lab final anatomy 2
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
270 Terms
teeth description
hard calcified structures in the sockets of the mandible and maxilla
teeth function
mastication
teeth location
in the mandible (lower jaw) and maxilla (upper jaw)
gingiva description
soft tissue surrounding the teeth acting like a tight collar around each tooth
gingiva function
protecting the teeth and underlying bone & forms a barrier against bacteria and maintains health of periodontal ligament
gingiva alt name
gums
gingiva location
around the neck of the tooth
crown description
visible part of a tooth above the gum line. Covered by enamel
crown function
protection and chewing
crown alternative name
corona
crown location
above the gum
enamel description
outermost layering covering the crown of the tooth. Hardest substance in the human body
enamel function
protection, force resistance, non-regenerative
enamel location
outer tooth
root description
portion embedded in the jawbone. Covered by cement attaching the tooth to the periodontal ligament
root function
anchoring and nutrient supply
root location
below the gums surrounded by bone
dentin description
protein-rich, bone-like material forming bulk of the tooth. Characterized by unique radial striations aka dentinal tubules
dentin function
shock absorber during biting and chewing. Supplies nutrients and provides sensation to the tooth.
dentin location
beneath enamel cap
cement description
calcified connective tissue covering outer surface of the tooth's root. Similar to bone but lacks blood vessels
cement function
attach tooth to periodontal ligament. Stabilizing tooth curing chewing
cement location
on the root of the tooth, beneath the gum line
mouth location
initial part of the digestive system bounded by lips and cheeks
mouth subdivisions
oral vestibule and oral cavity proper
oral vestibule
space between lips/cheeks and teeth/gums
oral cavity proper
area within the teeth and gums
pharynx location
