Pharmacodynamics- Dr. Clark Exam
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
249 Terms
Referred to as "cranio-sacral"
Parasympathetic system
Important cranial nerve in parasympathetic system
CN X (vagus)
PSNS has _____ pre-ganglion and _______ post-ganglion
Long; short
Referred to as "thoracolumbar system"
sympathetic nervous system
The SNS has ___ preganglionic fibers and ___ postganglionic fibers
Short; long
Which nervous system innervates more (has more extensive branching)?
SNS
Which NS decreases heart rate and cardiac output?
PSNS
Which NS dilates lung bronchioles?
SNS
Which NS stimulates glycogen breakdown and increase in blood glucose?
SNS
Which NS stimulates breakdown of fat and increase in blood fatty acids?
SNS
Which NS increase basal metabolism?
SNS
Which NS increases secretion of HCl & digestive enzymes, increasing gut motility?
PSNS
Which NS decreases secretion and intestinal motility?
SNS
Which NS relaxes urinary sphincter, contracts detrusor muscle, and promotes urination?
PSNS
Which NS constricts the rectal sphincter, relaxes wall muscles, and inhibits defecation?
SNS
Which NS constricts the iris?
PSNS
Which NS adjusts the eye for far vision?
SNS
Which NS promotes erection?
PSNS
Which NS promotes ejaculation?
SNS
Neurotransmitter always released at the pre-ganglia
Acetylcholine
Released at the post-ganglionic neuron in SNS
norepinephrine
Released at the post-ganglionic neuron in PSNS
Acetylcholine
Adrenal medulla produces...
A mixture of epi and NE, but mostly Epi
Synthesis of ACh
Acetyl CoA + Choline —> Acetylcholine + Coenzyme A (acetylation rxn)
Enzyme in synthesis of acetylcholine
CHAT
Release of ACh occurs when an action potential triggers ________ influx
Ca2+
What enzyme causes the breakdown of ACh
Acetylcholinesterase
Precursor for DA, NE, and Epi
Tyrosine
Rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of catecholamines
Tyrosine hydroxylase
Catecholamine that is produced in the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla, not in sympathetic neurons
Epi
Synthesis of DA, NE, and Epi
1. Tyrosine + Tyrosine hydroxylase
2. Dopa + Dopa decarboxylase
3. Dopamine + dopamine beta-hydroxylase
4. Norepinephrine + PMNT
5. Epinephrine
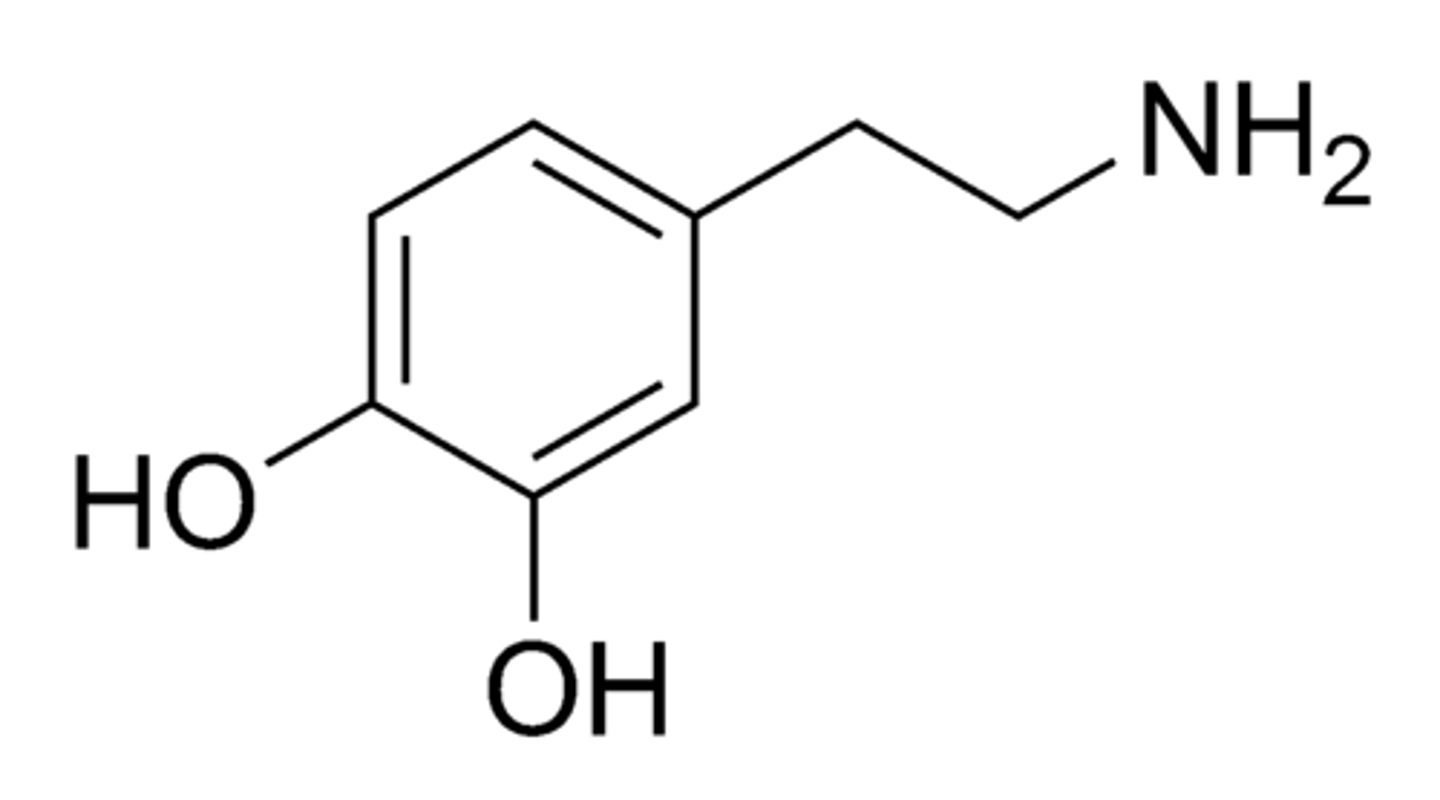
What is this structure?
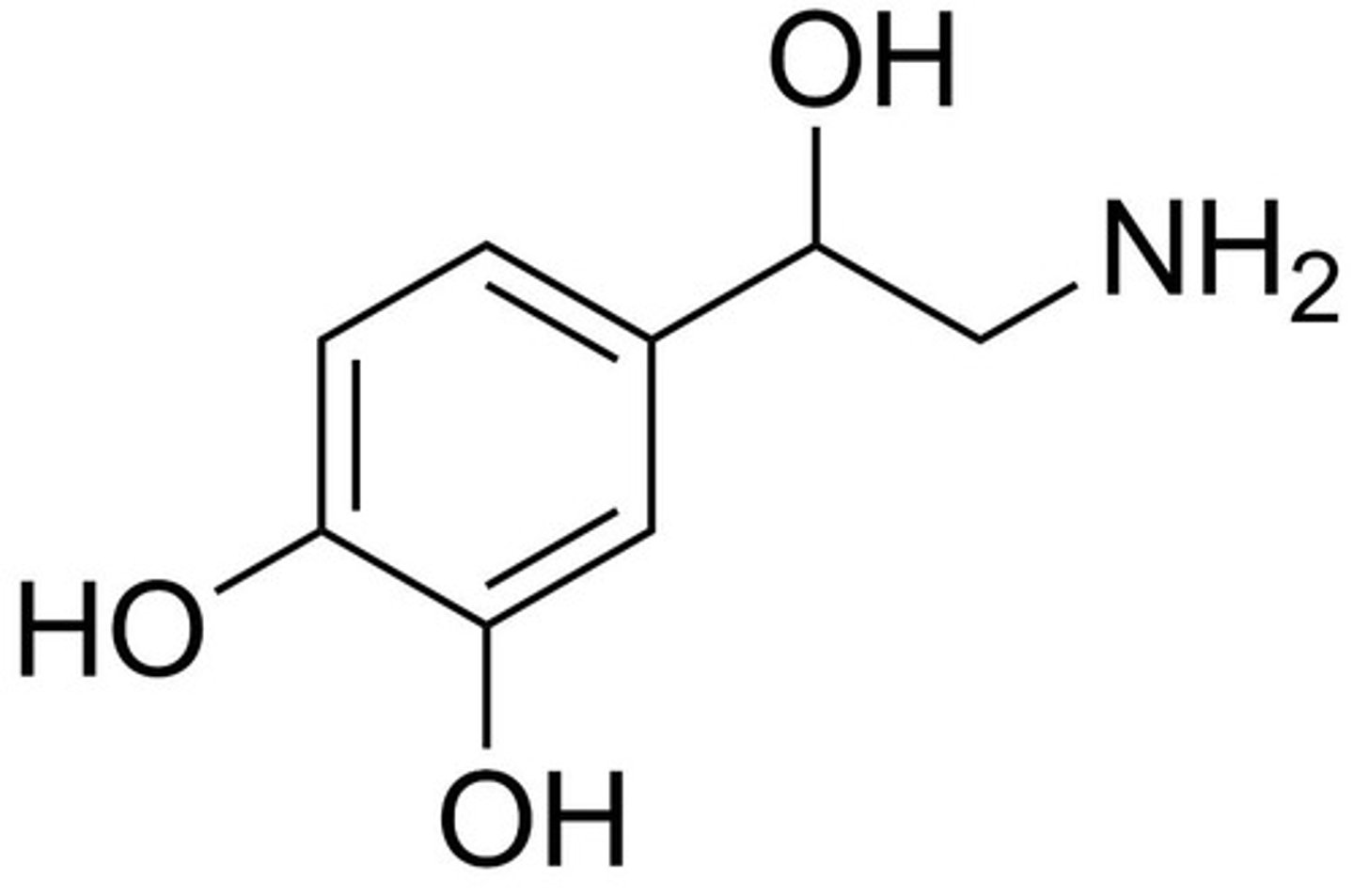
What is this structure?
