Art History Study Guide
1/54
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Baroque
A highly decorative and theatrical style of art, architecture, and music that emerged in Europe during the late 16th century and continued into the 18th century, characterized by dramatic use of light, bold colors, and intricate details.
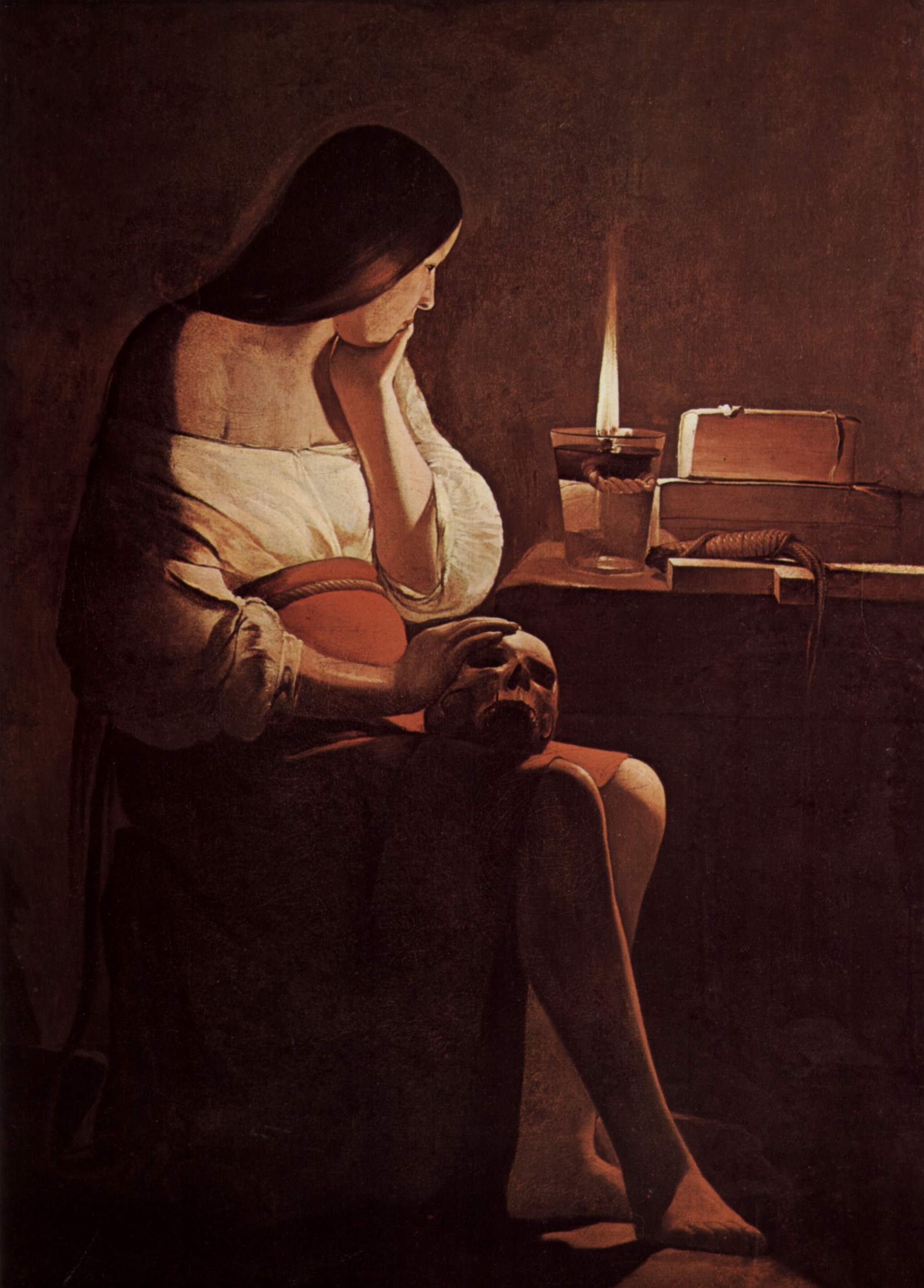

Chiaroscuro
A technique used in the visual arts to represent light and shadow as they define three dimensional objects. The overall composition is affected with strong contrasts of light and dark.

