Unit 1 - Basic Economic Principles
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
economics
science of scarcity
scarcity
unlimited wants but limited resources
microeconomics
study of small economic units such as individuals, firms, and markets
macroeconomics
study of the large economy as a whole or economic aggregates (ie. economic growth)
positive statements
based on facts; avoids value judgements (what is)
normative statements
includes value judgements (what ought to be)
trade-offs
all alternatives that we give up when we make a choice
opportunity cost
most desirable alternative given up when you make a choice
utility
satisfaction/enjoyment
marginal
additional
allocate
distribute
price
amount buyer pays
cost
amount seller pays to produce a good
investment
the money spent by businesses to improve their production (ie. new factory)
consumer goods
created for direct consumption (ie. pizza)
capital goods
created for indirect consumption (ie. oven)
4 factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
land
natural resources used to produce goods and services
labor
any effort a person devotes to a task for payment
capital
physical and human
physical capital
machines and tools
human capital
knowledge and skills
entrepreneurship
leaders that combine resources and make things (goal: maximize profits)
productivity
measure of efficiency that shows the number of outputs per unit of input
ceteris paribus
all other things constant
constant opportunity cost
resources are easily adaptable for producing either good (straight line PPC)
law of increasing opportunity cost
as you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost will increase (bowed out PPC)
productive efficiency
products produced in least costly way (any point of PPC)
allocative efficiency
products being produced are most desired by society (optimal point on PPC)
PPC
graph
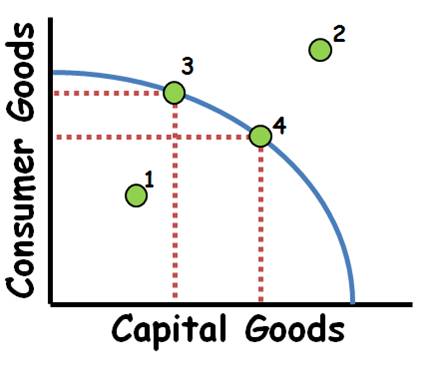
inefficient
point 1
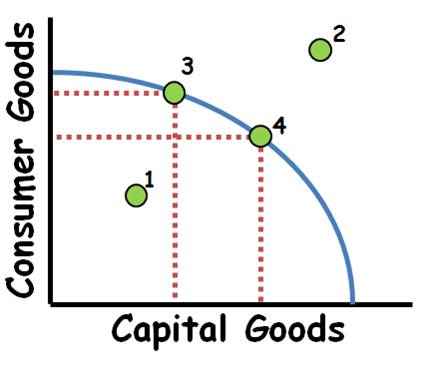
efficient
points 3 & 4
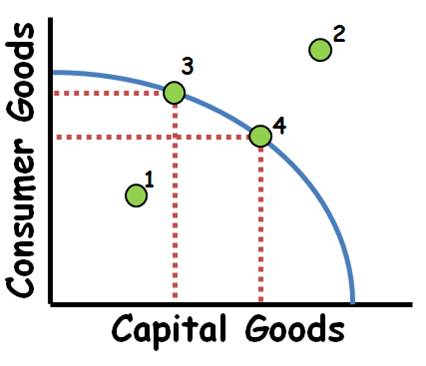
impossible/unattainable
point 2
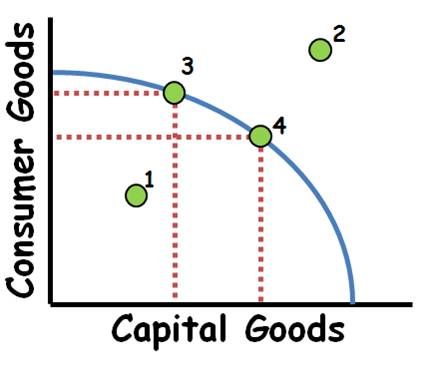
3 shifters of the PPC
change in quantity/quality of resources
change in technology
change in trade (consumption)
per unit opportunity cost (formula)
opportunity cost/units gained
absolute advantage
producer that produces most output OR requires least amount of inputs (resources)
comparative advantage
producer with lowest (per unit) opportunity cost
terms of trade
the agreed upon conditions that would benefit both countries
demand
the different quantities of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices
law of demand
there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
why does law of demand occur (2 reasons)
the substitution effect
the income effect
substitution effect
if price increases for a product, consumers will buy less of it and more of another substitute product
income effect
if price decreases for a product, the purchasing power increases for consumers (allowing them to purchase more)
law of diminishing marginal utility
as you consume more units of any good, the additional satisfaction from each added unit will start to decrease (less satisfaction)
shift
change in demand (same prices)
movement
change in quantity demanded
5 shifters of demand
tastes and preferences
number of consumers
price of related goods
income
future expectations
price of related goods
one good can be affected by a change in the price of another related good (substitutes & complements)
income
changes demand, but depends on type of good (normal and inferior)
normal goods
directly related (income increases, demand increases)
inferior goods
indirectly related (income increases, demand decreases)
future expectations
if you think the price will decrease in the future, the demand decreases
subsidy
government payment that supports a business or market (causes supply of a good to increase)
6 shifters of supply
prices/availability of resources
number of sellers
technology
government action (taxes/subsidies)
price of related goods
expectations of future profit
supply
different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices
law of supply
there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
equilibrium
point where supply and demand are balanced
price ceiling
maximum legal price a seller can charge for a product (causes shortage)
price floor
minimum legal price a seller can sell a product; must be above equilibrium to have an effect (causes surplus)
double shift rule
if two curves shift at the same time, either price or quantity will be indeterminate