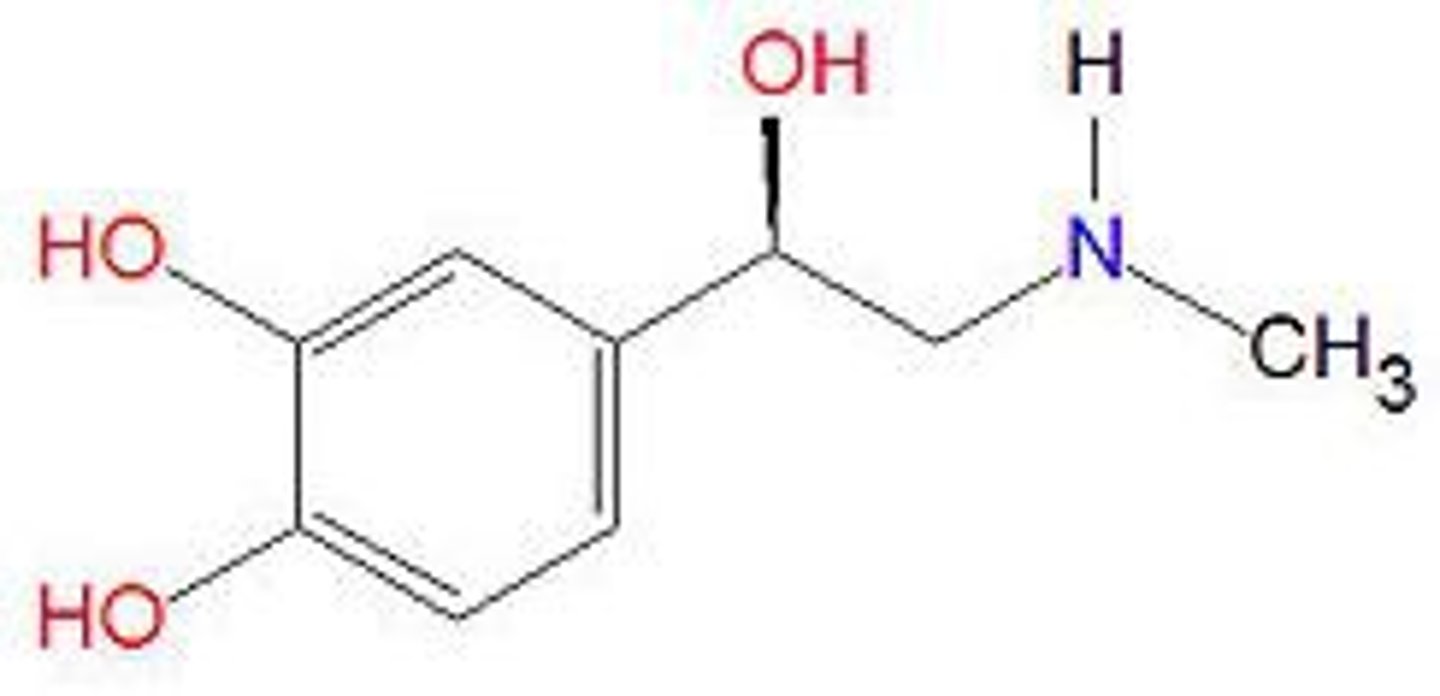
What is this structure?
How does MAO breakdown NE, Epi, and DA?
deamination
How does COMT breakdown NE, Epi, and DA?
