Psych Unit 1 Test (Brain, Senses, Sleep, etc.)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is the central nervous system made up of?
Brain and spinal cord
What is the peripheral NS split into?
Autonomic (controls self-regulated action of internal organs and glands) and Somatic (controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles)
Sympathetic
arousing (gas pedal)
increase in heart rate
decrease in digestion
increase in sugar release by liver
relaxes bladder
increase in epinephrine
Parasympathetic
calming (brake pedal)
stimulates digestion
contracts bladder
slows heart rate
Agonist
encourages neuron firing - mimics neurotransmitter and opens receptor site
Antagonist
discourages neuron firing - blocks reuptake/neurotransmitter from opening receptor site
Neuroplasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood
Medulla
base of brainstem - controls heartbeat and breathing
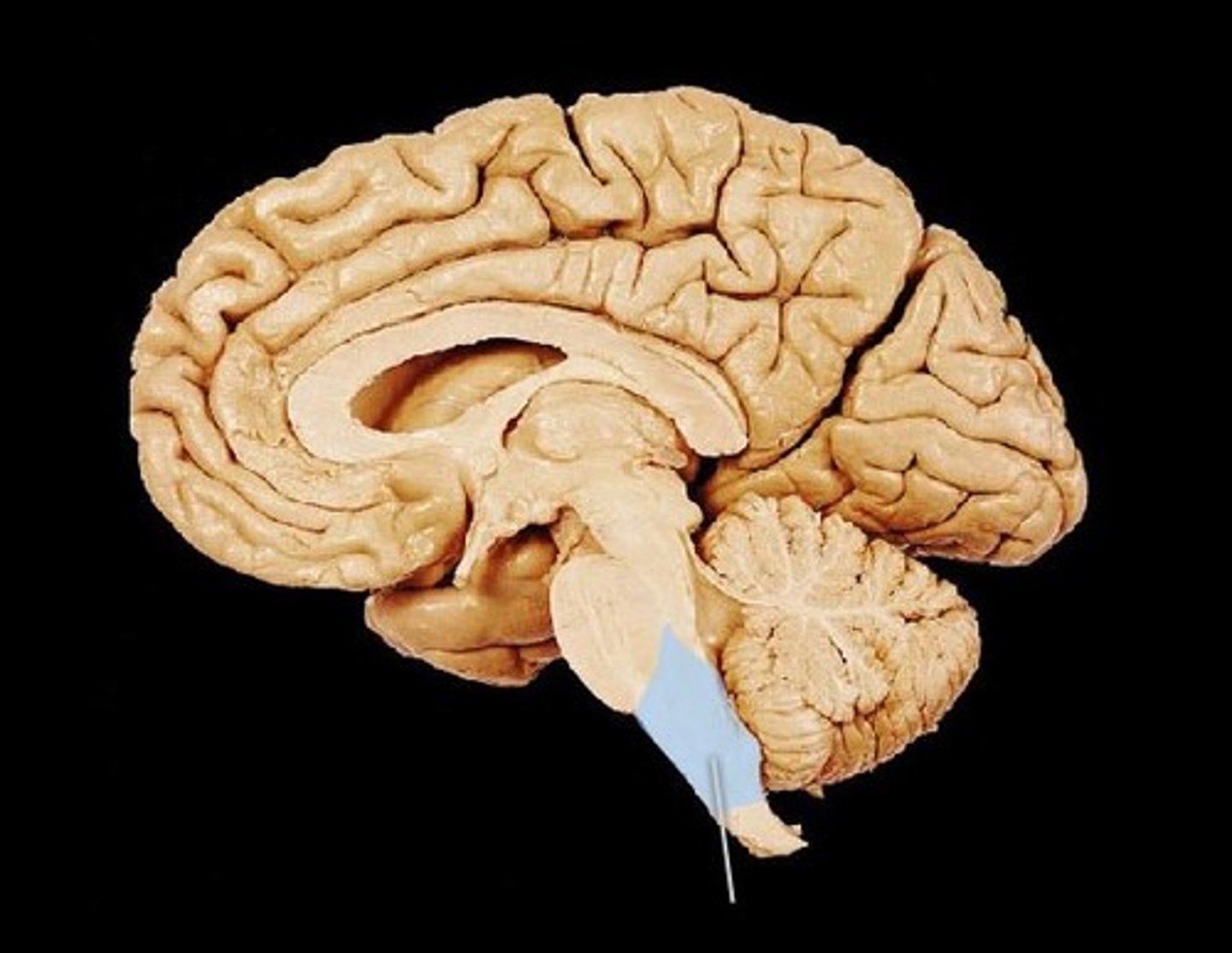
Pons
above medulla - controls sleep and helps coordinate movements
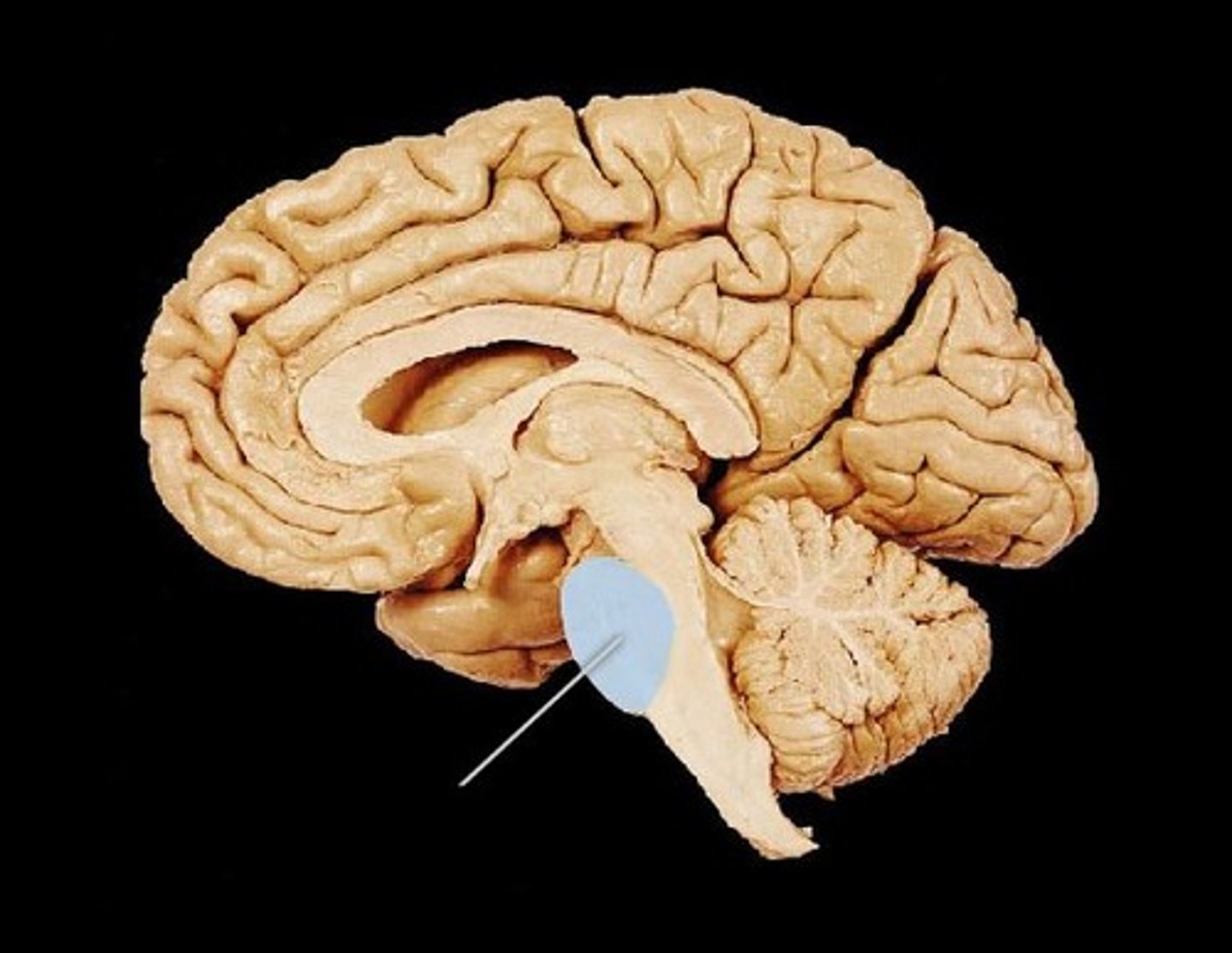
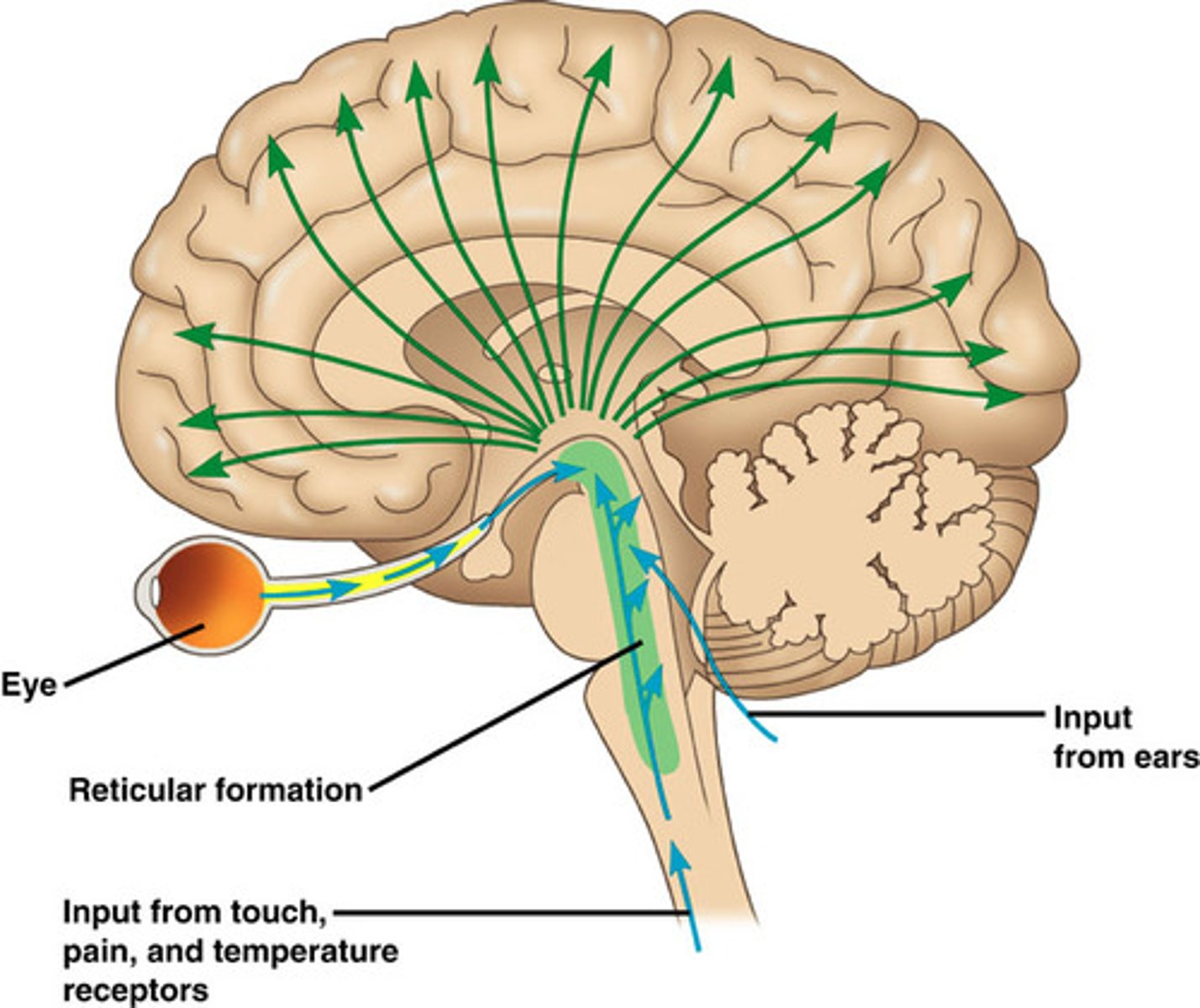
Reticular formation
nerve network - controls arousal and filters sensory information
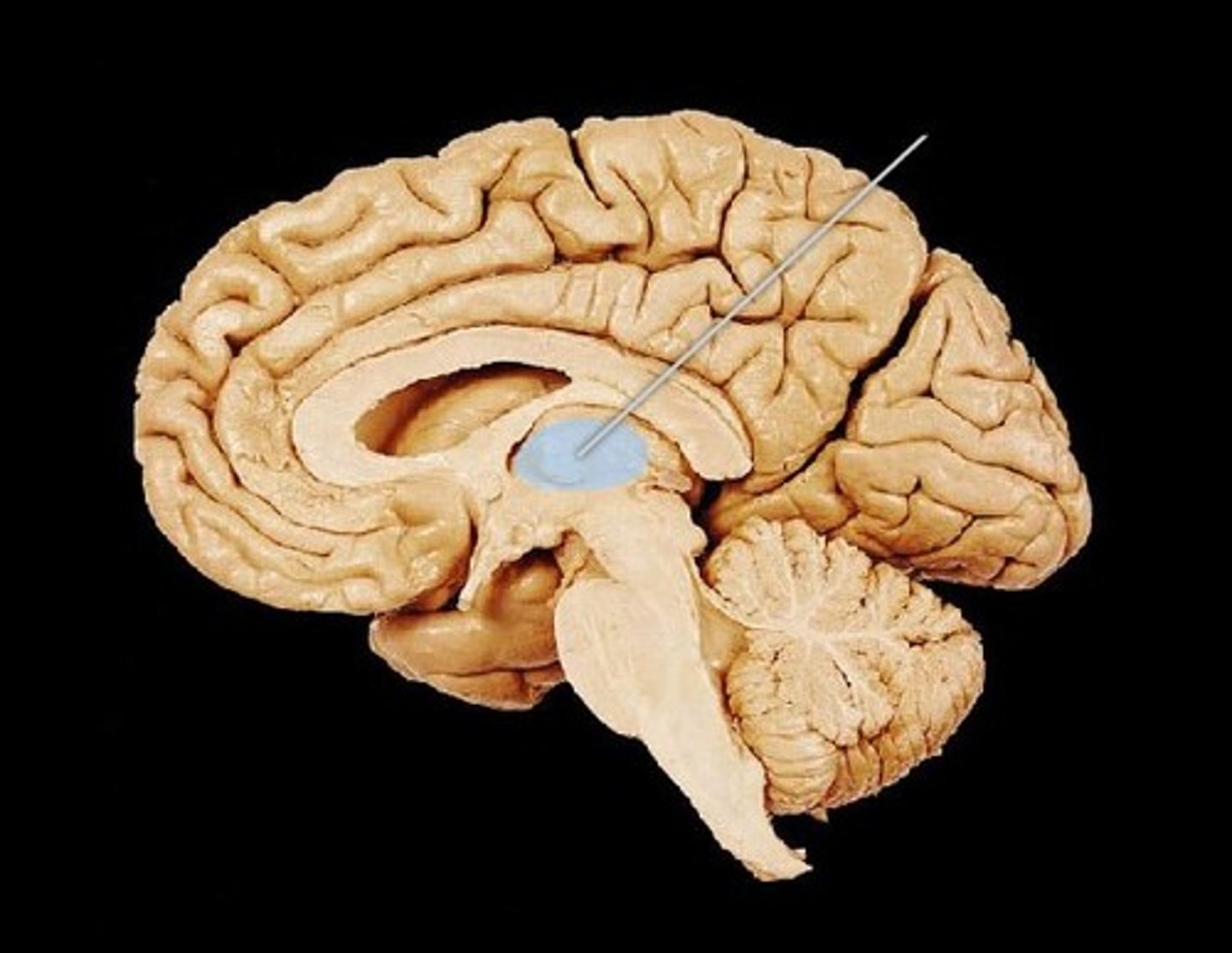
