Respiratory System
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Human respiratory system
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting of the trachea, bronchi, alveoli and lungs
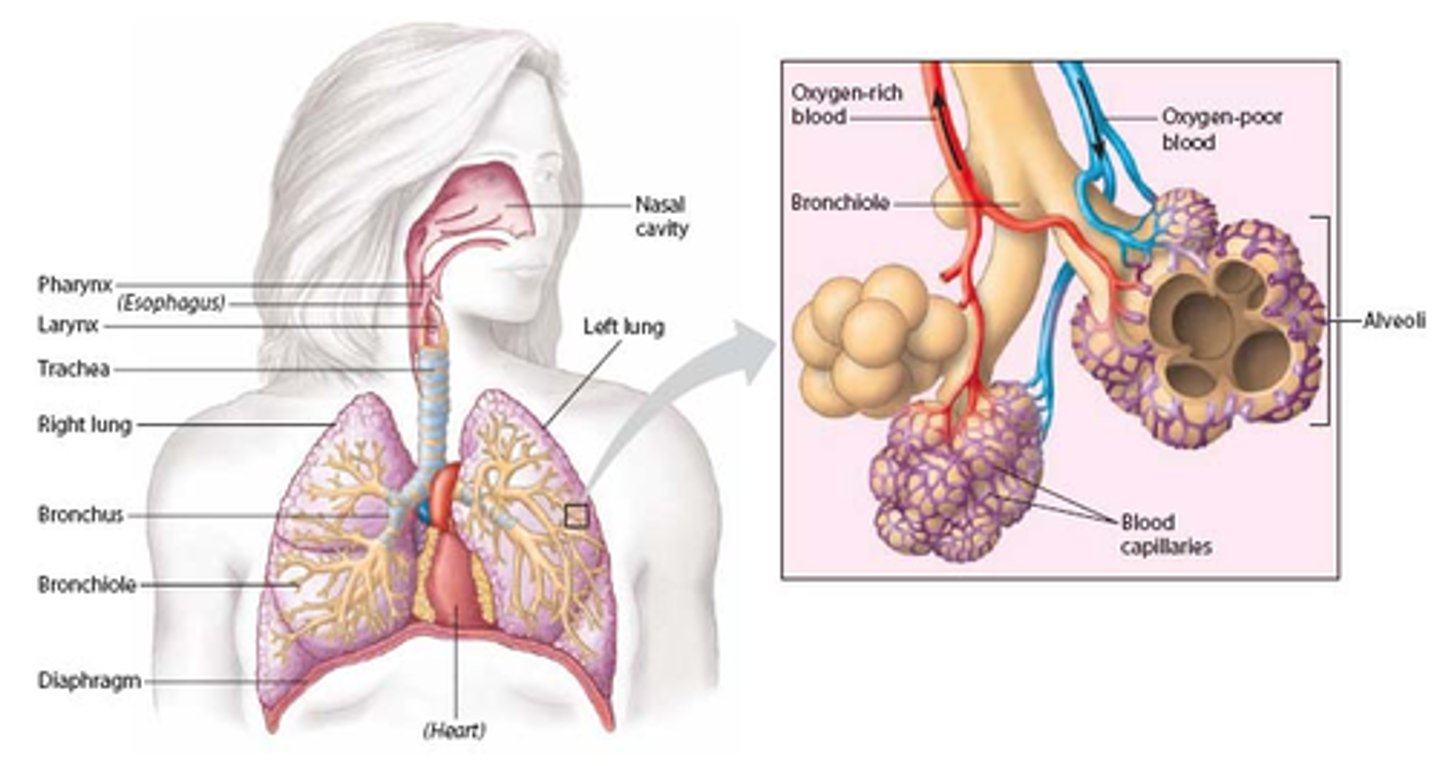
Need for a respiratory system
Large organisms require a complex respiratory system in order to obtain a sufficient volume of oxygen to maintain a high level of aerobic respiration and to remove an equivalent volume of waste carbon dioxide
Gaseous exchange
