AP BIO Unit 5 Review - "Heredity"
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
mitosis
results in daughter cells that are genetically identical; this is a result of asexual reproduction; no genetic variation; diploid cells; produces more diploid cells
meiosis
results in daughter cells that are genetically different from each other called gametes; sexual reproduction; results in haploid cells
gamete
sperm cell + egg cell; 50% of mom’s DNA, 50% of dad’s DNA
what does sexual reproduction do?
increase genetic variation by fusing 2 gametes that are genetically different, creating new combinations of genetic material in offspring; each gamete has half of the genetic material required to make a new organism
haploid
has only 1 set of chromosomes (23 in humans)
diploid
has 2 sets of chromosomes (46 in humans); 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes
meiosis I how many cells?
1 diploid cell —> 2 haploid cells
meiosis II how many cells?
2 haploid w/ copied chromosomes —> 4 haploid cells with uncopied chromosomes
homologous chromosomes
similar chromosomes inherited from parents
meiosis I vs meiosis II?
MI separates homologous chromosomes; MII separates sister chromatids
sister chromatids
copied chromosomes
prophase I
homologous chromosomes pair and condense (synapsis), meiotic spindle forms, centrosomes move to poles, nuclear envelope breaks down
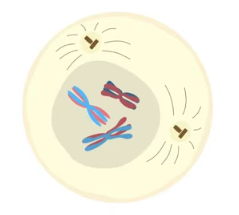
metaphase I
meiotic spindle aligns homologous chromosomes along “equator” at the metaphase plate
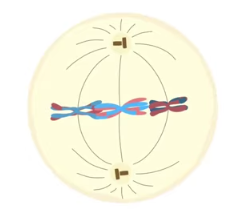
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes are separated and are pulled toward poles, sister chromatids remain attached
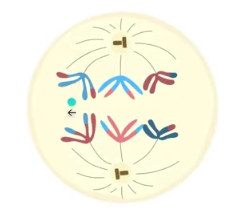
telophase I
meiotic spindle breaks down, new nuclear envelopes form, cleavage furrow/cell plate forms, chromatids decondense; cytokinesis occurs; 2 haploid daughter cells w/ duplicated chromosomes
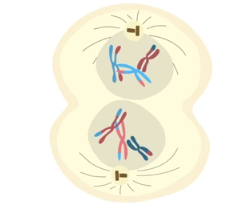
prophase II
meotix spindle re-forms, sister chromatids are connected to the meiotic spindle at centromeres
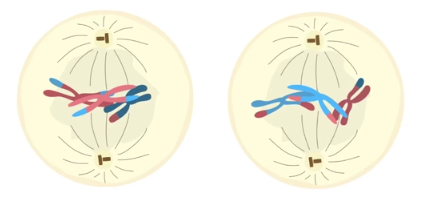
metaphase II
chromosomes align along the metaphase plate, kinetochores (protein that attaches to centromeres) attach
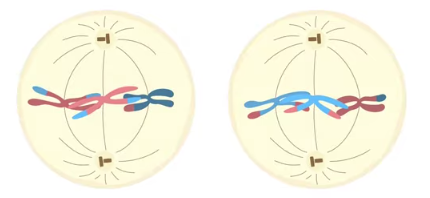
anaphase II
proteins at the centromeres break down, sister chromatids are pulled toward opposite sides of the cell
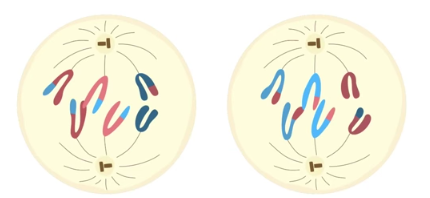
telophase II
spindle breaks down, new nuclear envelopes develop, cleavage furrow/cell plate forms, chromatids decondense, cytokinesis occurs; 4 haploid cells w/ unduplicated chromosomes
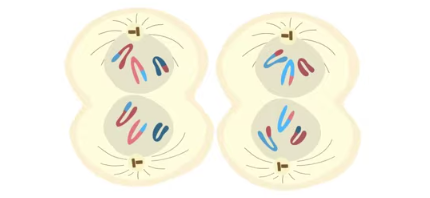
what happens when the sperm and egg fuse?
it has a random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes
why are all gametes genetically different?
independent/random assortment, crossing over, random fertilization
independent assortment
the alignment and distribution of homologous chromosomes during meiosis is random; 3 homologous pairs means i different combos of chromosomes for gametes to inherit
crossing over
the exchange of genes b/w homologous chromosomes during synampsis (PI)l results in recombination; greatly increases genetic variation by increasing combinations of genes gametes inherit
random fertilization
refers to the fact that no sperm or egg cell has a greater chance of fertilization than the other
what happens sometimes with meiosis?
