Small animal head and neck
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:29 PM on 3/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
what is in the temporal bone
the middle ear
ear canal
ear canal
2
New cards
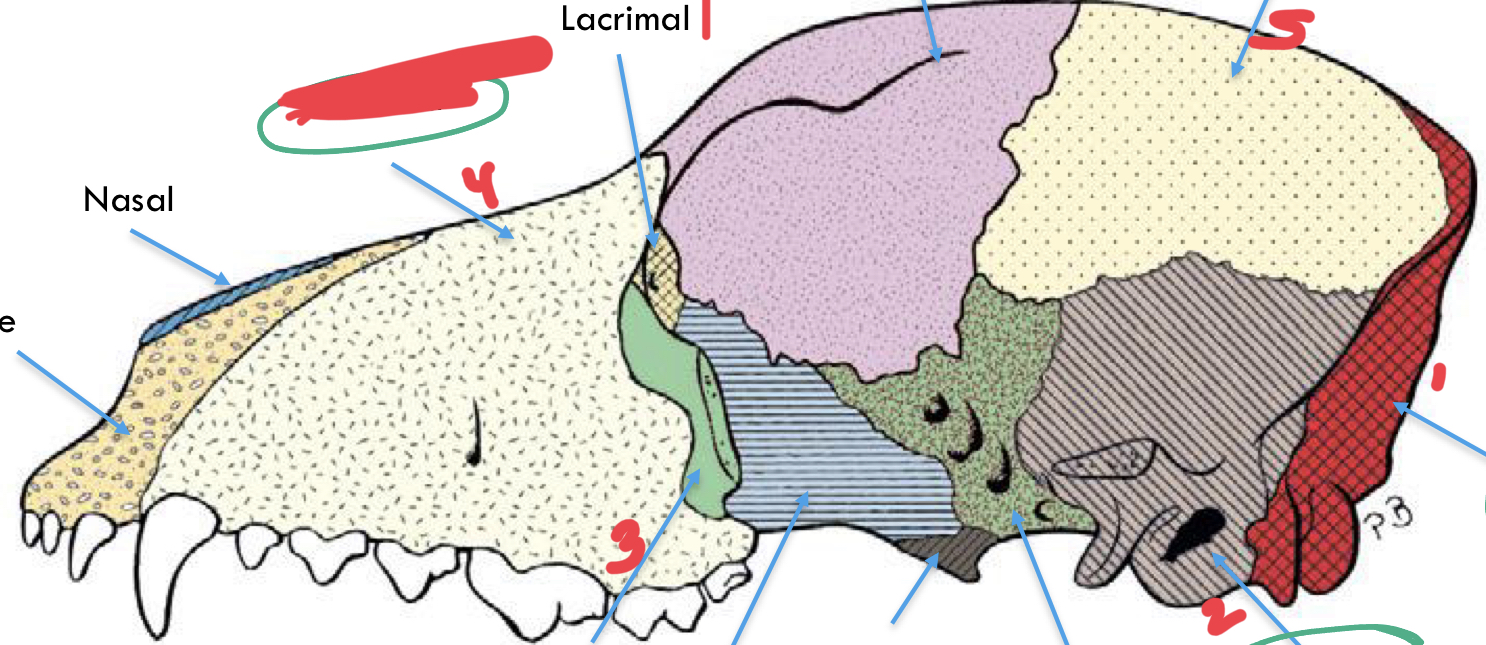
label the
maxilla
parietal
occipital
temporal
zygomatic
maxilla
parietal
occipital
temporal
zygomatic
1. occipital
2. temporal
3. zygomatic
4. maxilla
5. parietal
3
New cards
whats important about the zygomatic
it protects the eye
4
New cards
what is the canine dental formula
up 3142
down 3143
down 3143
5
New cards
which teeth are the carnasial or shearing teeth
p4 and M1
6
New cards
when do the permanent incisors come in for a dog
3-5 months
7
New cards
when do the permanent canine teeth for a dog come in
4-6 months
8
New cards
when do the permanent premolars come in for a dog
4-5 months
9
New cards
when do the permanent molars come in for a dog
5-7 months
10
New cards
what is the dental formula for felines
up 3131
down 3121
down 3121
11
New cards
when do the permanent incisiors come in for a cat
3\.5-5.5 months
12
New cards
when do the permanent canines come in for a cat
5\.5-6.5 months
13
New cards
when do the permanent premolars come in for a cat
4-5 months
14
New cards
when do the permanents molars come in for a cat
5-6 months
15
New cards
what does the condyloid process of the mandible articulate with
