AP Micro Unit 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
The Four Factors of Production
( 1 ) Land
( 2 ) Labor
( 3 ) Capital
( 4 ) Entrepreneurship
( 2 ) Labor
( 3 ) Capital
( 4 ) Entrepreneurship
2
New cards
Land
all natural resources that are used to produce goods and services
3
New cards
Labor
any effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid
4
New cards
Capital
Physical Capital: any human-made resource that is used to create other goods and service
Human Capital: any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience
Human Capital: any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience
5
New cards
Entrepreneurship
ambitious leaders that combine the other factors of production to create goods and services
6
New cards
Factor Prices (Factor Payments)
payments made for the use of the factors of production
( 1 ) Land is paid RENT
( 2 ) Labor is paid WAGE
( 3 ) Capital is paid INTEREST
( 4 ) Entrepreneurs are paid PROFIT
( 1 ) Land is paid RENT
( 2 ) Labor is paid WAGE
( 3 ) Capital is paid INTEREST
( 4 ) Entrepreneurs are paid PROFIT
7
New cards
What is Demand for Labor?
→ demand is the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages
→ there is an INVERSE relationship between wage and quantity of labor demanded
→ there is an INVERSE relationship between wage and quantity of labor demanded
8
New cards
What is Supply for Labor?
→ supply is the different quantities of individuals that are willing and able to sell their labor at different wages
→ there is a DIRECT (or positive) relationship between wage and quantity of labor supplied
→ workers have trade-off between work and leisure
→ there is a DIRECT (or positive) relationship between wage and quantity of labor supplied
→ workers have trade-off between work and leisure
9
New cards
Minimum Wage
a minimum amount employers are allowed to pay their workers → it’s a wage floor
10
New cards
Is increasing minimum wage good or bad?
Good Idea: we don’t want poor people living in the street, so we should make sure they have enough to live on
Bad Idea: increasing minimum wage too much leads to more unemployment and higher prices
Bad Idea: increasing minimum wage too much leads to more unemployment and higher prices
11
New cards
Marginal Resource Cost (MRC)
→ the additional cost of an additional resource (worker)
→ in perfectly competitive labor markets the MRC equals the wage set by the market and is constant
MRC = change in total cost / change in inputs
→ in perfectly competitive labor markets the MRC equals the wage set by the market and is constant
MRC = change in total cost / change in inputs
12
New cards
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
→ the additional revenue generated by an additional worker (resource)
→ in perfectly competitive product markets the MRP equals the marginal product of the resource times the price of the product
MRP = change in total revenue / change in inputs
→ in perfectly competitive product markets the MRP equals the marginal product of the resource times the price of the product
MRP = change in total revenue / change in inputs
13
New cards
Labor Market Imperfections
→ insufficient/misleading job information
* this prevents workers from seeking better employment
→ geographical immobility
* many people are reluctant or too poor to move so they accept a lower wage
→ unions
* collective bargaining and threats to strike often lead to higher than equilibrium wage
→ wage discrimination
* some people get paid differently for doing the same job based on race or gender (very illegal!)
* this prevents workers from seeking better employment
→ geographical immobility
* many people are reluctant or too poor to move so they accept a lower wage
→ unions
* collective bargaining and threats to strike often lead to higher than equilibrium wage
→ wage discrimination
* some people get paid differently for doing the same job based on race or gender (very illegal!)
14
New cards
What shifts the demand for labor?
( 1 ) Price of the output
→ if the price of the output goes up, the worker that produces the product becomes more valuable
( 2 ) Productivity of the worker
→ a more productive worker is more valuable to a business
( 3 ) Change in the price of other resources
→ substitute resources & complementary resources
→ if the price of the output goes up, the worker that produces the product becomes more valuable
( 2 ) Productivity of the worker
→ a more productive worker is more valuable to a business
( 3 ) Change in the price of other resources
→ substitute resources & complementary resources
15
New cards
What shifts the supply of labor?
