Required Practical 2 - Microbiology
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What antiseptic techniques can be used to avoid contamination?
Spray working area with disinfectant and wipe dry
Wash hands with antibacterial wash
Flame the neck of the culture bottle
Lift the lid of the agar plate at an angle
Dip spreader in ethanol and pass through Bunsen flame before spreading bacteria
Use forceps to place antibiotic discs
Describe how you could investigate the effect of antibiotics on bacterial growth using zones of inhibition
Divide agar plate with bacteria into three segments
Use forceps to place filter paper disc with antiseptic in each zone
Loosely tape lid onto agar plate to allow oxygen to reach bacteria
Incubate at 25°C for 48 hours
Measure the diameter of clear zones (zones of inhibition) using a ruler from two opposite directions - calculate mean of measurements
Calculate area of clear zones
How would you measure the zone of inhibition?
Use a ruler to measure from a point on one side to a point directly opposite (with lid still in place). Measure again at 90° to first diameter measurement in order to calculate a mean.
Why should you not completely seal the Agar plate?
To allow oxygen to enter the agar plate, preventing the growth of harmful anaerobic bacteria.
Why is it necessary to measure the diameter of the zone of inhibition twice?
Clear zones are not always uniform - taking more than one measurement allows a mean diameter to be calculated.
What equation is used to calculate the area of clear zones?
Area = πr2
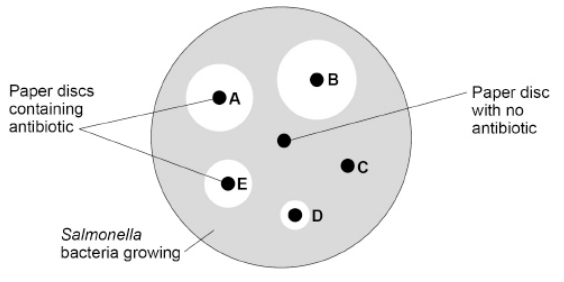
Most cases of food poisoning do not need to be treated with antibiotics.
However, some patients may need to take antibiotics to recover.
Scientists investigated the effectiveness of five different antibiotics on the Salmonella bacteria in the outbreak.
Antibiotics A, B, C, D and E were used in the investigation.
The figure below shows the results.
Describe two aseptic techniques the scientists should have used in the investigation.
Disinfect their hands and sterilise the petri dish before use.