Radiographic Procedures 2 (215) Exam 3 Questions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
2.5 mm aluminum
The required minimumtotal filtration for an x-ray unit that is being used about the 70 kVp range is:
a.) 0.5 mm aluminum equivalent
b.) 1.5 mm aluminum equivalent
c.) 2.0 mm aluminum equivalent
d.) 2.5 mm aluminum equivalent
Radiopaque
A substance, pathology, or contrast agent that incresed the attenuation of the primary beam would be considered:
a.) destructive
b.) radiopaque
c.) filtration
d.) radiolucent
Single phase
The type of generator that has 100% ripple is the:
a.) half wave
b.) high frequency
c.) single phase
d.) 3 phase
a, c, & d
Which of the following are true of negative contrast agents?
a.) they cause the anatomy to become more radiolucent
b.) they cause the anatomy to become more radiopaque
c.) their use results in more exposure to the IR, if technical factors are not adjusted
d.) air and carbon dioxide are the most common types
e.) a & c
f.) b & c
g.) a, c, & d
Inherent filtration
The mirror in the collimator box, the dielectric oil, and the beryllium window are all examples of:
a.) rectification
b.) inherent filtration
c.) compensating filtration
d.) added filtration
Increase
Does severe ascites require an increase or decrease in kVp?
Decrease
Does advanced COPD require an increase or decrease in kVp?
Increase
Does acromegaly require an increase or decrease in kVp?
Decrease
Does osteoporosis require an increase or decrease in kVp?
Air/gas, fat, fluid, bone, metal
List the 5 general types of materials found in the body in order from least dense to most dense.
Close collimation down to the size of the anatomy of interest so less soft tissue is seen in the image
Given the image of the large patient chest x-ray shown in the Field Size Limitation presentation, what would have been the best way to improve the image quality on a repeat?
35%, 5%
The minimum amount of adjustment to exposure technique should be no less than a ___% change in mAs, or a ___% change in kVp.
Beam hardening
When low energy photons are filtered from the primary beam, the result is a higher average photon energy in the beam. This is known as:
a.) beam softening
b.) remnant radiation
c.) beam hardening
d.) half value layer
Half value layer, mm AL equivalent
The beam penetrability is measured by determining the ____. The enit of measurement is ____.
a.) half value layer, mm AL equivalent
b.) rectification, half value layer
c.) kV, lp/mm
d.) mm AL equivalent, lp/mm
Compensating filters can be used on feet or shoulders
What are two body parts or situations that might benefit from the use of a Ferlic or other type of compensating filter?
Excessively wide collimation
Lower signal to noise ration would likely be a result of:
a.) too little filtration
b.) excessively wide collimation
c.) high frequency x-ray generatory
d.) all of the above
Osteoblastic, increase
____ pathologies result in abnormally increased bone formation, and requires a(n) _____ in exposure technique.
a.) osteolytic, decrease
b.) osteolytic, increase
c.) osteoblastic, decrease
d.) osteoblastic, increase
Destructive, additive
Active osteomyelitis is considered a(n) _____ pathological condition, whereas chronic osteomyelitis is considered a(n) ____ condition.
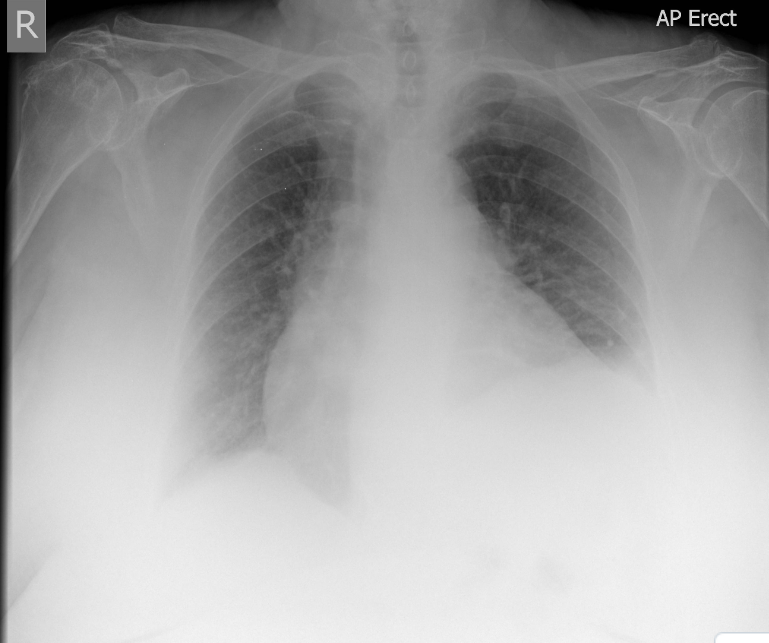
Collimate, increase kVp
Given the image, a technologist could ____ and ____ on a repeat radiograph. This would result in lower patient dose and better penetration of the hilar region.
True
TRUE or FALSE: off-focus radiation constitutes as much as 25% of the primary beam, and could be considered a source of image noise.
The collimation automatically limits the radiation field to the size of the cassette
Positive beam limitation (PBL) is when:
a.) the collimation automatically limits the radiation field to the size of the cassette
b.) the tech collimate more tightly to the patient
c.) the tech properly collimates to the patient
d.) collimation is opened wide to compensate for patient motion
True
TRUE or FALSE: Changing technique at a level that is below the minimum change necessary to produce a noticeable result, just serves to increase unnecessary patient dose.