Impasto (pl. impasti)
A painting technique where thick layers of paint are applied to a canvas or surface creating a textured and three-dimensional effect. The word originates from the Italian word for “paste” or “dough” which reflects the thick and heavy application of paint.
Genre (both meanings)
type or category of a painting / indicates the content or topic of a particular picture
allegory
symbol

Caravaggio
Conversion of St. Paul
Rome, Italy
ca. 1601
Oil on canvas

Caravaggio
Entombment of Christ
ca. 1603
Ol on canvas

Gianlorenzo Bernini
Apollo and Daphne
1624
Marble

Gianlorenzo Bernini
Ecstasy of St Teresa
Rome, Italy
1650
Gilded bronze, marble, paint, plaster

Diego Velaquez
Las Meninas
1656
Oil on Canvas

Rembrandt van Rijn
Self-Portrait
ca. 1660
Oil on Canvas

Jan Vermeer
The Letter
1666
Oil on canvas

Jan Vermeer
Allegory of the Art of Painting
ca. 1670
Oil on canvas
Neoclassicism
a movement that revived art from Greek and Roman art, empathizing simplicity, clarity, and idealized forms, often characterized by the use of classical themes and subject matter with a focus on line and composition.
Romanticism
an artistic and intellectual movement that emphasized emotion, individualism, and the glorification of nature, often reacting against the rationalism of the Enlightenment.
Hudson River School
a mid 19th century American art movement of landscape painters who created a self-consciously “American” style and was also influenced by Romanticism
Salon of the Rejected (Salon des Refuses)
a French exhibition held in 1863 where artworks rejected by the official Paris Salon jury were displayed, essentially displaying art that was deemed too radical or unconventional by the established art world at the time
Impressionism
in the 19th century, based on the practice of painting out of the doors and spontaneously “on the spot” rather than in a studio from sketches.
Post-Impressionism
An art movement in the 19th century which was known for its vivid colors, thick paint application, and distinctive brush strokes. Artists emphasized geometric forms, distorted forms for expressive effect, and used unnatural or arbitrary colors.
Formalism
response to Impressionism and Post-Impressionism which is the study of art by analyzing and comparing its form and style. It emphasizes the purely visual aspects of a work, such as its form, color, line, shape, texture, and composition opposed to meaning or historical context.

Jacques-Louis David
The Oath of the Horatti
1784
Oil on canvas

Francisco Goya
Third of May
1808 - 1814
Oil on canvas

Theodore Gericault
Raft of Medusa
1818-1819
Oil on canvas

Eugene Delacroix
Tiger Hunt
1854
Oil on canvas

Thomas Cole
Kaaterskill Falls
1825-1826
Oil on canvas

Thomas Cole
The Oxbow
1836
Oil on canvas

Frederick Edwin Church
The Heart of the Andes
1859
Oil on canvas

Édourard Manet
Le Déjeuner sur l'Herbe (the Picnic)
1863
Oil on canvas
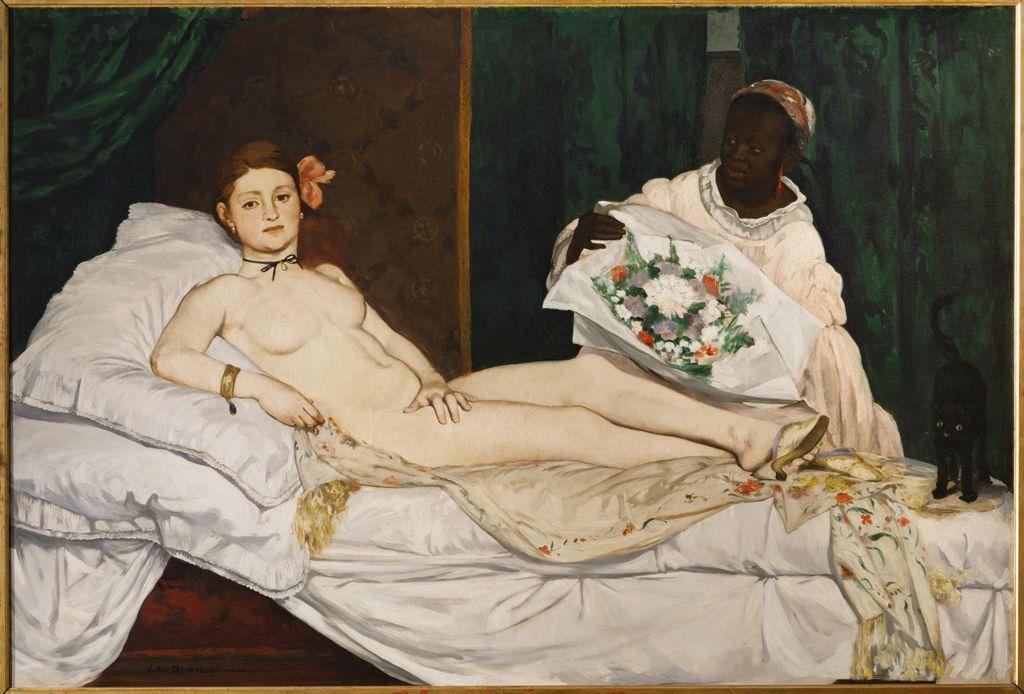