Thalamus
relay station for incoming and outgoing sensory information (EXCEPT SMELL)
I think of it as the two a's in thalamus are passing the baton (the l in thalamus) between one another, like in a relay
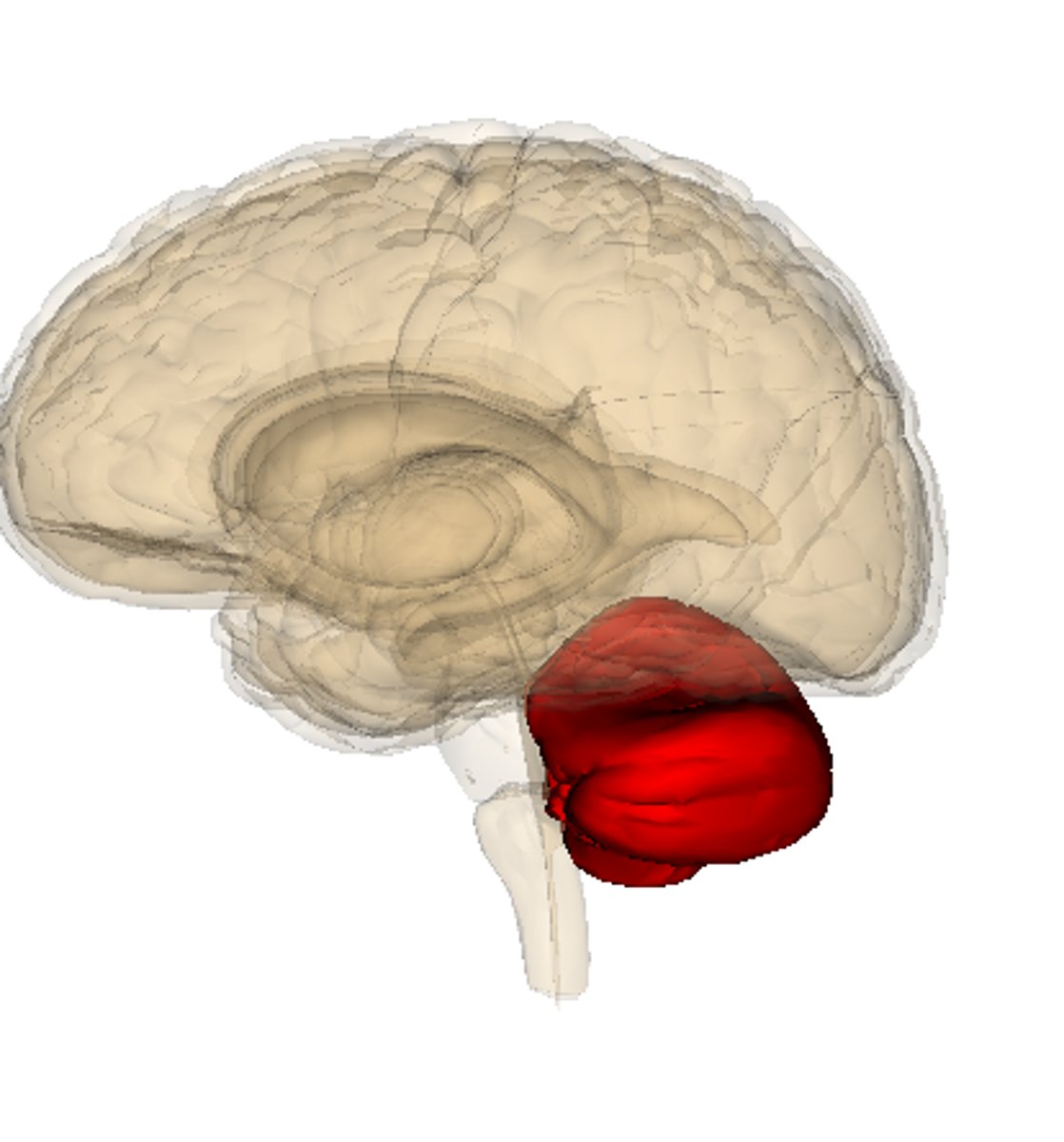
Cerebellum
rear of the brain stem - processing sensory input, coordinating movement and balance, nonverbal learning and memory
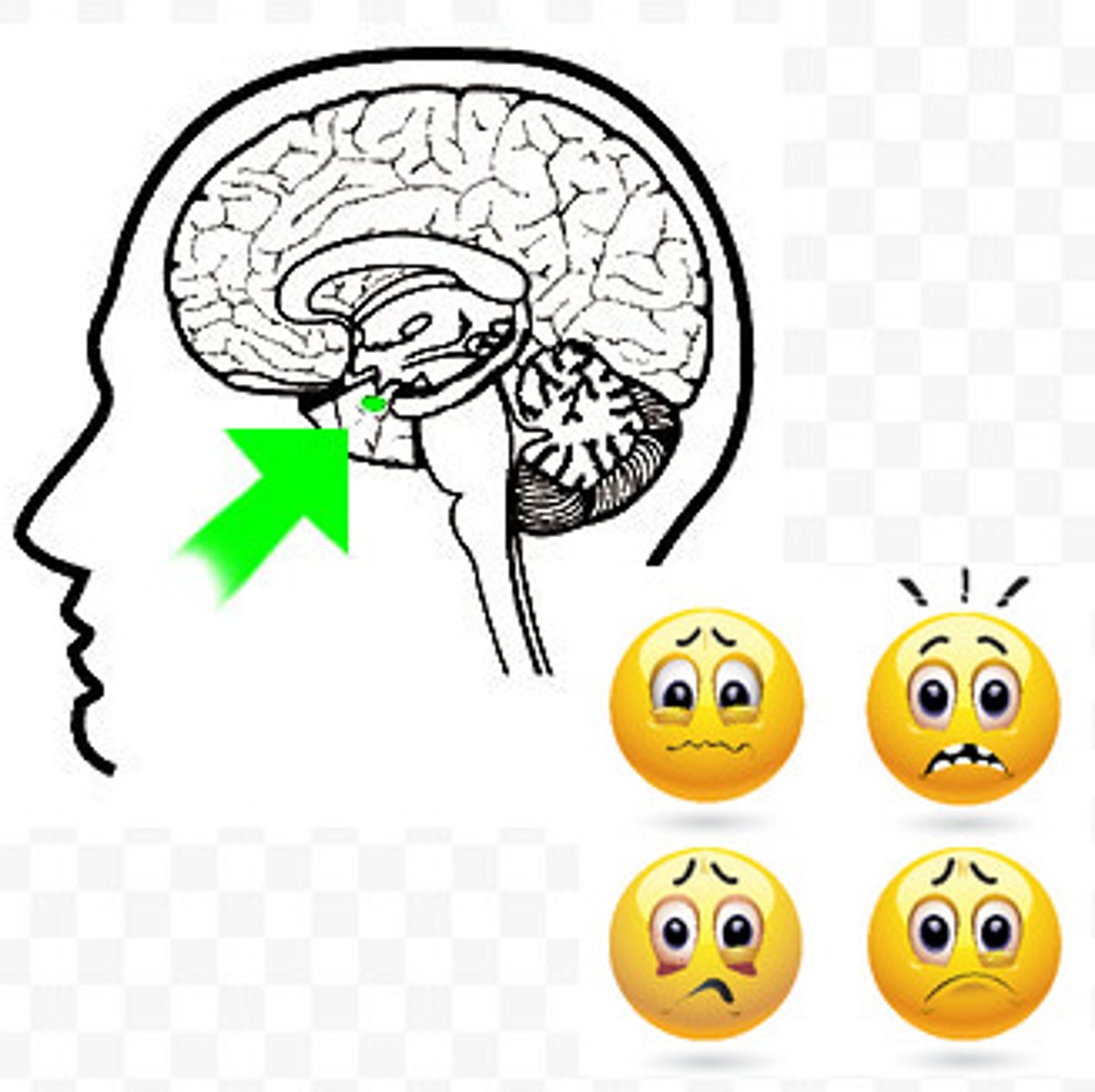
Amygdala
lima bean sided clusters - linked to emotion, fear, and aggression
aggression begins with A and so does amygdala
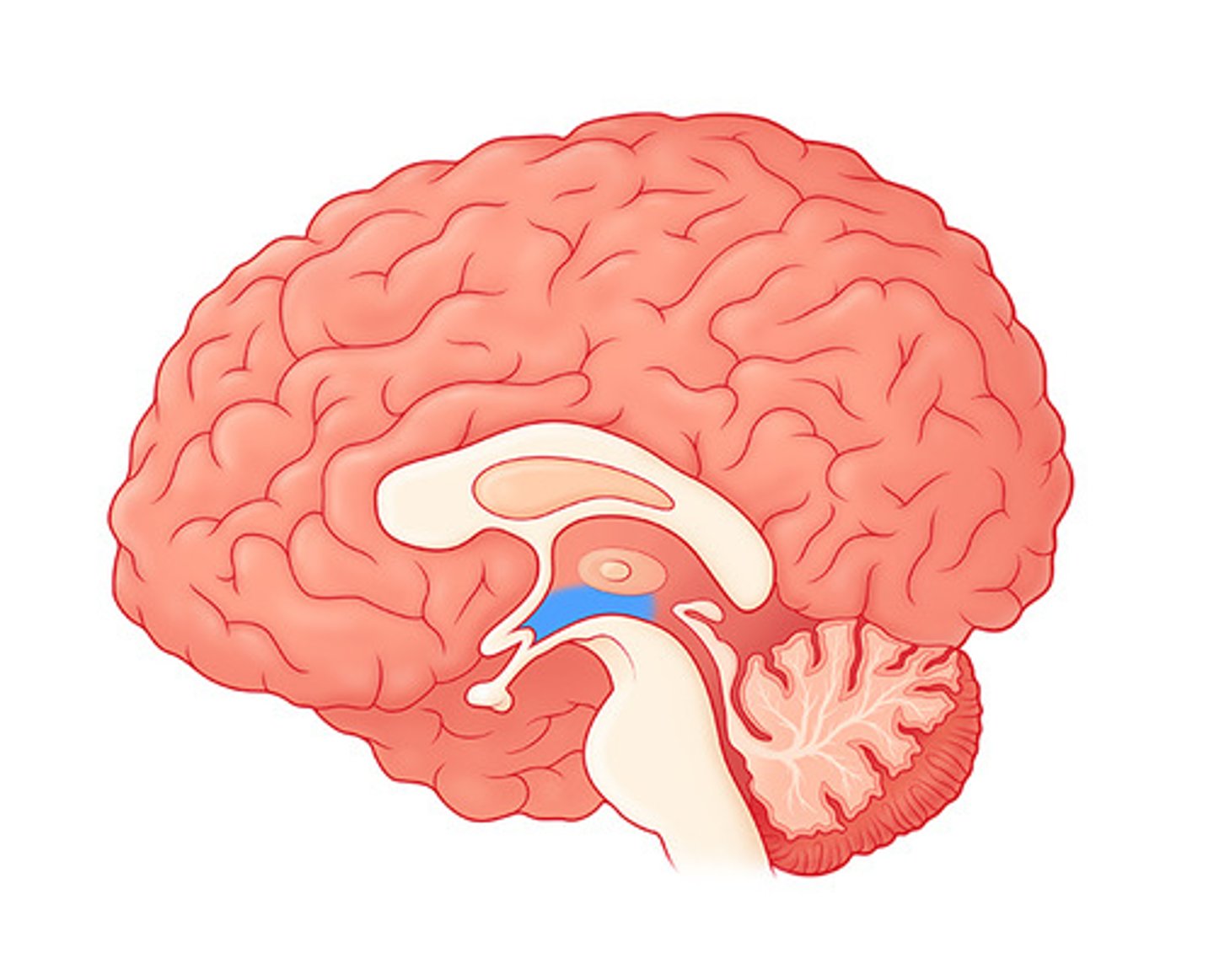
Hypothalamus