The process where oxygen is taken in and exchanged for carbon dioxide which is a waste product of respiration
Sites of gas exchange
The alveoli of the lungs and respiring cells around the body
Oxygen
A gas that is needed for aerobic respiration to release energy, oxygen is transported into the body by the respiratory system and around the body by the circulatory system
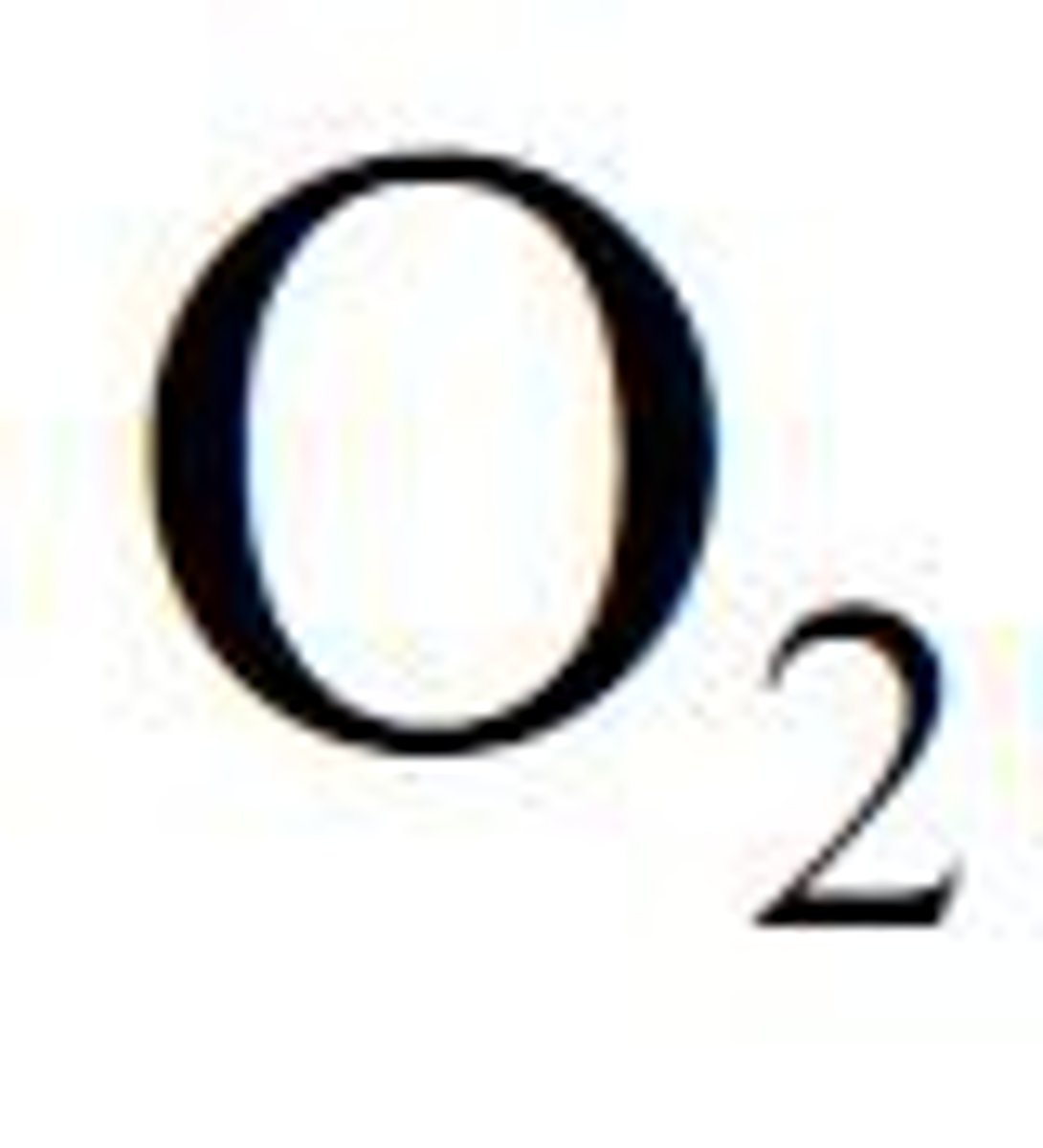
Carbon dioxide
