8.1 Cranial Nerve Examination
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
What tests are used for vision and light reflex?
Tracking object - assessing that the animal can see
Menace response - for vision assessment but the pathway involves other areas of brain and facial nerve
Pupillary light reflex (PLR) - reflex to bright light. useful for localising blindness
Menace response - for vision assessment but the pathway involves other areas of brain and facial nerve
Pupillary light reflex (PLR) - reflex to bright light. useful for localising blindness
2
New cards
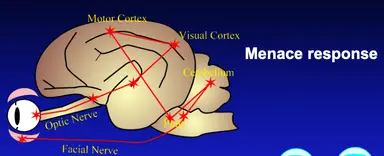
What is the nervous pathway for the menace response?
Optic nerve
Optic chiasm
Relays through thalamus and then up to visual cortex
Motor cortex
Pons
Cerebellum
Facial nerve - eye closes
Learned response - animal needs to be mature enough to close eye in response to object
Optic chiasm
Relays through thalamus and then up to visual cortex
Motor cortex
Pons
Cerebellum
Facial nerve - eye closes
Learned response - animal needs to be mature enough to close eye in response to object
3
New cards
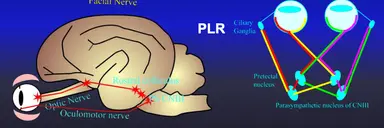
What is the nervous pathway for the pupillary light reflex (PLR)?
Response to light
Light goes through optic nerve to optic chiasm
Relays through rostral colliculus
PS CNIII
Oculomotor nerve
Light goes through optic nerve to optic chiasm
Relays through rostral colliculus
PS CNIII
Oculomotor nerve
4
New cards
How will PLR be different in an animal if they have an optic nerve lesion?
Pupil won’t constrict when light shines
Reflex to light unable to pass
Reflex to light unable to pass
5
New cards
How can we use PLR to determine a central lesion?
No menace response - assume eye, optic nerve and optic chiasm are functioning normally
Eyes remain dilated - pupil unable to respond to light
Eyes remain dilated - pupil unable to respond to light
6
New cards
What are symptoms cerebellar disease?
Animal gait
Bobbing of head - common tremor in cerebellar disease
Bobbing of head - common tremor in cerebellar disease
7
New cards
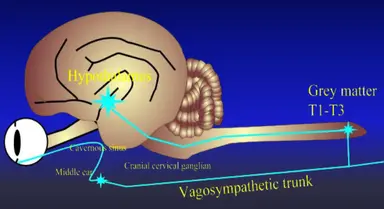
What is Horner syndrome? What can cause it?
Collection of signs:
Miosis (constricted pupil)
3rd eyelid protrusion
Sunken globe
Narrowed palpebral aperture
Due to damage to sympathetic supply to eye
Lesion in PLR pathway
Miosis (constricted pupil)
3rd eyelid protrusion
Sunken globe
Narrowed palpebral aperture
Due to damage to sympathetic supply to eye
Lesion in PLR pathway
8
New cards
What is the phenylepinephrine test?
Used for Horner syndrome
Lack of sympathetic supply to eye
Add epinephrine can reverse Horner syndrome
Result - dilation of eye. other eye not affected
Closer to the eye the lesion is, the more quickly the eye will respond to epinephrine
Lack of sympathetic supply to eye
Add epinephrine can reverse Horner syndrome
Result - dilation of eye. other eye not affected
Closer to the eye the lesion is, the more quickly the eye will respond to epinephrine
9
New cards
What is nystagmus?
Rhythmical, repetitive movement of the eye
Eyes should be able to retain position centrally in head
Physiological, spontaneous, positional
Can indicate vestibular syndrome if not physiological- keep eyes central in body
Eyes should be able to retain position centrally in head
Physiological, spontaneous, positional
Can indicate vestibular syndrome if not physiological- keep eyes central in body
10
New cards
What is strabismus?
Both eyes dont line up in the same direction
Combatant, vestibular
Combatant, vestibular
11
New cards
What is hydrocephalous?
Skull failed to fuse as brain has been expanding
12
New cards
What is lateral strabismus?
Occular motor nerve innervates: medial, dorsal, rectal and ventral oblique muscles
Lateral - ends up dominant as not controlled by occular motor neuron
Deviation of eye laterally as muscle pulling eye laterally
Lateral - ends up dominant as not controlled by occular motor neuron
Deviation of eye laterally as muscle pulling eye laterally
13
New cards
What is trochlear nerve palsy?
Trochlear nerve - twists the eye ball
Noticeable in animals that dont have round pupil e.g horse, ruminants, cats
Deviation of eyeball
May have compensatory head tilt to opposite side
Noticeable in animals that dont have round pupil e.g horse, ruminants, cats
Deviation of eyeball
May have compensatory head tilt to opposite side
14
New cards
What is medial strabismus?
Due to problem with cranial nerve VI
CN VI innervates lateral rectus
Eyeball pulled medially
CN VI innervates lateral rectus
Eyeball pulled medially
15
New cards
What is vestibular strabismus?
Lift head up and pupil deviates downwards
16
New cards
What is extraocular muscle weakness?
Autoimmune disease of extraocular muscle
Eyes disappear into head
Severe weakness and eyes deviated down
Responds to steroids
Eyes disappear into head
Severe weakness and eyes deviated down
Responds to steroids
17
New cards
How can we assess facial sensation?
Trigeminal nerve
Palpebral reflex
Corneal reflex
Sensation head (ear, lip, nose)
Assessing cranial nerve V-VII
Facial sensation - trigeminal nerve
Facial movement - facial nerve
Palpebral reflex
Corneal reflex
Sensation head (ear, lip, nose)
Assessing cranial nerve V-VII
Facial sensation - trigeminal nerve
Facial movement - facial nerve
18
New cards
What muscles are in the head?
Masticatory muscles:
Temporal muscle mass
Jaw tone - opening mouth
Innervated by trigeminal nerve
Temporal muscle mass
Jaw tone - opening mouth
Innervated by trigeminal nerve
19
New cards
What is bilateral trigeminal palsy?
Difficulty closing jaw - trigeminal nerve
Dysphagia - swelling problems as unable to close jaw
Dysphagia - swelling problems as unable to close jaw
20
New cards
How can we assess facial muscles?
Innervated by facial nerve
Palpebral reflex
Corneal reflex
Menace response
Facial symmetry
Palpebral reflex
Corneal reflex
Menace response
Facial symmetry
21
New cards
What nerve control facial functions?
Swallowing/gag reflex - CNIX and X
Oesophageal function/regurgitation - CNX
Vocalisation - CNX
Tongue movement - CNXII
Oesophageal function/regurgitation - CNX
Vocalisation - CNX
Tongue movement - CNXII
22
New cards
What can an inability to swallow indicate?
Glossopharyngeal or vagus nerve
CN nuclei in medulla
Neuromuscular diseases:
Polymyositis, myasthenia gravis, hereditary myopathies
CN nuclei in medulla
Neuromuscular diseases:
Polymyositis, myasthenia gravis, hereditary myopathies