DT GCSE AQA
1/259
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
260 Terms
3 Main elements of a system
Input, process, output
What are systems used for?
To add additional functionality to designs
What is an input
component which either adds energy or information to a system
example of an input
switch
sensor
what are programmable microcontrollers
computer chips that can be programmed to perform specific tasks
what do programmable microcontrollers do
provide functionality and intelligence to products and systems
what can programmable microcontrollers do
Counting
Timing
Decision making
Advantages of programmable microcontrollers
Reduces size of circuit - programming replaces physical components
They can be reprogrammed many times - so changes can be made without replacing actual components
They have pins for connecting several input and output devices - adding to flexibility
What is an output
components which provide information to the outside world
Examples of output components
lamp or buzzer
components that emit light and sound
What products use output components
speaker
What products use input components
keyboard
webcam
microphone
what is a design brief
A design brief is the statement a client gives the designer outlining what they want their product to be like
What is a design specification
List of criteria a product needs to address.
functionality
application of use, ease of working
aesthetics
surface finish, texture, colour
environmental factors
could materials be renewable
could they be upcycled
which material would have the least environmental impact
FSC - forest stewardship council
Availability
ease of sourcing and purchase
Social factors
social responsibility
cultural factors
sensitive to cultural influences
What is collaboration
Working with others on proposals and solve problems as well as gathering data.
advantages of collaboration
improve range and quality of items
designers can feed off the ideas of others
disadvantages of collaboration
issues with communication
different time zones
different access
different units of measurement
what is User Centered designed
product is designed to fulfill the wants and needs of the consumers
advantages of user centered design
helps companies understand any potential issues and how the product can be modified even after the launch
disadvantages of user centered design
extra time
not targeted towards overall market
cost
what is systems approach
Plans the layout for the correct inputs, processes and outputs things that need logical and ordered methods
advantages of systems approach
easy to understand
disadvantages of systems approach
might need to be edited a lot
may be issues with programming
what is iterative design
each iteration gets better as a result of the small refinements being made after each design
iterative design advantages
leads to desired quality and functionality
iterative design disadvantages
time consuming
uses lots of material
high cost
How to avoid design fixation
use of mood boards
different approaches to design generation
modelling
quick sketches
CAD
abstract drawings which can be interpreted
what are the different types of movement
linear
oscillation
reciprocation
rotary
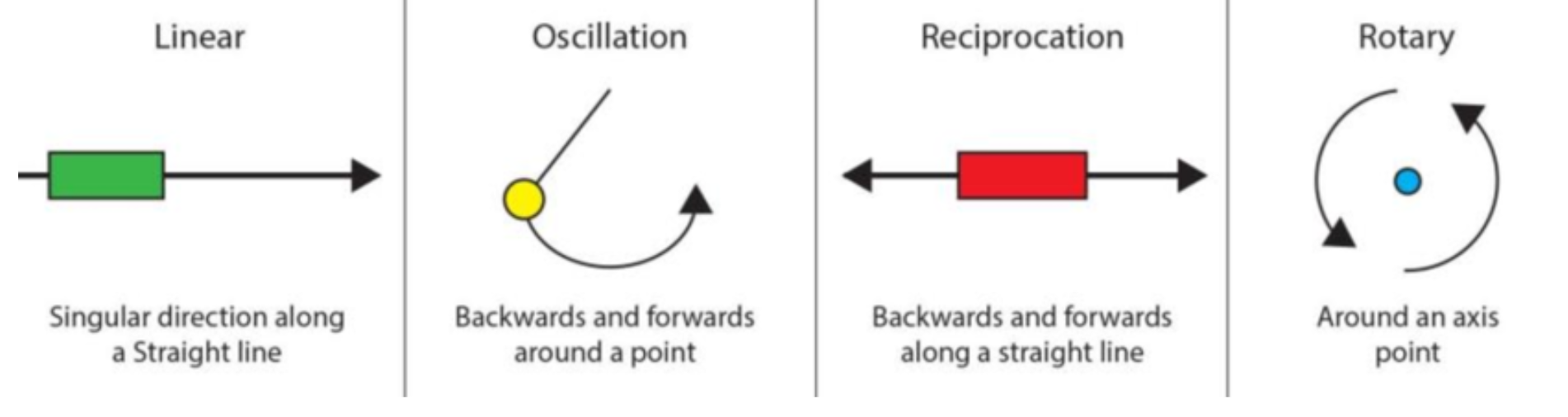
First order lever
pivot point in center
load then pivot then effort
e.g. seesaw
Second order lever
pivot point at one end
load in the center