( 1 ) Education and training
( 2 ) Availability of alternative options
( 3 ) Immigration and mobility of workers
( 4 ) Cultural expectations
( 5 ) Working conditions
( 6 ) Preferences for leisure
( 2 ) Availability of alternative options
( 3 ) Immigration and mobility of workers
( 4 ) Cultural expectations
( 5 ) Working conditions
( 6 ) Preferences for leisure
16
New cards
Derived Demand
the demand for resources is derived (determined) by the products they produce
17
New cards
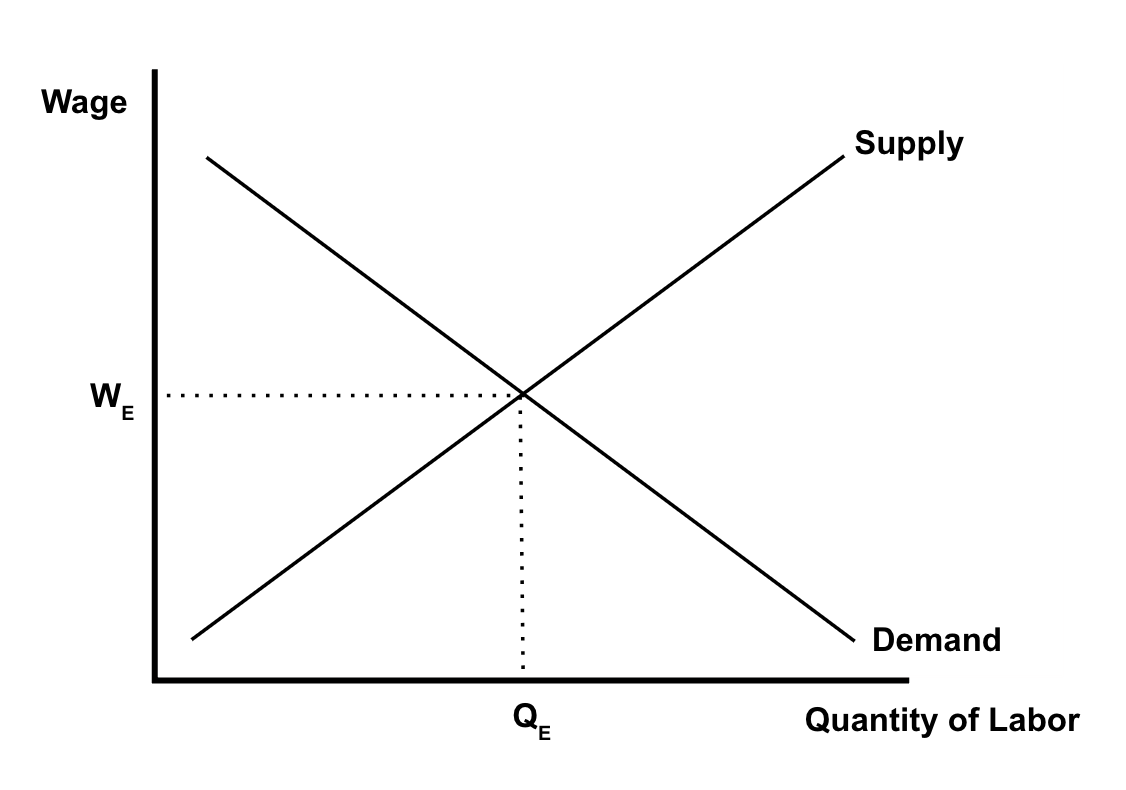
Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics
→ many small firms are hiring workers
* no one firm is large is large enough to manipulate the market
→ many workers with identical skills
→ wage is constant
→ workers are wage takers
* firms can hire as many workers as they want at a wage set by the industry
* no one firm is large is large enough to manipulate the market
→ many workers with identical skills
→ wage is constant
→ workers are wage takers
* firms can hire as many workers as they want at a wage set by the industry
18
New cards
How do you know how many resources (workers) to employ?
continue to hire until MRP = MRC
19
