Psych Ch. 4-6
5.0(2)Studied by 13 people
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:23 PM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Issues of Developmental Psychologists
Nature v.s. Nurture
Continuity v.s. Stages
Stability v.s. Change
Continuity v.s. Stages
Stability v.s. Change
2
New cards
Temperament
A person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
3
New cards
Assimilation
Interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing concepts & understandings (schemas)
4
New cards
Accomodation
Adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
5
New cards
Object Permanence
Understanding that items and people still exist even when you can't see or hear them. Discovered by Jean Piaget
6
New cards
Conservation
The principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects. Piaget believed this to be a part of concrete operational reasoning
7
New cards
Egocentrism
In Piaget’s theory, the preoperational child’s difficulty taking another’s point of view
8
New cards
Attachment
An emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation
9
New cards
Social Identity
The “we” aspect of our self-concept; the part of our answer to “Who am I?” that comes from our group memberships
10
New cards
Identity
Our sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent’s task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles
11
New cards
Intimacy
In Erikson’s theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental task in young adulthood
12
New cards
Emerging Adulthood
A period from about age 18 to the mid-twenties, when many in Western cultures are no longer adolescents but have not yet achieved full independence as adults
13
New cards
Erikson’s Adulthood Stages
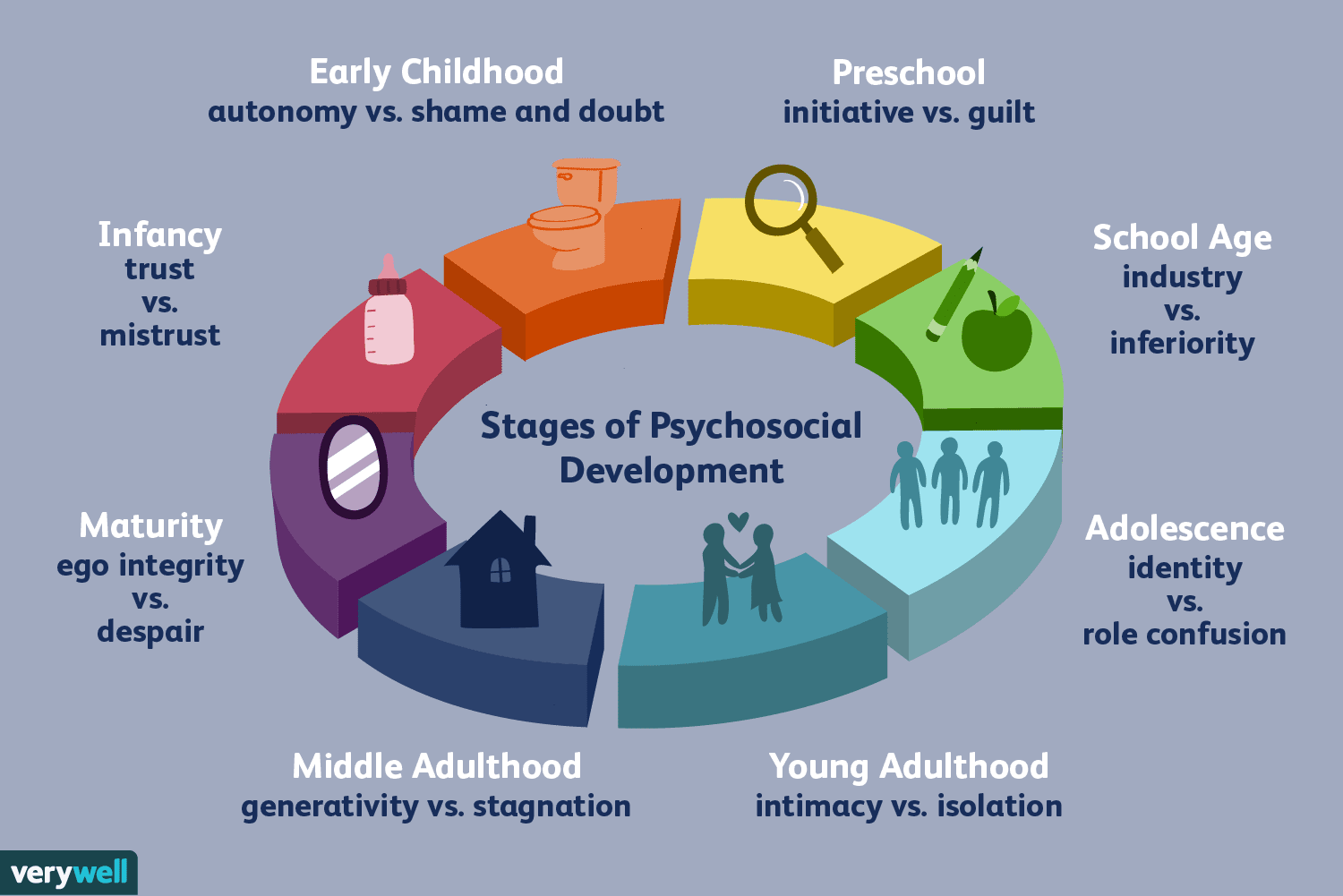
14
New cards
Piaget’s
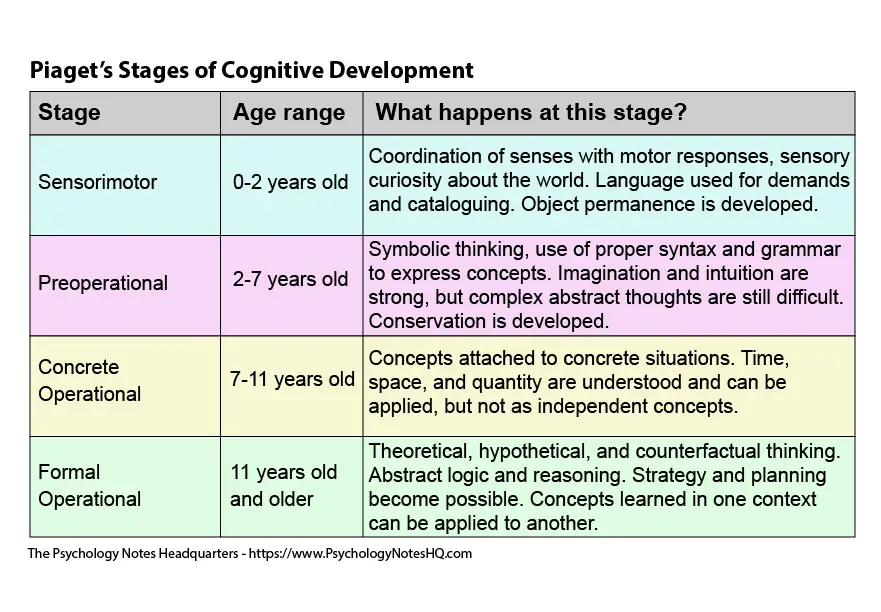
15
New cards
Social Clock
The culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
16
New cards
Menopause
The time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce
17
New cards
Sex
In psychology, the biologically influenced characteristics by which people define *males* and *females*
18
New cards
Gender
In psychology, the socially influenced characteristics by which people define *men* and *women*
19
New cards
Primary Sex Characteristics
The body structures (such as ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
20
New cards
Secondary Sex Characteristics
Non-reproductive sexual traits, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
21
New cards
Spermache
First ejaculation
22
New cards
Menarche
The first menstrual period
23
New cards
Role
A set of expectations about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave
24
New cards
Gender Role
A set of expected behaviors, attitudes, and traits for males or for females
25
New cards
Gender Identity