funnel-shaped muscular tube connecting nasal cavity and mouth to larynx and esophagus
pharynx subdivisions
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
nasopharynx
posterior to nasal cavity above the soft palate
oropharynx
posterior to oral cavity, extending from soft palate to esophagus
laryngopharynx
posterior to the larynx, extending from the epiglottis to the esophagus
esophagus location
begins at laryngopharynx and extends to stomach, passing through diaphragm
esophagus subdivisions
upper third, middle third, lower third
stomach location
upper left quadrant of peritoneal cavity, mostly hidden by liver and diaphragm
stomach subdivisions
cardia, fundus, body, pyloric part
cardia
entry point for food from the esophagus
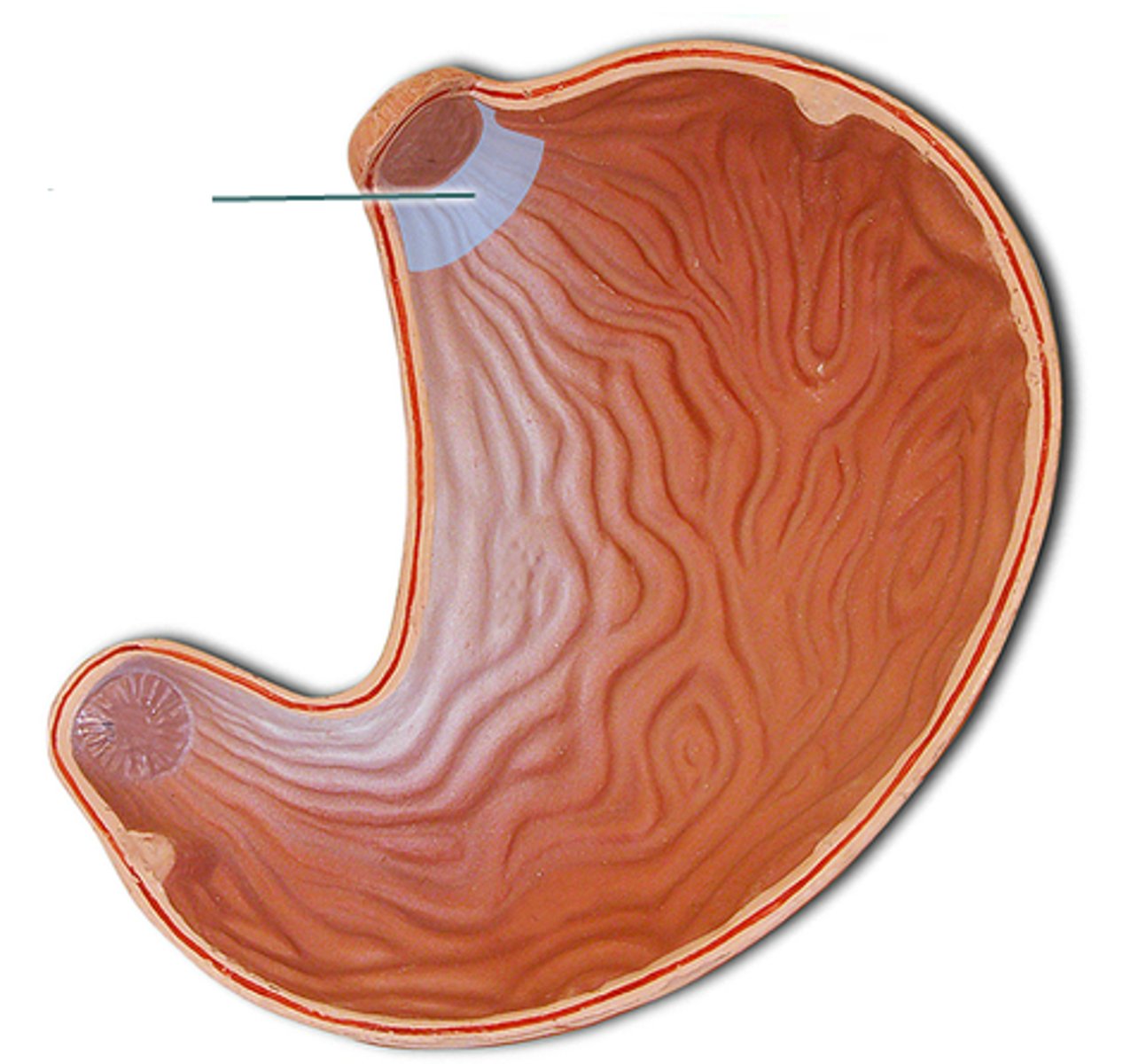
fundus
dome-shaped top part beneath the diaphragm
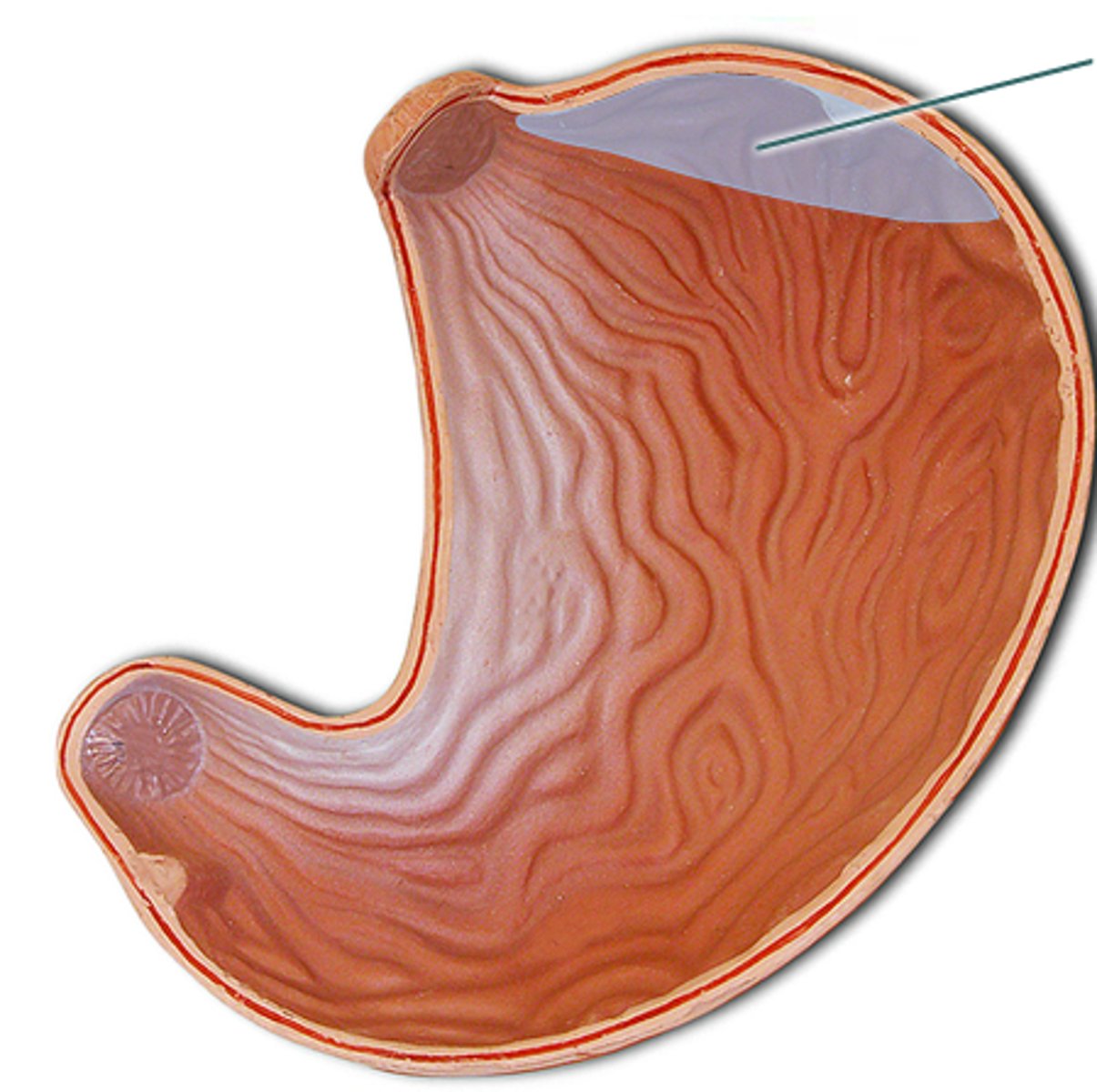
body of the stomach
main central region
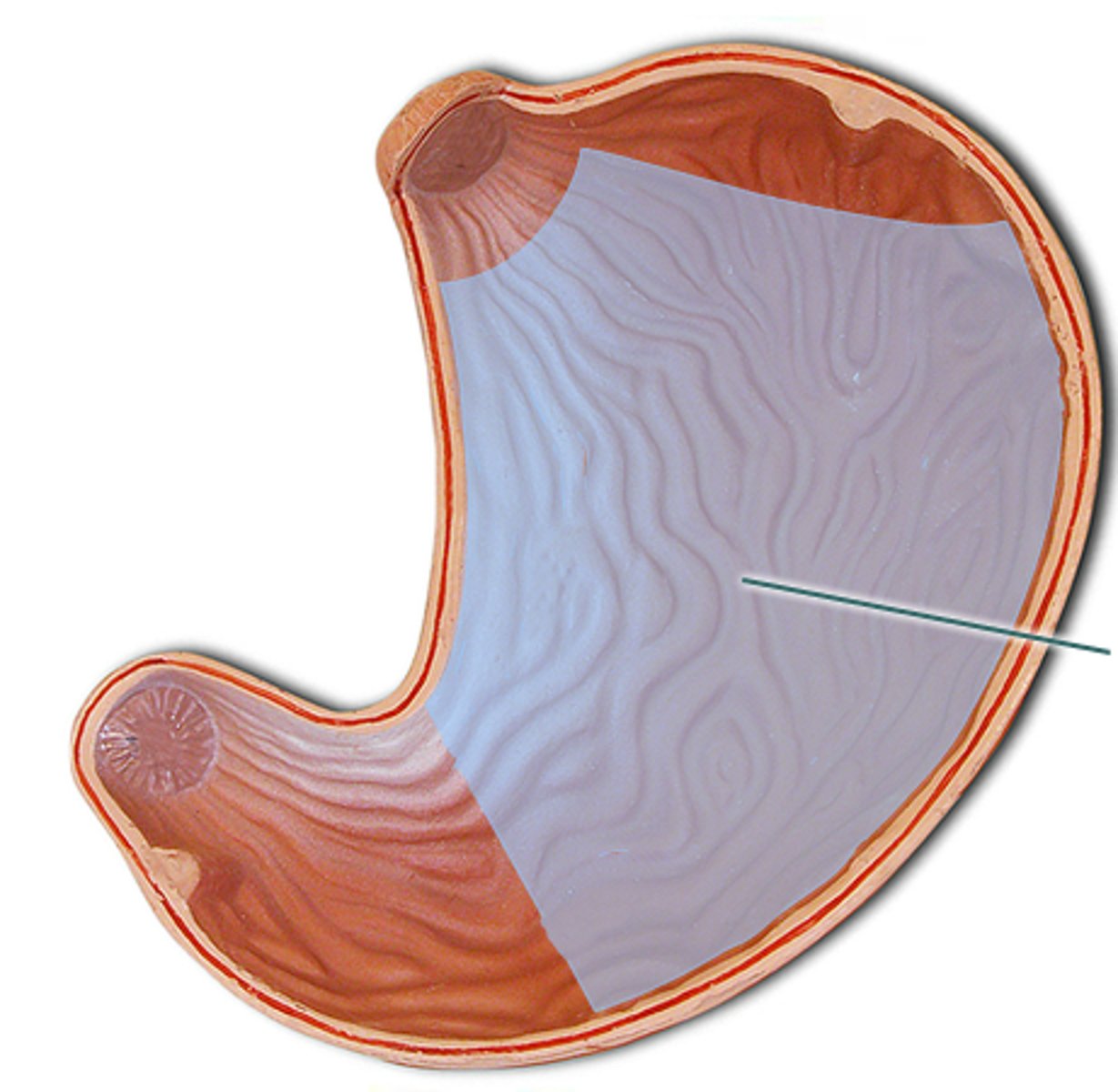
pyloric part
includes pyloric antrum, canal, and ends at pylorus
