TryHackMe Glossary
1/307
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
308 Terms
AWS - Amazon Web Services
Comprehensive cloud computing platform offered by Amazon. It provides a wide range of services such as computing power, storage, databases, networking, analytics, and more, delivered over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.,
AppLocker
Windows feature that allows administrators to control which applications and scripts users are allowed to run on a system.,
Apache
The most widely used web server software. Developed and maintained by Apache Software Foundation, it is an open source software available for free
ARP - Address Resolution Protocol
Is responsible for finding the MAC (hardware) address related to a specific IP address. It works by broadcasting an query, "Who has this IP address? Tell me." And the response is of the form, "The IP address is at this MAC address."
ACL - An Access Control List
Is a list of permissions that determine who can access a specific resource in a computer network. It is used to grant or deny access to files, folders, printers, and other network resources.,
AV
Antivirus software is a program or set of programs that are designed to prevent, search for, detect, and remove software viruses, and other malicious software like worms, trojans, adware, and more.,
AES - The Advanced Encryption Standard
Is a symmetric block encryption algorithm. It can use cryptographic keys of sizes 128, 192, and 256 bits.
ASM
A low-level programming language that uses symbolic code as a direct representation of machine code. It enables a programmer to write instructions that the computer's processor can execute directly. Each line corresponds to a specific machine operation, often based on a sequence of numbers, letters, and symbols
API - Application Programming Interface
Is a set of rules and protocols for building software and applications. An API allows different software programs to communicate with each other. It defines methods of communication between various components, including the kinds of requests that can be made, how they're made, the data formats that should be used, and conventions to follow.
AMSI - Antimalware Scan Interface
It is a standardized Windows interface enabling Windows applications to seamlessly communicate with any existing antimalware solutions present on the system. ATT&CK The Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge or MITRE ATT&CK is a guideline for classifying and describing cyberattacks and intrusions.,
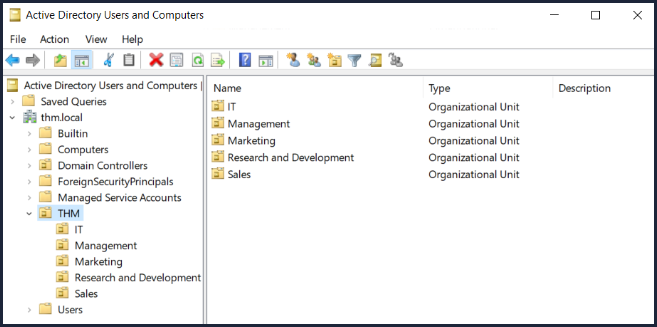
AD - Active Directory
Is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It stores information about network objects such as computers, users, and groups. It provides authentication and authorisation services, and allows administrators to manage network resources centrally.,
APT - An advanced persistent threat
Is a stealthy threat actor, typically a nation state or state-sponsored group, which gains unauthorized access to a computer network and remains undetected for an extended period.,
ACAO - Access-Control-Allow-Origin
It is a header included in the response from one website to a request originating from another website, and identifies the permitted origin of the request. A web browser compares the Access-Control-Allow-Origin with the requesting website's origin and permits access to the response if they match.,
AKS - Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Is a managed Kubernetes service from the Azure Cloud Service Provider.,
AES-GCM
AES-GCM (Advanced Encryption Standard - Galois/Counter Mode) is an authenticated encryption algorithm that combines the AES encryption with the GCM mode of operation. It provides both confidentiality (encryption) and integrity (authentication) by generating an authentication tag to verify the authenticity of the encrypted data,
AES-CCM
AES-CCM (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter with CBC-MAC) is an authenticated encryption mode that combines AES encryption with the Counter (CTR) mode for confidentiality and the CBC-MAC (Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code) for integrity. It ensures both data encryption and authentication, protecting against tampering and providing data authenticity.,
AI
Artificial Intelligence is technology that enables computers and machines to simulate human behaviour, like learning and reasoning.,
BSIMM
Building Security In Maturity Model (BSIMM) is a study of real-world software security initiatives and reflects the current state of software security.,
BPF
The Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF) is a technology used in certain computer operating systems for programs that need to, among other things, analyze network traffic. BPF supports filtering packets, allowing a userspace process to supply a filter program that specifies which packets it wants to receive.,
Blue Team
A blue team comprises cyber security and technology professionals whose aim is to protect an information system from impending cyber threats by performing and implementing defensive actions.,
BYOD
Bring Your Own Device is the term given for devices that are owned by an employee but are usually used for work-related activities. For example, an employee uses their personal device to access emails. A BYOD policy outlines what type of devices are acceptable, what behaviour is acceptable, as well as any necessary steps to secure the device (for example, requiring anti-virus),
BIOS
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is a boot firmware that provides runtime services for the operating system (OS). The BIOS starts, checks specific hardware components, and loads the OS depending on boot priority.,
BOF
Beacon Object Files (BOF) is a set of compiled code written in a C-language that interacts with the Windows API to enable additional functionality within a C2 agent.,
Burp Suite
Burp Suite is an integrated platform for performing security testing of web applications. It includes various tools for scanning, fuzzing, intercepting, and analysing web traffic. It is used by security professionals worldwide to find and exploit vulnerabilities in web applications.,
Boot Sector
First sector of a disk partition that contains the BIOS Parameter Block, bootstrap code, and volume metadata.,
CVE
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), this term is given to a publicly disclosed vulnerability,
CMS
Content Management System (CMS). These web applications are used to manage content on a website. For example, blogs, news sites, e-commerce sites and more!,
CIA
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) is the opposite of Disclosure, Alternation, and Destruction (DAD).,
CVSS
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard for assessing the severity of computer system security vulnerabilities. It provides a numerical score indicating the severity and characteristics of a vulnerability, allowing organizations to prioritize and manage their vulnerability management processes. CVSS scores range from 0 to 10, with 10 being the most severe. It considers metrics such as attack vector, attack complexity, privileges required, and user interaction to determine the final score.
