psychology - learning & cognition
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/149
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
1
New cards
Learning
The process of acquiring new & relatively enduring information & behaviors.
2
New cards
Habituation
An organism’s decreasing response to a stimulus w/ repeated exposure to it.
3
New cards
Associative learning
Learning that certain events occur together. Two stimuli (CC) or response + consequences (OC).
4
New cards
Cognitive learning
Acquisition of mental info, whether by observing events, watching others, or through language.
5
New cards
Classical conditioning
Type of learning where you learn to link 2 or more stimuli & anticipate events. Also referred to as CC.
6
New cards
Behaviorism
Psychology should only study observable behavior. Prioritizes objectivity.
7
New cards
Neutral stimulus (NS)
In CC, a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning.
8
New cards
Unconditioned response (UR)
In CC, an unlearned, naturally occurring response.
9
New cards
Unconditioned stimulus (US)
In CC, a stimulus that automatically/naturally triggers a response.
10
New cards
Conditioned response (CR)
In CC, a learned response to a previously neutral stimulus.
11
New cards
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
In CC, a stimulus that after association with a US triggers a CR.
12
New cards
Acquisition
In CC, initial stage when NS & US are linked so NS begins triggering CR.
13
New cards
Parts of learning
Change, behavior, experience
14
New cards
Higher-order conditioning
Procedure where CS in one conditioning experience is paired w/ new NS, creating a new (often weaker) CS.
15
New cards
Extinction (In CC)
Diminishing of a CR; occurs in CC when a US doesn’t follow a CS.
16
New cards
Spontaneous recovery
Reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished conditioned response.
17
New cards
Generalization
Tendency after conditioning for similar stimuli to elicit similar responses.
18
New cards
Discrimination
In CC, learned ability to distinguish CS & stimuli that do not signal a US.
19
New cards
Trace conditioning
Form of CC. CS begins & ends before US is presented.
20
New cards
Delayed conditioning
Form of CC. CS begins, US is presented, and then CS ends.
21
New cards
Simultaneous conditioning
Form of CC. CS & US present & end at the same time.
22
New cards
Backward conditioning
Form of CC. US is presented before CS.
23
New cards
Temporal conditioning
Form of CC. CS implemented for a fixed time period before the presentation of the US.
24
New cards
Respondent behavior
Behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus.
25
New cards
Operant behavior
Behavior that operates of the environment, producing consequences.
26
New cards
Biofeedback
System for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension.
27
New cards
Contiguity model (CC model)
Conditioning will occur whenever a CS & a US are paired closely. Since been debunked. First introduced by Pavlov.
28
New cards
Contingency model (CC model)
CS must reliably predict US for conditioning to occur. First introduced by Rescarla & Wagner.
29
New cards
Instrumental learning
Producing an environmental change that affects an organism’s behavior. Consequences after behavior. Introduced by Thorndike.
30
New cards
Thorndike’s law of effect
Behaviors are encouraged when followed by satisfying consequences & discouraged when annoying consequences.
31
New cards
Positive reinforcement
Behavior followed by desired stimulus.
32
New cards
Negative reinforcement
Behavior prevents an undesired stimulus.
33
New cards
Escape (reinforcement)
Occurs when a behavior terminates an aversive event.
34
New cards
Avoidance (reinforcement)
Occurs when a behavior happens in the presence of a signal that informs the organism that an aversive event is likely.
35
New cards
Positive punishment
Behavior followed by aversive stimulus, making behavior less likely to reoccur.
36
New cards
Negative punishment (omission training)
Appetitive stimulus prevented or removed after a behavior.
37
New cards
Primary reinforcers
Stimuli biologically relevant to organisms and capable of increasing probability of organism’s behavior toward them. No prior experience required for reinforcement.
38
New cards
Secondary (or conditioned) reinforcers
Neutral, but has taken on the reinforcing properties of a primary reinforcer by being associated w/ it.
39
New cards
Shaping
Technique where successive approximations of a behavior are reinforced. Behavior comes closer & closer to target behavior during training. Makes it possible to condition unlikely behaviors.
40
New cards
Chaining
Operant technique where an organism is required to perform several different behaviors in sequence before reinforcement. Complex strings can be maintained by one use of reinforcement this way.
41
New cards
Extinction (In OC)
Occurs in OC when a behavior stops resulting in the expected result. Not caused by prevention or avoidance.
42
New cards
Discriminative stimulus (S^D)
Stimulus that signals or informs organism of the availability of consequence. Valuable for behavior determination.
43
New cards
Continuous reinforcement
Every target behavior reinforced. Quickest way to train new behavior. Easily extinguished when no longer reinforced - extinction occurs.
44
New cards
Intermittent (or partial) reinforcement
Only some target behaviors are reinforced.
45
New cards
Fixed-ratio (Fr) reinforcement
Fixed/unchanging number of target responses before reinforcement is given. Procedures high rate of responding after brief pauses after reinforcement.
46
New cards
Variable-ratio (Vr) reinforcement
\# of responses required for reinforcement varies around some average, organism never nows how many responses are required for next reinforcement. AKA gambler’s schedule.
47
New cards
Fixed-interval (Fi) reinforcement
First target response after fixed interval of time is rewarded. Responses increase towards end of interval. “Scalloping.”
48
New cards
Variable-interval (Vi) reinforcement
Similar to Fi, but interval of time is random. Responses tend to be steady.