Édouard Manet
Olympia
1863
Oil on canvas

Edgar Degas
The Rehersal
1874
Oil on canvas

Claude Monet
Impression: Sunrise
1872
Oil on canvas

Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
At the Moulin Rouge
ca. 1895
Oil on canvas
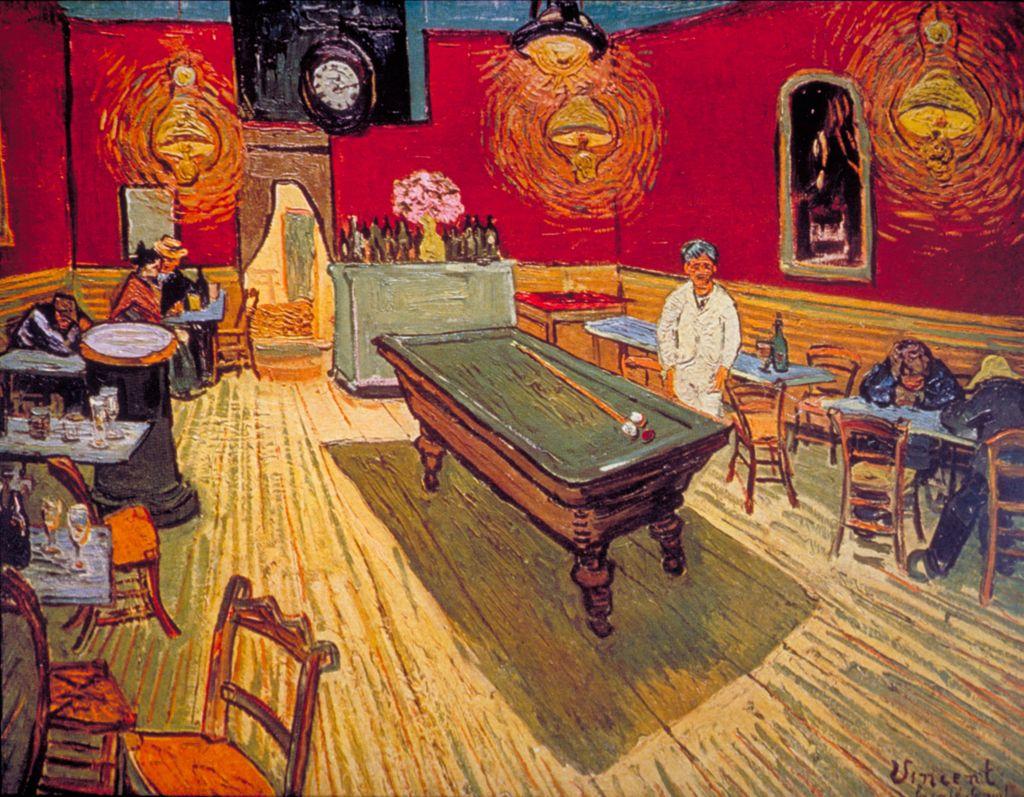
Vincent Van Gogh
The Night Café
1888
Oil on canvas
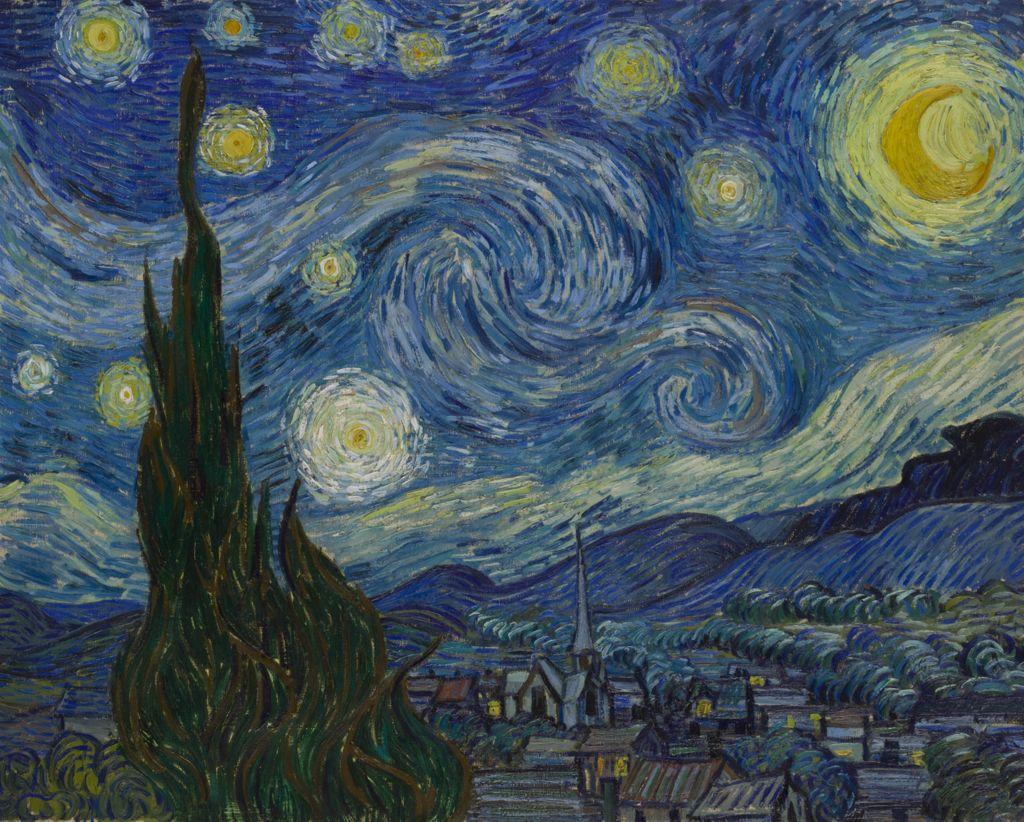

