Intro Organic Chemistry (need to add isomerism)
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Empirical formula
The simplest ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
Molecular formula
The formula showing the actual ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
Structural formula
Gives the number and type of atoms in a molecule and shows how they are bonded together
Skeletal Formula
A straight line represents a carbon - carbon bond.
Homologous Series
They show a gradual change in physical properties.
They have similar chemical properties.
Alkene - General Formula
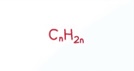
Halogenoalkane General Formula
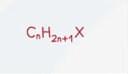
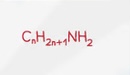
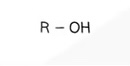
Alcohol General Formula
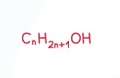
Aldehyde General Formula
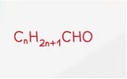
Ketone General Formula

Carboxylic Acid General Formula

Ester General Formula
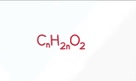
Amine General Formula
Nitrile General Formula

Structural Formula - Alkene
Structural Formula - Halogenoalkane

Structural Formula - Alcohol
Structural Formula - Aldehyde
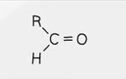
Structural Formula - Ketone
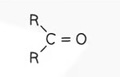
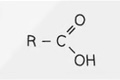
Structural Formula - Carboxylic acid
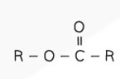
Structural Formula - Ester
Structural Formula - Amine
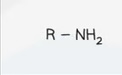
Structural Formula - Nitrile

Nomenclature - What does the stem of the name come from?
The longest carbon chain
Nomenclature - How are the side chains and functional groups’ position decided?
Numbering the carbon atoms from the side that gives the lowest possible numbers in the name
How are side chains shown in structural formulas?
Through brackets: ()
How do you indicate more than one of the same alkyl side-chain or functional groups in a compound?
In front of its name is added: di- (for two), tri- (for three) or tetra-(for four)
How are multiple alkyl side-chains ordered?
In alphabetical order
How are adjacent numbers separated?
By a comma: ,
How are numbers and words separated?
By a hyphen: -
What are the two types of isomerism?
structural
Stereo
Structural isomerism
This occurs when substances have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
What we the different types of structural isomers?
chain
Position
Functional group
Chain isomers
They belong to the same homologous series but have a different carbon chain (e.g branched).
What are the similarities in chain isomers?
Chemical properties
What are the differences on chain isomers?
Boiling point
Why do branched chain isomers have lower boiling points?
branched chain molecules cannot pack as closely together and have weaker VdW between their molecules which take less energy to break.
Position isomers
they have their functional groups in different positions
DO NOT WRITE AS ‘POSITIONAL’
Functional group isomers
They have the same molecular formula but different functional groups and so belong to different homologous series.
What is sterioisomerism?
This occurs when substances have the same molecular and structural formula but have a different spatial arrangement of their atoms.
What is a example of sterioisomerism?
E/Z isomerism
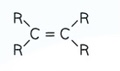
What is E/Z isomerism?
When a carbon - carbon double bond prevents rotation and each carbon on the double bond has two different groups attached to it.
When does the Z form of E/Z isomerism occur?
When two atoms of each pair of higher atomic number, therefore higher priority group, are on the same side of the C=C double bond.
When does the E form of E/Z isomerism occur?
When two atoms of each pair of higher atomic number, therefore higher priority group, are on different sides of the C=C double bond.