O-methylation rxn
Receptors present on the presynaptic terminal and modulate its own release and uptake process
Autoreceptors
Receptors that regulate the synthesis/release of mediators other than its own ligand
Heteroreceptors
2 types of cholinergic receptors
nicotinic and muscarinic
What kind are muscarinic receptors
G-protein coupled
subtypes of muscarinic receptors
M1, M3, and M5- stimulate IP3/DAG pathway
M2 and M4- inhibition of cAMP
M2 also elevates K+ excretion
Which Cholinergic receptor has a slower but more prolonged response
Muscarinic
Which cholinergic receptor operates as a ligand operated channel?
Nicotinic
How do nicotinic receptors work?
2 molecules of Ach binds to receptor, ion channel opens, Na enters, local depolarisation
2 subtypes of nicotinic receptors
Nn (neuronal) and Nm (muscular)
Which Cholinergic receptor has an instantaneous response?
Nicotinic
All adrenergic receptors are
G-protein coupled receptors
Types of alpha receptors
A1: 1A, 1B and 1D - activation of IP3/DAG
A2: 2A, 2B, and 2D - inhibition of cAMP
Also, 2A elevates the K+ conductance
IP3 can elevate intracellular _____ levels
Ca2+
3 types of beta receptors
B1, B2, and B3- activate cAMP
What is the action of all choline esters?
Stimulate muscarinic receptors... activate PSNS
Which choline ester is given orally?
Bethanechol
Which choline ester is given as an inhalant?
Methacholine
Is muscarine used as a drug?
No
Is nicotine used as a drug?
Yes
Where is muscarine found naturally?
In a variety of mushrooms
What are the side effects of mushroom poisoning?
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urination
Defecation
How is mushroom poisoning treated?
Atropine
Where is pilocarpine found naturally?
In the leaves of Pilocarpus plants in S. America
Pilocarpine is very _____ (Lipid/water) soluble and ________________ (can/cannot) enter the CNS
Lipid, can
Only alkaloid agent given therapeutically?
Pilocarpine
What is pilocarpine used for?
glaucoma, emergency lowering of intraocular pressure
Nicotine initially acts as a _____ but in large doses becomes a _____.
Stimulant; blocker
can nicotine cross the blood brain barrier?
Yes, but this can result in convulsions
How do you treat toxicity from irreversible ACHESE inhibitors?
Atropine
FLuids
Oxygen
Oximes
Diazepam
How/Where does pralidoxime work to treat neurotoxicity?
Reactivates AChE at the NMJ to reverse respiratory paralysis
(Pralidoxime is charged so it cannot enter the CNS)
What are the side effects from overactivation of the PSNS?
Diarrhea
Urination
Miosis
Bronchorrhea
Bronchospasm
Emesis
Lacimation
Laxation
Salivation
What agents are short-acting AChE inhibitors?
Alcohols, Edrophonium
Edrophonium is used to diagnose what
myasthenia gravis
What agents are the medium acting AChE inhibitors?
Carbamates, -imine drugs
Most AChE inhibitors are _________________ in action
Intermediate
Physostigmine is used for
treatment of Glaucoma
Neostigmine is used for
MG
Pyridostigmine is used for
myasthenia gravis
What agent was administered prophylactically during the Gulf war?amb
Pyridostigmine
Ambemonium is used for
MG
Demacarium is used for
Glaucoma
What agents are the irreversible AChE inhibitors?
Organophosphates
What agents were used as war gases and pesticides?
Organophosphates
Atropine is used as a Cholinergic ____________________ (agonist/antagonist)
Antagonist (inhibits PSNS)
Relationship between dosage and response to atropine
Low doses- salivary glands are affected
Medium doses- heart and eye
High doses- GI and urinary
Doses that are high enough to decrease GI acid secretion will also affect the salivary glands!
What are the side effects of atropine
Dry mouth
Urinary retention
Constipation
Tachycardia
Overdose with atropine results in total block of ________________________ function
Parasympathetic
signs of atropine toxicity
Dry as a bone, blind as a bat, red as a beet, mad as a hatter
What is used to treat atropine toxicity?
Physostigmine
What is scopolamine used for?
Motion sickness and promote amnesia
Scopolamine is ______ lipid soluble than atropine
More... it has more pronounced effects
Ipratropium is used for
COPD
tiotropoium is used for
COPD
Tiotropium is dosed _______ a day and ipratropium is dosed _____ times a day
Once; four
tropicamide is used for
Mydriasis (eye drops)
Used as a long-acting tropicamide
Cyclopentolate
Benztropine is used for
Parkinson's disease
Trihexyphenidyl is used for
parkinsons disease
Tolterodine is used for
Overactive urinary bladder
fesoterodine is used for
overactive urinary bladder
Oxybutynin is used for
overactive bladder
Trospium is used for
overactive bladder
Darifenacin is used for
overactive bladder
Solifenacin is used for
overactive bladder