Vincent van Gogh
Starry Night
1889
Oil on canvas
Modernism
Took place during the late 19th century to mid 20th century, it was characterized by a rejection of traditional values & styles, and search for new ways to represent the modern world.
Fauvism
Was an art movement that emerged in France in the early 20th century, characterized by bold, vibrant colors and loose brushwork
Cubism
A revolutionary new approach to representing reality that began in the early 20th century and emphasized the two-dimensionality of the canvas resulting in paintings that appear fragmented and abstracted
Surrealism
An art movement that began in the 1920s and was defined by a desire to explore the unconscious mind, the poetic, the revolutionary and challenge conventional reality
Abstract Expressionism
An American art movement characterized by large-scale, non-representational paintings that emphasize the artist’s emotional expression through spontaneous brushstrokes, gestural marks, and vibrant colors, often conveying a sense of movement and energy, rather then depicting recognizable objects
Pop Art
An art movement that emerged in the 1950s and flourished in the 1960s in America and Britain, drawing inspiration from sources in popular and commercial culture

Henri Matisse
Woman with a Hat
1905
Oil on canvas

Henri Matisse
Harmony in Red (The Red Room)
1908-1909
Oil on canvas

Pablo Picasso
Gertrude Stein
1907
Oil on canvas
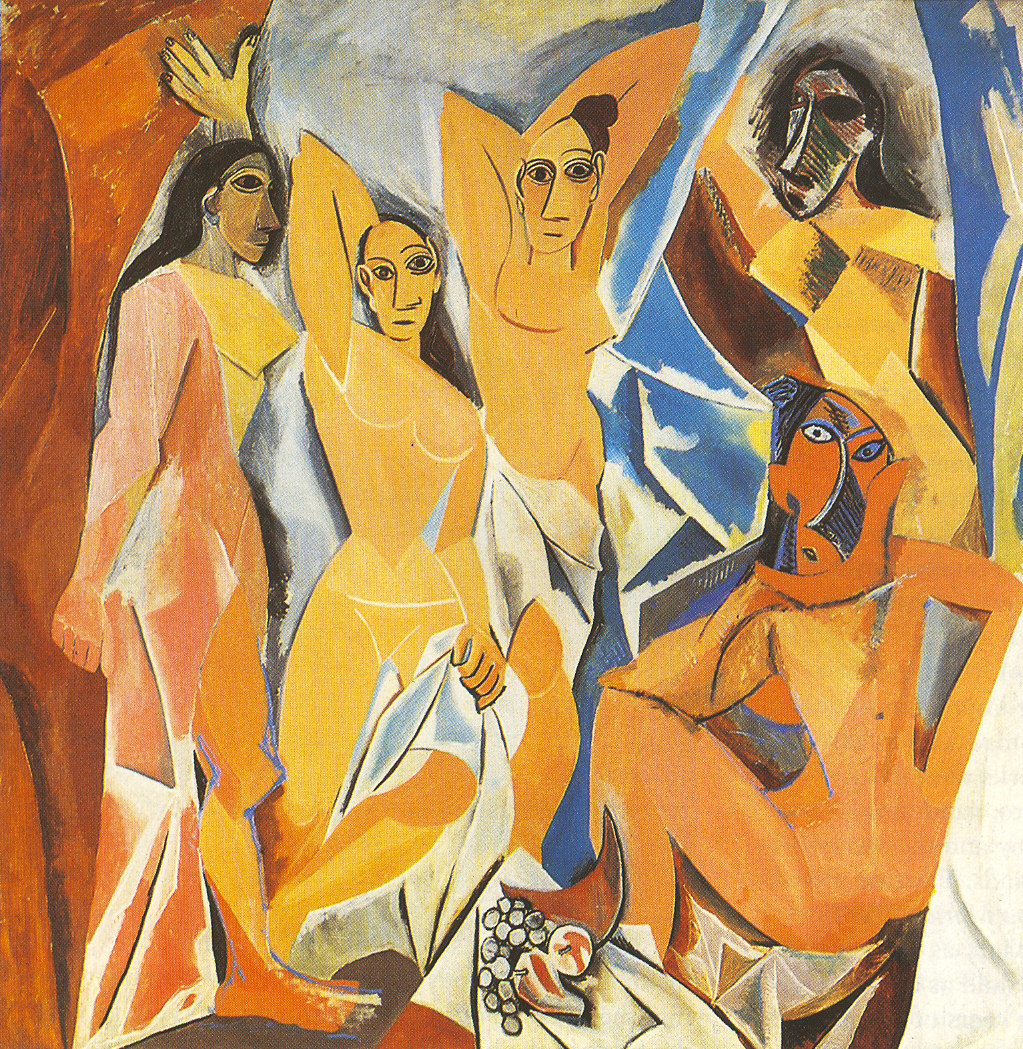
Pablo Picasso
Les Demoiselles d’Avignon
1907
Oil on canvas
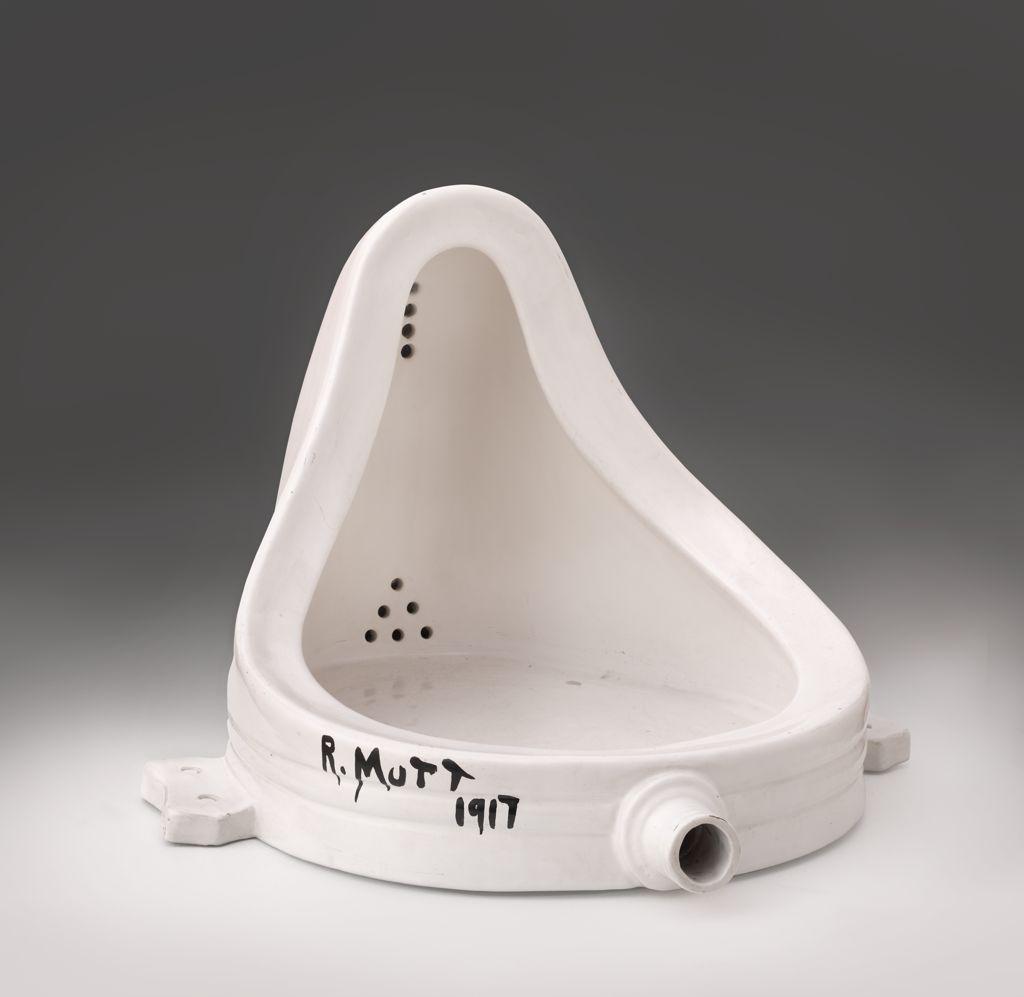