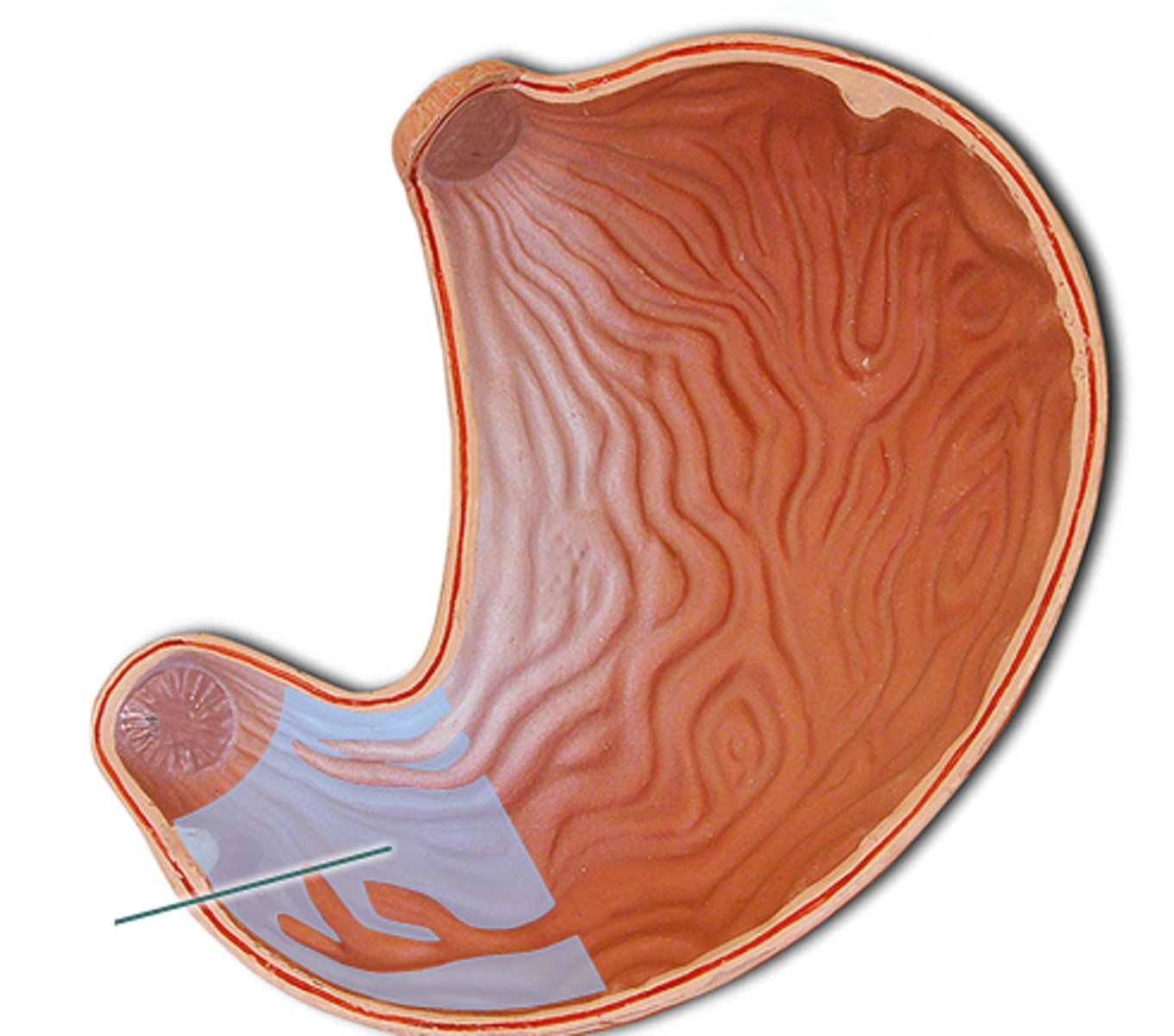
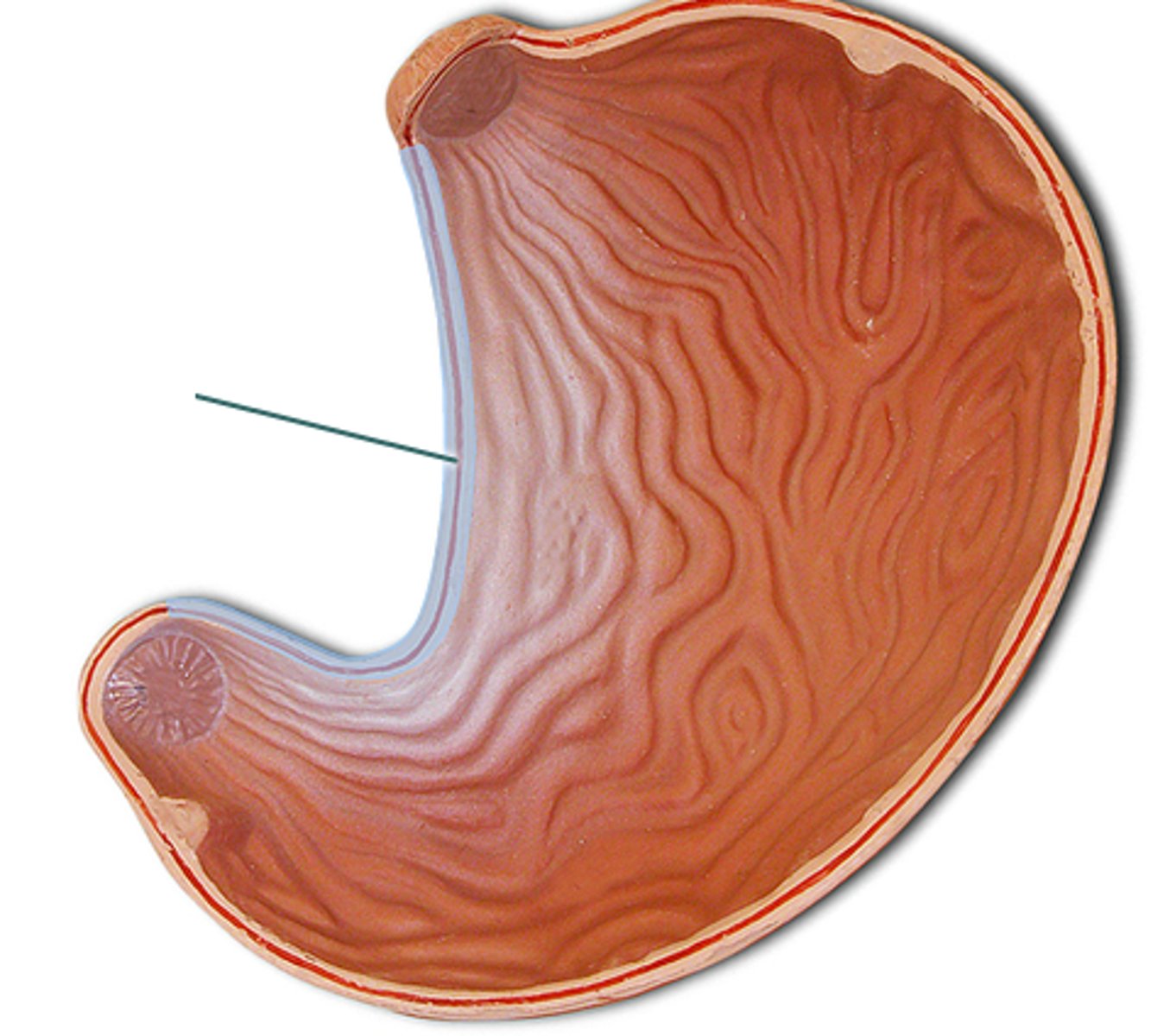
stomach gross anatomy
has backwards c shape with two curvatures: greater and lesser
greater curvature
larger curve on the right
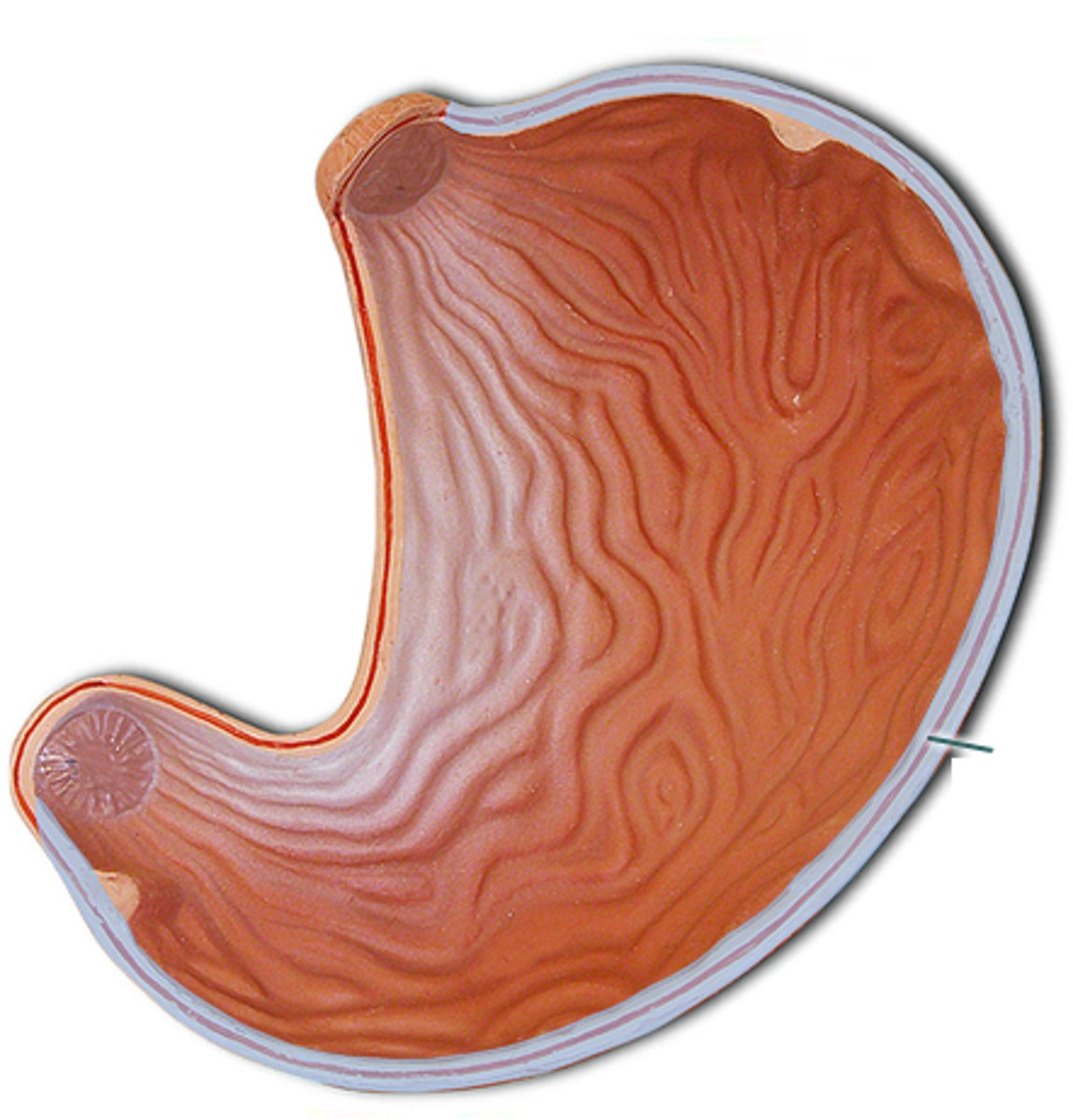
lesser curvature
smaller curve on the left
small intestine location
extending from pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the ileocecal valve, which meets the large intestine
small intestine subdivision
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
duodenum
shortest section, curves around pancreas and is mostly retroperitoneal
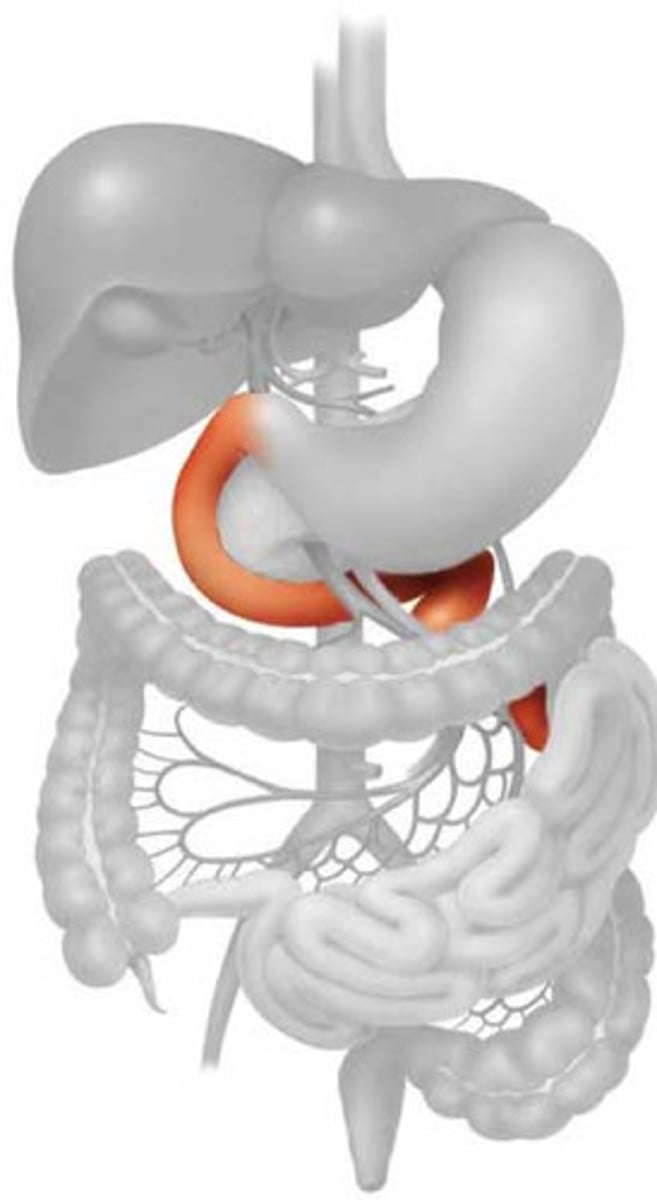
jejunum
extends from duodenum to the ileum
ileum
longest section, ends at the ileocecal valve
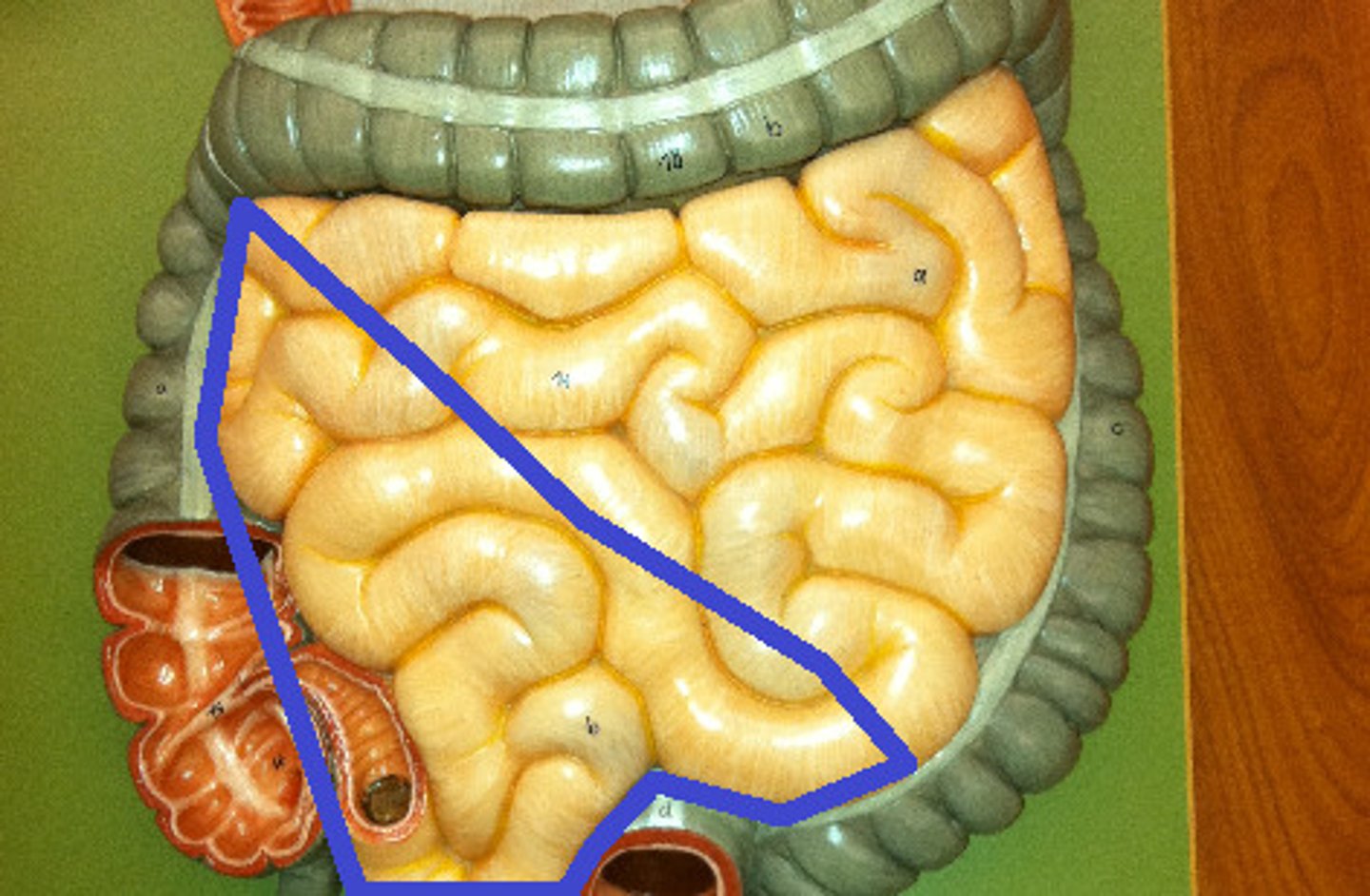
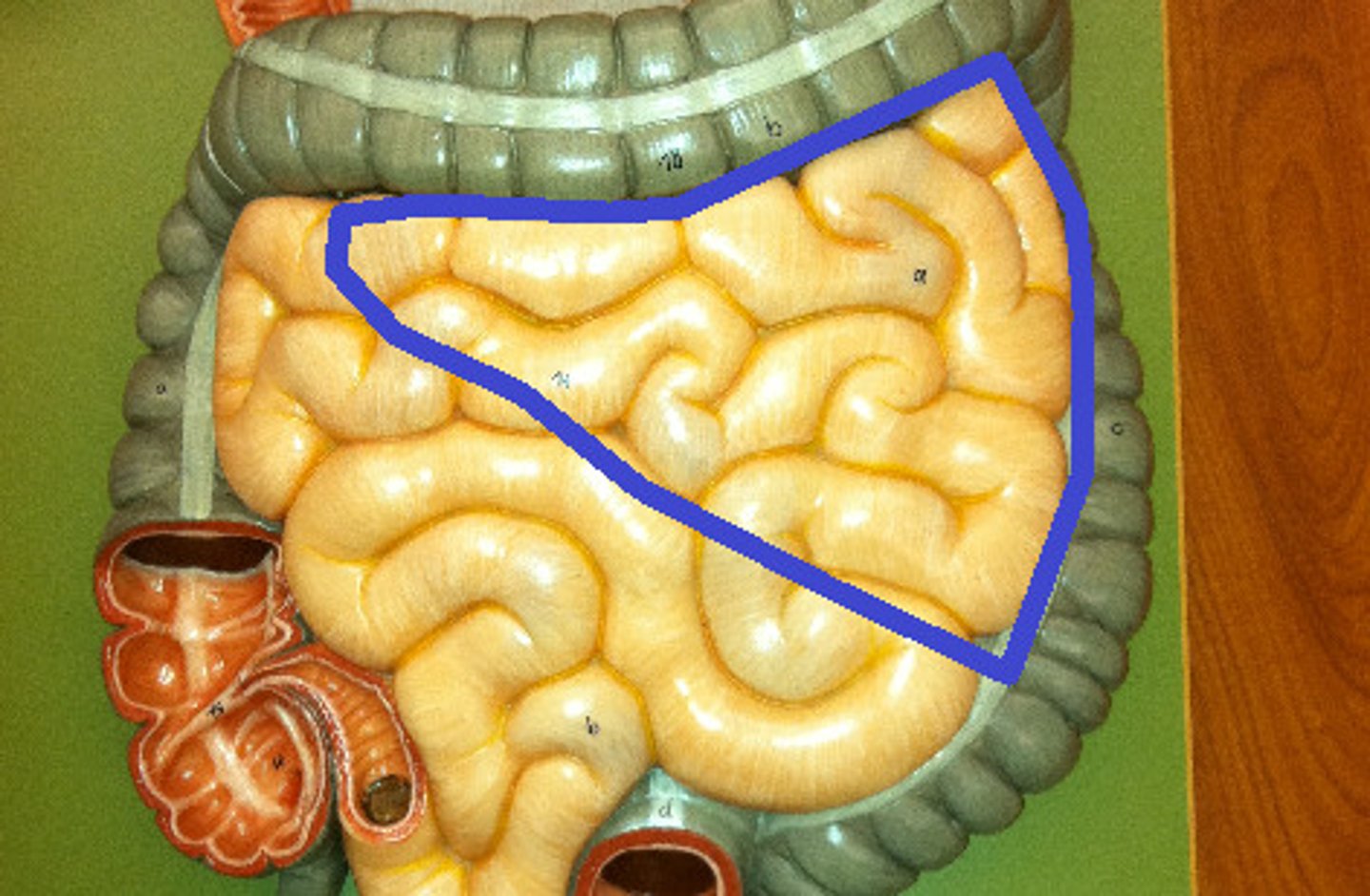
large intestine location
in abdominal cavity encircling the small intestine. Begins at ileocecal valve and extends to the anus
large intestine subdivisions
cecum, colon, rectum, anal canal