CTI
Cyber Threat Intelligence is evidence-based knowledge about adversaries, including their indicators, tactics, motivations, and actionable advice against them.,
CI
Continuous Integration is a software development practice that involves automatically building, testing and implementing changes to an application's source code,
CSF
Cyber Security Framework (CSF) is a set of guidelines and measures for organisations to manage and improve their cybersecurity posture by identifying, assessing, and managing their cybersecurity risks. command-line application Command-line applications are computer programs designed to be used from a text interface; think of it as if you're using an application without a user interface.,
Chewba-QA
A hairy, bear-like creature that performs Quality Analysis in DevOps,
CD
Continuous Deployment is a software development term for deploying code to production environments automatically without any interaction from a human. For example, the automation of tests and then deployment of the code.,
CI/CD
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery. They are a set of practices and principles that enable automated software releases.,
C2
Command and Control (C2) Infrastructure are a set of programs used to communicate with a victim machine. This is comparable to a reverse shell, but is generally more advanced and often communicate via common network protocols, like HTTP, HTTPS and DNS.,
Command Injection
Command Injection is a vulnerability that occurs when an attacker manipulates input fields to inject malicious commands into a vulnerable application. This can lead to unauthorised execution of arbitrary commands on the targeted server, potentially resulting in data breaches, system compromise, or unintended operations.,
CSRF
Cross-site request forgery (also known as CSRF) is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to induce users to perform actions that they do not intend to perform. It allows an attacker to partly circumvent the same origin policy, which is designed to prevent different websites from interfering with each other.,
CPU
A central processing unit (CPU)—also called a central processor or main processor—is the most important processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry,[1] and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs).,
CTO
Chief Technology Officer is the person that is responsible for an organisations technology. Working together with the CIO, they run a company's IT infrastructure.,
CNN
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are incredible ML structures that have the ability to extract features that can be used to train a neural network. In essence, CNNs are normal neural networks that simply have the feature-extraction process as part of the network itself.,
CLI
CLI, or Command Line Interface, is a text-based interface used to interact with a computer operating system or software by typing commands. Unlike graphical user interfaces (GUIs), CLIs rely on input commands and display text output, offering a precise and efficient way to perform tasks, automate processes, and manage system resources.
Container
Containers are packages of software that bundles up code, and all its dependencies so it can be run reliably in any environment.,
CORS
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a mechanism for integrating applications. CORS defines a way for client web applications that are loaded in one domain to interact with resources in a different domain.,
CSP
A Cloud Service Provider is a company which offers scalable cloud computing resources on demand. The cloud resources CSPs offer include computing power, data storage and applications.,
CIS
CIS (Centre for Internet Security) is a non-profit organisation that helps collect and define standards that can be implemented as preventative measures against cyber attacks,
Cluster Hardening
The process of securing a Kubernetes cluster following best security practices.,
CA
A CA, or Certificate Authority, is a trusted organisation that verifies the digital identity of entities like websites, individuals, or companies by issuing digital certificates.,
Cronjob
A scheduled task defined on a Linux system to execute automatically based on predefined parameters such as time intervals or user actions.,
Chain of custody
Process of documenting the complete journey of evidence during a legal case lifetime, from the collection to final presentation in court.,
DAD
Disclosure, Alternation, and Destruction (DAD) is the opposite of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA).,
DPI
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is an advanced method of examining and managing network traffic. Unlike traditional packet filtering that only inspects packet headers (like IP addresses and port numbers), DPI delves into the data payload of a packet. This allows it to identify, categorize, and control specific applications, services, or protocols, as well as detect malicious content such as viruses, spam, or intrusions. DPI is used for various purposes including network security, policy enforcement, traffic shaping, and data loss prevention.
DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is the protocol responsible for resolving hostnames, such as tryhackme.com, to their respective IP addresses.,
DES
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric encryption block encryption algorithm which uses a cryptographic key size of 56 bits. AES became the new standard in 2001.,
DAST
Dynamic Application Security Testing scans running aplications for vulnerabilities
DOS
A computer operating system that provides a file system for operations such as reading, writing, and erasing data on a disk. It is a non-graphical line-oriented command-driven computer operating system designed for the IBM PC. Several variations of DOS were developed, such as MS-DOS (Microsoft) and PC-DOS (IBM).,
DFIR
Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR) is a comprehensive discipline combining two critical areas of cybersecurity:
Digital Forensics: This involves the scientific collection, preservation, analysis, and presentation of digital evidence from various sources (e.g., computers, mobile devices, networks) to uncover the cause, scope, and impact of a security incident or cybercrime. Its goal is to reconstruct events, identify perpetrators, and support legal proceedings.
Incident Response: This is a structured approach to managing and addressing the aftermath of a security breach or cyberattack. It typically follows a lifecycle that includes:
Preparation: Establishing policies, teams, and tools.
Identification: Detecting and assessing the incident.
Containment: Limiting the damage and preventing further spread.
Eradication: Removing the root cause of the incident.
Recovery: Restoring affected systems and services to normal operation.
Post-Incident Activity: Learning from the incident and improving defenses.
DFIR teams work to minimize damage, restore operations, and gather actionable intelligence from cyber incidents.
DMARC
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance, or DMARC, is a technical standard that helps protect email senders and recipients from spam, spoofing, and phishing.,
DAQ
Data Acquisition library, for packet I/O. The DAQ replaces direct calls to libpcap functions with an abstraction layer that facilitates operation on a variety of hardware and software interfaces without requiring changes to Snort.,
DACL
Discretionary Access Control Lists are used by Windows systems to specify who can access a given resource. While they are often referenced when talking about files, they also apply to other components as registry keys, services and scheduled tasks.,
DMZ
A DMZ or demilitarized zone is a perimeter network that protects and adds an extra layer of security to an organization’s internal local-area network from untrusted traffic. The end goal of a demilitarized zone network is to allow an organization to access untrusted networks, such as the internet, while ensuring its private network or LAN remains secure,
DevOps
DevOps is a set of practices, tools, and a cultural philosophy that automate and integrate the processes to build software.,
DKIM
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email security standard designed to make sure messages aren't altered in transit between the sending and recipient servers.,
DLL
A DLL file, short for Dynamic Link Library, is a library that contains code and data that can be used by more than one program at the same time. For example, in Windows operating systems, the Comdlg32 DLL performs common dialog box related functions. Each program can use the functionality that is contained in this DLL to implement an Open dialog box. It helps promote code reuse and efficient memory usage.,
DLP
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software detects potential data breaches/data ex-filtration transmissions and prevents them by monitoring,[1] detecting and blocking sensitive data while in use (endpoint actions), in motion (network traffic), and at rest (data storage).,
Dynamic Analysis
The process of analyzing malware by running it in a controlled environment like a sandbox.,
DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.,
DREAD
DREAD is a system used by Microsoft to assess risk to computer security threats. It is an acronym that stands for the following five categories:
Damage: How much damage can be caused if the vulnerability is exploited?
Reproducibility: How easy is it to reproduce the attack?
Exploitability: How easy is it to exploit the vulnerability?
Affected Users: How many users will be affected by the vulnerability?
Discoverability: How easy is it for an attacker to discover the vulnerability?
