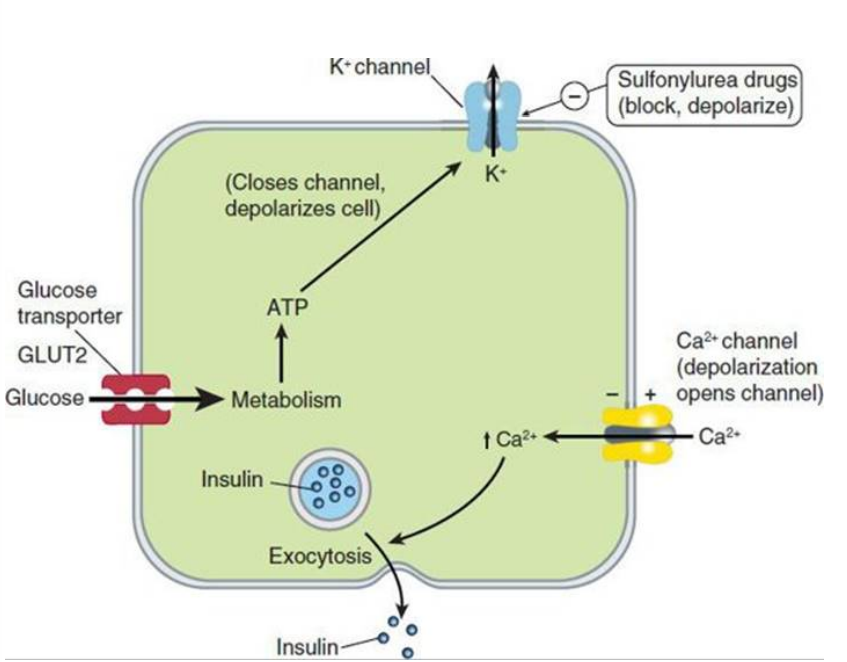
These agents are oral insulin secretagogues ; they cause insulin release from pancreatic beta cells
They bind to the SUR1 (sulfonylurea receptor), and block ATP- sensitive K+ channels resulting in depolarization. The voltage gated Ca2+ channels open, resulting in Ca2+ influx and triggering the insulin release
Long term use also reduces serum glucagon, which may contribute to hypoglycemic effects
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas AEs
hypoglycemia, weight gain
Sulfonylureas Precautions
caution must be used in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction ; caution must also be used in patients with a sulfa allergy
Meglitinides Agents
Repaglinide, Nateglinide
They are oral insulin secretagogues ; Have similar action to sulfonylureas, but they bind to distinct regions on the SUR1 molecule
Repaglinide, Nateglinide
Approved for Type 2 DM
Since they have fast onset and short duration of action, they are recommended in patients with irregular meal schedules and in patients who develop late postprandial hypoglycemia when taking a sulfonylurea
They are used instead of sulfonylureas in patients with a history of sulfa allergy
Meglitinides
Repaglinide, Nateglinide
Repaglinide, Nateglinide AEs
hypoglycemia ; weight gain (Repaglinide)
Biguanides Agent
Metformin
Indication: Type 2 DM
Biguanides
Metformin
It reduces the hepatic glucose production and intestinal absorption of glucose; it does not alter insulin secretion. These effects are believed to be due to an increase in the activity of AMP kinase, a key intracellular regulator of energy homeostasis.