directs eating, drinking, body temperature
helps govern the endocrine system (hormones) via the pituitary gland
linked to emotion and reward
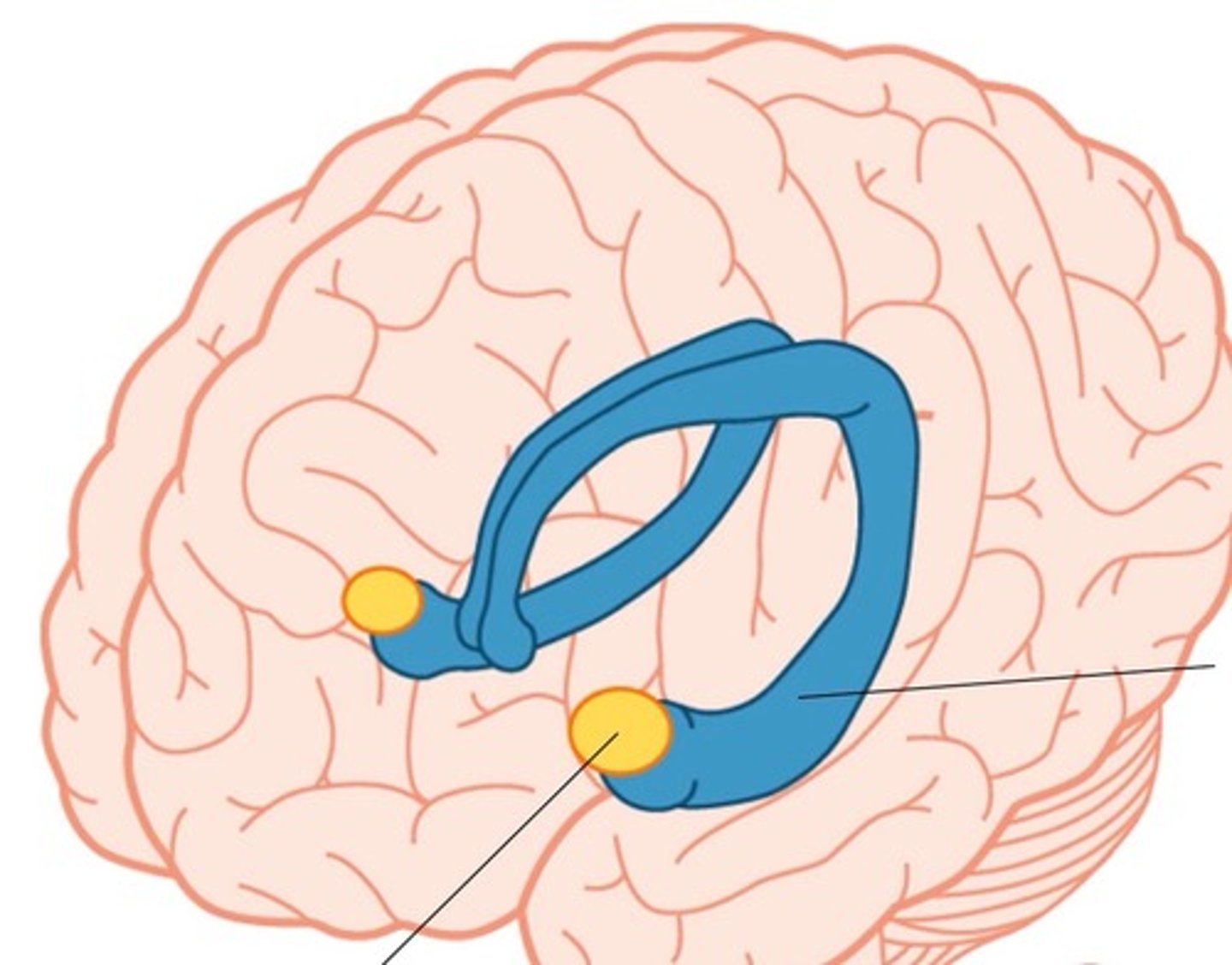
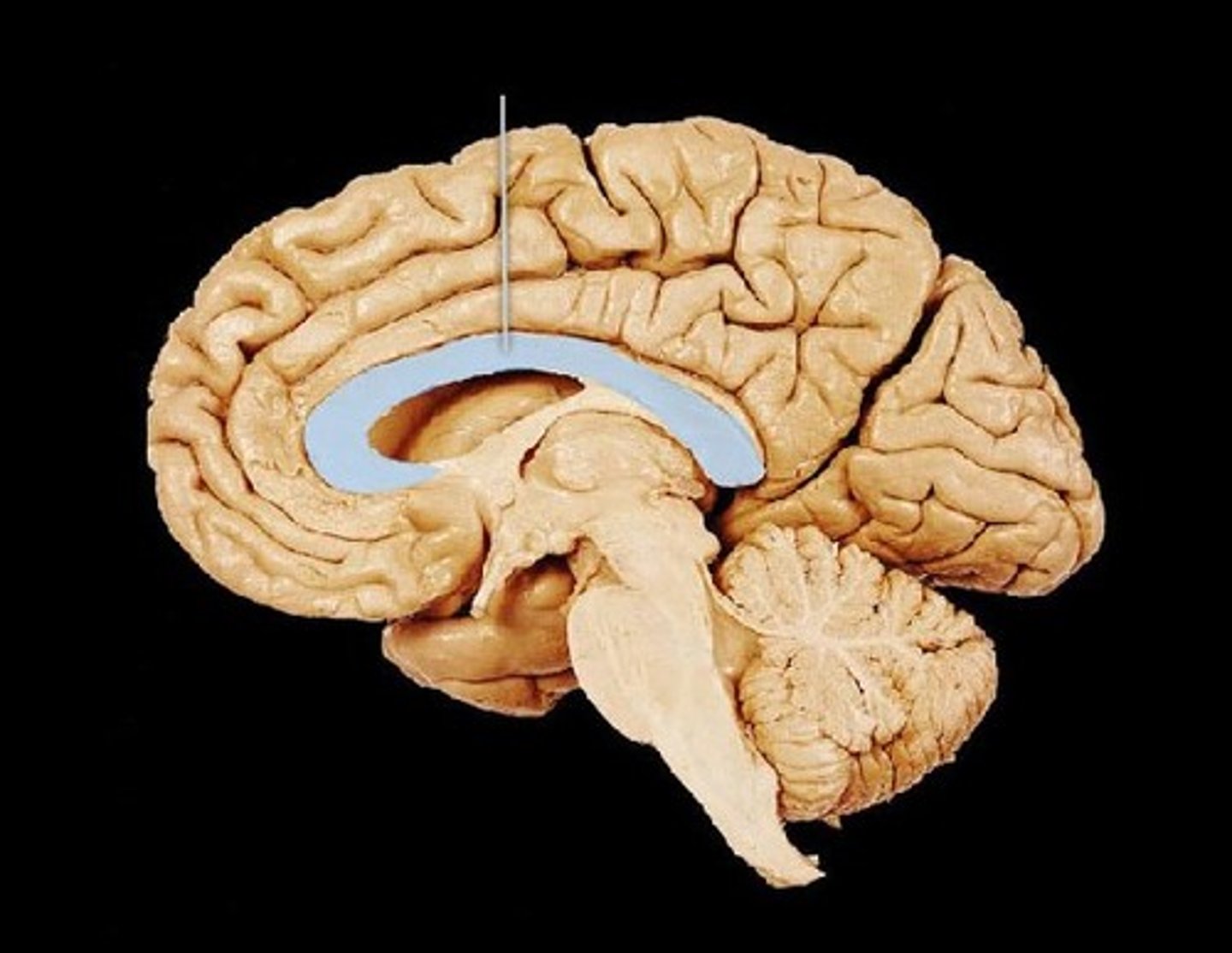
Hippocampus
small structure with two arms that wrap around the thalamus (blue in picture) - storage for conscious memories
Think of it like you have to remember how to get around a new campus
Cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres
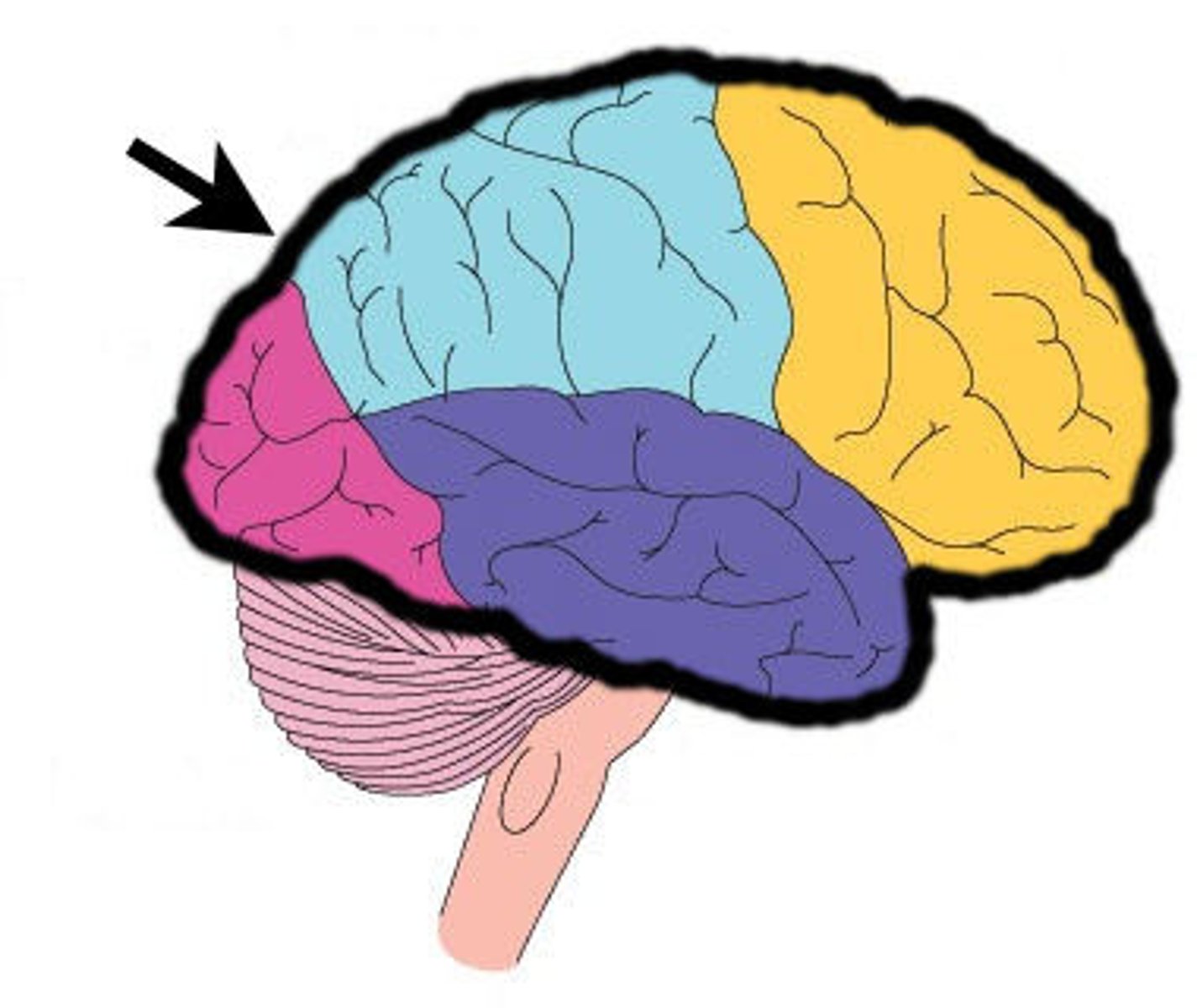
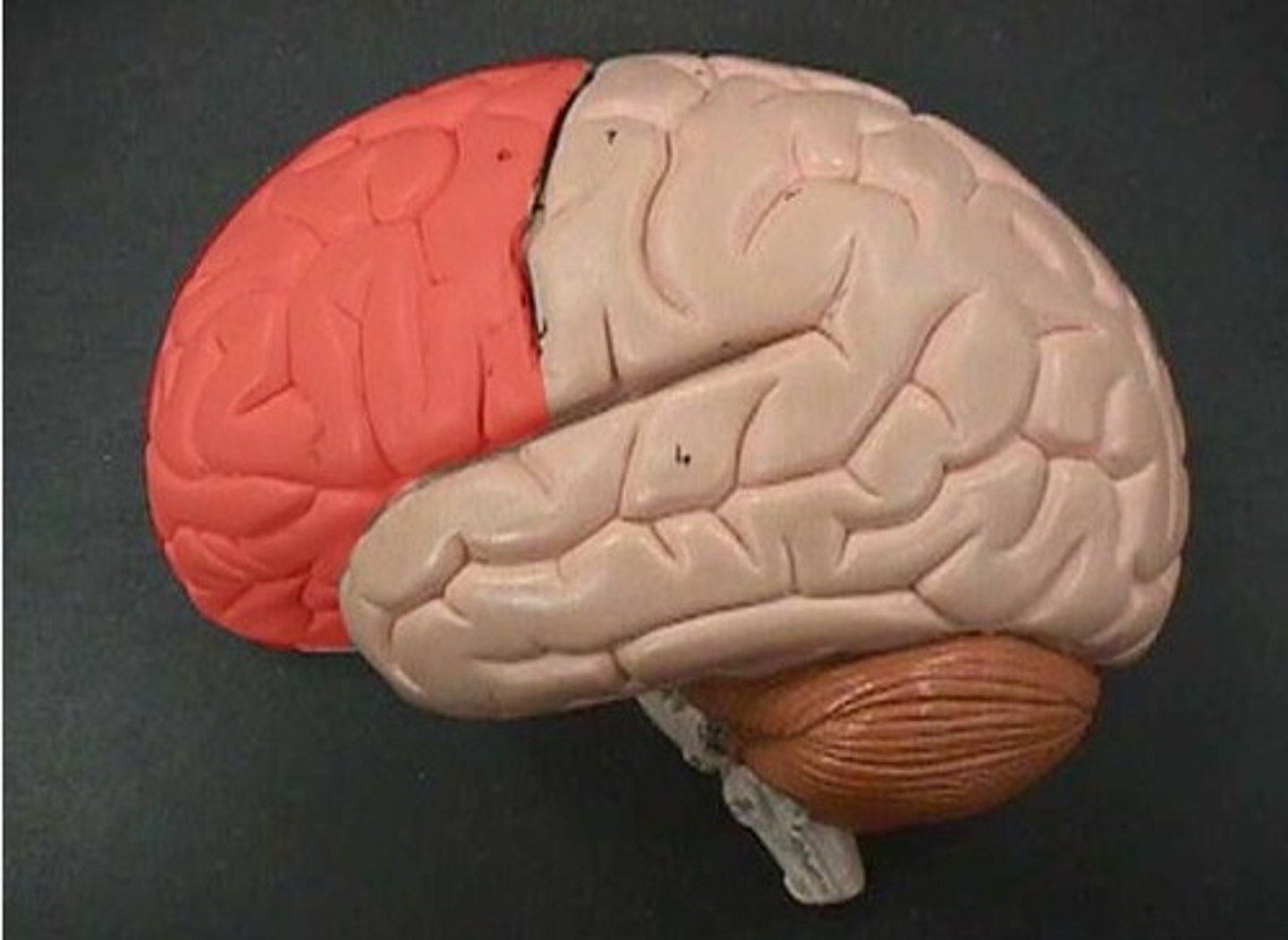
Frontal lobe
speaking, motor movement, judgement, and decision making