Marcel Duchamp
Fountain
found object (readymade) 1950, after original version 1917
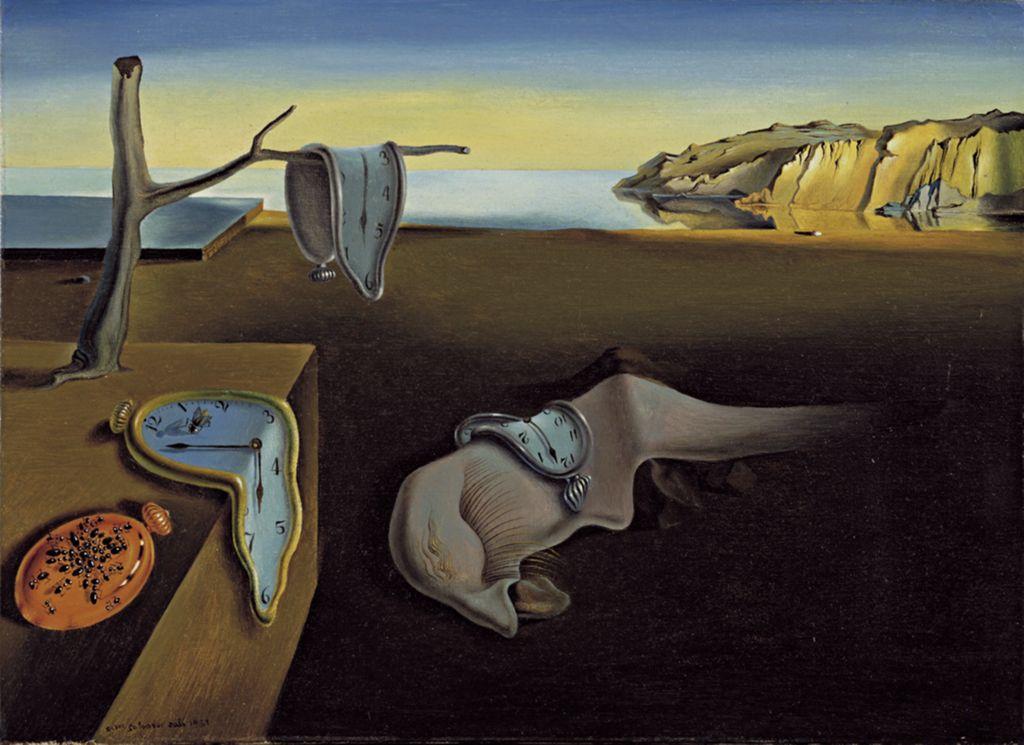