A waste product of respiration that needs to be removed from cells via the blood and removed from the body via the respiratory system

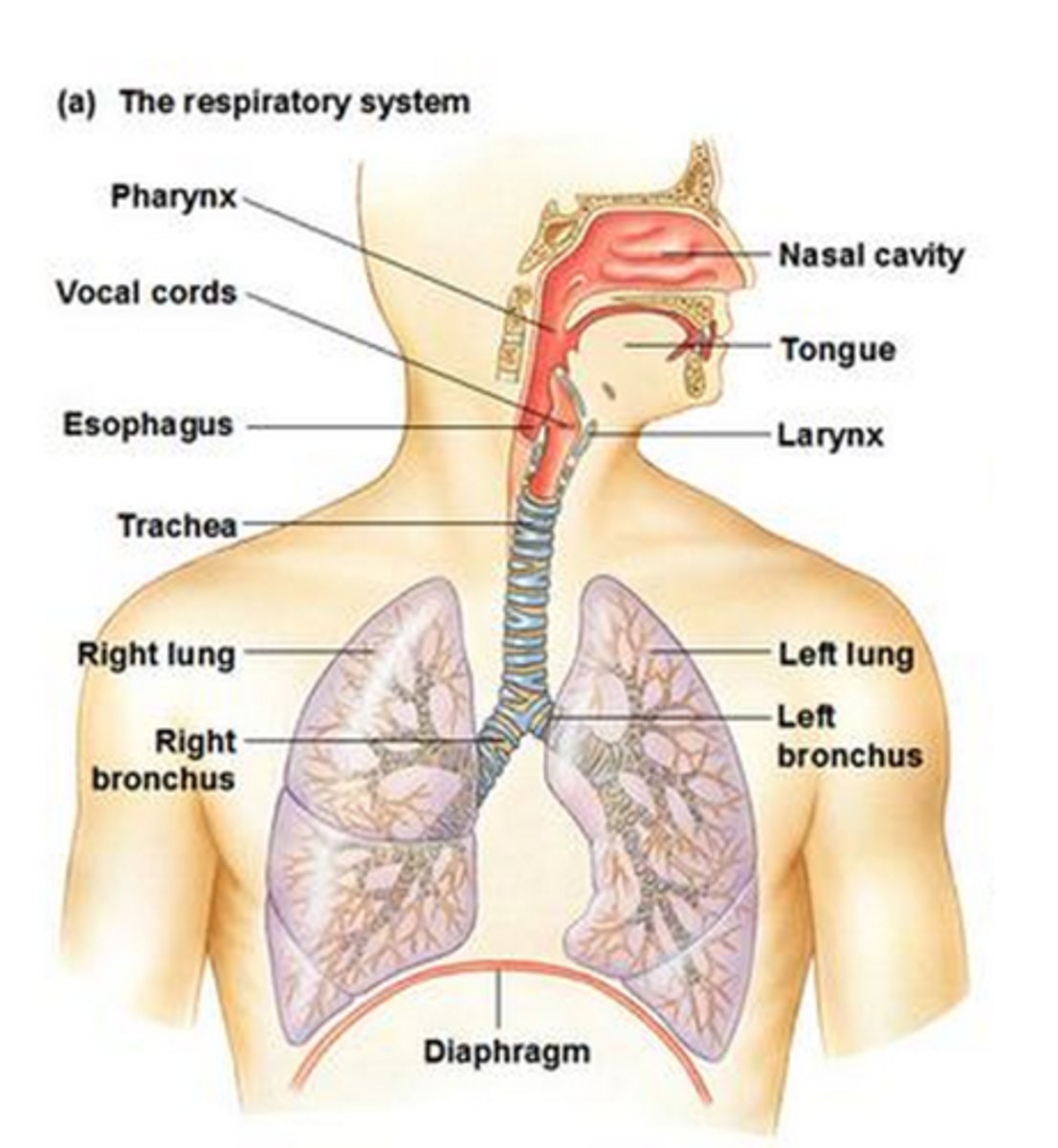
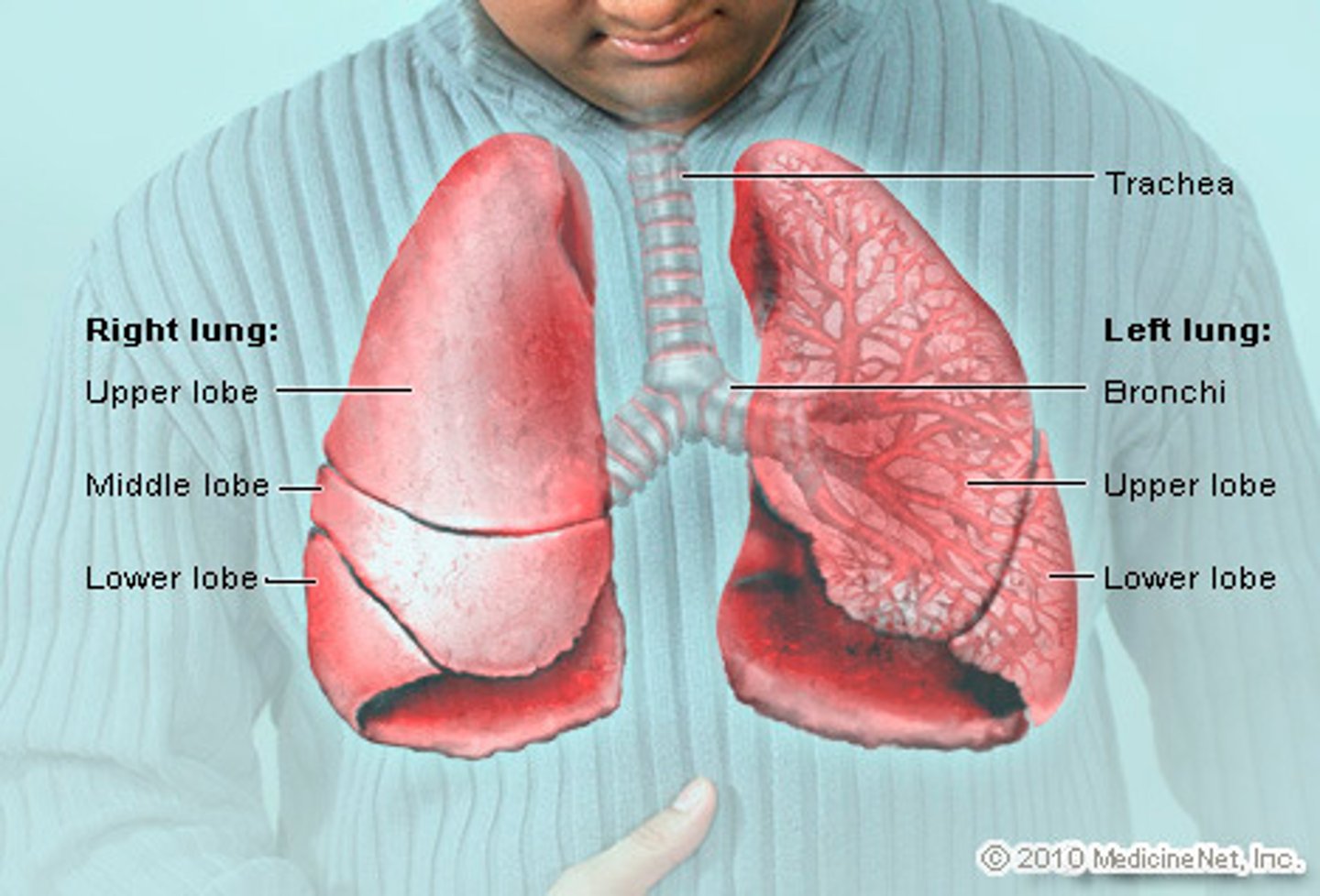
Lungs
The main organs of the respiratory system, responsible for gas exchange where oxygen is exchange with carbon dioxide in the blood
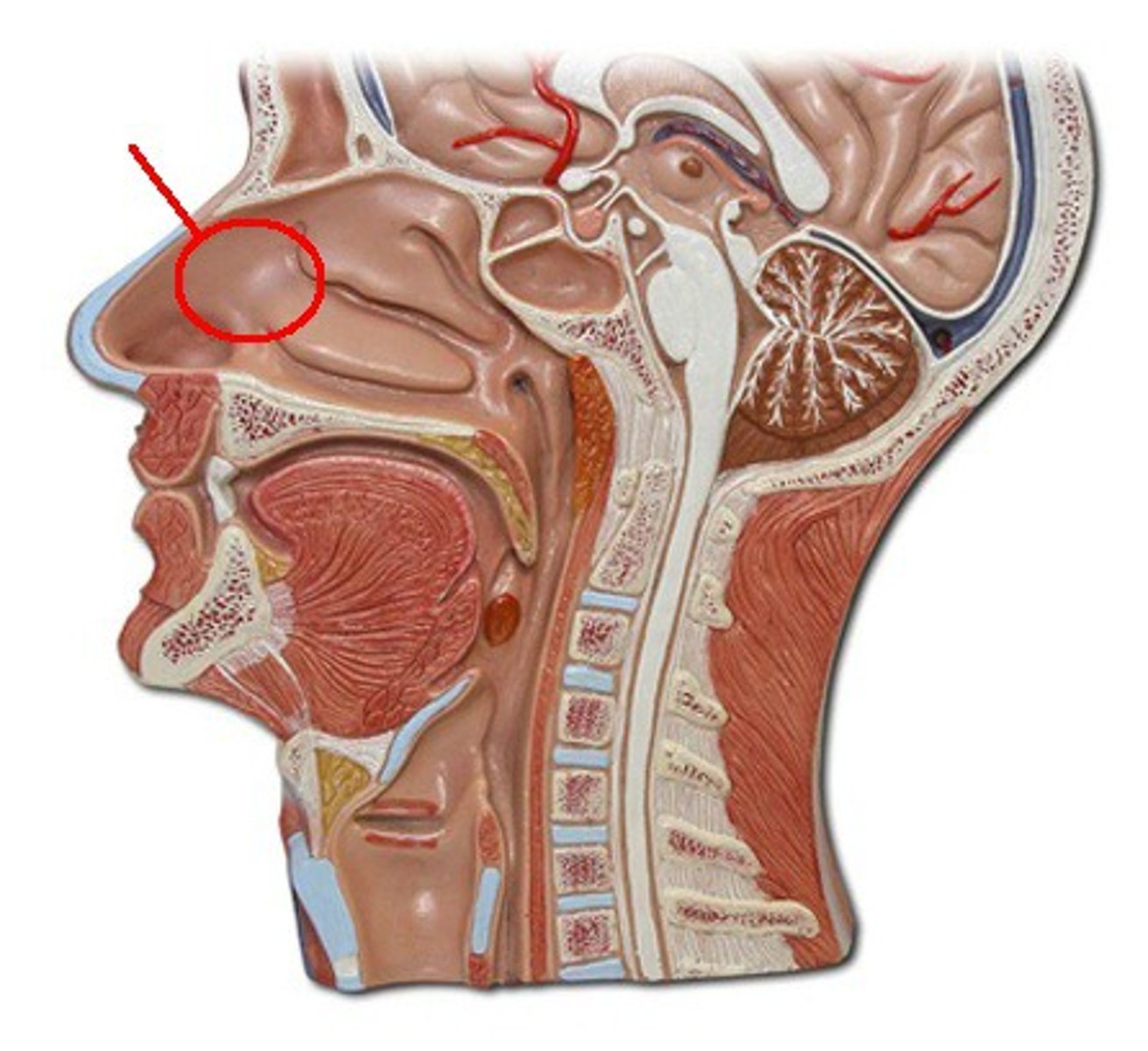
Nasal cavity
A hollow space behind the nose that regulates the flow of air into the respiratory system
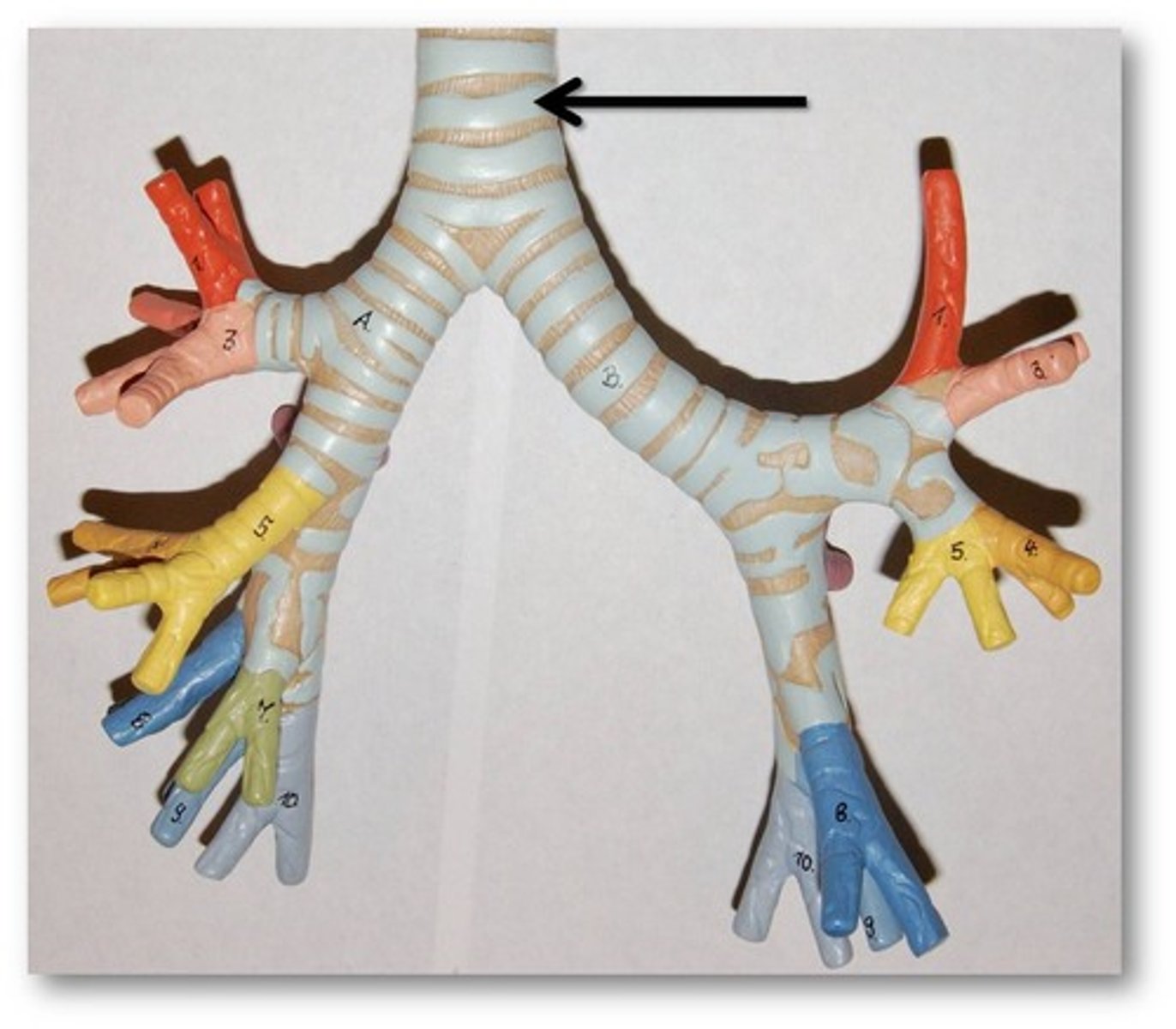
