Investigating Temperature Practical
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Enzyme
Biological catalysts which speed up reactions without being used up
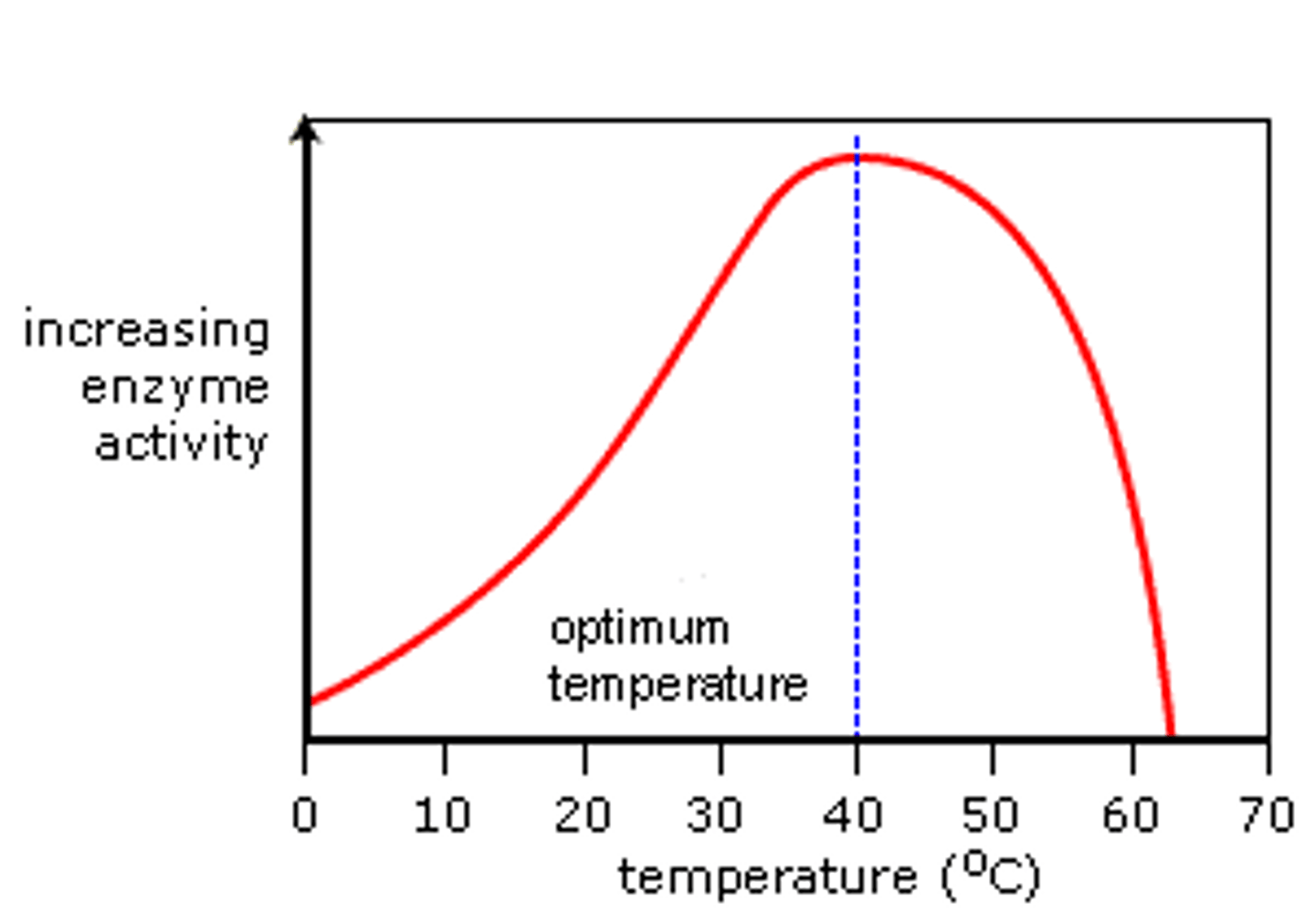
Enzymes and temperature
The enzyme rate increases as temperature increases up to an optimum, after which the enzyme becomes denatured
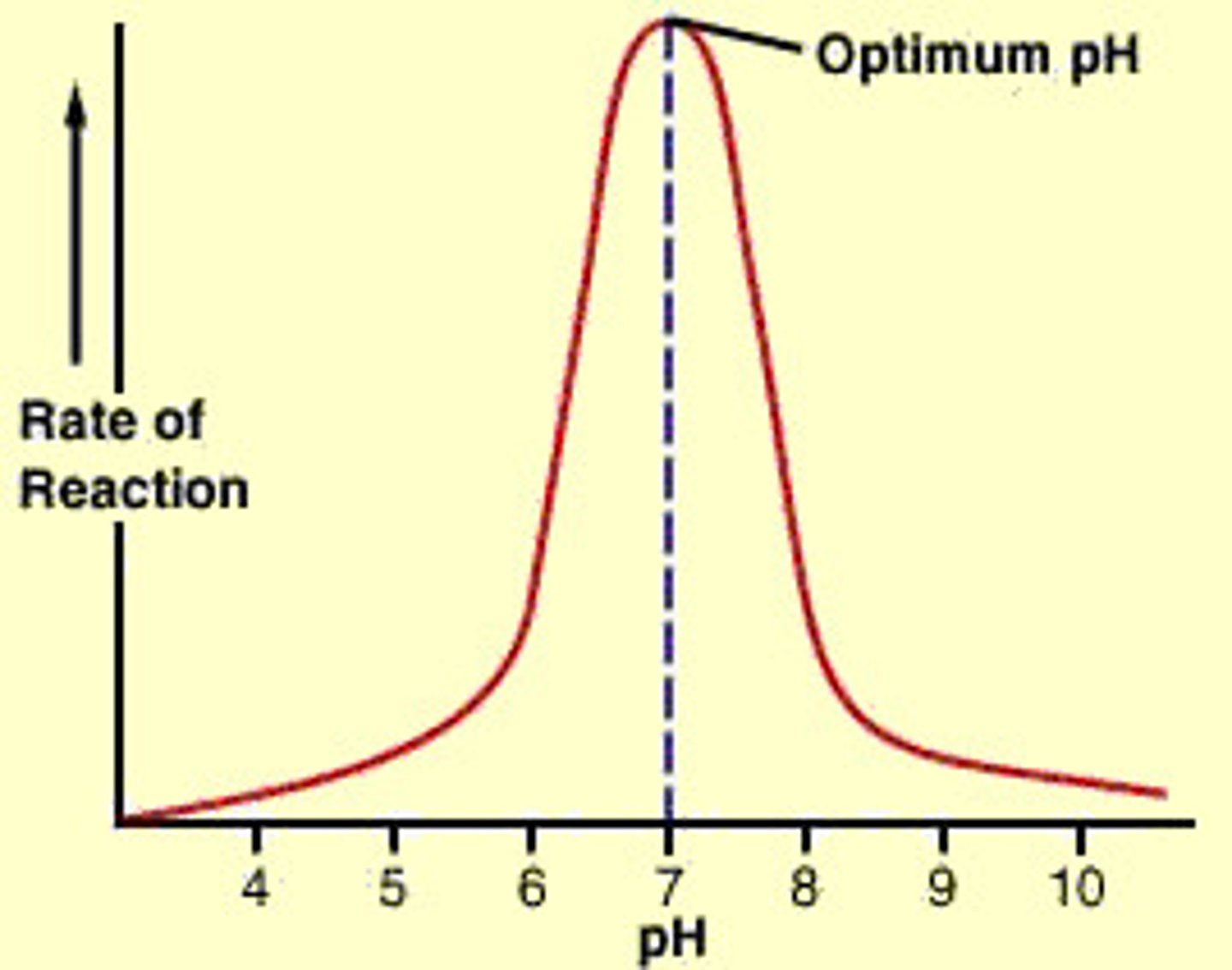
