6.4- Photorespiration and Photosynthesis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Photorespiration
an undesirable process which competes with carbon fixation, forming useless byproducts. Occurs when RuBisCo binds O2 instead of CO2
Oxygen is a competitive inhibitor of RuBisCo
4 Types of Photosynthesis:
C2
C3
C4
CAM
C2 (photorespiration)
photorespiration
Takes place in all plants.
Some plants cannot prevent C2, resulting in inefficient photosynthesis.
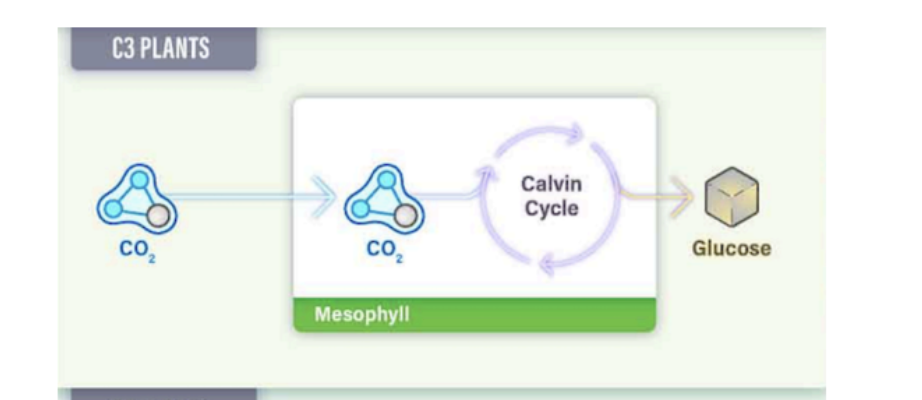
C3
normal photosynthesis;
Takes place in all plants within mesophyll cells.
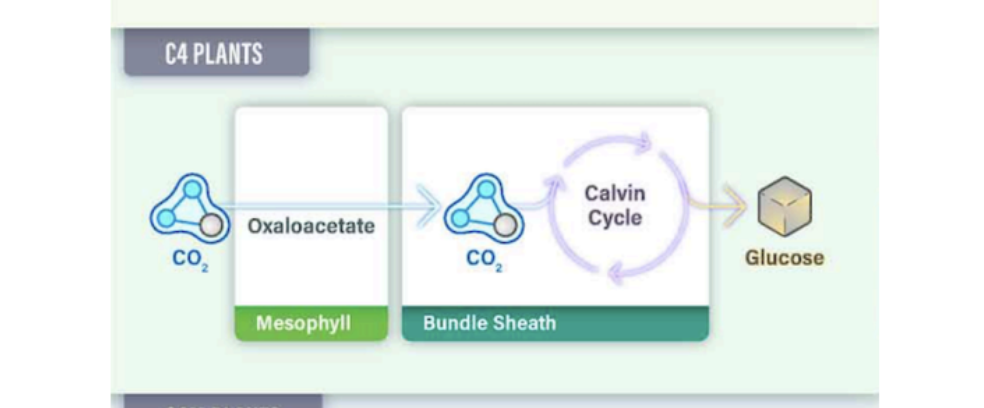
C4 photosynthesis
prevents photorespiration by physically separating light and dark reactions (spatial separation)
Plant leaf anatomy (external to internal): mesophyll cells → bundle-sheath cells → vascular tissue.
Oxygen can reach mesophyll cells, but not the deeper bundle-sheath cells.
C4 plants undergo the dark reactions in the bundle- sheath cells instead of the mesophyll cells.
4 C4 Photosynthesis Steps:
1. CO2 combines with PEP to form malate.
2. Malate is transported to bundle sheath cells and converted to CO2 +pyruvate.
3. Pyruvate shuttled to mesophyll cells and converted back to PEP.
4. CO2 enters Calvin Cycle in bundle-sheath cells.
O2 cannot access bundle-sheath cells, minimizing photorespiration.
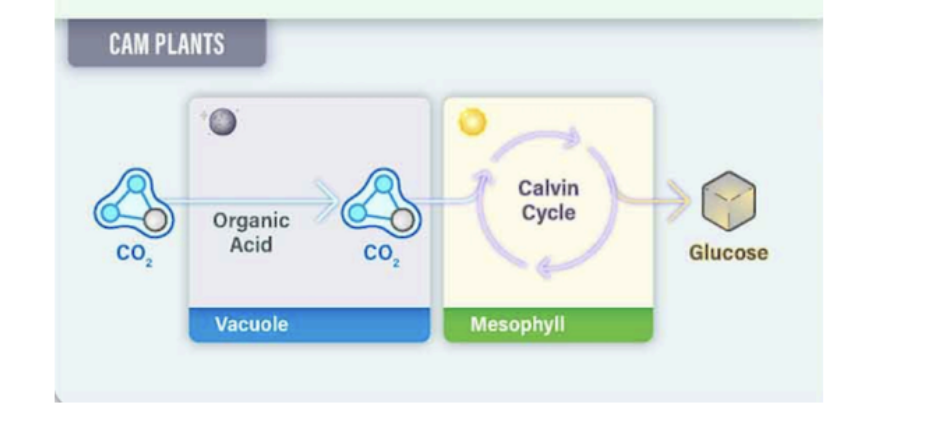
CAM:
minimizes water loss via temporal separation instead of spatial.
Common in plants from dry environments (e.g. cactus).
Stomata = Pores in the bottom of leaves that facilitate gas exchange.
In most plants, stomata are always open for continuous gas exchange and water loss (transpiration).
In CAM plants, stomata are only open at night to prevent excess water loss.
However, the light reactions cannot produce ATP/NADPH without sunlight, so the Calvin cycle is inactive.
3 CAM Photosynthesis Steps:
1. CO2 combines with PEP to form malic acid at night (carbon fixation).
2. Malic acid is stored in plant vacuole.
3. During the day, malic acid is converted back into CO2, which enters the Calvin cycle.