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
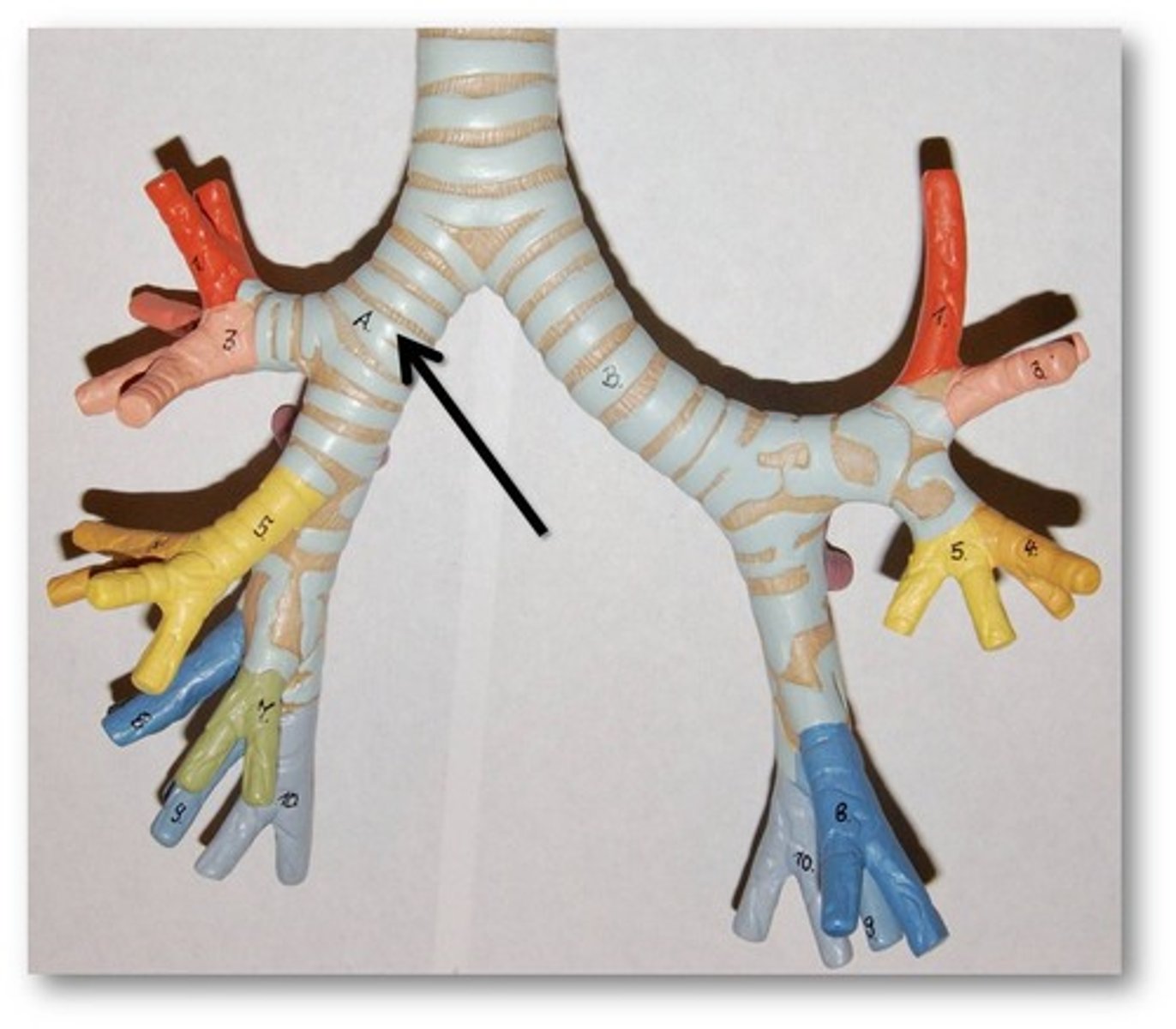
Bronchi
Two short branches at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs
Bronchioles
Airways in the lungs that are made up of multiple branches, leads from the bronchi to the alveoli
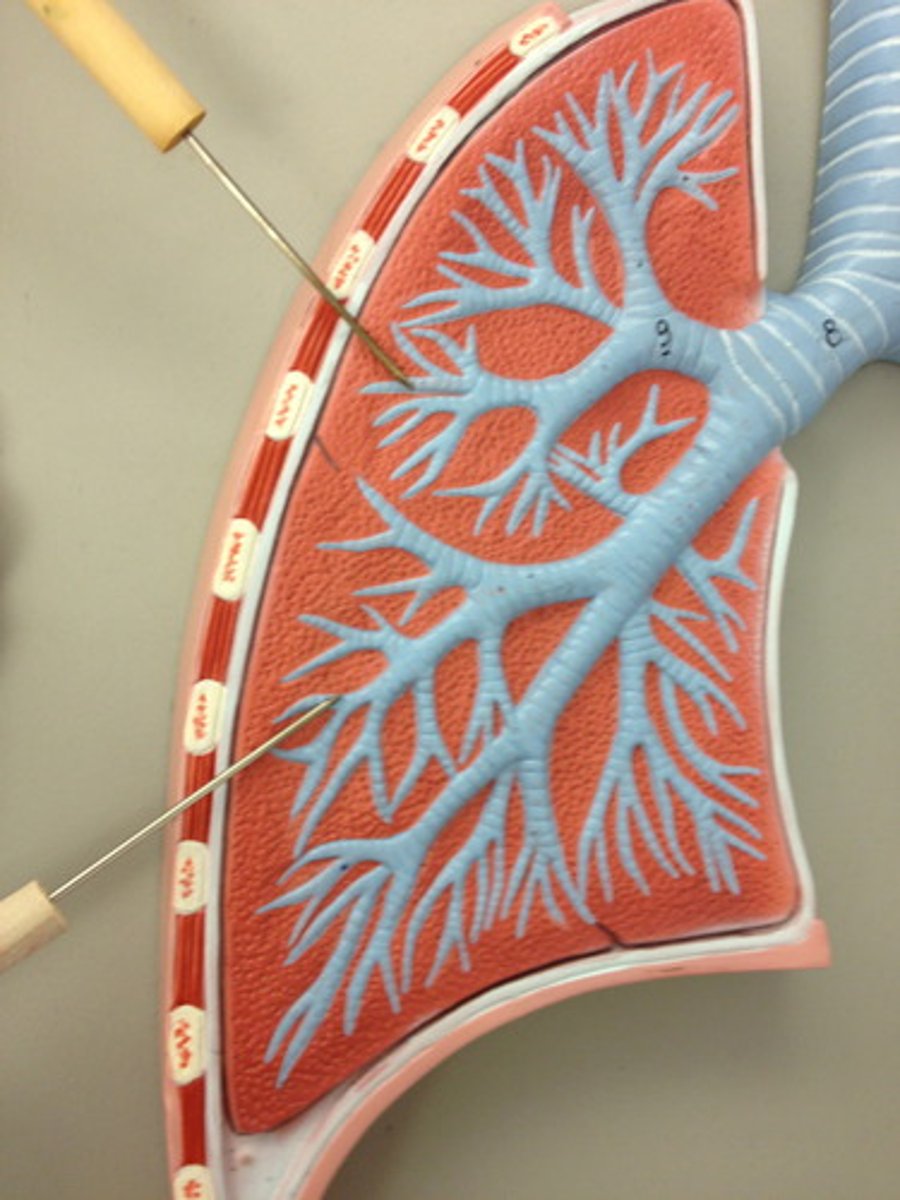
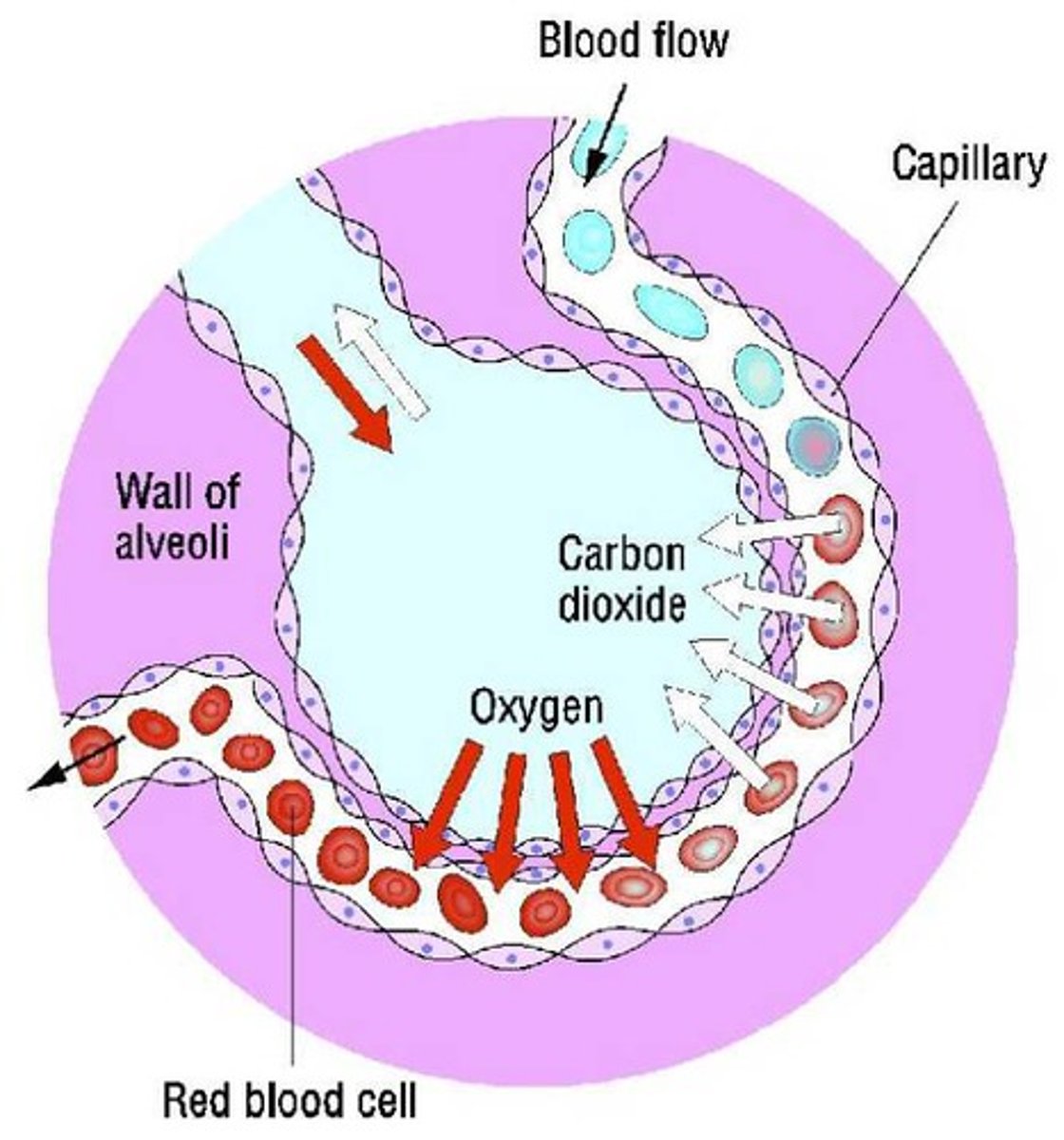
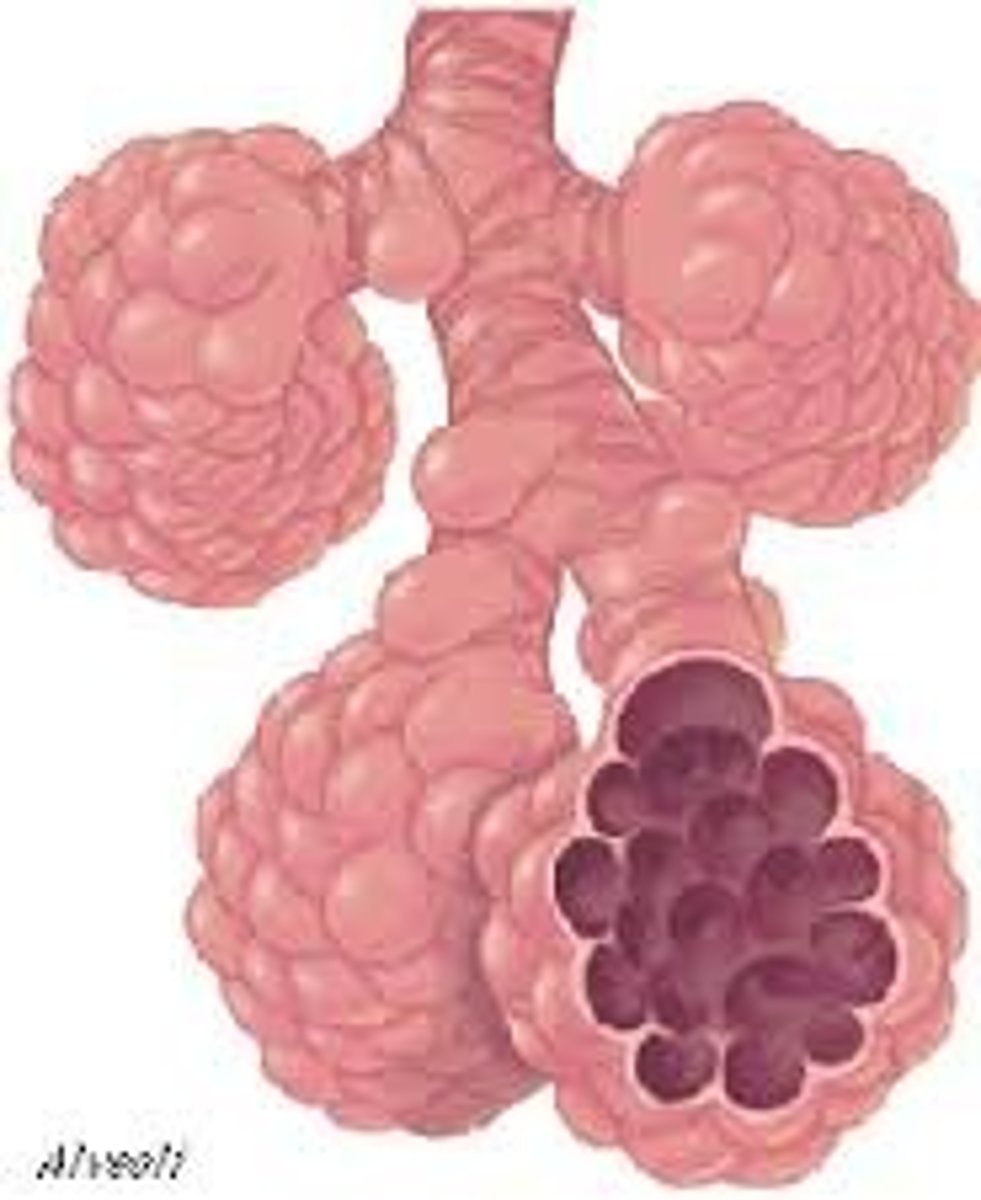
Alveoli
Tiny sacs of lung tissue where gaseous exchange takes place with the blood