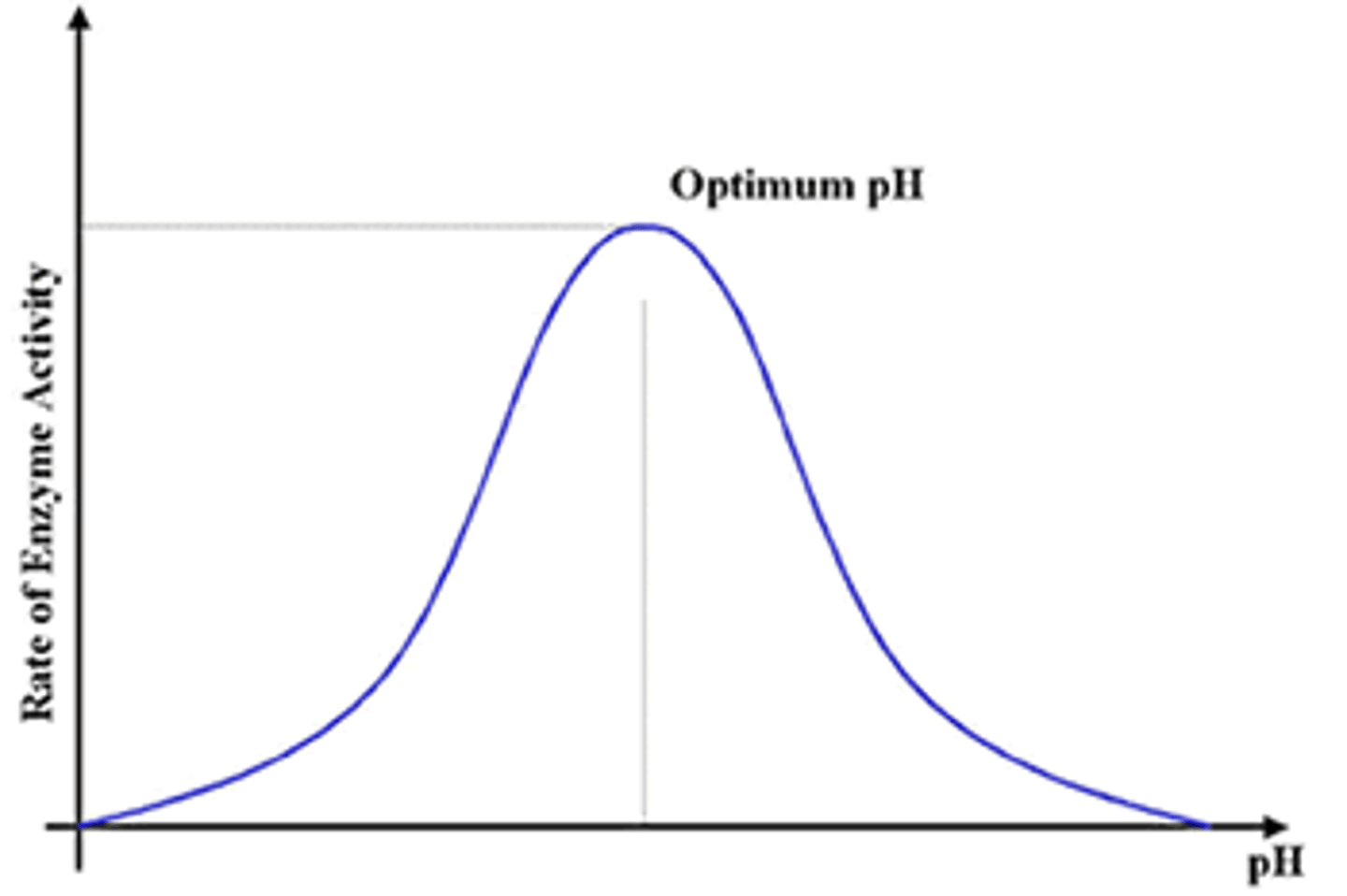
Enzymes and pH
The reaction rate decreases as the pH moves away from the enzyme's optimum pH
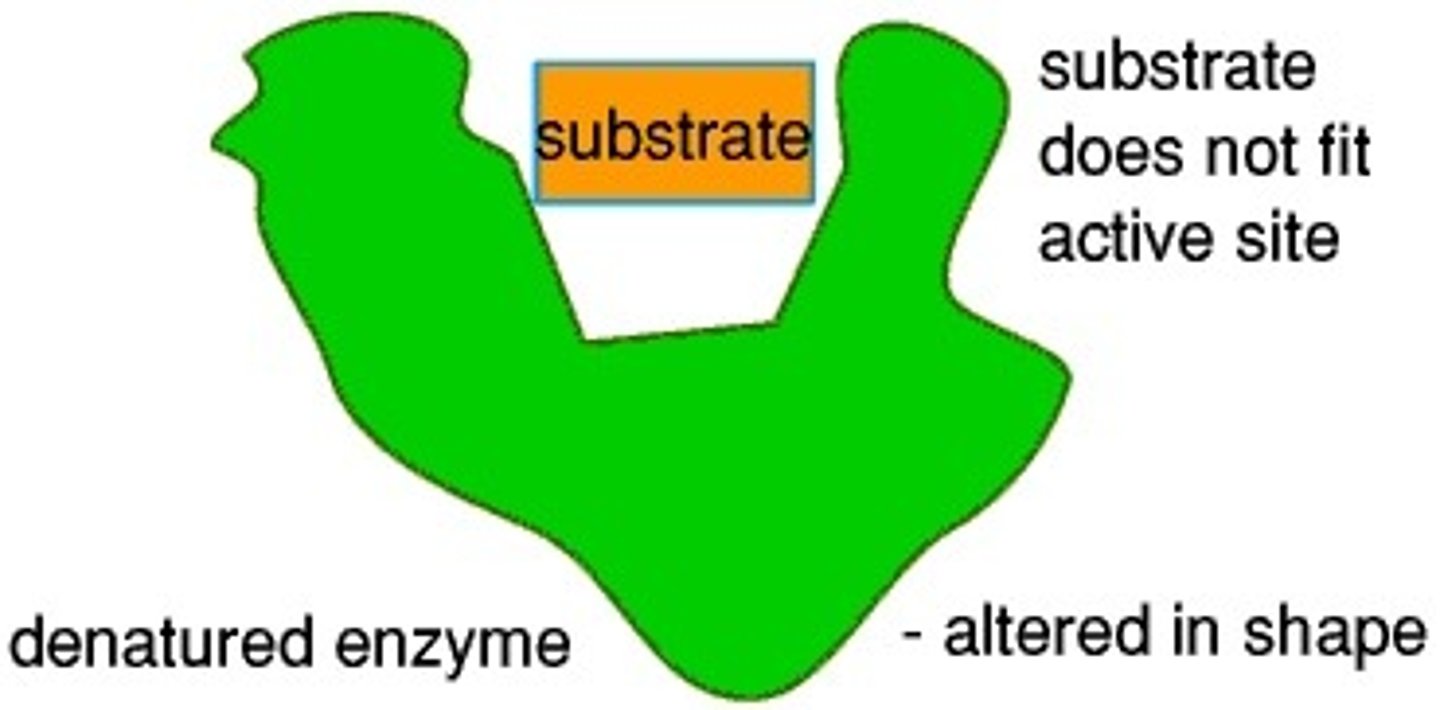
Denature
When the active site changes shape and can no longer bind to a substrate due to unsuitable temperature or pH
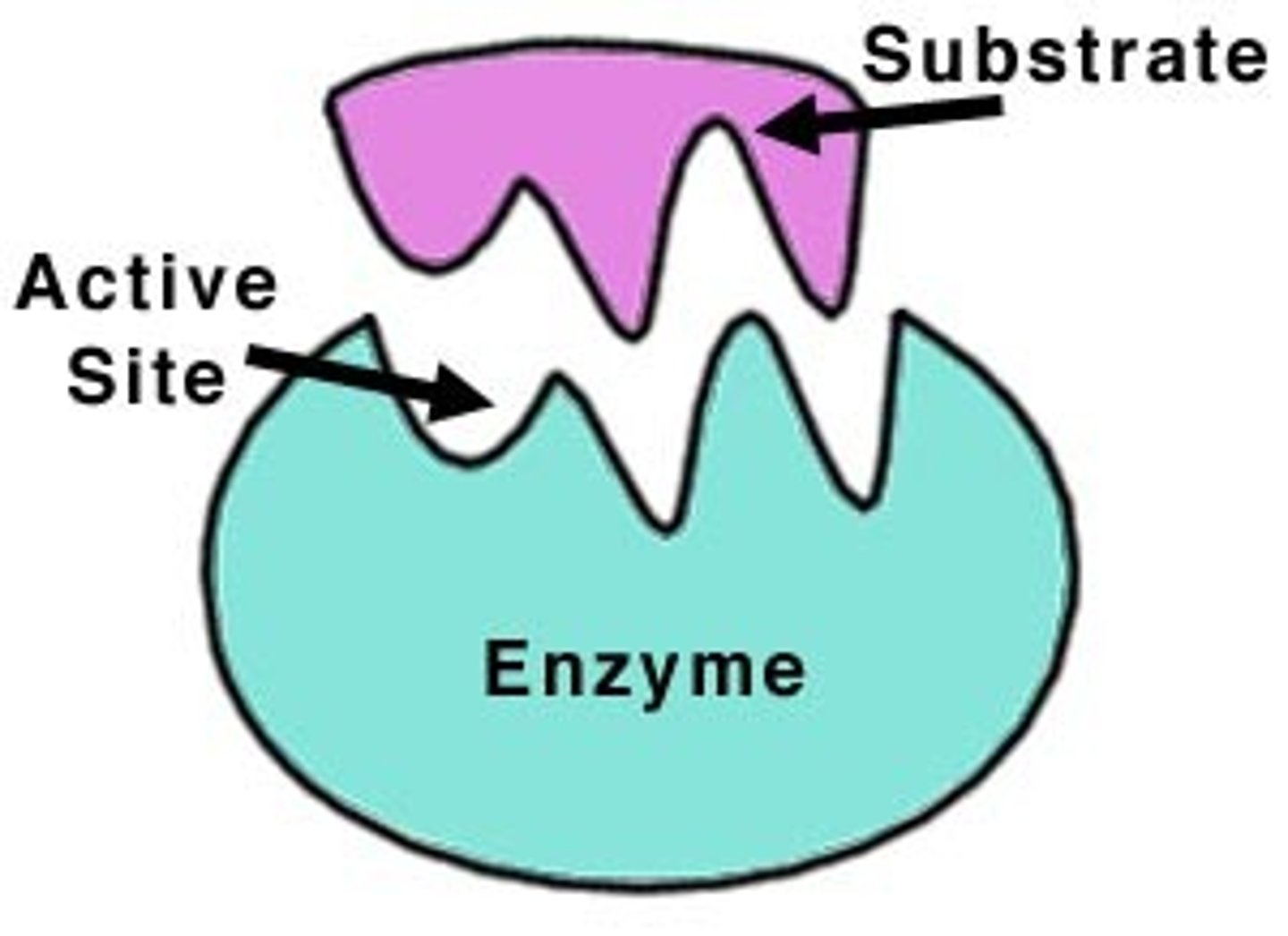
Active site
The part of an enzyme where the substrate binds
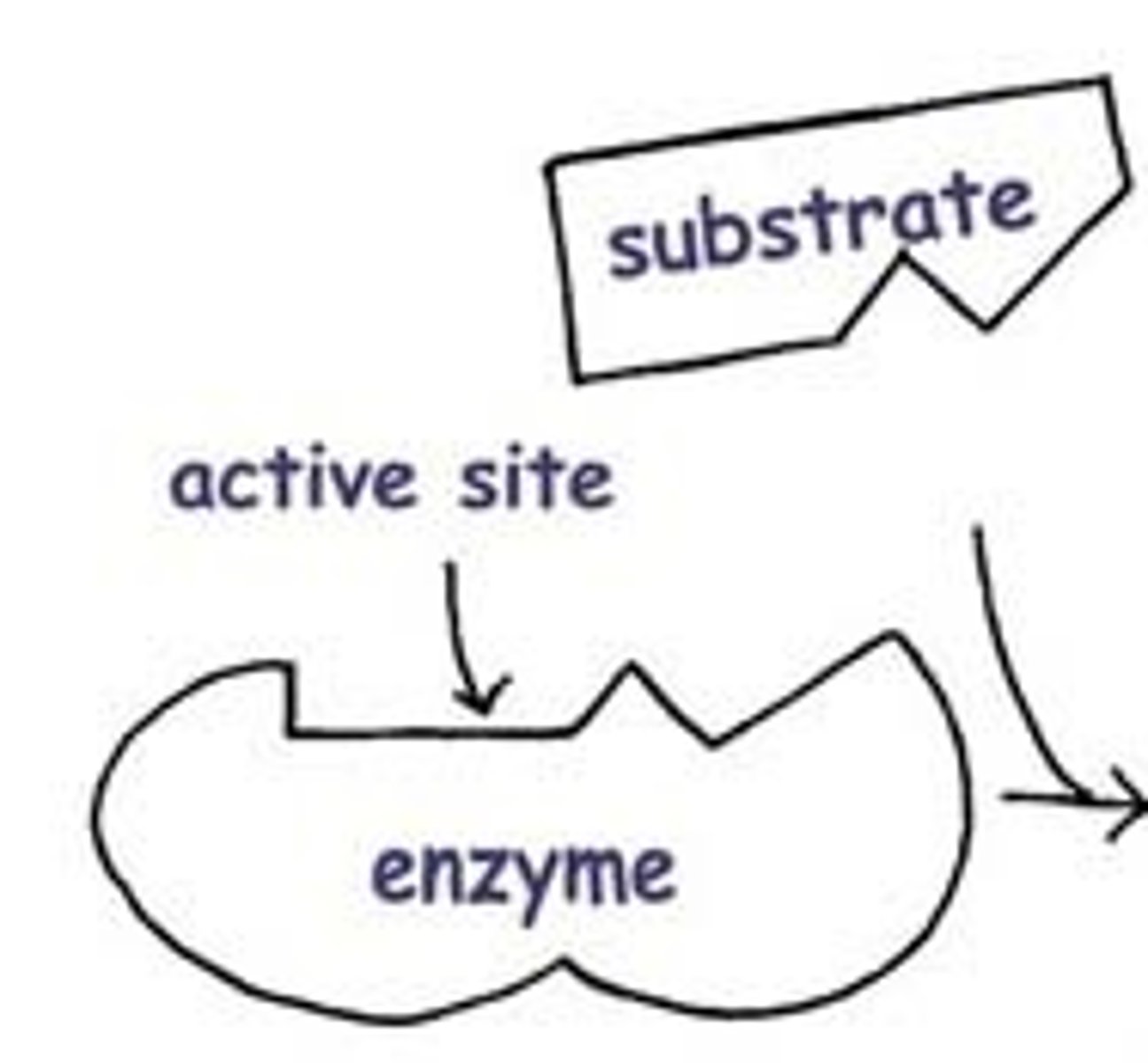