what is this joint called
what is this joint called
mandibular fossa of temporal bone
\
* temporomandibular joint hinge joint
\
* temporomandibular joint hinge joint
16
New cards
how do you know if you luxated your TMJ
if your teeth don’t articulate
17
New cards
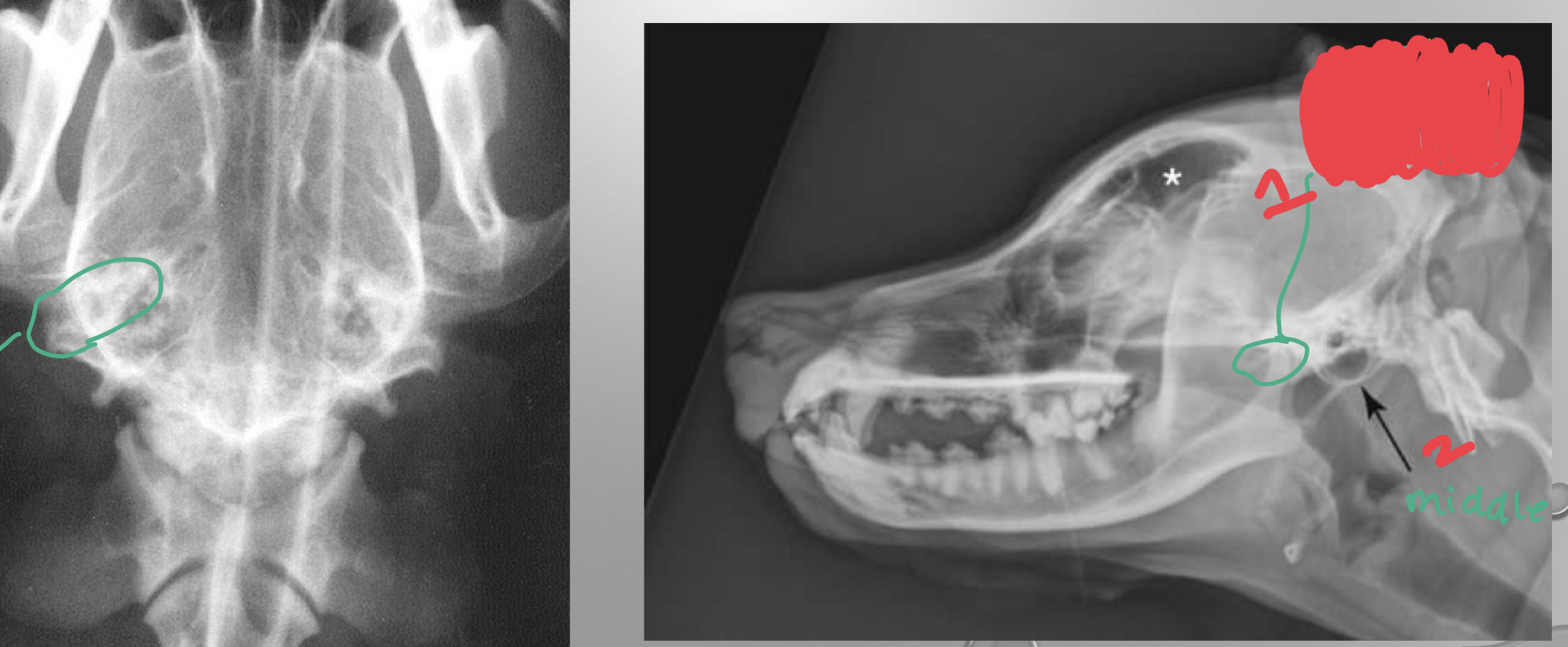
identify
1. TMJ
2. tympani joint
18
New cards
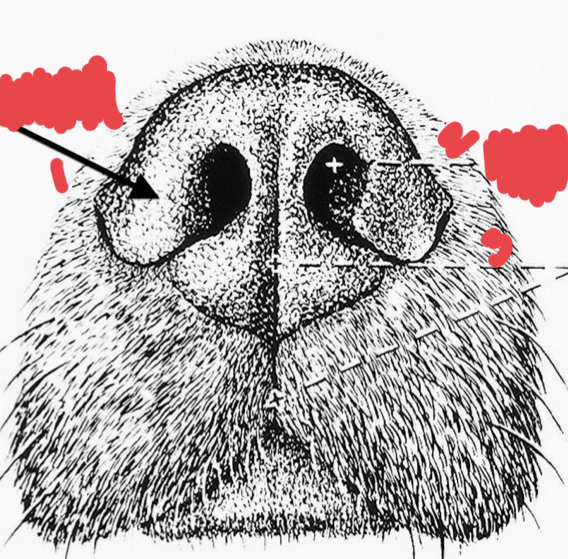
identify
philtrum
nostril
alar fold
philtrum
nostril
alar fold
1. alar fold
2. nostril
3. philtrum- center of the nose
19
New cards
what is the pharynx a crossroad for
* nasal cavity
* oral cavity
* airway
* oral cavity
* airway
20
New cards
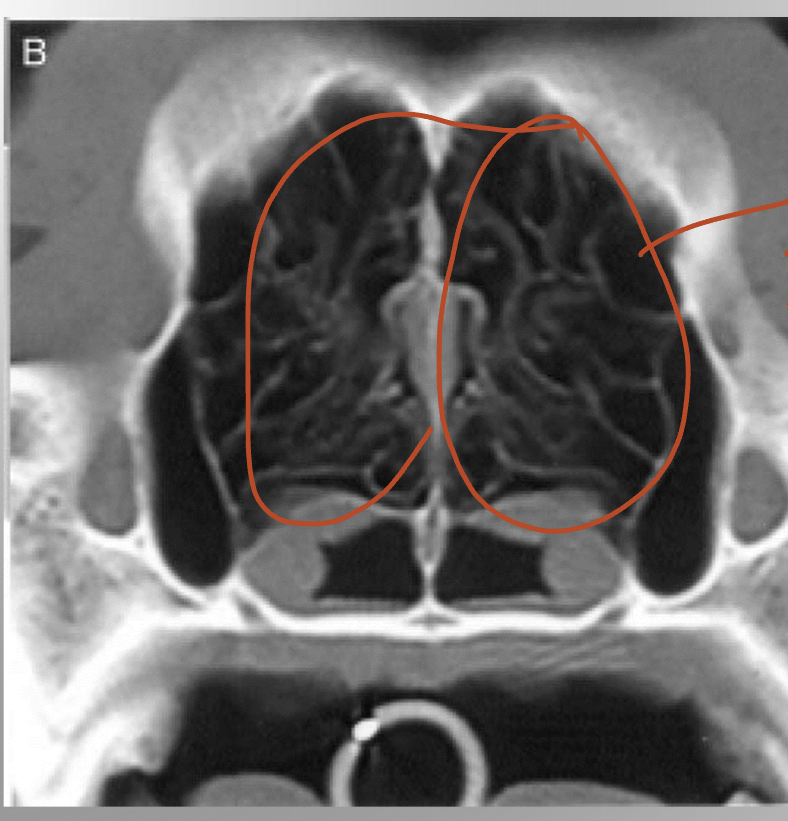
identify and explain what it does
nasal turbance
* humidify air
* catches dirt
* humidify air
* catches dirt
21
New cards
where to place a nasogastric tube
pass the tube ventral middle= ventral meatus
22
New cards
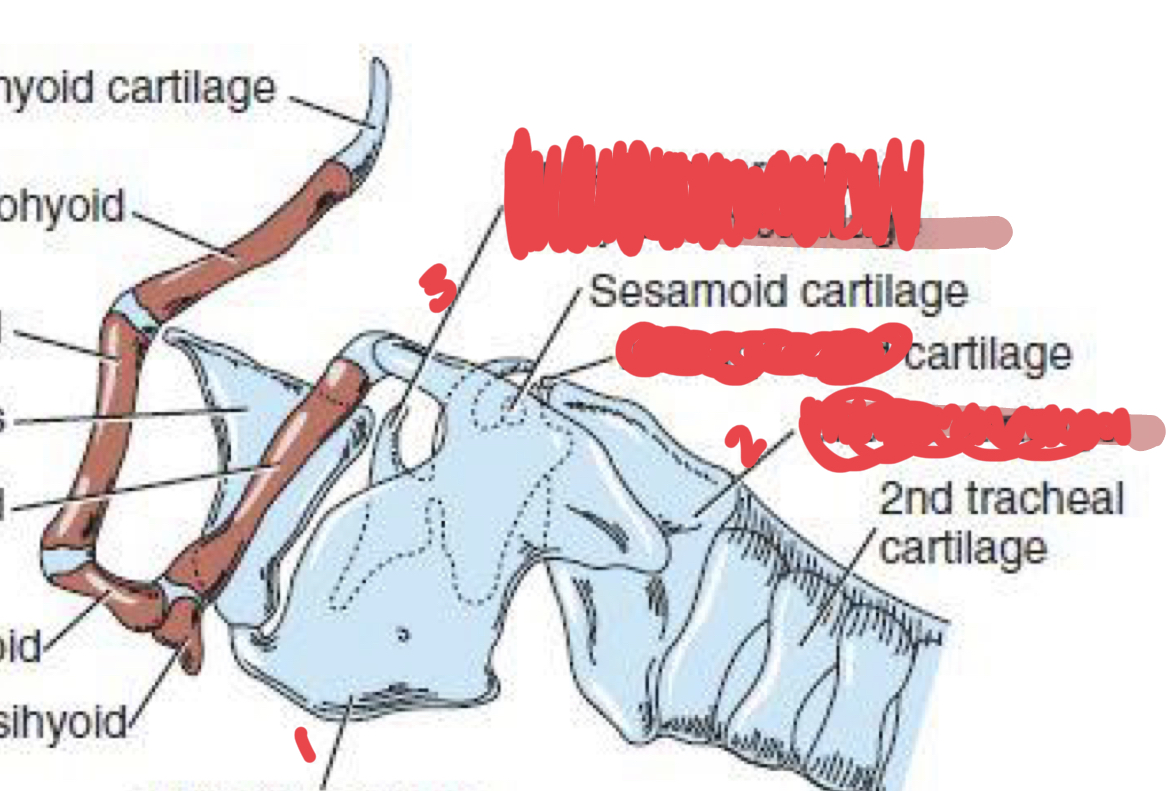
identify
cricoid cartilage
arytenoid cartilage
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
arytenoid cartilage
thyroid cartilage
1. thyroid cartilage
2. cricoid cartilage
3. arytenoid cartilage
23
New cards
what are the processes of the arytenoid and identify
1. corniculate
2. cuneiform
24
New cards
case
* 10 yr MN lab
* difficulty breathing
* exercise intolerance
* stridorous
* struggling to breath cant get air in