An effective exchange surface
Has a large surface area, a good blood supply, is well ventilated for gas exchange and has a thin membrane for diffusion
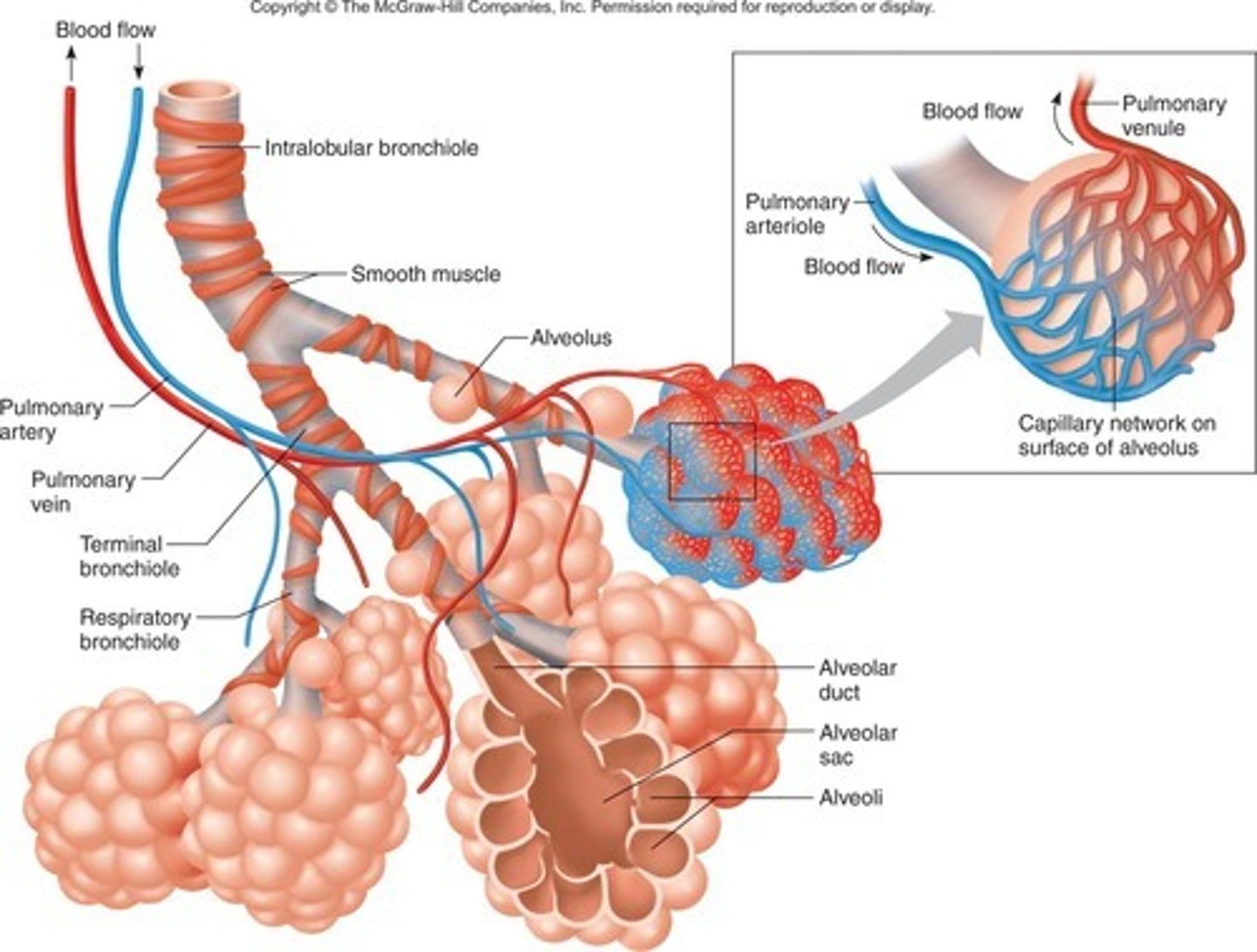
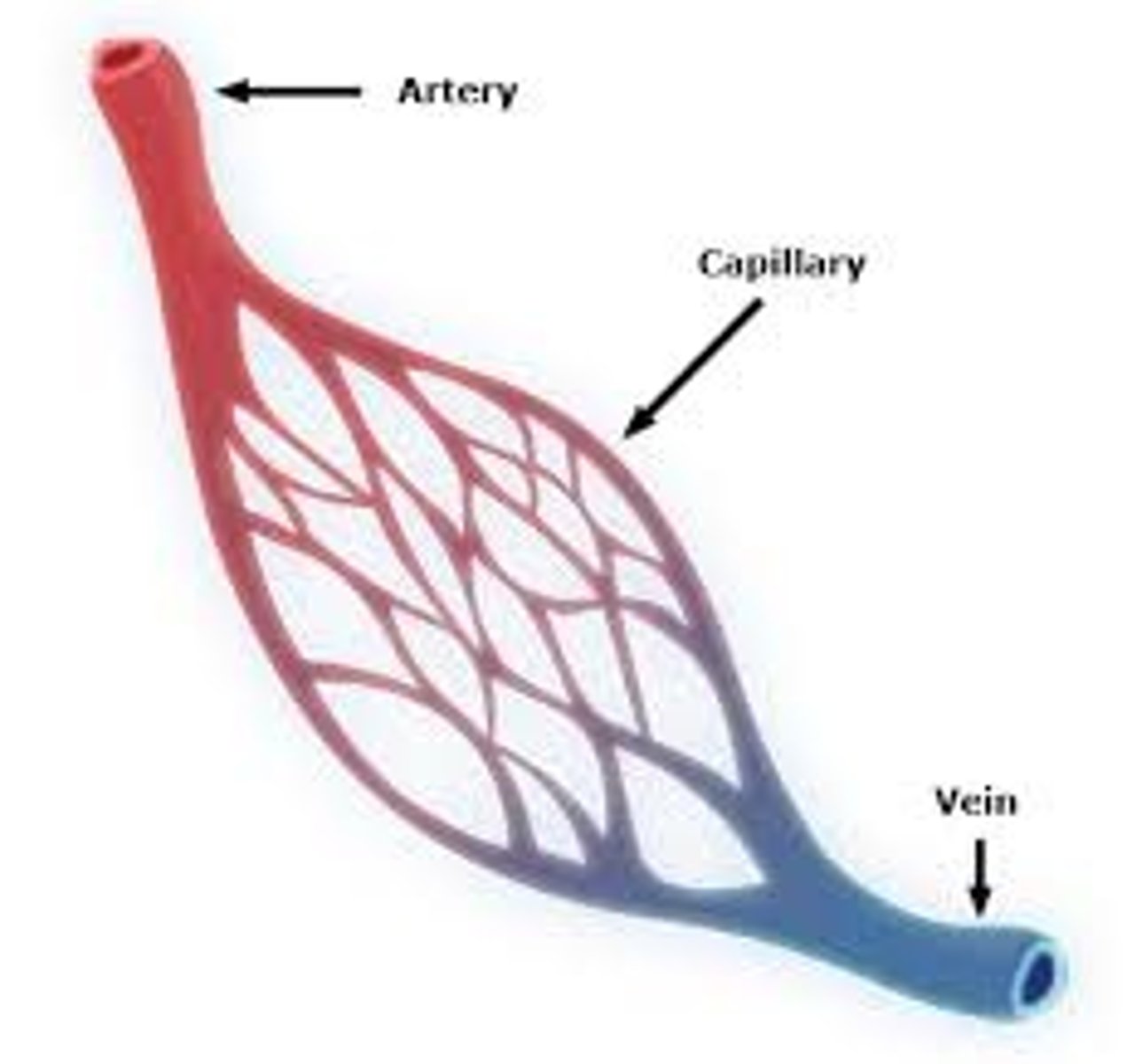
Capillary network
An interconnecting network of capillaries surrounding the alveoli for optimised gas exchange
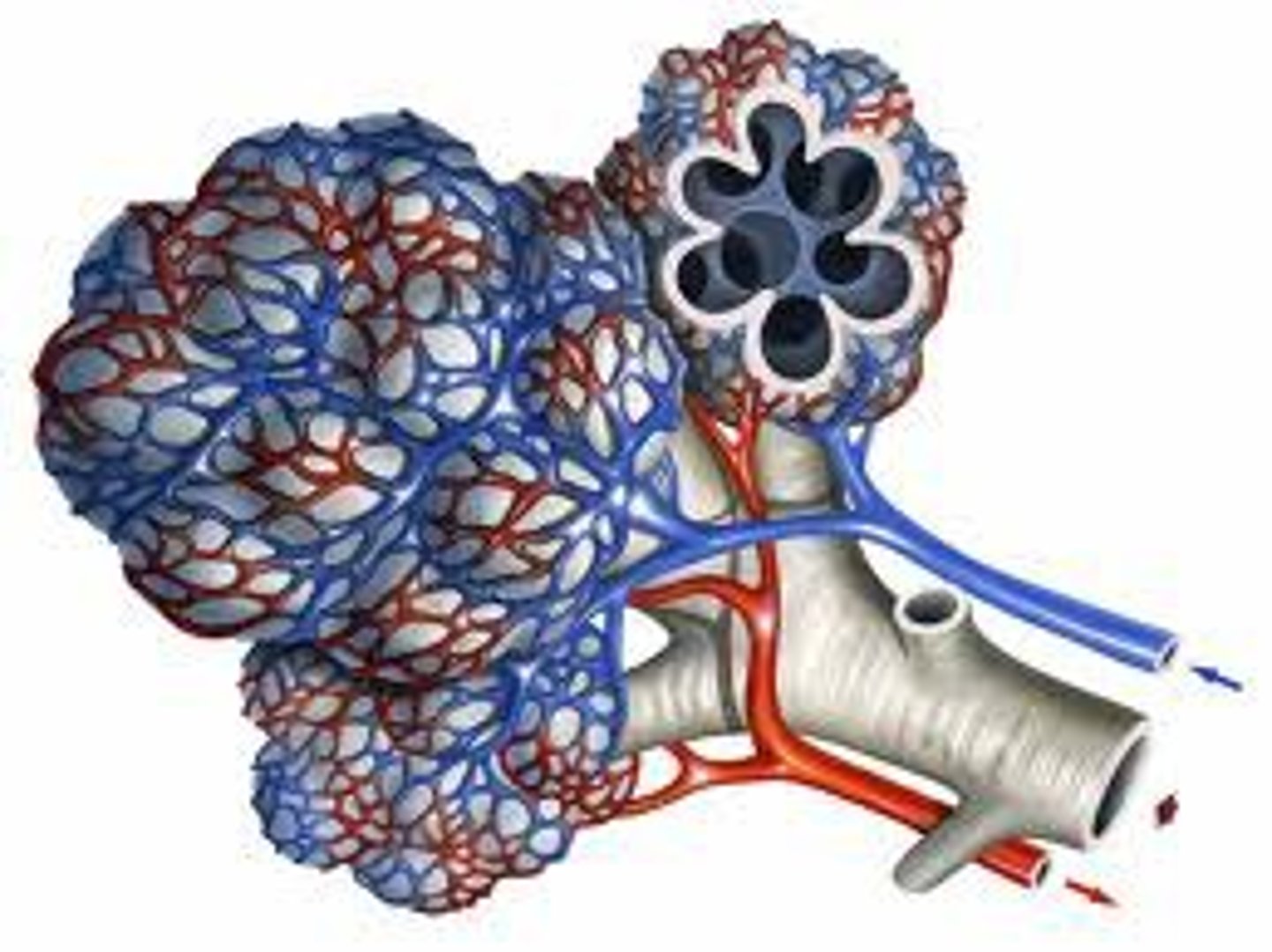
Capillaries
Small and thin blood vessels where the exchange of molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place, they consist of a single layer of cells