there can be mistakes and the chromosomes won’t fully separate; nondisjunction, which can result in an aneuploidy
nondisjunction
incorrect separation of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids when seperated
aneuploidy
an incorrect # of chromosomes (not haploid)
trisomy 21
someone with down syndrome; someone with down syndrome inherited 1 more chromosome from #21 from their mom or dad
locus
where a gene is located on a chromosome
patterns of inheritence
can be determined w/ test crosses
alleles
versions of the same gene
what determine’s the offspring’s traits?
the different combination of alleles
p generation
1st gen from mendel (purple and white)
f1 gen (AA x aa from p)
mendel got 4 purple flowers (all Aa)
f2 gen (f1 x f1) (Aa x Aa from f1)
¼ were white; ¾ were purple (1/4 AA, 2/4 Aa. ¼ aa)
dominant
only 1 gene is required to express the purple flower trait (A)
recessive
2 copies are required to express the trait (a)
genotypes
homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, heterzygous
heterozygous (Aa) x heterzygous (Aa)
4/4 heterozygous (Aa)
monohybrid cross
each parent is a hybrid and always results in a 3:1 dominant to recessive ratio
pedigree key
men are squares, women are circles, filled in is affected
how to determine if a gene is dominant for pedigree
do all affected individuals have an affected parent
are all of these instances true: all affected makes have an affected mother, affected fathers have all affected daughters, affected fathers have no affected sons (if yes, x-linked, if no, autosomal)
how to determine is a gene is recessive from a pedigree
do all affected individuals NOT have an affected parent
are most affected individuals male (if yes, x-linked, if no, autosomal)
do all traits follow mendelian patterns?
no
complete dominance (non-mendelian genetics)
there is a dominant allele and a recessive alleles together; the dominant hides the recessive (A - black a - white)
incomplete dominance (non-mendelian genetics)
there are no dominant alleles; the 2 alleles blend (b - black, w - white, results in grey)
codominance (non-mendelian genetics)
there is more than 1 dominant allele; both show separately (B - black, W - white)
sex linked traits
genes on sex chromosomes (mainly on X - not Y)
pleiotropy
1 gene affects multiple phenotypes; traits do not segregate independently (ex. chicken frizzle)
mitochrondrial inheritance
involves genes located in chromosomes in the mitochrondria; only passed down by mothers (mitochrondria + chloroplasts located in egg cells)
polygenic traits
characteristics, such as human height, skin color, etc., is determined by 2 or more genes rather than a single gene
epistasis
the expression of 1 gene is masked, inhibited, or modified by 1 or more other genes, influencing how genotypes translate into phenotypes
x-inactivation
in female mammals where 1 of the 2 x chromosomes is randomly silenced in each somatic cell during early embryonic development (ex. calico cats)
recombinant
new combinations of traits (result of crossing over)
multiple alleles (non-mendelian genetics)
many traits have more than 2 alleles; this creates the possibility of multiple different phenotypes (ex. ABO blood)
what did Thomas hunt Morgan breed?
fruit flies mutant male w/ white eyes (w) x true breeding wild type female (wt)
what did Thomas hunt morgan discover?
he got a 3:1 ratio, the only ones w/ white eyes were male; he then discovered that genes located on chromosomes in a linear order can be linked, yet “croos over” to separate
genetic mapping
we use data from dihybrid crosses to map out where on a chromosomes a gene can be found; the farther apart 2 genes are, the more space there is between them; more space = more places crossing over can happen; more recombinant crossing over = farther apart the genes are
phenotypic plasticity
when the same genotype can produce different phenotypes
temperature affect on phenotype
during embryonic development (ex. reptile gender, Siamese cats)
periodism affect on phenotype
hares are white if there is less daytime and brown if there’s more daytime
pH affect on phenotype
hydrangeas soil - basic soil = pink, acidic soil = blue
UV affect on phenotype
skin color - melanin
stress affect on phenotype
bluehead wrasse, female —> male
identical twins
epigenetic markers (DNA expressed differently
what does chi square measure?
if there is a statistically significant difference between observed and expected frequencies in categorical data; checks null hypothesis
how to calculate chi-square value?
find O, E, O-E, (O-E)², (O-E)² / E, then add all the (O-E)² / E, then find the degrees of freedom (red, blue, etc) subtract by 1. If it is below the 0.05 critical value, fail to reject the null hypothesis, results are likely due to chance. If it is above the 0.05 critical value, reject the null hypothesis, results are not due to chance
Achondroplastic dwarfism is a dominant genetic trait that causes severe malformation of the skeleton. Homozygotes for this condition are spontaneously aborted naturally (the homozygous condition is lethal) but heterozygotes will develop to be dwarfed. Matthew has a family history of the condition, although he does not express the trait. Jane is an achondroplastic dwarf. Matthew and Jane are planning a family of several children and want to know the chances of producing a child with achondroplastic dwarfism. If Matthew and Jane have three children, what are the chances that the first two children will not express the trait but that the third child will be an achondroplastic dwarf
1/8
Red-green color blindness in humans is inherited as a sex-linked recessive gene. A colorblind woman marries a normal man. Which of the following is true of their children?
daughters will be carriers, sons will be colorblind
In pea plants, the gene for white flowers(f) and the gene for short height(h) are on different chromosomes. The respective dominant alleles for each of these genes produce purple flowers and tall plants. From the cross that is FfHh x FfHh, what is the probability of having an offspring whose phenotype is dominant for both traits?