Also increases peripheral insulin sensitivity
Its glucose lowering action does not depend on functional pancreatic beta cells
Biguanides
Agent: Metformin
Biguanides Advantages
rarely causes hypoglycemia and weight gain
Biguanides AEs
GI distress, has potential to cause lactic acidosis (characterized by nonspecific symptoms: NV, abdominal pain, lethargy, hyperventilation, and hypotension)
Biguanides CIs
Due to an increased risk of lactic acidosis, metformin should not be used in patients with CHF, renal impairment, or who are seriously ill
Metformin should be temporarily discontinued before iodinated contrast, due to the potential for acute kidney injury and increased risk for lactic acidosis
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
Indications: Type 2 DM
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
These agents are insulin sensitizers; they act to decrease insulin resistance
They bind to a specific intracellular receptor, PPAR-y (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma), a member of the nuclear-receptor family
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
They predominantly affect liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
IN THE LIVER
decrease glucose output and insulin levels
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
IN MUSCLEa
these agents increase glucose uptake
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
IN ADIPOSE TISSUE
these drugs increase glucose uptake and decrease fatty acid release and may increase the release of hormones such as adiponectin and resistin
The actions of these drugs require the presence of insulin
Can reduce plasma glucose and TG
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
Indications: Type 2 DM
Thiazolidinediones Agents
Thiazolidinediones AEs
edema, weight gain
Thiazolidinediones Precautions
cause an increased risk for fractures and bladder cancer, can cause or exacerbate CHF
Thiazolidinediones CIs
heart failure, liver disease
A-Glucosidase Inhibitors Agents
Agents: Acarbose, Miglitol
Act as competitive, reversible inhibitors of pancreatic a- amylase and intestinal a-glucosidase enzymes; they act in the lumen of the intestine
Inhibition of a-glucosidase prolongs the digestion of carbohydrates and reduces peak plasma glucose levels
A-Glucosidase Inhibitors Agents
Agents: Acarbose, Miglitol
Indications: Type 2 DM ; helpful in reducing postprandial glucose
A-Glucosidase Inhibitors Agents
Agents: Acarbose, Miglitol
A-Glucosidase Inhibitors Agents
Agents: Acarbose, Miglitol
AEs
GI distress and flatulence
A-Glucosidase Inhibitors Agents
Agents: Acarbose, Miglitol
CIs
intestinal diseases such as intestinal obstruction & inflammatory bowel disease
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 agonists
GLP-1 agonists
GLP-1 agonists AGENTS
Exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, albiglutide, dulaglutide
Type 2 DM ; also cause weight loss ; therefore, liraglutide is also approved for weight management
GLP-1 agonists
Exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, albiglutide, dulaglutide
GLP-1 agonists
Exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, albiglutide, dulaglutide
AEs
GI distress
GLP-1 agonists
Exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, albiglutide, dulaglutide
Precautions
increased risk for acute pancreatitis and thyroid tumors
Analogs of the hormone incretin (GLP-1)
Increase glucose-dependent insulin secretion; decrease inappropriate glucagon secretion, slow gastric emptying, decrease food intake, and promote B-cell proliferation
GLP-1 agonists
DPP-4 inhibitors
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors Agents
Sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin
Type 2 DM
DPP-4 inhibitors Agents
Sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin
DPP-4 inhibitors Agents
Sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin
AEs
rhinitis and URTI ; may cause pancreatitis
DPP-4 is responsible for the proteolysis of incretins, including GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide
These agents inhibit DPP-4 to increase active incretins. This leads to an increase in insulin synthesis and release and suppresses glucagon production in a glucose-dependent manner.
They may also improve beta cell function
DPP-4 inhibitors Agents
Amylin Analogs Agent
Pramlintide
Indication: used in combination with insulin for Type2 DM
Amylin Analogs Agent
Pramlintide
Amylin Analogs Agent
Pramlintide
AEs
nausea, hypoglycemia, gastroparesis
Amylin is a polypetide stored and secreted by beta cells of the pancreas ; it is cosecreted with insulin to reduce blood sugar. Concentrations are abnormally low in patients with DM.
Pramlintide can reduce postprandial glucose through prolongation of gastric emptying, reduction of prostprandial glucagon secretion, and reduction of caloric intake through centrally mediated appetite suppression.
Causes weight loss and reduces postprandial glucose levels
Amylin Analogs Agent
Pramlintide
SGLT2 inhibitors
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 inhibitors Agents
Canagliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin
Indications: Type 2 DM
SGLT2 inhibitors Agents
Canagliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin
SGLT2 inhibitors Agents
Canagliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin
Advantages
weight loss and a modest decrease in BP
SGLT2 inhibitors Agents
Canagliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin
AEs
include genitourinary infections and increased serum potassium
SGLT2 inhibitors Agents
Canagliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin
CI
severe renal impairment
SGLT2 is the main site of filtered glucose reabsorption
These agents inhibit SGLT2 in the proximal renal tubules; this results in reduced reabsorption of filtered glucose from the tubular lumen and lowers the renal threshold for glucose (RTG)
Reduction of filtered glucose reabsorption and lowering of RTG results in increased urinary excretion of glucose, thereby reducing plasma glucose concentrations.
SGLT2 inhibitors Agents
Canagliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin
Produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas
Structurally similar to secretin, VIP, and gastric inhibitory peptide
Glucagon
Glucagon secrition is inhibited by
elevated plasma glucose, insulin, and somastostatin
Glucagon secrition is stimulated by by
amino acids and sympathetic stimulation and secretion
for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia ; can be used as a diagnostic aid in which it provides intestinal relaxation prior to radiologic examination
Glucagon
Glucagon AEs
: low incidence of NV
Stimulates adenylate cyclase to produce increased cAMP
It increases blood glucose by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver
In general, its actions oppose the actions of insulin
Large doses produce marked relaxation of the smooth muscle in the stomach, intestines and colon.
Glucagon
Indication: for hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia
Diazoxide
Diazoxide AEs
sodium retention, GI distress, and changes in circulating white blood cells
: this agent opens ATP-dependent potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells, resulting in inhibition of insulin release.
Diazoxide