DoS
Denial of Service (DoS) is an attack on the target's availability to make the target service/system unavailable to legitimate users.,
DDoS
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks the target's availability. It is "distributed" because it is launched from many sources, usually a botnet.,
DC
A domain controller is a server that manages security authentication requests in a Windows Server network. It stores user account information and controls access to resources on the network. It is a critical component for managing and securing a network infrastructure.,
DirBuster
DirBuster is a free and open-source web application security scanner. It can be used to find hidden directories and files on web servers. It can use various techniques to brute-force directories and files, including dictionary attacks, brute-force attacks, and hybrid attacks.,
DevSecOps
Fosters the same culture and principles as Devops with the addition of security into the development process, ensuring security is integrated from an early stage.,
DAIR
Dynamic Approach to Incident Response is a framework used to handle the Incident Response process. It is mapped on the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle,
EDR
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) is a series of tools that monitor devices for activity that could indicate a threat.,
EVTX
An EVTX file is a Windows XML event log file. It is a file format used to store event logs generated by the Windows Event Logging system.,
EPP
An endpoint protection platform (EPP) is a solution deployed on endpoint devices to prevent file-based malware attacks, detect malicious activity, and provide the investigation and remediation capabilities needed to respond to dynamic security incidents and alerts.,
EC2
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows you to rent virtual PCs on the cloud. The machines can be used just as any regular PC, and their specs can be dimensioned according to your specific needs. entropy The measure of randomness of data in a file is known as entropy. Entropy is very useful in identifying compressed and packed malware. Packed or compressed files usually have a high entropy.,
Elastic SIEM
Elastic SIEM is a security information and event management (SIEM) platform that helps organisations collect, analyse, and respond to security threats. It can collect data from various sources, including logs, events, network traffic, and cloud metadata. It can use machine learning to identify and prioritise threats. It can automate response actions, such as blocking malicious traffic or isolating infected hosts.,
ELK
ELK stands for Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. These are three open-source tools that are commonly used together to collect, store, analyse, and visualise data.,
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a distributed, scalable, and highly available search engine. It is used to store and index data so that it can be quickly searched and analysed.,
ESI
Electronically Stored Information (ESI) is a broad concept that includes public or private information stored in an electronic or digital medium, such as data available from computers (including email), CD-ROM discs, DVDs, Internet, cloud storage, personal digital assistants (PDAs), smart phones, tablets, GPS systems, satellites, and drones. ESI includes writings, drawings, graphs, charts, photographs, sound recordings, images, video recordings, data compilations, computer-aided design files such as blueprints or maps, metadata, equipment/process control and data logging system files, and any other data that is stored electronically.,
EKS
Elastic Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a managed Kubernetes service from the Amazon Web Services Cloud Service Provider.,
EXIF
Images store metadata (date and time, camera settings, GPS coordinates, etc.) within them. This metadata of image files is stored in a standardized format known as Exchangeable Image File Format (EXIF).,
ECC
ECC is a way to encrypt data using smaller keys while still providing strong security. It is based on the math of elliptic curves.,
EXT
The EXT file system (Extended File System) is a family of journaling file systems used in Linux, designed for efficient data storage and retrieval. It includes multiple versions—EXT, EXT2, EXT3, and EXT4—each improving performance, reliability, and features like journaling and extended attributes.,
FISMA
FISMA is an acronym that stands for the Federal Information Security Modernization Act. FISMA is United States legislation that defines a comprehensive framework to protect government information, operations and assets against natural or man-made threats. FISMA was signed into law part of the Electronic Government Act of 2002.,
Firewall
A security tool, hardware or software that is used to filter network traffic by stopping unauthorized incoming and outgoing traffic.,
FTP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a protocol designed to help the efficient transfer of files between different and even non-compatible systems. It supports two modes for file transfer: binary and ASCII (text).,
File system
The on-disk data structures and logic an OS uses to organise, name, store and retrieve files (e.g. FAT32, NTFS, ext4).,
File Carving
The process of reconstructing files directly from raw data using the file headers/footers.,
File header
A unique sequence of binary at the start of a file identifying its format ,
FGSM
Fast Gradient Sign Method is a white-box adversarial attack that perturbs data classification in AI models.,
GUI
The graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicators such as primary notation, instead of text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs),which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.,
Gobuster
Gobuster is a free and open-source directory and file enumeration tool. Penetration testers and security professionals use it to find hidden directories and files on web servers.,
Git
Git is a distributed version control system used for tracking changes in files and coordinating work among multiple contributors. It provides efficient branching, merging, and collaboration capabilities for software development projects.,
GPG
GPG stands for GNU Privacy Guard. It is a free and open-source encryption software that uses public-key cryptography. GPG can be used to encrypt files and messages, and to sign files and messages. Encryption makes it so that only the intended recipient can decrypt the file or message while signing makes it so that the recipient can verify that the file or message was sent by the person it claims to be from.,
Ghidra
A software reverse engineering framework developed by the National Security Agency (NSA) in the United States. Comprising of a suite of software analysis tools. Ghidra disassembles executables into code that humans can understand.,
GPO
Group Policy Object (GPO) is a feature in Windows Server that allows administrators to control user and computer settings across the network. It provides a centralised way to manage and configure operating systems, applications, and user settings.,
GRUB
GRUB stands for Grand Unified Bootloader. It is available from the GNU project and is a common bootloader shipped with many Linux distributions.,