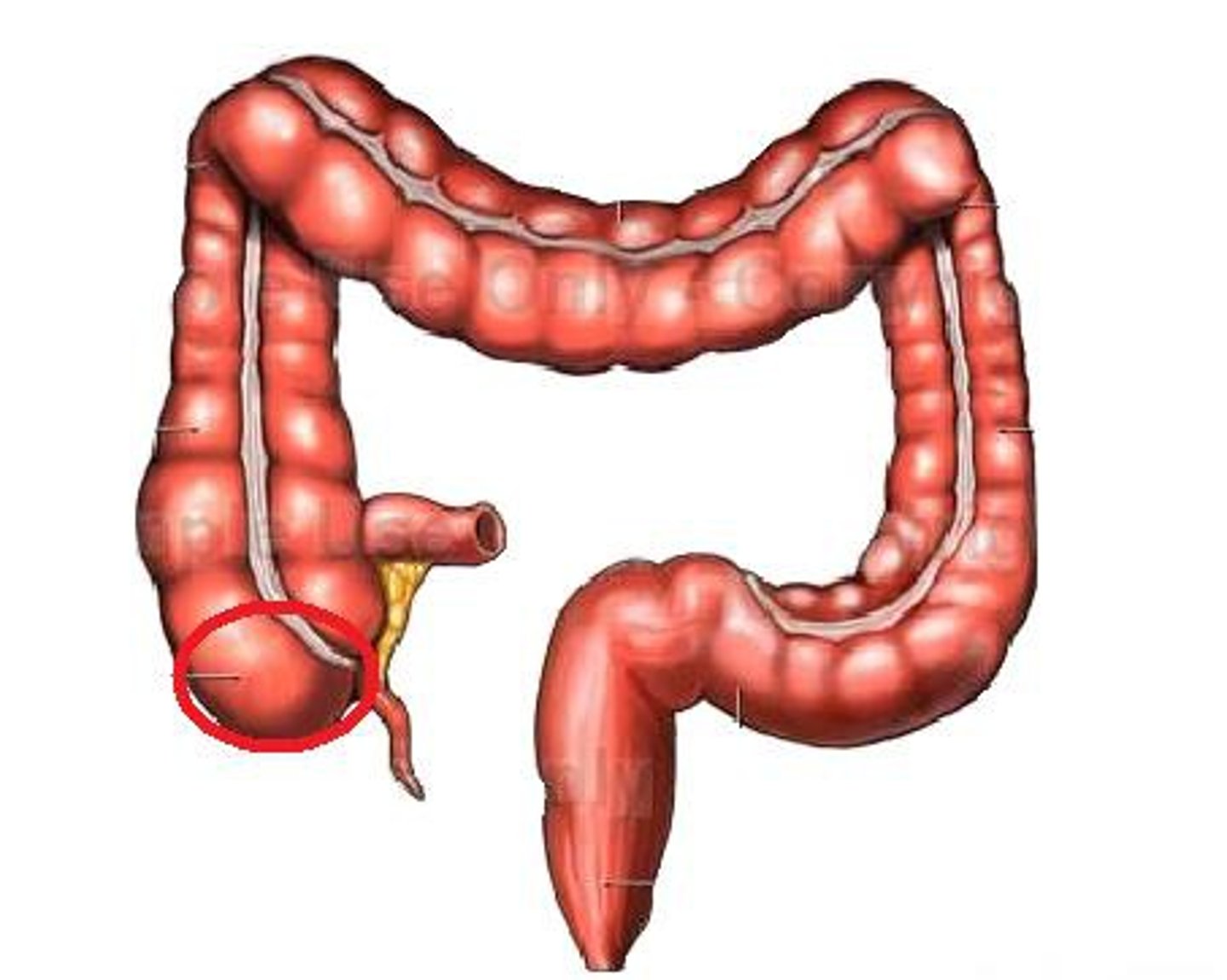
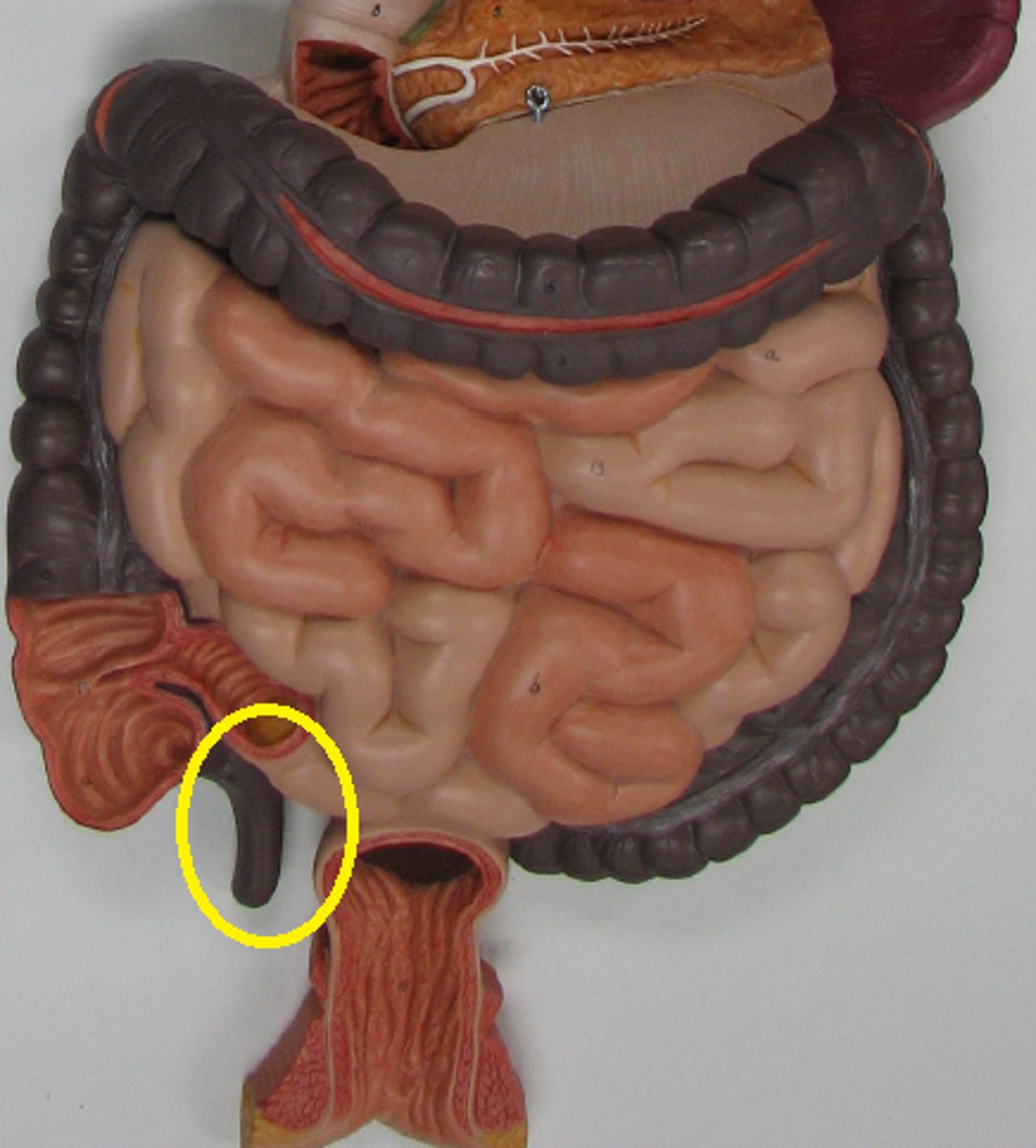
cecum
first part, below the ileocecal valve (includes the appendix)
colon
divided into ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid sections
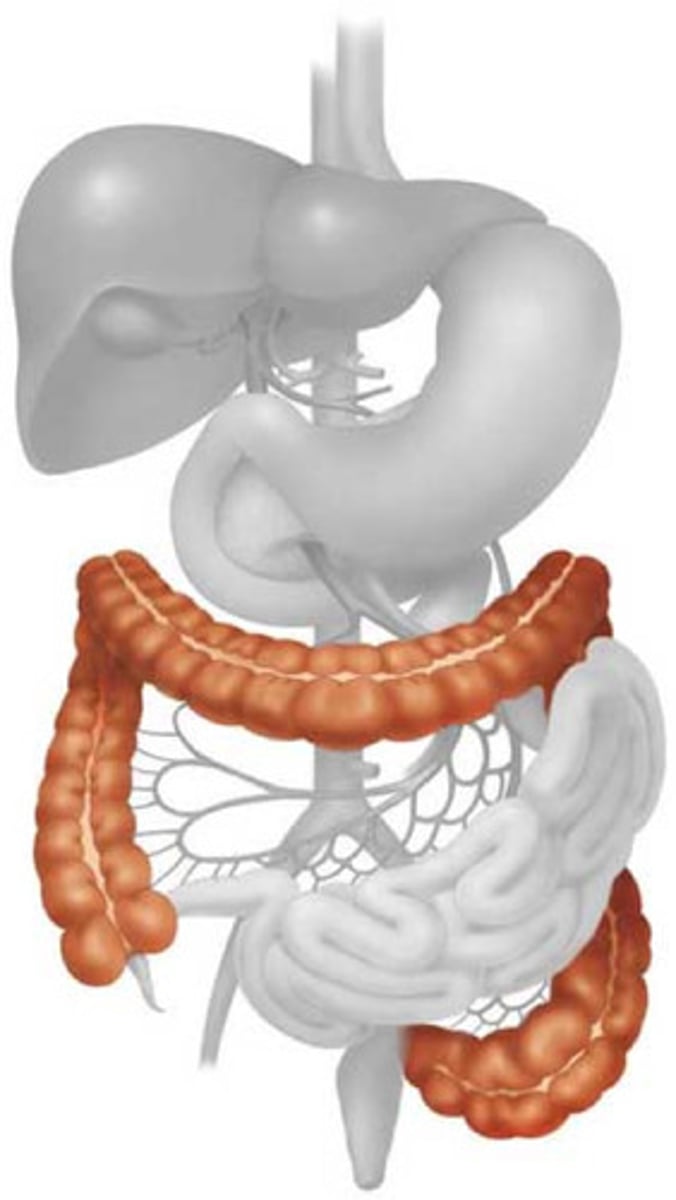
rectum
leads into anal canal
anal canal
ends at the anus
anus location
At end of digestive tract and opening through which feces are expelled from the body
anus subdivision
levator ani muscle
pharyngeal constrictor muscle location
pharynx
lower esophageal sphincter location
between esophagus and stomach
upper esophageal sphincter location
top of esophagus
pyloric sphincter location
between stomach and duodenum
ileocecal valve location
from ileum to large intestine
external anal sphincter location
encircles anus
internal anal sphincter location
inside of anus
external urethral sphincter
males : between prostate and penis. females : near vaginal opening
anorectal sphincter location
around the anus
