Audiology Exam 1 - Not completed yet
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Raegan
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the role of the external ear?
The external ear collects and conducts sound to the middle ear, amplifies frequencies between 2000 Hz and 4000 Hz, protects the middle ear, and aids in sound localization.
What structures make up the outer ear?
The outer ear includes the auricle (pinna), external auditory canal, and tympanic membrane.
What is the function of the tympanic membrane (TM)?
The tympanic membrane vibrates in response to sound waves, transmitting vibrations to the ossicles in the middle ear.
What are the ossicles, and what is their function?
The ossicles are the malleus, incus, and stapes, which transmit sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the inner ear.
What is the Eustachian tube's primary function?
The Eustachian tube equalizes pressure in the middle ear to atmospheric pressure and allows drainage of fluid from ME.
How does the middle ear match the impedance of the sound coming from the OE?
It matches the impedance by increased sound pressure since the stapes footplate is much smaller than the tympanic membrane, and because of the lever action since the malleus is longer than the incus.
What is the significance of the oval window?
The oval window is where the stapes footplate transmits sound vibrations into the fluid-filled inner ear.
What is the role of the stapedius muscle?
The stapedius muscle protects the inner ear by contracting in response to loud sounds and is innervated by the facial nerve (CN VII).
What are the three main sections of the inner ear?
The inner ear consists of the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
What fluid is found in the cochlea?
The cochlea contains perilymph in the scala vestibuli and scala tympani, and endolymph in the scala media.
What is the function of hair cells in the cochlea?
Hair cells in the cochlea convert sound vibrations into neural impulses that are sent to the brain.
What is the function of the round window?
The round window allows for the displacement of fluid in the cochlea, accommodating the movement caused by the stapes at the oval window.
What happens to sound pressure without the middle ear?
Without the middle ear, approximately 30 dB of sound pressure would be lost due to the change in medium from air to fluid.
What is the cone of light?
The cone of light is a reflection seen on the tympanic membrane during otoscopic examination, indicating a healthy TM.
What is the anatomy of the tympanic membrane?
The tympanic membrane has three layers: outer skin, middle fibrous connective tissue, and inner mucus membrane.
What is the significance of the pars tensa?
The pars tensa is the majority of the tympanic membrane, tightly stretched and responsible for sound transmission.
What is the anatomy of the cochlea?
The cochlea consists of a bony labyrinth and a membranous labyrinth, with structures such as the scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani.
What are the semicircular canals responsible for?
The semicircular canals are responsible for detecting rotational movements and maintaining balance.
How does sound travel through the ear?
Sound travels through the outer ear as air vibrations, is transmitted through the middle ear as mechanical vibrations, and is converted to fluid waves in the inner ear.
What is the function of the ampulla in the semicircular canals?
The ampulla contains hair cells that detect changes in head position and movement.
What is the role of the vestibule?
The vestibule is involved in balance and spatial orientation, containing structures that respond to gravity and linear acceleration.
What is the significance of the bony labyrinth?
The bony labyrinth houses the inner ear structures and protects the delicate membranous labyrinth within.
What is the function of the scala media?
The scala media contains endolymph and is where the organ of Corti, containing hair cells, is located.
What is the function of the organ of Corti?
The organ of Corti is responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals for the auditory nerve.
What are the three scalae of the cochlea?
Scala Vestibuli, Scala Media, and Scala Tympani.
What fluid fills the Scala Vestibuli?
Perilymph.
What fluid fills the Scala Media?
Endolymph.
What is the role of the tectorial membrane in the cochlea?
It hovers over the organ of Corti and interacts with hair cells during sound transduction.
What is the function of the stria vascularis?
It provides oxygen and nutrients to the cochlea.
What is the tonotopic organization of the cochlea?
High-frequency sounds are processed at the base, while low-frequency sounds are processed at the apex.
What happens to the perilymph when the stapes rocks in at the oval window?
It is displaced from the scala vestibuli to the scala tympani, causing the round window to bulge outward.
What is the traveling wave in the cochlea?
A wave that increases in amplitude as it moves from the base to the apex along the basilar membrane.
What is the role of the cochlear nucleus in the auditory pathway?
It is the first synapse point for all 8th nerve fibers.