49
New cards
Aversive conditioning
Punishment most likely to be effective when intense & occurs immediately after behavior. Aversive means “causes dislike.”
50
New cards
Learned helplessness
Decrease in organism’s response after exposure to uncontrollable aversive events. Introduced by Seligman, who believed this helped explain depression.
51
New cards
Application of operant conditioning
Educational strategies (pop quizzes), behavior modification techniques, token economics, behavior therapy for disorders, animal training
52
New cards
Cognitive learning emphasizes…
…role of mental processes.
53
New cards
Insight learning
Sudden awareness of a solution to a problem. AKA epiphany.
54
New cards
Latent learning
Learning in the absence of apparent reinforcement.
55
New cards
Observational learning
Learning that takes place by watching another individual model the learning task. Introduced by Banduo.
56
New cards
Role of biology in learning
Learning is adaptive, enhances ability to survive. Important behaviors are reinforced, harmful behaviors punished. Similar to natural selection, but behavior changes within a lifetime.
57
New cards
Biological constraints
Innate predispositions that influence the likelihood of conditioning. Instinct can cause conditioning to not work (instinctive drift). Language is reinforced as an infant by what adults say around you. Culture influences choices & favorites. Environment can limit learning opportunities.
58
New cards
Parts of declarative/explicit memory
Working memory, episodic memory, semantic memory
59
New cards
Parts of nondeclarative/implicit memory
Priming, conditioning, motor-procedural memory
60
New cards
Multiple systems model
Memory is made up of multiple memory systems that can work independently of one another. Declarative & nondeclarative memory.
61
New cards
Declarative memory
A memory system controlled consciously, intentionally, flexibly. Involves effort & intention. Mnemonics are helpful. Mediated by hippocampus & frontal lobes. Declines with age.
62
New cards
Working memory
Short-term memory system that allowed us to store & process limited amounts of information of an immediate sense. Lasts 2-18 seconds. Mental calculations.
63
New cards
Episodic memory
Long-term memory system that stores information about specific events/episodes of your life.
64
New cards
Semantic memory
Long-term memory system that stores general knowledge.
65
New cards
Nondeclarative memory
Influential memory without our knowledge. Mediated by cortieal areas, cerebellum, & basal ganglia.
66
New cards
Priming
Automatic or unconscious process that can enhance the speed/accuracy as a result of past experience of a response.
67
New cards
Repetition priming
From repetition, just reading.
68
New cards
Semantic priming
Associating with other things
69
New cards
Procedural memory
Memory of processes involved in completing a task after the task is well learned & has become automatic.
70
New cards
Partial report method
Asking a person to recall only a portion of the stimuli they were asked to remember.
71
New cards
Whole report method
Asking a person to recall the entire stimuli they were asked to remember.
72
New cards
Sensory register
System that works briefly & stores info received until it is further processed.
73
New cards
Iconic memory
Memory for visual info
74
New cards
Echoic memory
Memory for auditory info
75
New cards
Working memory
Short-term system to store and process info currently being thought about. Small capacity. Info typically encoded acoustically.
76
New cards
Chunking
Grouping information together in your brain. Increases capacity and memory.
77
New cards
Parts of Baddeley’s model of working memory
Phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, episodic buffer, central executive
78
New cards
Baddeley’s model of working memory diagram
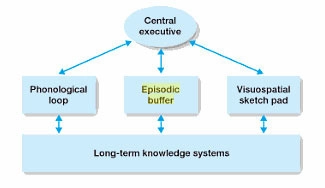
79
New cards
Phonological loop
Short-term vocal store.
80
New cards
Visuospatial sketchpad
Short-term visual & spatial store.
81
New cards
Episodic buffer
Integrates info from phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, & long-term memory.
82
New cards
Central executive
Controls other parts of Baddeley’s model of working memory.
83
New cards
Serial position
Effect an item’s position on a list has on how well it’s recalled.
84
New cards
Primacy effect
Concept that first items of a list are more likely to be remembered. Eliminated by spaced studying.
85
New cards
Recency effect
Concept that last items of a list are more likely to be remembered. Eliminated by distractions.
86
New cards
Prospective memory
Memory of tasks to be completed in the future. Requires working & long-term memory. 2 parts: intention & awareness.
87
New cards
Information processing model
Long-term memory encoded, stores, & retrieves info. Influences later access.
88
New cards
Level of processing framework
Info is processed differently depending on instructions & the task can vary from shallow to deep processing. Deep = better memory.
89
New cards
Shallow processing
Focuses of physical characteristics over meaning of an item.
90
New cards
Deep processing
Focuses on meaning of an item.
91
New cards
Massed practice
Individual attempts to learn material all in one setting. AKA cramming. Not as effective as spaced practice for retention.
92
New cards
Spaced practice
Studying at spaced intervals. Good for retention.
93
New cards
Self-referent encoding
Organize info around your own experiences to elaborate better. Use personal connections.
94
New cards
Distinctiveness
Items unique to each other are better remembered.
95
New cards
Von Restorff effect
More likely to remember something different to it’s surroundings. Think black swan in a group of white swans.
96
New cards
Organization
Organizing info by category improves recall.
97
New cards
Subjective organization
Imposing a personal organizational strategy on an otherwise random group of info.
98
New cards
Testing effect
Taking a memory test can also enhance later retention.
99
New cards
Recognition (type of retrieval)
Recognizing familiar info. Think multiple-choice quiz.
100
New cards
Recall (type of retrieval)
Retrieval from memory. Think short-response quiz.