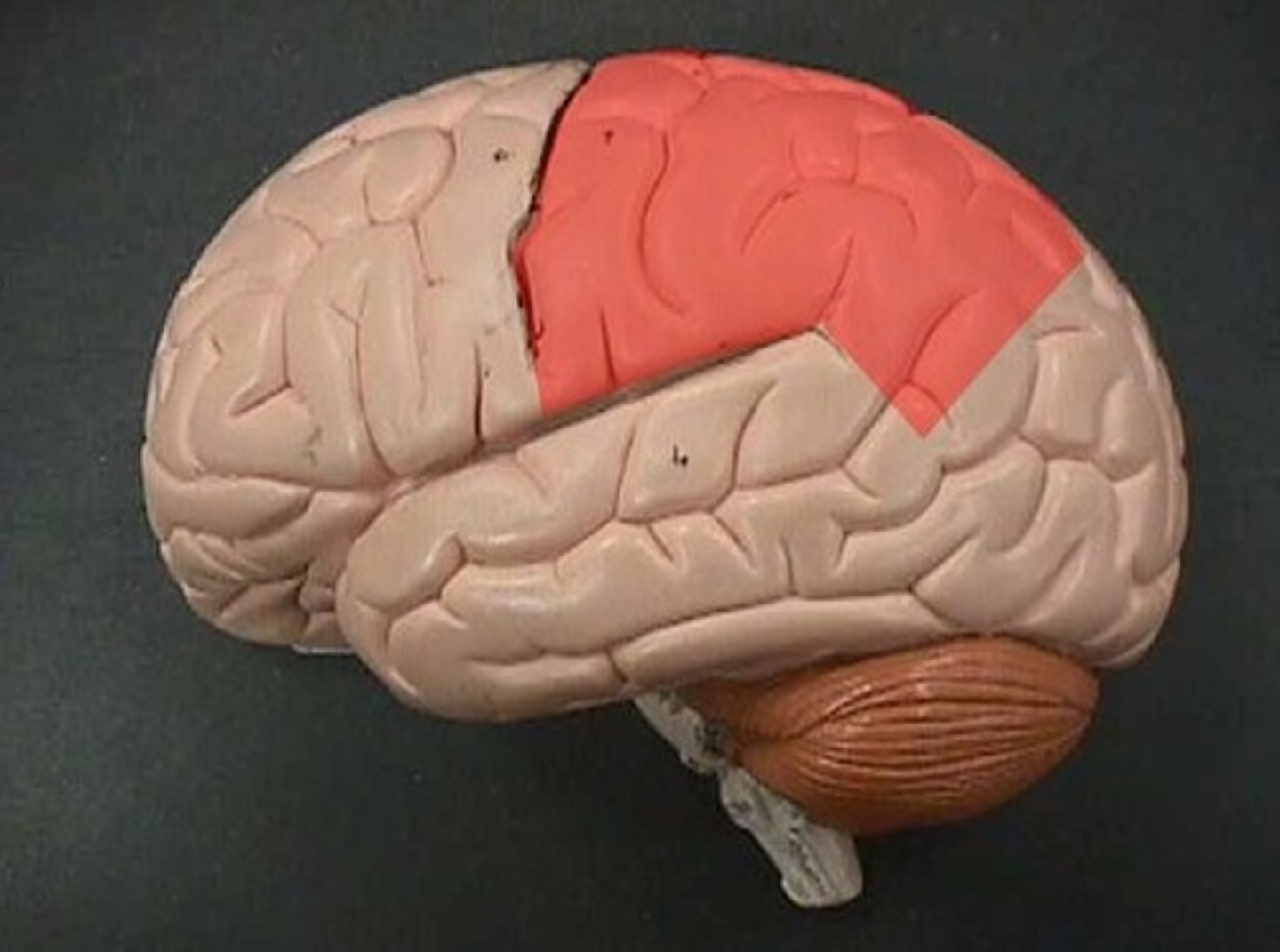
Parietal lobe
receives and processes sensory input for touch and body position
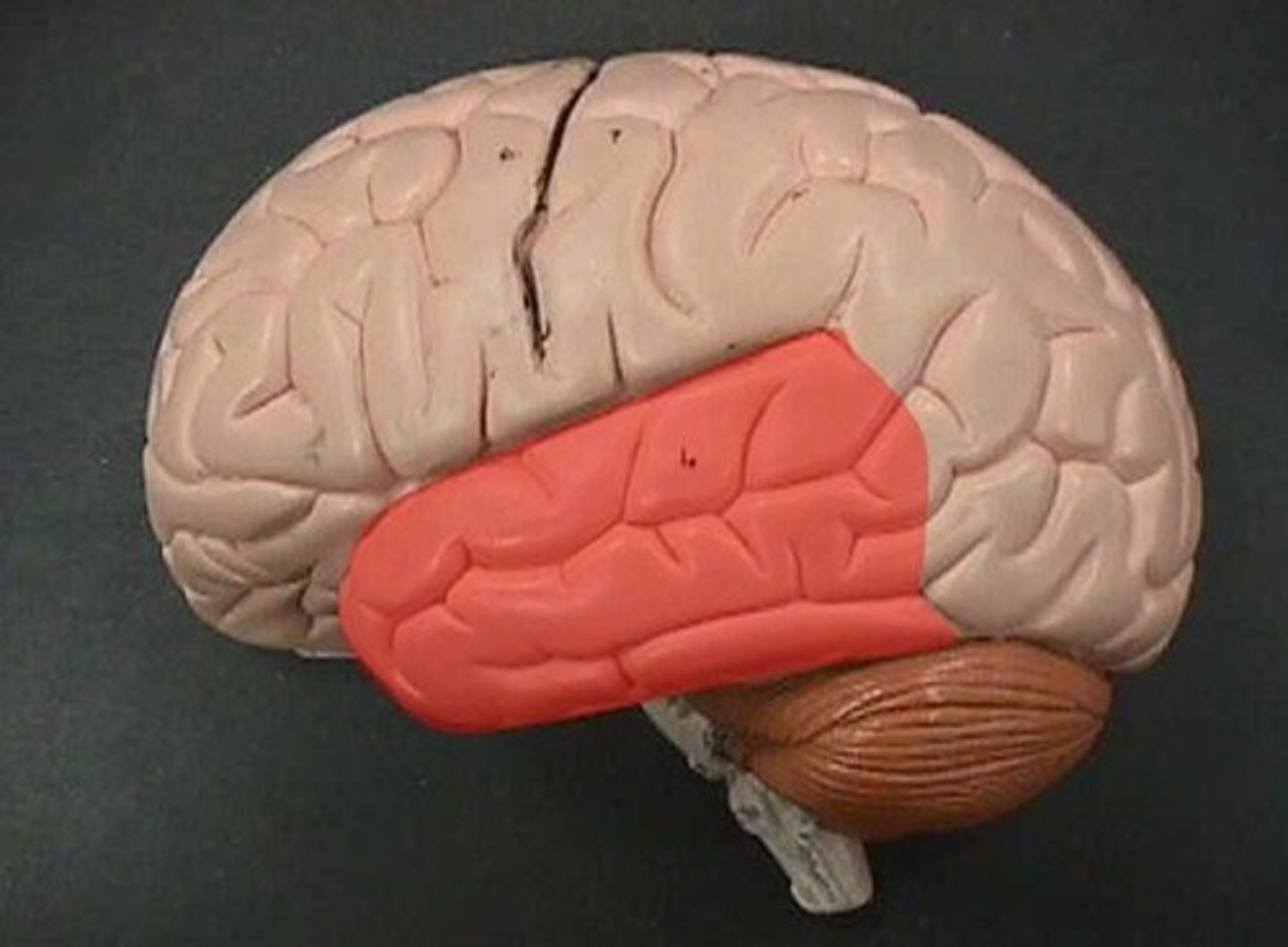
Temporal lobe
receives auditory information primarily from opposite ear
Occipital lobe
receives visual information, primarily from opposite visual field
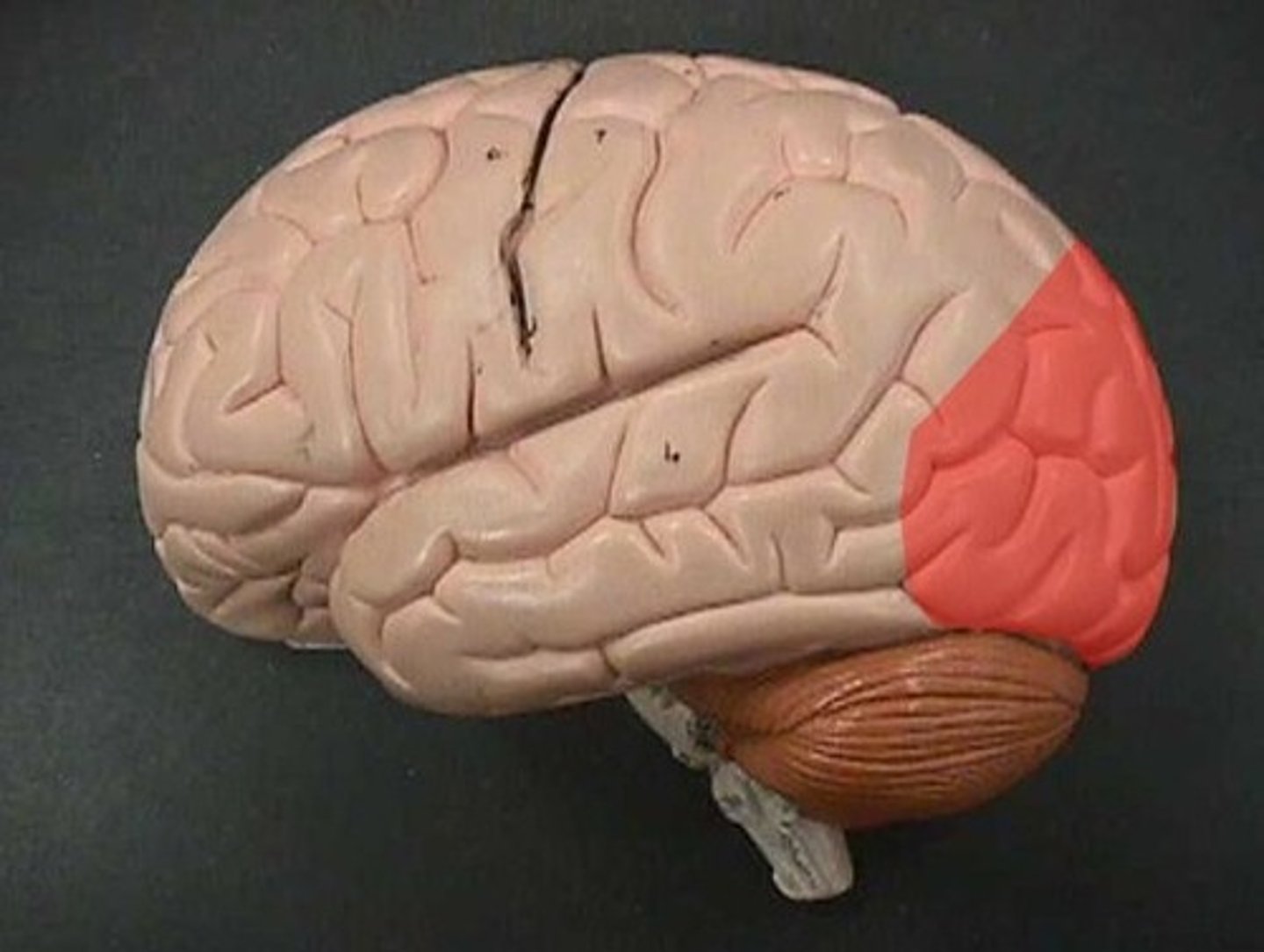
Broca's area
language center located in the left frontal lobe
involved in expressive language
if damaged, you are not able to speak
boca in Spanish means mouth
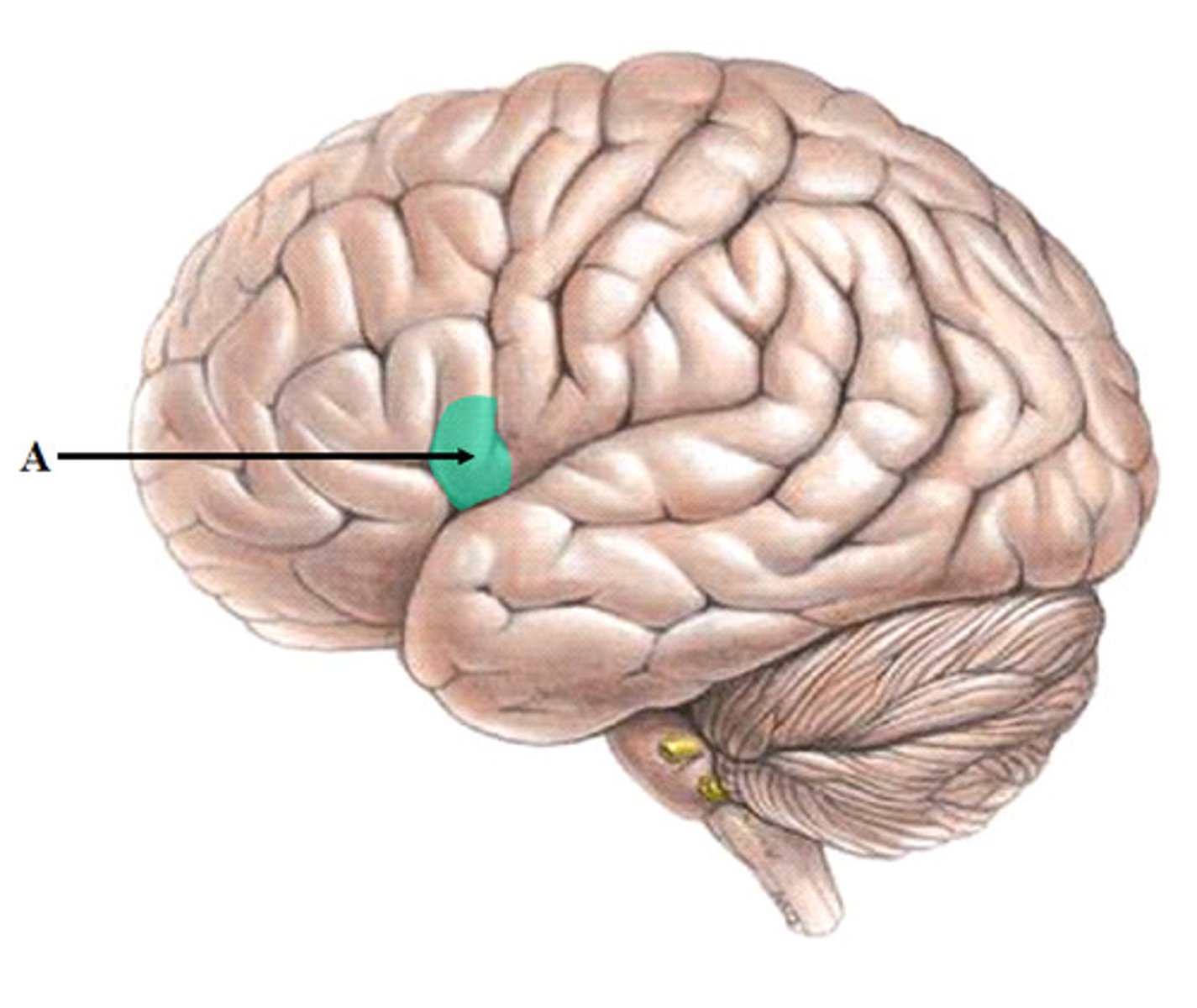
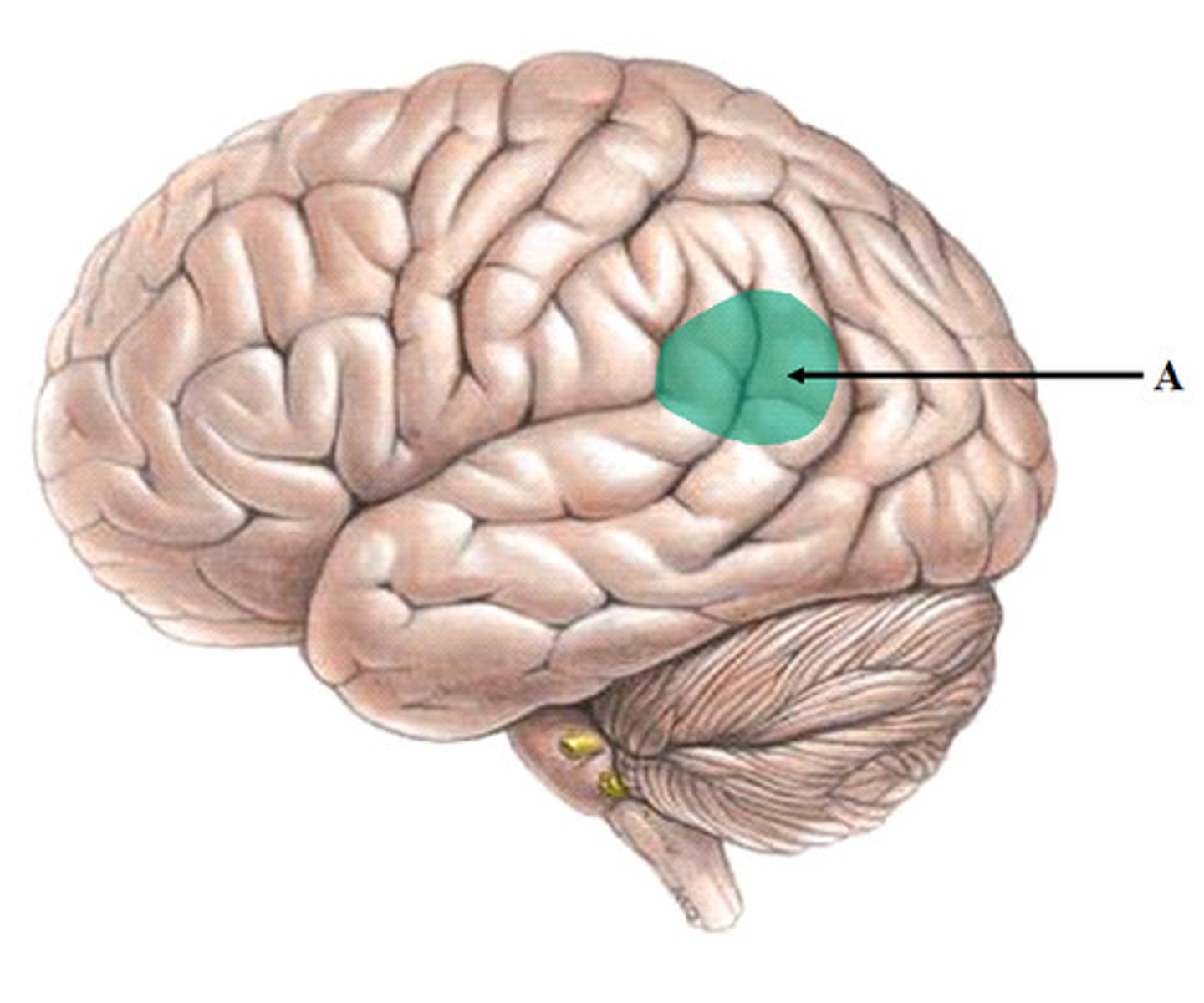