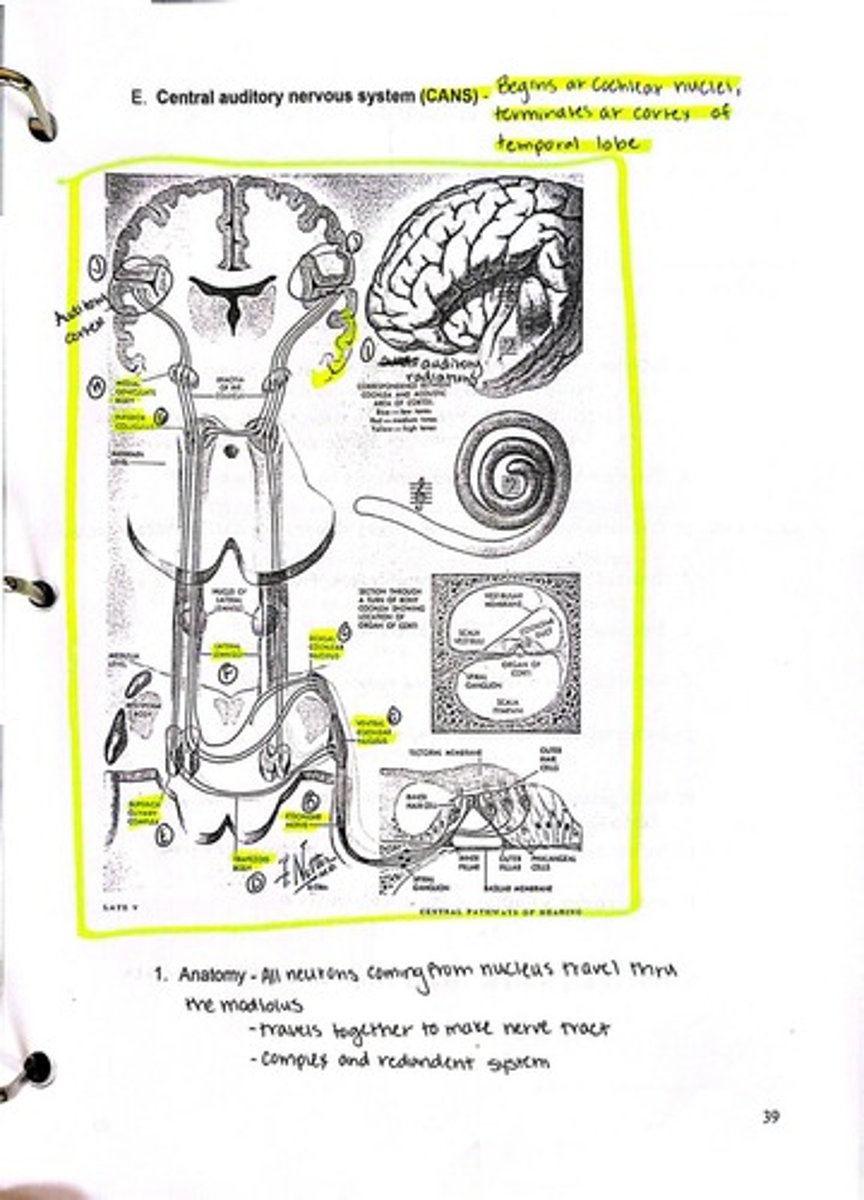
What are the two functions of the superior olivary complex (SOC)?
Localizing sound source by time and intensity, and reflexively stimulating the stapedius muscle.
What is the pathway of the first order neuron in the auditory system?
From the cochlea to the ipsilateral cochlear nucleus.
What is the role of the inferior colliculus in the auditory pathway?
It serves as another neural center and crossover point for auditory signals.
What is the final destination of auditory signals in the brain?
The auditory cortex located in the superior temporal gyrus.
What is the function of the efferent system in the auditory pathway?
It carries information from the cortex to the cochlea, providing an inhibitory effect on background noise.
What is the significance of the modiolus in the cochlea?
It is a bony structure through which the 8th nerve and spiral ganglion cells travel.
What is the function of the basilar membrane?
It supports the organ of Corti and plays a crucial role in sound wave transduction.
What is the role of hair cells in the cochlea?
They convert mechanical vibrations into electrical impulses.
What is the difference between inner and outer hair cells?
Inner hair cells are not embedded in the tectorial membrane, while outer hair cells are.
What is the significance of the cochlear duct?
It contains the scala media and is filled with endolymph.
What is the role of the auditory radiations?
They are pathways that transmit auditory information from the medial geniculate body to the auditory cortex.
What happens during the shearing action of the stereocilia on hair cells?
It elicits a chemical release at the cell base, triggering neural impulses.
What is the cochlear portion of the 8th nerve responsible for?
It transmits auditory information from the cochlea to the brain.
What is the significance of the vestibular membrane?
It separates the scala media from the scala vestibuli.
What is the role of the axon in a neuron?
It sends signals to the next neuron in the pathway.
What is the function of synapses in the auditory pathway?
They are spaces between neurons where signals are transmitted.
What is the role of the lateral lemniscus?
It is a pathway through the brainstem for auditory nerve fibers.