Our sense of being male, female, or some combination of the two
26
New cards
Asexual
Having no sexual attraction to others
27
New cards
Sexual Response Cycle
The four stages of sexual responding described by Masters and Johnson - excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution
28
New cards
Sexual Dysfunction
A problem that consistently impairs sexual arousal or function
29
New cards
Sexual Orientation
An enduring sexual attraction toward member’s of one’s own sex (homosexual), the other sex (heterosexual), or both sexes (bisexual)
30
New cards
Social Script
Culturally modeled guide for how to act in various situations
31
New cards
Factors Influencing Teenager Sexual Behavior
* Minimal communication about birth control
* Guilt related to sexual
* Alcohol Use
* Mass media norms of unprotected promiscuity
* Guilt related to sexual
* Alcohol Use
* Mass media norms of unprotected promiscuity
32
New cards
Sensation
The process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
33
New cards
Perception
The process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
34
New cards
Bottom-up Processing
Analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information
35
New cards
Top-down Processing
Information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
36
New cards
Absolute Threshold
The minimum stimulus energy needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
37
New cards
Difference Threshold
The minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time. We experience the difference threshold as a *just noticeable difference*
38
New cards
Subliminal
Below one’s absolute threshold for conscious awareness
39
New cards
Parallel Processing
The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain’s natural mode of information processing for many functions
40
New cards
Visual Cliff
A laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
41
New cards
Perceptual Constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change
42
New cards
Perceptual Adaptation
The ability to adjust to changed sensory input, including an artificially displaced or even inverted visual field
43
New cards
Gestalt
An organized whole. Gestalt psychologists emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces f information into meaningful wholes
44
New cards
Frequency
The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
45
New cards
Pitch
A tone’s experienced highness or lowness; depends on frequency
46
New cards
Hypnosis
A social interaction in which one person (hypnotist) suggests to another (subject) that certain perceptions, feelings, thoughts, or behaviors will spontaneously occur
47
New cards
Parapsychology
The study of paranormal phenomena, including ESP and psychokinesis
48
New cards
Dissociation
A split in consciousness, which allows some thoughts and behaviors to occur simultaneously with others