\
* 10 yr MN lab
* difficulty breathing
* exercise intolerance
* stridorous
* struggling to breath cant get air in
\
laryngeal paralysis
* airway doesnt open
* give dopram to stimulate deep breathing
* they go into respiratory failure and die
* airway doesnt open
* give dopram to stimulate deep breathing
* they go into respiratory failure and die
25
New cards
explain laryngeal paralysis
* idiopathic neuropathy
* no certain reason for this
* something is happening to the nerves
* recurrent laryngeal nerve is very long goes from chest to the neck
* innervates almost all of the muscles of the larynx
* cricoarytenoideus dorsalis
* most important bc it opens larynx
* potentially part of a more generalized degenerative poly neuropathy
* may be weak on their hindlimbs at the same time
* no certain reason for this
* something is happening to the nerves
* recurrent laryngeal nerve is very long goes from chest to the neck
* innervates almost all of the muscles of the larynx
* cricoarytenoideus dorsalis
* most important bc it opens larynx
* potentially part of a more generalized degenerative poly neuropathy
* may be weak on their hindlimbs at the same time
26
New cards
how do you fix laryngeal paralysis cricoid
* mimic what cricoarytenoideus dorsalis does
* you tie aryntenoid cartilage to **cricoid** or thyroid so that it permanently stays open one side