New cards
Profit Maximizing Rule for Combining Resources
MRPx/MRCx = MRPy/MRCy = 1
this means that the firm is hiring where MRP = MRC for each resource x and y
this means that the firm is hiring where MRP = MRC for each resource x and y
20
New cards
Least Cost Rule
MPx/Px = MPy/Py
21
New cards
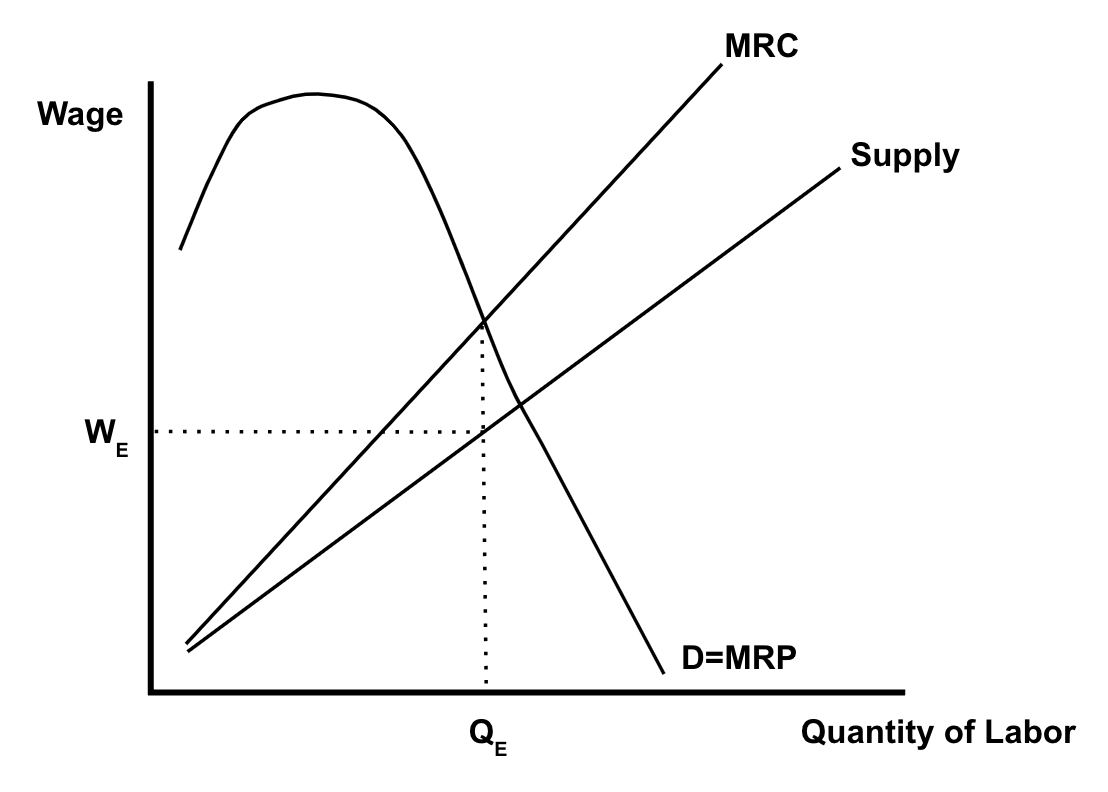
Imperfect Competition (Monopsony) Characteristics
→ one firm hiring workers
* the firm is large enough to manipulate the market
→ workers are relatively immobile
→ firm is wage maker
* to hire additional workers the firm must increase the wage
* the firm is large enough to manipulate the market
→ workers are relatively immobile
→ firm is wage maker
* to hire additional workers the firm must increase the wage
22
New cards
What is the difference between the product market and factor market?
product market is where good/services are sold by businesses and factor market is where factors of production (labor) are sold by households to businesses
23
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Graph
24
New cards
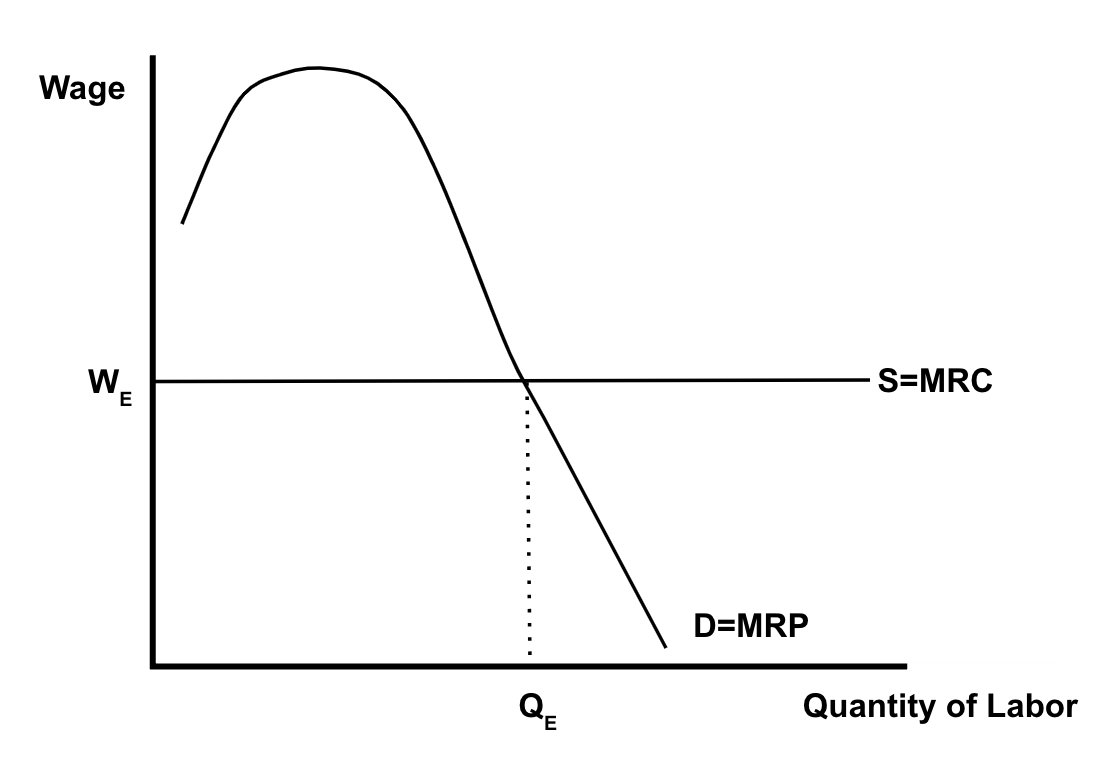
Perfectly Competitive Labor Firm Graph
25
New cards
Monopsony Graph