9/16
In the spring and summer, the fur of the arctic fox contains a pigment called melanin that gives the fox's fur a darker color. In the fall and winter, the fur of the arctic fox is white. Which of the following most likely explains how the changing seasons result in changing the fur color in an arctic fox?
environmental factors cause changes in gene expression resulting in seasonal variations in pigment production
A genetic counselor is consulted by a young man about developing Huntington's disease, an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele of a single gene. The young man explains that his cousin was recently diagnosed with Huntington's disease and the news caused him to consider his own risk of developing the disorder. Which of the following questions will best help the genetic counselor to evaluate the risk of the young man developing Huntington's disease and transmitting to his children?
were your parents or grandparents ever diagnosed with Huntington’s disease?
A certain species of plant has four unlinked genetic loci, W, X, Y and Z. Each genetic locus has one dominant allele and one recessive allele. For a plant with the genotype WwXxYyZz, what is the probability that the plant will produce a gamete with the haploid genotype of Wxyz?
1/16
Blood typing is often used as evidence in paternity cases in court. In one case, the mother had blood type B and the child had blood type O. Which of the following blood types could the father NOT have?
AB
Two parents are both true breeding for a complete dominance trait but they have different phenotypes than each other. Two individuals from their F1 generation are then mated together. What are the expected phenotype probabilities for the F2 generation?
3/4 , 1/4
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inherited autosomal disease caused by a recessive allele. If two individuals who are carriers of PKU have two children, what is the probability that NEITHER child will have PKU?
9/16
In domesticated cats, two alleles for a sex linked (X linked) gene code for hair color. One allele codes for orange and the other codes for black hair. Cats can be all orange, all black, or they can be calico , a coat characterized by randomly arranged patches of orange and black fur. All of the following are typically possible EXCEPT
A calico female and an orange male can produce a male calico cat
The genetic phenomena that causes the calico coat pattern in cats is called
x-inactivation
When homozygous red snap-dragons are crossed with homozygous white snap-dragons, all the F-1 generation are pink. (a blend of red and white) This type of inheritance is called
incomplete dominance
In humans, red-green color blindness is a sex linked recessive trait. If a man and a woman produces a color blind son, which of the following must be true
the mother carries the allele for color blindness
In fruit flies of the genus Drosophila, the allele for vestigial wings is recessive to the allele for round wings, and the allele for brown eye color is recessive to the allele for red eye color. A scientist crossed flies that are both heterozygous for both traits and determined the number of offspring with each combination of phenotypes. The scientist performed a chi-square analysis to determine if the data are consistent with the expectations for independent assortment. The chi-square calculated value for the experiment was 6.03 Based on the chi-square calculated value, which of the following statements is most accurate?
The chi-square calculated value is less than the critical value; therefore the null hypothesis should be accepted.
An African violet grower observes that genetically identical African violets growing near walls of the greenhouse in winter have white flowers, that plants growing farther away from the walls have pale blue flowers and that plants growing nearest the center have dark blue flowers. Which of the following best explains the difference in flower color of the African violets in the greenhouse.
An enzyme responsible for flower color does not fold into its correct shape in cooler temperatures and the greenhouse is warmest in the center
Given the parents AABBCc x AabbCc, assume complete dominance and independent assortment. What proportion of the offspring will be expected to have the same phenotype as the first parent?
3/4
The relative location of four genes on a chromosome can be mapped from the data below on crossover frequencies. Which of the following represents the relative positions of these four genes on the chromosome?
CABD
A man with blood type A is injured in a car accident. Because the accident happened in a remote area no type A donor could be found. In this emergency situation the emergency room doctor decided to give the man blood of a type other than type A. Which of the following blood types could be given to the man without causing a reaction?
type O
When pure breeding tall pea plants were crossed with pure breeding short pea plants, all members of the F1 generation were tall. Which of Mendel’s conclusions is demonstrated by this example?
some genes are dominant over others
A student in a biology class crossed a male Drosophila Melanogaster having a gray body and long wings with a female D. Melanogaster having a black body and apterous wings. The following distribution of traits was observed in the offspring. Which of the following is supported by the data?
Genes for the two traits are located close together on the same chromosome and crossing over occurred between the two gene loci.