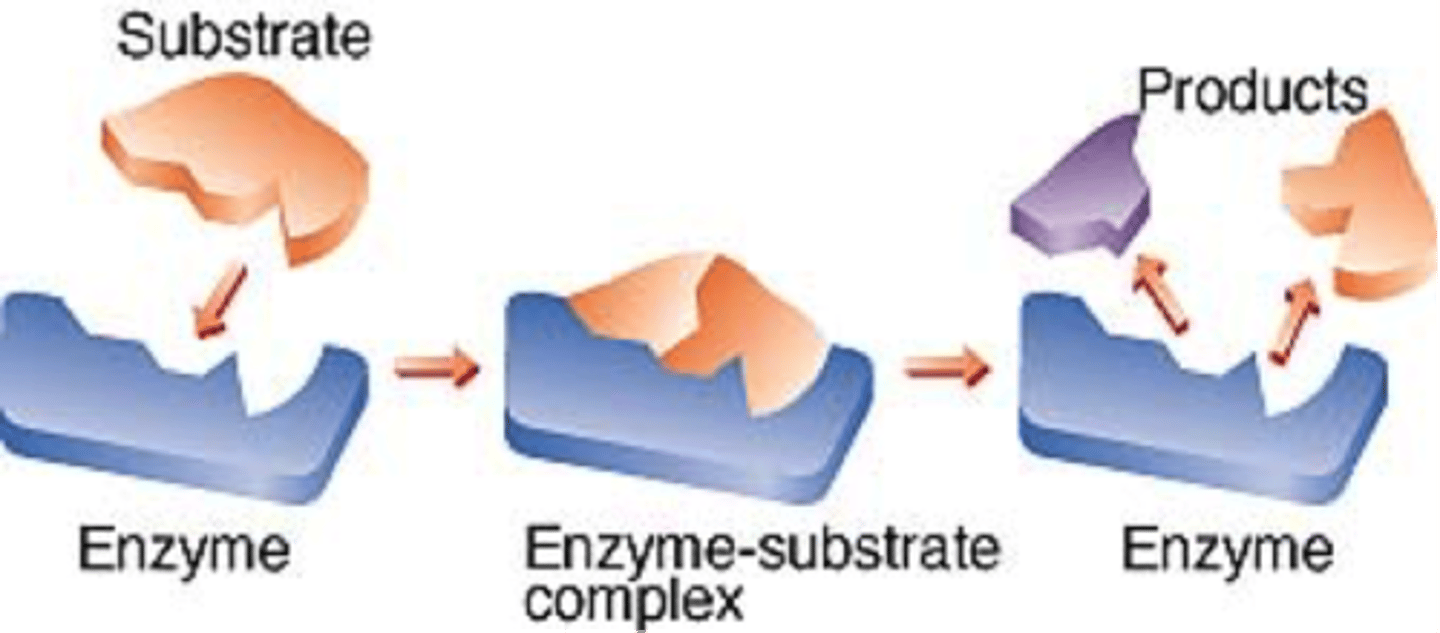
Substrate
Reactant of an enzyme catalysed reaction
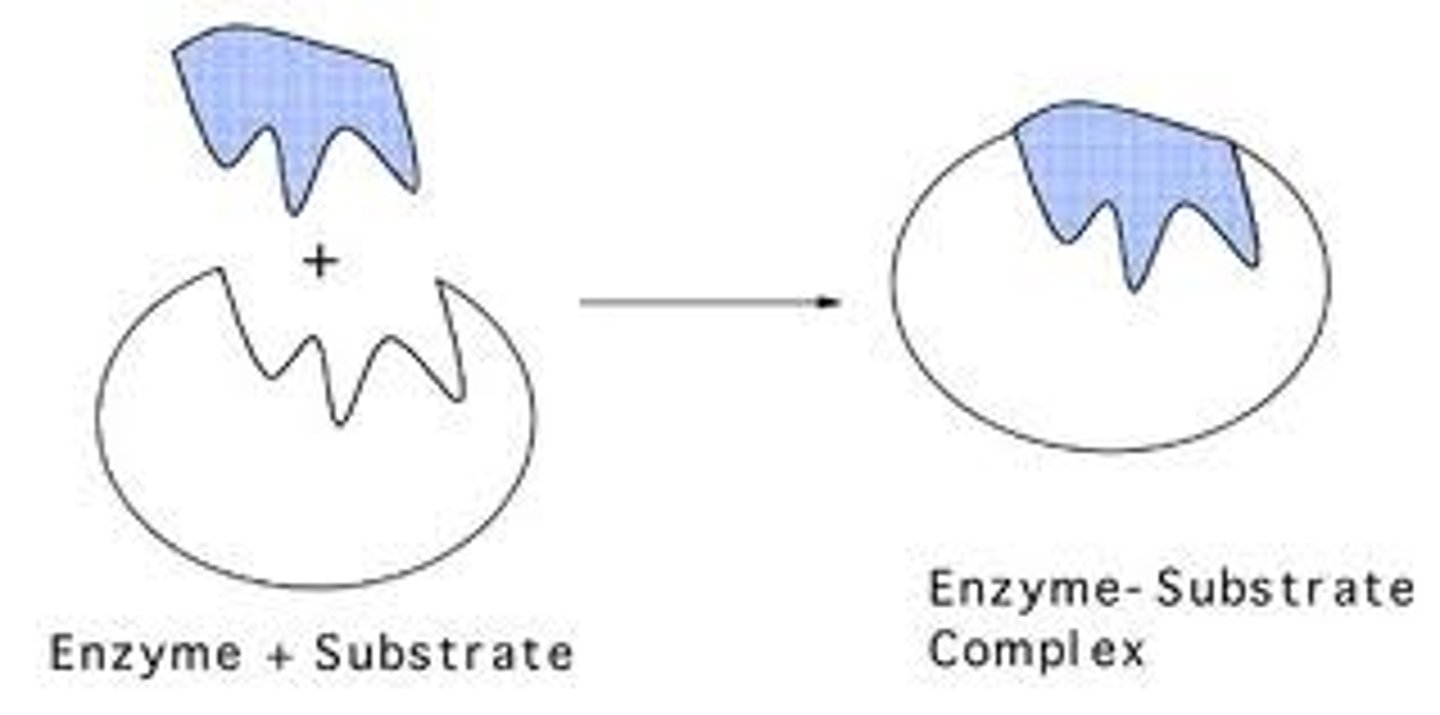
Product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
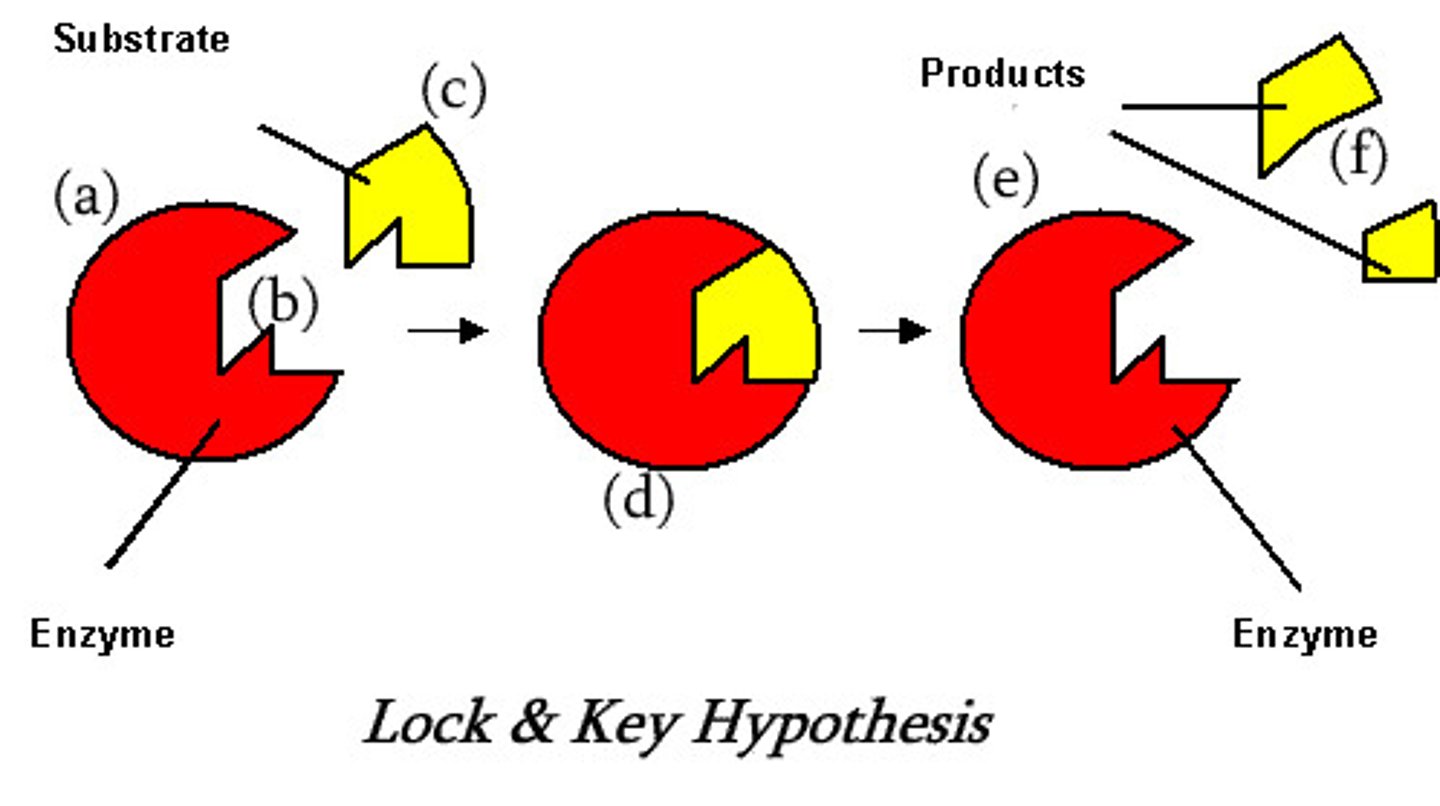
Lock and key theory
When a substrate fits into its enzyme just like a key fits a lock
Optimum rate
An ideal pH or temperature value that results in maximum enzyme activity