Salvador Dali
The Persistence of Memory
1931
Oil on Canvas

Charles Demuth
I Saw the Figure 5 in Gold
1928
oil/cardboard

Georgia O’Keefe
Jack in the Pulpit No.4
1930
Oil on canvas

Edward Hopper
Nighthawks
1942
Oil on canvas

Jacob Lawrence
Migration of the Negro Series panel no.1 during world war there was a great migration North by Southern Negroes
1940-1941
Tempera on masonite

Frida Kahlo
The Two Fridas
1939
Oil on canvas

Jackson Pollock
Number 1.
1950 (Lavender Mist)
oil, enamel, and aluminum paint on canvas
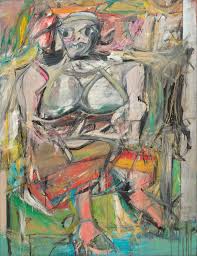
Willem De Kooning
Woman I
1950-1952
Oil on canvas
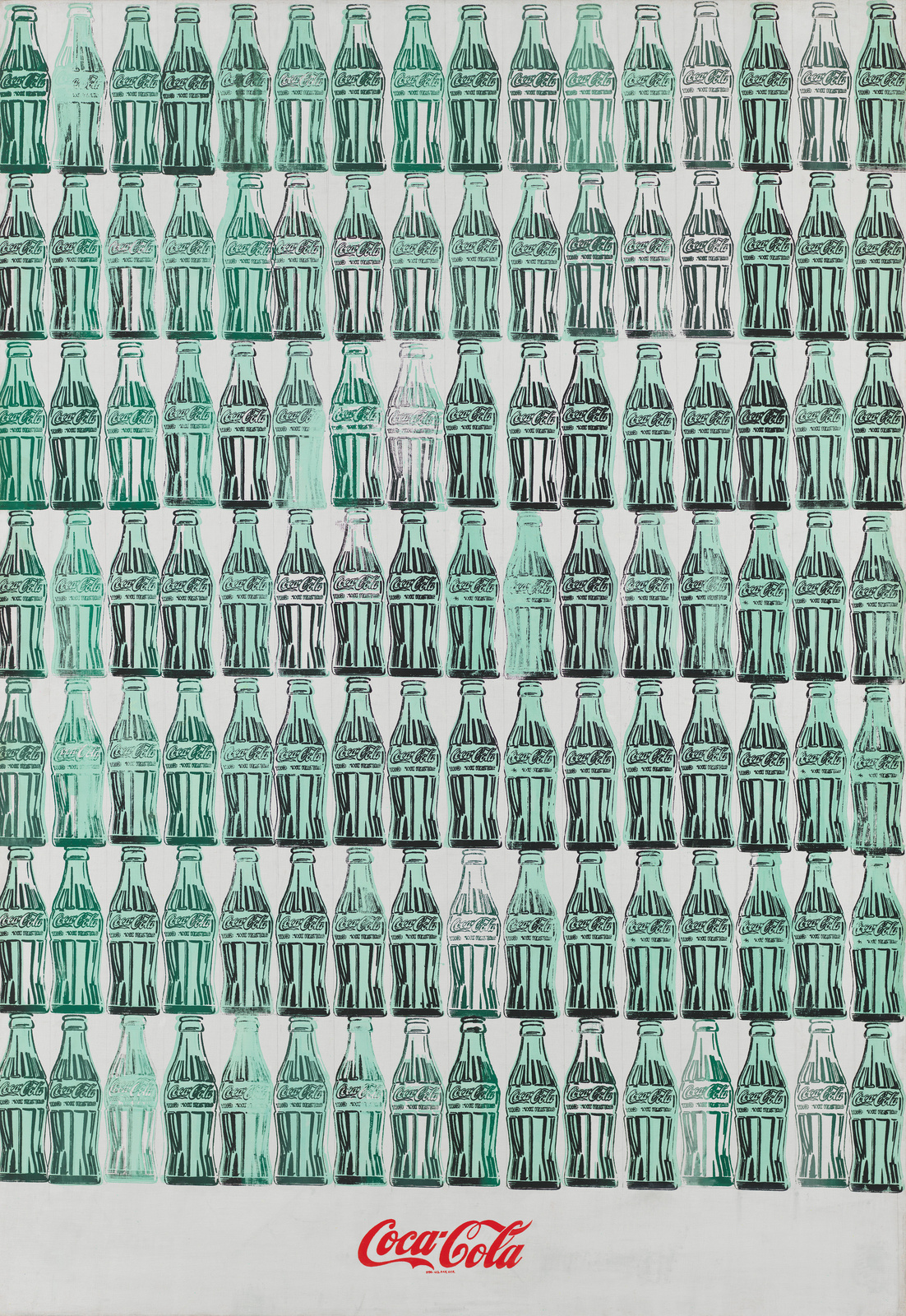