effort at opposite end to point
e.g. wheelbarrow
third order lever
pivot point at one end
effort in middle
load at opposite end to point
e.g. tweezers
how to calculate mechanical advantage
load = mechanical advantage x effort
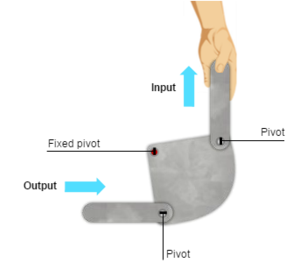
Bell crank
used to change the direction of movement through 90 degrees using 2 moving pivots and a fixed pivot point
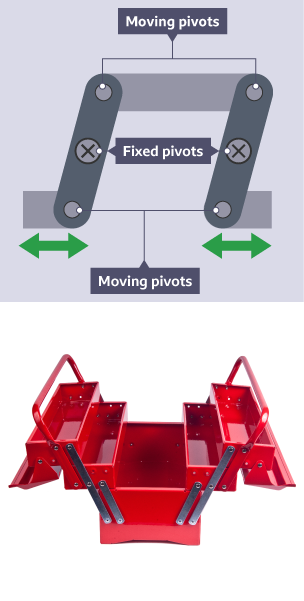
push-pull
also called parallel motion linkages
input and out motion the same
they may be created for avoiding a fixed component or making 2 parts of an object move at the same time
CAMS and followers
used to convert rotary movement to reciprocating movement
Circular cam
off center pivot - follower moves um and down
e.g. pistons or steam engines
Pear cam
stationary for half a turn then rises and falls gently
e.g. carousel horses
Snail or drop cam
remains stationary for half a turn then rises and falls quickly
only rotate in one direction
drops at regular intervals
e.g. production lines - make regular cuts
heart-shaped or constant velocity cam
follower rises and falls steadily with uniform velocity
no stationary period
flat follower
flat bottom that sits on the cam
cope well under load
aren’t accurate
lots of friction
Point or knife follower
very accurate
quick to wear away at the pointed edge
roller follower
accurate
low on friction
can withstand load
more costly to produce
what are gear trains
series of cog wheels
drive gear is powered and other gears are driven by this wheel
what are pulleys and belts
create a mechanical advantage for moving objects
prototype
a single sometimes highly specialised item is produced
workers highly skilled
unit cost higher
prosthetics, machinery, wedding dresses
personalisation
mass produced item adapted to an individual
personalised coffee cup
Batch
usually up to 1000 units
works along various different production points where different processes are complete
workers skilled in a few different processes
used for seasonal products or if only a limited number of products are needed or the product is seasonal
mass
large scale
automation may be used in the factory where large amounts of CAD/CAM is used
injection moulding or casting may be used
high set up costs
why are product manufactured in various ways
Products are manufactured in various quantities, depending upon demand and the requirements for the product.
continuous
mass production - products are made 24 hours a day 7 days a week
low cost consumable items due to high demand and continuous nature
e.g. toilet paper
what is a production aid
They are used to ensure the shape of your design is accurate and can be used repeatedly to ensure the same shape is produced each time.
what is a jig
holds a material in place and guides cutting told to ensure that a process can be repeated accurately and consistently.
what is a former
solid shape that is placed in a vacuum former to create a hollow mould
What is a template
tool used to mark out shapes repeatedly - ensuring information is being placed correctly
what is a mould
a cavity or matrix that shapes a plastic or fluid substance into a desired product - the substance is poured or forced into the mould then allowed to harden
what is a die
wooden block with mounted steel knives used to cut, crease and perforate card and paper - used to cut precise shapes from various materials.