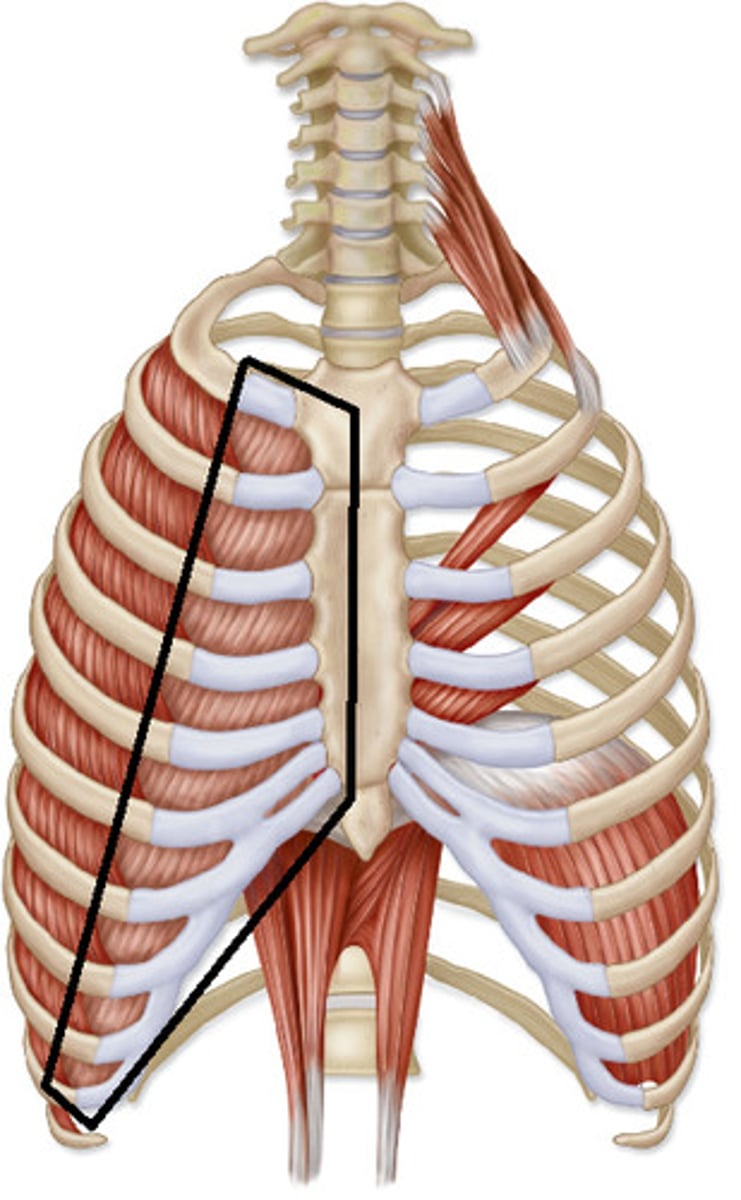
Diaphragm
A large muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps control breathing, when the diaphragm pulls down and contracts to become flat, air can easily enter the lungs
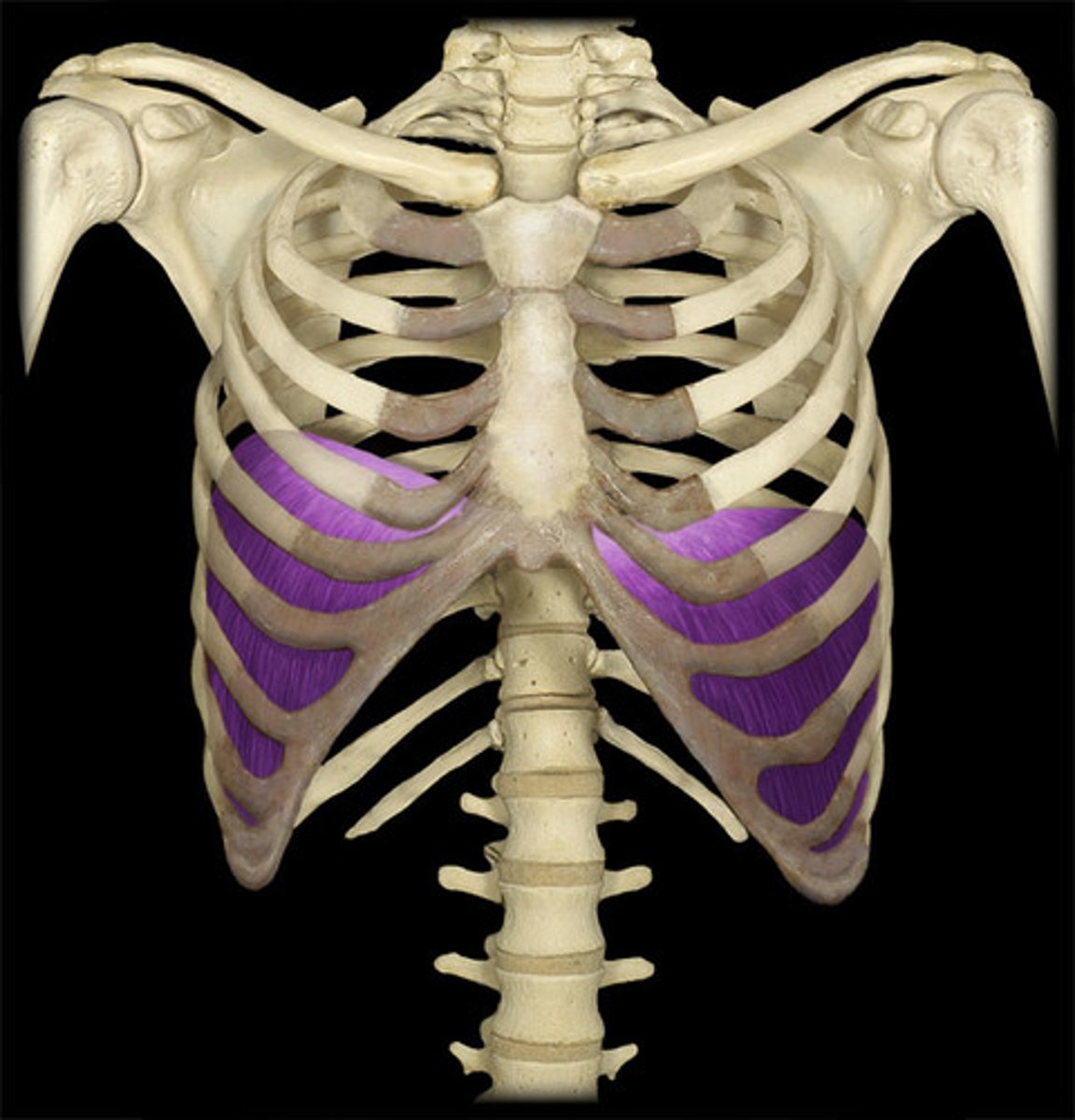
Intercostal muscles
Muscles in between the ribs which move the rib cage during breathing
Pleural membrane
Double-layered membrane that encloses and protects each lung