Wernicke's area
language center located in the left temporal lobe
involved in receptive language
if damaged, can lead to aphasia (inability to understand speech)
Wernicke is German and most people are not able to understand the German language
Circadian Rhythm
the 24-hour cycle of day and night - impacts sleep-wake cycles, temperature, hormonal and digestive cycles
What are the two sleep stages
Non-REM and REM
NREM (Non-REM)
non-rapid eye movement sleep
encompasses all sleep stages except for REM
REM
rapid eye movement sleep
a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occurred
Insomnia
persistent problems in either falling or staying asleep
Narcolepsy
sudden attacks of overwhelming sleepiness, usually lasting less than 5 minutes
Sleep Apnea
stop breathing during sleep
Night terrors
target mostly children who may sit up or walk around, talk incoherently, experience doubled heart and breathing rates, and appear terrified while asleep - seldom wake up during episode and recall little or nothing the next morning
occurs in NREM because you're NOT paralyzed
Cornea
eye's clear protective outer layer covering the pupil and iris
Pupil
small adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light passes
Iris
a ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil
Retina
the light sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones
Rods
retinal photoreceptors that detect black, white, and gray and are sensitive to movement
Cones
retinal photoreceptors that are concentrated near the center of the retina and function in daylight or in well-lit conditions
Blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells (rods or cones) are located there
Color blindness
one in 50 people, usually male, lack functioning red or green-sensitive cones, or sometime both