Hardwood properties
Sourced from Deciduous trees
Slower growing
More expensive than softwoods
Worldwide
Types of Hardwood
Beech
Oak
Mahogany
Balsa
Ash
Softwoods Properties
Coniferous trees
Faster Growing
Cheaper than Hardwoods
Used by inexpensive furniture brands
Prone to having knots
Knots can affect the structure of the woods and leave holes id the dop out when dried
Types of softwoods
larch
pine
spruce
Manufactured Boards properties
Manufactures from timbers combined with adhesives
Can be made from waste material
Available in large consistent thickness sheets without faults
Suitable flat pack furniture
Can have a veneer pf plastic or tin wood attached to disguise the board and make it more attractive of functional
can be recycled
Types of Manufactured Boards
Medium Density Fiberboard
Plywood
Chipboard
Stock Forms of Manufactured Boards
Boards - varying thicknesses
Mouldings - Dowels, crown, pediment, dado, reed
Planks - varying thicknesses up to 3600mm lengths
Why standardized sizing
consistency of manufacture
availability of specific sizing
availability of materials
components can be efficiently arranged to reduce waste and costs
quality materials are used in manufacture
Examples of Standard Components
Butt hinges
Piano Hinges
Countersunk screws
pan head screws
slotted screw
corner block fitting
cam lock fitting
Absorbency
The ability of a material to take in moisture
Density
The mass of a material in a standard volume of space
Fusibility
The ease at which the material can be fused together or the temperature required to melt
Conductivity
electrical - allows the flow of electricity to pass through it
thermal - allows heat to transfer through it
insulation - the ability of a material to prevent the transfer of heat or electricity
Strength
Compressive - the ability to withstand being crushed or shortened by pushing forces
Tensile - the ability to resist stretching or pulling forces
Hardness
The ability to resist abrasive wear and indentation through impact
Toughness
The ability of a material to withstand an impact
Malleability
The ability of a material to bend or be hammered into another shape without breaking
Ductility
The ability of a material to be drawn out into wires
Elasticity
The ability of a material to be stretched or deformed and then return to its original shape.
What contributes to choosing materials
Cost
Availability
Working properties
Process of Timber production
Trees are felled
Branches removed
Cut to a suitable length to transport
Logs to timber mills
Timber is debarked and converted into planks
Planks are seasoned
Moisture levels are reduced to 6-8% for internal use and 9-14% for external use
Timber if checked for warping, cracks and damage
Maybe PAR
Examples of Timber Conversion
Through and through sawn
Quarter sawn
Air seasoning
A structure with a solid roof and open sides is used to ensure there is airflow around the timber
Timber is stacked using spacing
Dried naturally
For 25mm woods 3-4 months for softwoods 6 months for hardwoods
Kiln seasoning
Timber is stacks within the kiln and spacing planks are used
water is heated to produce steam
over time the humidity
Timber remains in the kiln for 2-5 days
Warping shapes
bow
crook
kink
cup
twist
how MDF is made
trees are felled
timber is debarked
broken down into chips
wood chips washed
Further broken down into fibres
wax and resin is mixed in
pressed and heated to the desired thickness
it is sanded
cut to shape
manufacture of plywood
Gluing at least three layers of sheet timber together at right angles to each other - laminating
Examples of wastage processes
cut
saw
drill
chisel
sand
plane
Surface treatment step by step
Timber is assembled
filler is applied
sanded low grit 40-80
finer grit 120-180
finer grit 220-240
primer applied paint primer needed, stain/ varnish - no primer needed
if primed the primer will be sanded with a fine grit 240 grit paper
final finish
Wax
applied with a cloth with a direction of the grain
Multiple layers needed to be applied to achieve the required finish
can be applied over paint
does not yellow or crack over time
Varnish
applied with a brush
can be oil or water based
provides a tough water resistant finish
available in a variety of wood colours
dries slowly, can be difficult to clean
discolours over time
Oil
rubbed into the grain with a cloth
multiple layers required
easier to apply than wax and more durable
longer drying times
easily repaired
Paint
applied with a brush
knots can produce stains if not sealed
A primer or undercoat is needed to prepare
wide variety of colours
can crack and discolour over time
Spray Paint
health and safety consideration needed for application
well ventilated area and mask required to ensure it is not inhaled
primer/ undercoat required
wide variety of colours
Lamination
Process used to create curved shapes in Timber
layers of thin timber is glued together and clamped
Living Hinge
Cuts which allow the timber to flex. They can then be laminated.
What are Alloys
Alloys are a mix of a minimum of 1 metal and other materials. Often to change their working properties.
Examples of Metal
Brass - Copper and Zinc
Stainless Steel - Iron, Chromium and Carbon
High speed steel - Iron, Carbon, Chromium, Tungsten