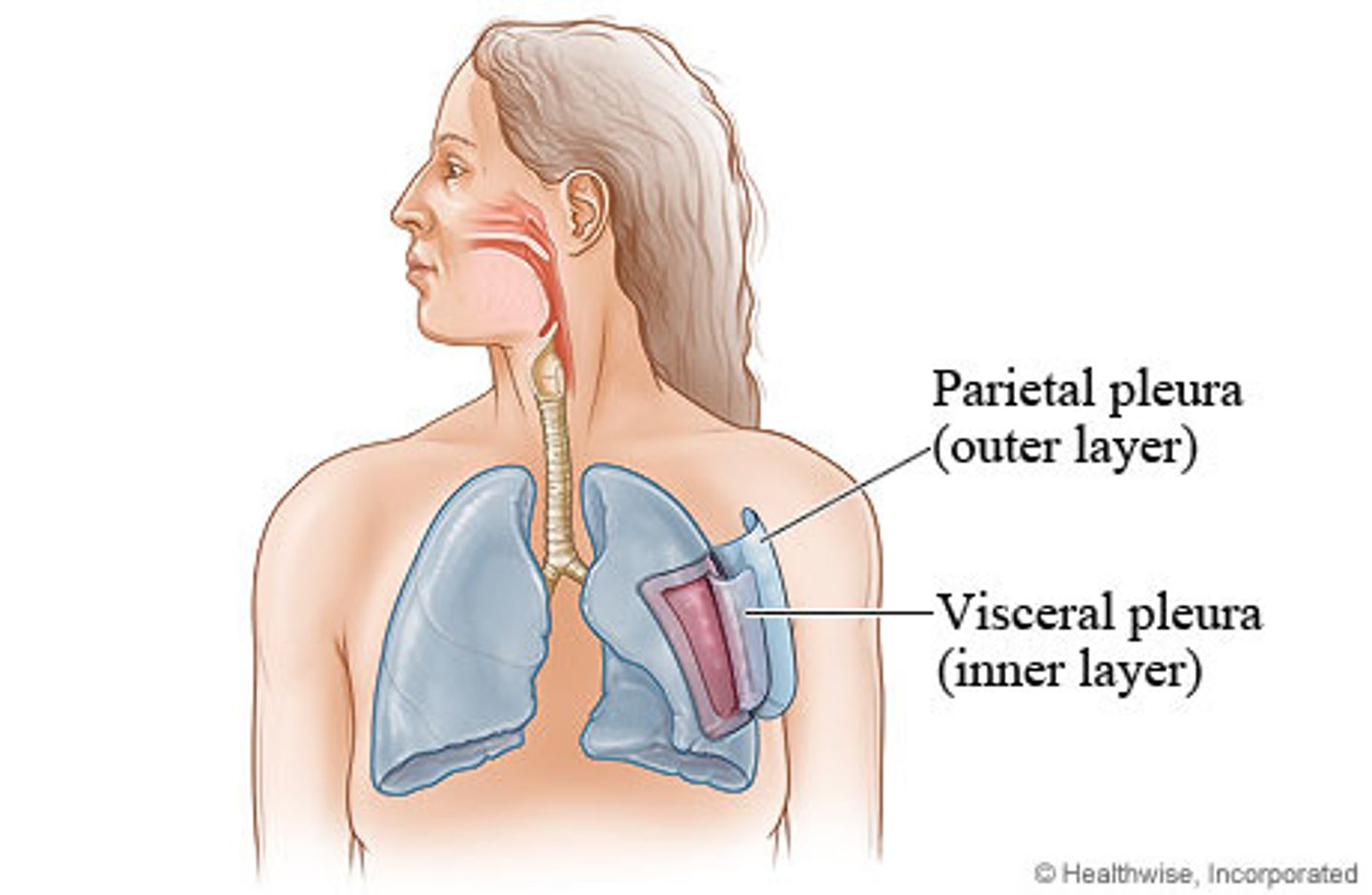
Pleural fluid
Fluid necessary to prevent friction between the pleural membranes
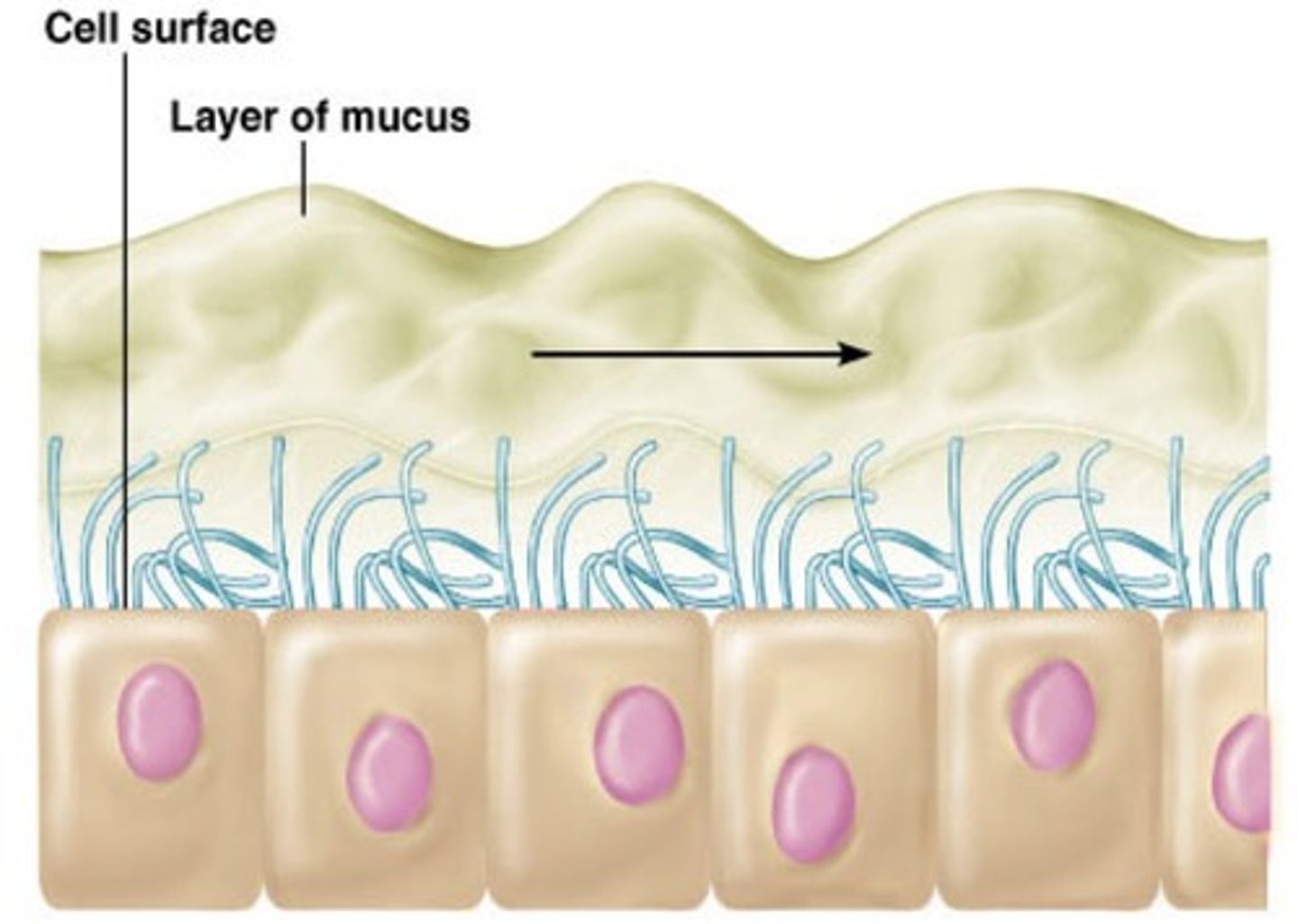
Mucus and cilia
Help protect the respiratory system, particles and bacteria stick to mucus and the cilia moves the mucus out of the respiratory system to the back of the throat
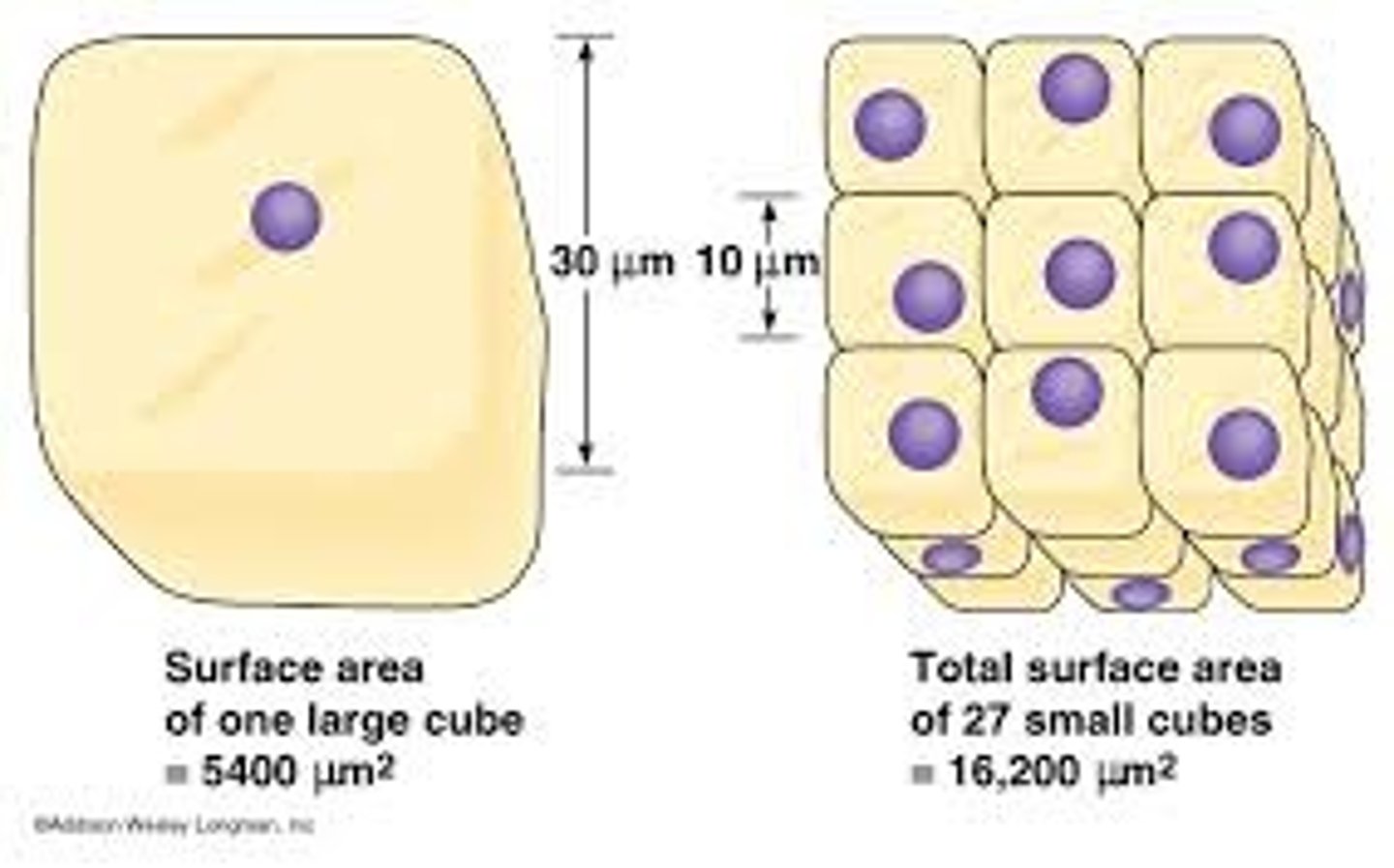
Surface area to volume ratio
The amount of surface area in relation to how large something is, a larger surface area to volume ratio leads to faster diffusion rates