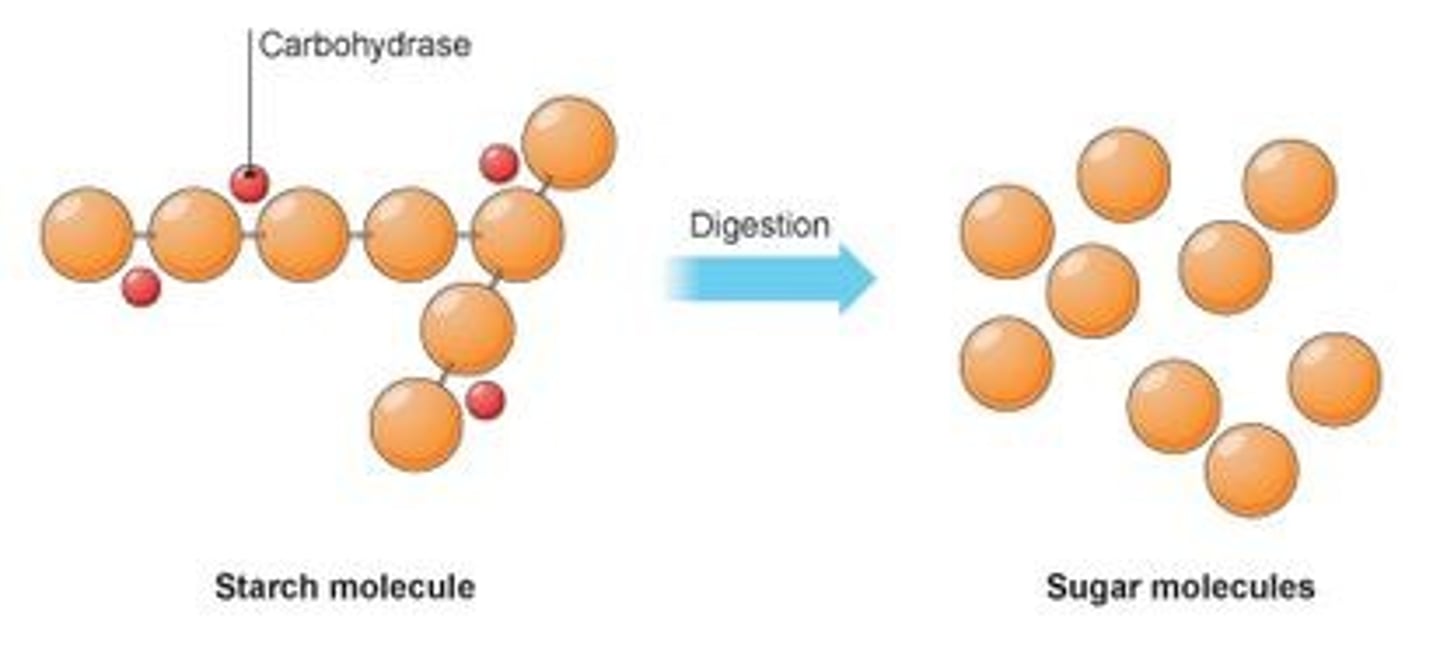
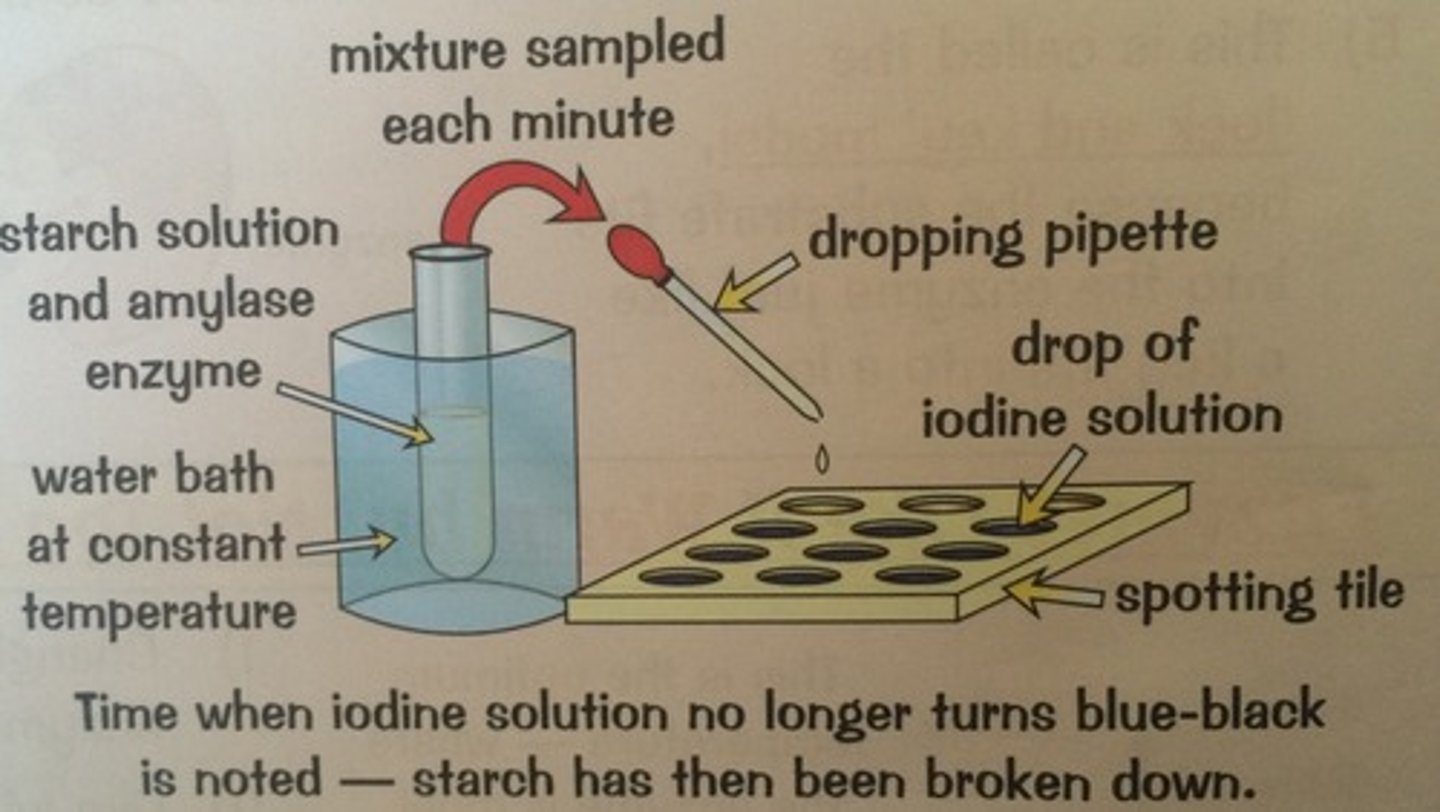
Amylase
A carbohydrase enzyme that breaks starch down into sugars
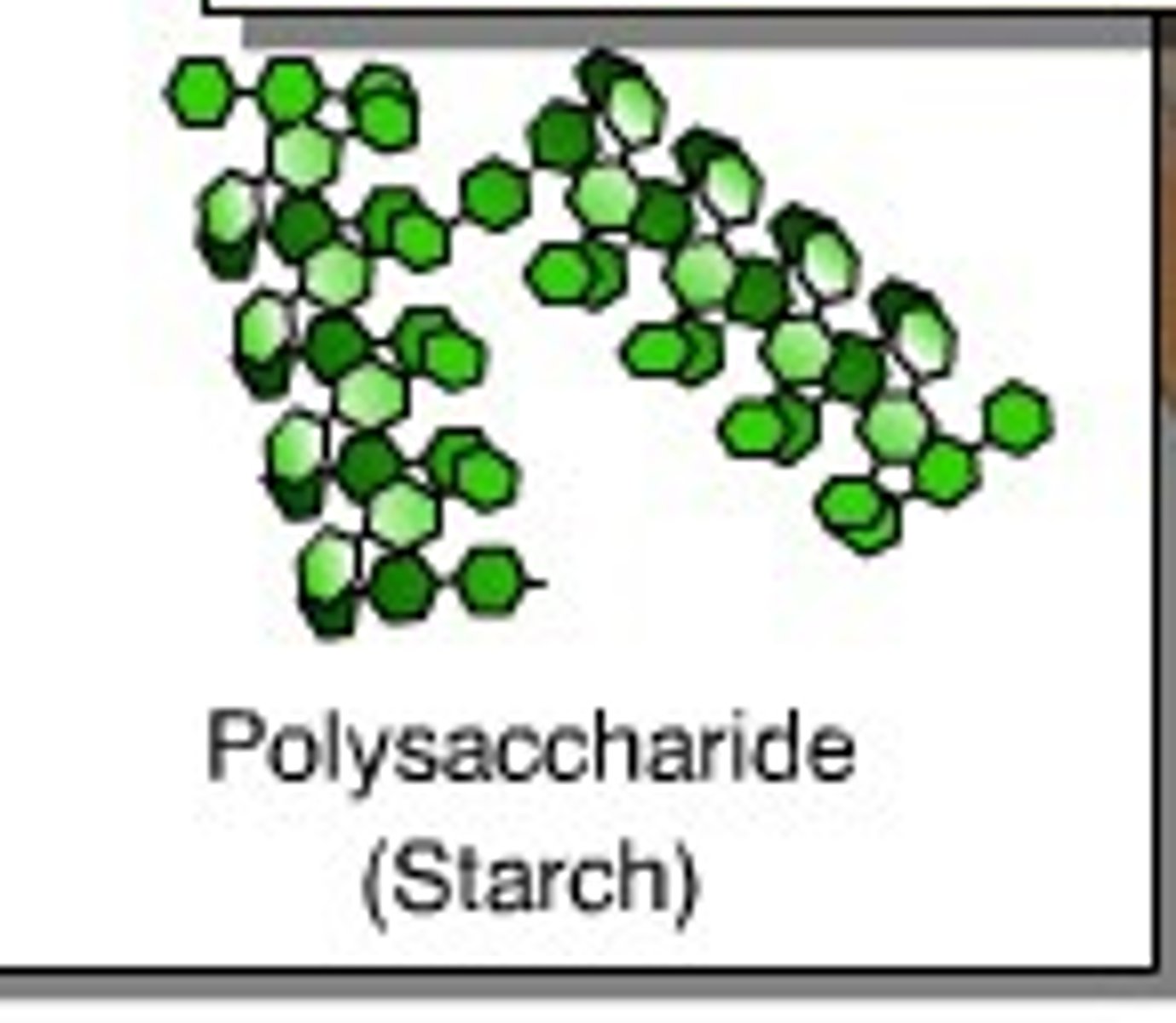
Starch
A large carbohydrate found in plants made up of many glucose molecules
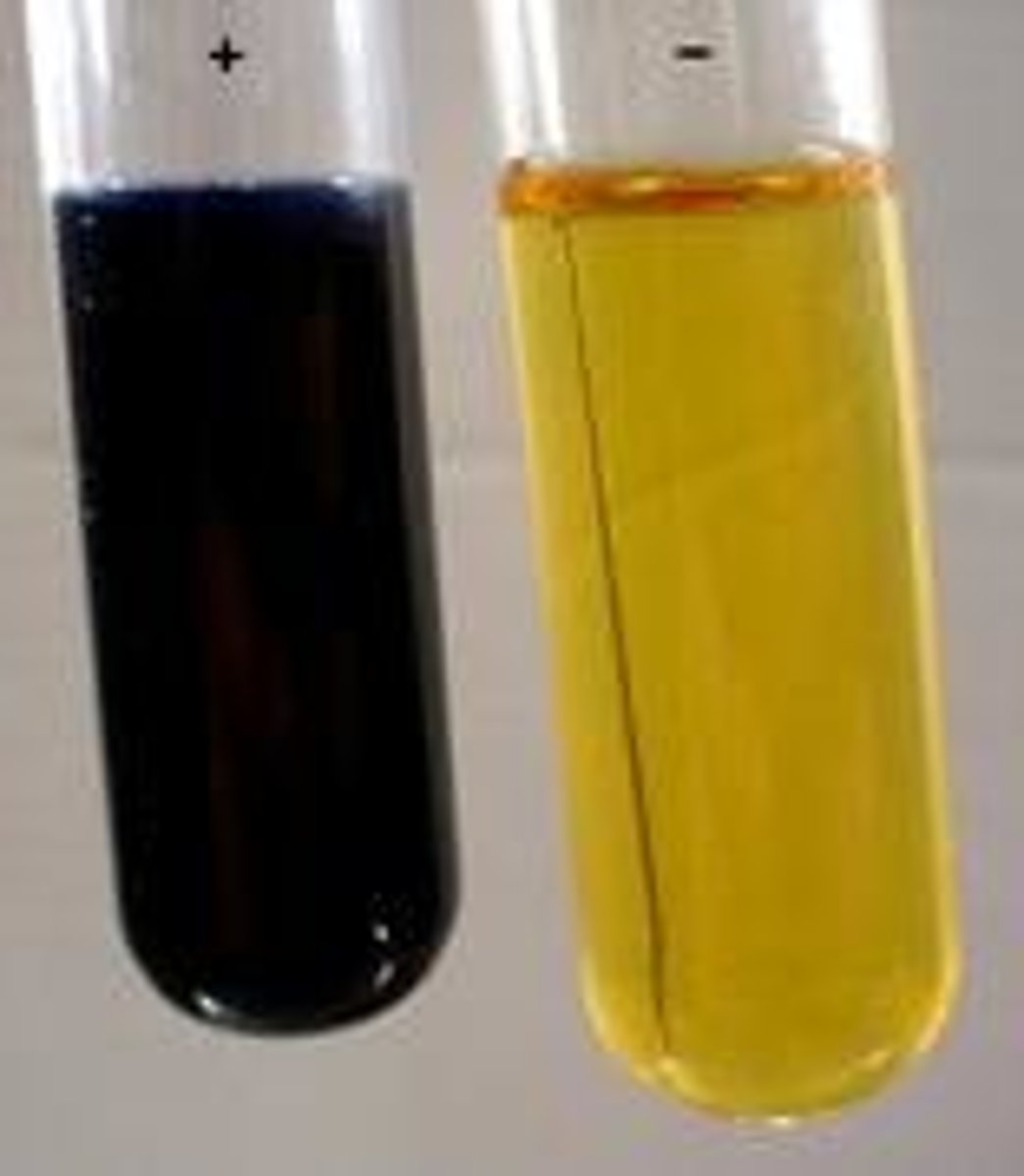
Iodine solution