Andy Warhol
Green Coco-Cola Bottles
1962
Oil on canvas
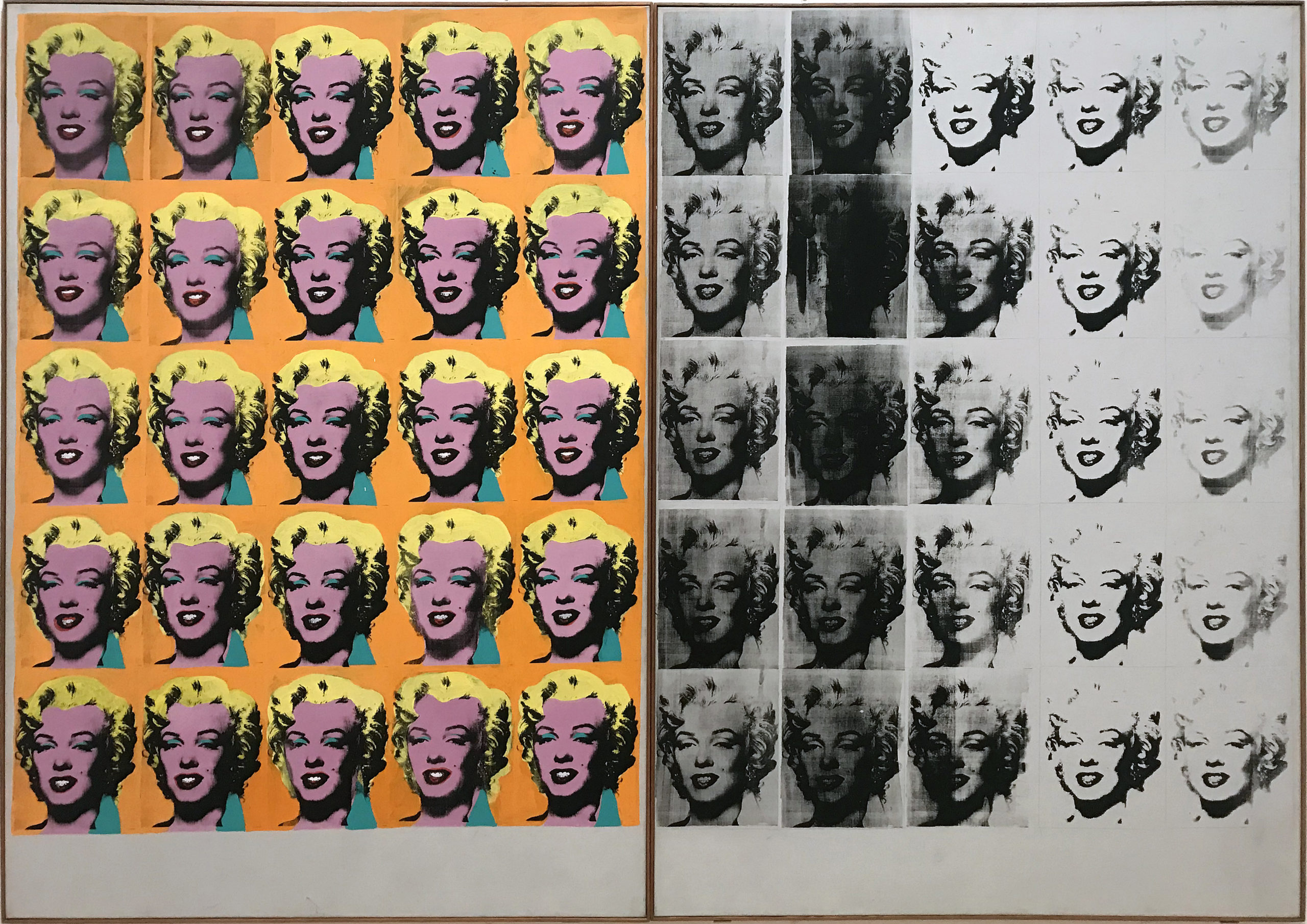

Andy Warhol
Marilyn Diptych
1962
Oil, acrylic, and silkscreen enamel on canvas