liver function
processing nutrient-rich blood, detoxifying chemicals, metabolizing drugs, producing bile (aid in digestion), storing vitamins/minerals, and converting ammonia to urea
liver location
right hypochondriac and epigastric regions, under the diaphragm, mostly under the rib cage
liver associated ducts
right and left hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct, cystic duct
right and left hepatic ducts
drains bile from liver lobes
common hepatic duct
carries bile towards duodenum
cystic duct
connects gallbladder to common hepatic duct, forming bile duct
falciform ligament structure
separates liver's right and left lobes, suspends liver from diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall
round ligament structure
fibrous remnant of fetal umbilical vein, running along inferior edge of falciform ligament. Aka ligamentum teres
porta hepatis structure
gateway to the liver allowing passage of blood and bile
gallbladder function
stores and concentrates bile. Releases bile into digestive tract when needed, particularly after eating fatty foods
gallbladder location
beneath right lobe of the liver
gallbladder associated ducts
cystic duct, bile duct, hepatopancreatic ampulla
bile duct
formed by union of cystic duct and common hepatic duct from the liver, leading to hepatopancreatic ampulla
hepatopancreatic ampulla
where the bile duct and pancreatic duct unite, allowing bile and pancreatic juices to enter the duodenum
pancreas exocrine function
produces pancreatic juice containing enzymes that breakdown proteins, fats, and carbs
pancreas endocrine function
releases hormones like insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose levels
pancreas location
soft tadpole-shaped gland located in the abdomen, lying deep to the greater curvature of the stomach
pancreas associated ducts
main pancreatic duct, accessory pancreatic duct, hepatopancreatic ampulla
main pancreatic duct
carries pancreatic juice from pancreas to the duodenum
accessory pancreatic duct
empties directly into the duodenum
carb absorbable unit
monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose)
protein absorbable unit
amino acids and small peptides
lipids absorbable unit
fatty acids and monoglycerides. reassembled into triglycerides
cellular respiration pathways
1. glycolysis
2. citric acid cycle (krebs)
3. oxidative phosphorylation
glycolysis cell location
cytosol
citric acid cycle cell location
mitochondrial matrix
oxidative phosphorylation cell location
inner mitochondrial matrix
carb reactions
glycolysis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis
glycolysis
converts glucose into pyruvic acid
glycogenesis
polymerizes glucose to form glycogen
glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen back into glucose monomers
gluconeogenesis
forms glucose from non-carb precursors
lipid reactions
beta oxidation, lipolysis, lipogenesis
beta oxidation
converts fatty acids into acetyl CoA
lipolysis
break down lipids to fatty acids and glycerol