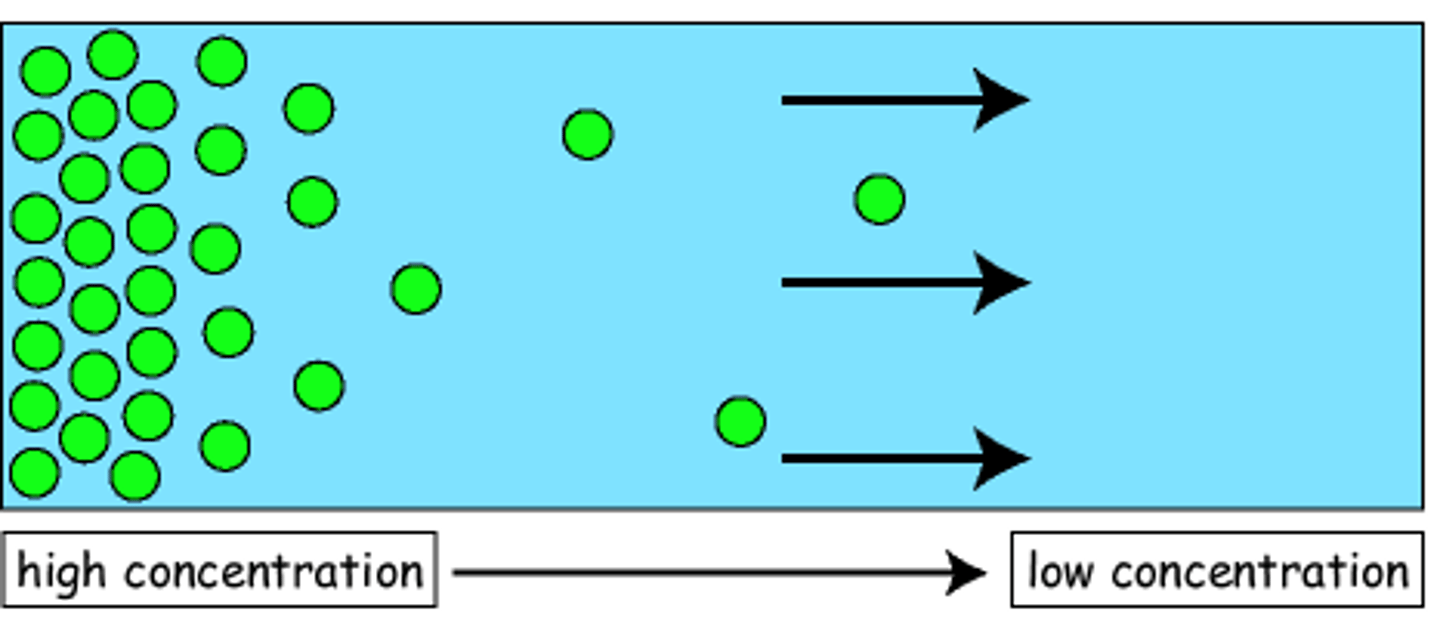
Diffusion
The movement of substances such as gas particles or substances in solution, from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
Adaptations of the respiratory system
Large surface area due to multiple branches of bronchioles and many alveolar sacs, good blood supply for quick diffusion, well ventilated, ventilation is optimised by effective involuntary muscular action