Turns from orange to blue-black in the presence of starch, will remain orange if starch has been broken down by amylase

Buffer solution
A solution that controls and keeps the pH of a solution to a specific range
Water bath
A container of water heated to a given temperature, the temperature can be adjusted for each test

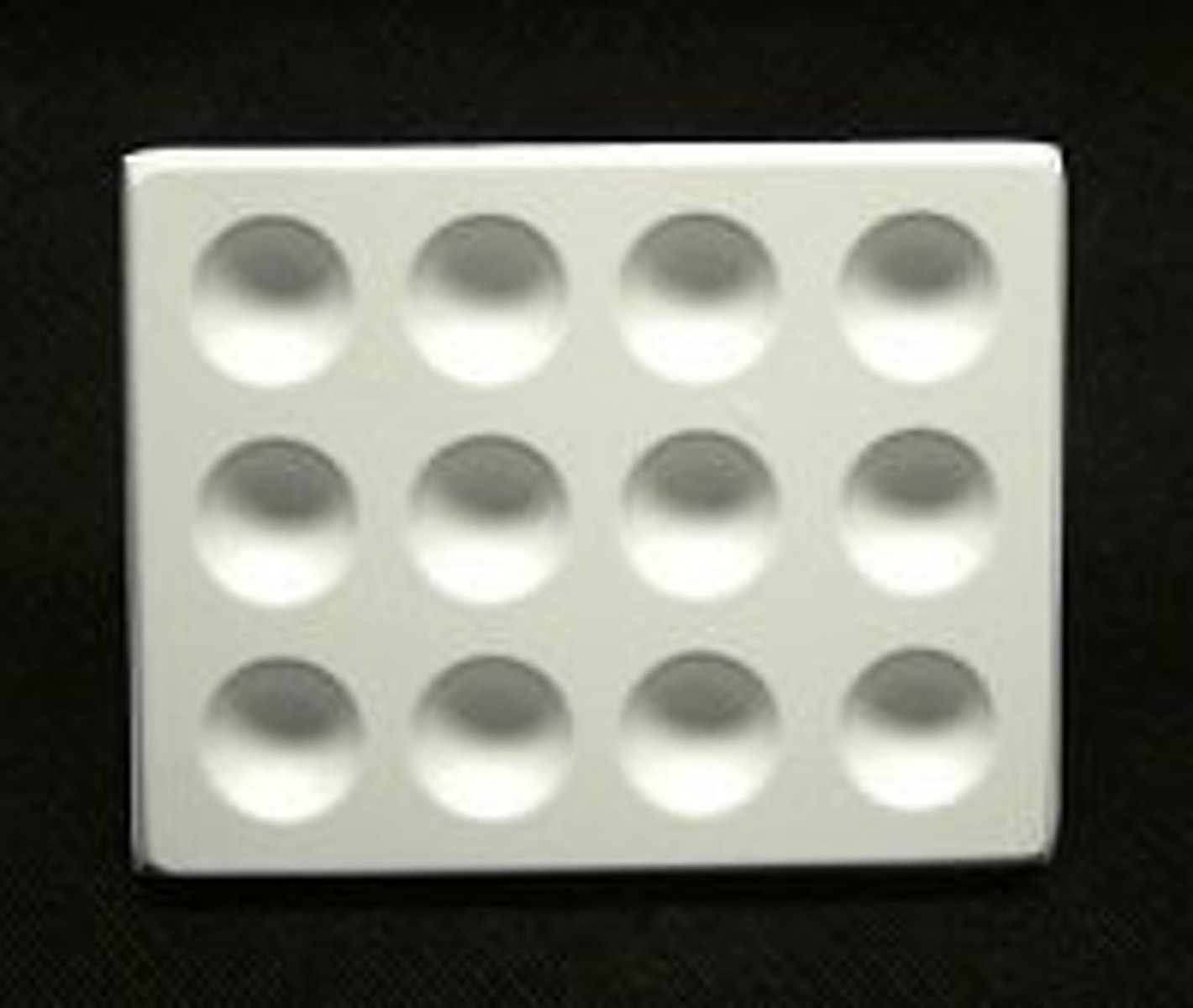
Spotting tile
Equipment used to observe the colour changes of small quantities of reacting mixtures

Time taken for starch to break down
The dependent variable or factor that is measured in this experiment to investigate temperature and enzyme activity
Temperature of solutions
The independent variable or factor that is changed in this experiment to investigate temperature and enzyme activity, for example the first test could be carried out at 20 degrees Celsius and the second test could be at 30 degrees Celsius
Temperature ranges
A wide range of temperatures should be tested, the temperature intervals should be relatively small so the estimated optimum temperature value can be more accurate
pH
A variable that should be controlled in this experiment to ensure the results are valid, can be controlled with a buffer
End of reaction
The reaction can be confirmed as complete when iodine on the spotting tile no longer changes colour from orange to blue-black
Examples of other control variables
To ensure the results are valid the volumes and concentrations of all solutions should be controlled
Expected results
Amylase will break down starch effectively at an optimum temperature, this can be identified as the temperature condition that causes iodine to remain orange the quickest