Use the small body habitus button (which will turn lower kVp and reduce the ± density setting for the AEC system)
When performing a chest x-ray on a petite elderly woman with osteoporosis and advanced emphysema, it would make sense to:
a.) raise kVp
b.) use the widest collimation possible
c.) use the small body habitus button (which will turn lower kVp and reduce the ± density setting for the AEC system)
d.) use more filtration
Hypersthenic
Of the following, which body habitus might require an increase in kVp to achieve the least amount of patient dose?
a.) hypersthenic
b.) sthenic
c.) asthenic
d.) hyposthenic
Doubling
A switch from a 3 phase unit to a single phase unit would requre approximately a ____ in overall technique, in order to maintain the same exposure to the IR.
a.) doubling
b.) 50% reduction
c.) 35% increase in mAs
d.) 50% increase in kVp
It is possible to clip necessary anatomical information, resulting in a repeat
The hazard of collimating too tightly is that:
a.) the radiologist might miss an appendicitis diagnosis on a chest x-ray
b.) subject contrast will be too high
c.) it is possible to clip necessary anatomical information, resulting in a repeat
d.) the detector won’t get enough disnal
Three phase, high frequency
The greater efficiency of modern x-ray generators comes from the use of ____ or ____ technology.
a.) three phase, semi-conductor
b.) three phase, high frequency
c.) high frequency, rectifier
d.) single phase, constant potential
All of the above
Earlier forms of beam limitation involved the use of:
a.) lead diaphragms
b.) cones
c.) cylinders
d.) all of the above
Signal to noise ratio (SNR)
Of the following, which will be decreased by exessively wide collimation?
a.) signal to noise ration (SNR)
b.) noise
c.) scatter production
d.) IR exposure
True
TRUE or FALSE: If someone was taking my x-ray images, or those of someone I care about, I would want them to include only anatomy that was necessary to the study (to the best of their abilities) in order to reduce the likelihood of negative radiation effects.
Bowel obstruction, destructive
What is the pathology shown in this image? Is it considered additive or destructive?
A decrease in either the thickness, density or atomic number of the anatomy of interest
A destructive pathological condition results in:
a.) a decrease in spatial resolution
b.) a decrease in either the thickness, density or atomic number of the anatomy of interest
c.) an increase in either the thickness, density, or atomic number of the anatomy of interest
d.) a dercease in IR exposure
True
TRUE or FALSE: Collimating to the anatomy of interest is likely to increase subject contrast, in the majority of diagnostic studies.
Soft tissue
The effects of excessively wide collimation are most pronounced when there is a high proportion of _____ in the anatomy being imaged.
a.) bone
b.) air
c.) soft tissue
d.) compensating filtration
Brings the total filtration of the unit up to federal requirements
Added filtration is important because it:
a.) brings the total filtration of the unit up to federal requirements
b.) compensates for more dense anatomic parts
c.) cleans up scatter radiation
d.) all of the above
False
TRUE or FALSE: Excessive scatter due to wide collimation will result in a blurry radiographic image.
A compensating filter
To even out variations in radiographic exposure caused by drastic differences in anatomical density, it would make sense to use:
a.) added filtration
b.) inherent filtration
c.) a compensating filter
d.) more total filtration
Greater entrance skin exposure
Having inadequate filtration would result in:
a.) greater entrance skin exposure
b.) low subject contrast
c.) excessive IR exposure
d.) high subject contrast
No change in technique, adjustment just for part thickness
When compensating for a cast, pure fiberglass would likely require _____, while dry plaster would probably require _____.
a.) no chnage in technique, a doubling of kVp
b.) a 15% increase in mAs, a doubling of mAs
c.) no change in technique, adjustment just for part thickness
d.) adjustment for part thickness, no change in technique
Aluminum
_____ is considered the standard filtering material, and the filtering capacity of all other absorbers are measured by comparing them to it.
a.) copper
b.) tungsten
c.) aluminum
d.) lead
True
TRUE or FALSE: When performing post-reduction (follow up) x-rays on patient with a wet plaster cast, it might be necessary to raise kVp and/or mAs to compensate.
All of the above
Full-wave rectification of the electrical supply:
a.) prevents electrons from going backwards through the tube, and destroying the filament
b.) results in twice as many photons being produced for a set mAs, than in a half rectifed unit
c.) has 120 pulses per second going across the tube, for a single phase generator
d.) all of the above
Half value layer
The thickness of an absorber that will reduce the intensity of the primary beam by one half is known as the:
a & c
Excessively wide collimation will most likely result in:
a.) decreased subject contrast
b.) increased subject contrast
c.) increased patient dose
d.) decreased brightness
e.) a & c
f.) b & d
60 pulses, and half the exposure to the IR
A full-wave rectified unit burned out a rectifier, and is operating as a half-wave rectified unit. How many pulses per second are there, and what happens to the overall amount of exposure from a set (fixed) technique (in comparison to what would happen if it was full-wave rectified)?
a.) 120 pulses, and half the exposure to the IR
b.) 120 pulses, and nothing - rectification doesn’t affect IR exposure
c.) 60 pulses, and a slight decrease in the exposure to the IR
d.) 60 pulses, and half the exposure to the IR
e.) 120 pulses, and a slight decrease in the exposure to the IR
Low energy photons from the primary beam are removed
When the proper amount of total filtration is present:
a.) the subject contrast increases
b.) the subject contrast decreases
c.) low energy photons from the primary beam are removed
d.) low energy photons from the remnant beam are removed
Caliper
The _____ is a very effective device used in measuring part thickness, and creating technique charts that standardize image quality and minimize patient dose. It is rarely used in contemporary radiology practice for determining technique, as it tends to be uncomfortable for the patient.
False
TRUE or FALSE: A switch from half-wave to full-wave rectification or vice-versa will affect the penetrability of the beam.