* mostly thyroid
* you tie aryntenoid cartilage to **cricoid** or thyroid so that it permanently stays open one side
* mostly thyroid
27
New cards
what risk does a dog have when they get a procedure to fix laryngeal paraylisis
aspiration ammonia bc airway doesnt close
28
New cards
CASE
* 3yr MN french bulldog
* chronic snoring
* stertorous breathing
* upper airway breathing
* inspiratory dyspnea at times
* trouble breathing
* 3yr MN french bulldog
* chronic snoring
* stertorous breathing
* upper airway breathing
* inspiratory dyspnea at times
* trouble breathing
brachycephalic upper airway syndrome
* stenotic nares
* smaller weak openings
* air difficult to get in
* enlongated soft palate
* bigger and pushed into the airway
* hypoplastic trachea
* stenotic nares
* smaller weak openings
* air difficult to get in
* enlongated soft palate
* bigger and pushed into the airway
* hypoplastic trachea
29
New cards
what is the secondary effect for brachycephalic upper airway
* everted laryngeal saccules
* vocal chords get inflammed
* vocal chords get inflammed
30
New cards
how do you help bulldogs breathe better
cut part of alar fold to let airway in
rhinoplasty
rhinoplasty
31
New cards
how to fix brachycephalic upper airway
cutting the soft palate to be shorter
32
New cards
explain everted laryngeal saccules
* chronic increased respiratory effort can evert the soft tissue between the vocal folds
* can obstruct the airways
* you just cut them out
* can obstruct the airways
* you just cut them out
33
New cards
how many parathyroids are there
4
* 2 external parathyroid glands
* 2 internal parathyroid glands
* 2 external parathyroid glands
* 2 internal parathyroid glands
34
New cards
what do the parathyroid glands do
produce parathyroid hormone
increases ca levels
increases ca levels
35
New cards
what happens if there is a parathyroid tumor
you will have hypercalcuim
36
New cards
what is the thyroid slip
when u palpate a cats neck while its extended
* place thumb and index finger on each side of the trachea and swept downwards from the larynx to the sternum
* palpation of a freely moveable, subcutaneous nodule or a “blip” that slips under the fingertips determines the presence of an enlarged thyroid gland
* you shouldnt be able to feel anything
* should be done routinely
* place thumb and index finger on each side of the trachea and swept downwards from the larynx to the sternum
* palpation of a freely moveable, subcutaneous nodule or a “blip” that slips under the fingertips determines the presence of an enlarged thyroid gland
* you shouldnt be able to feel anything
* should be done routinely
37
New cards
what diagnostic tool should you use check if cat has hyperthyroidism
nuclear scintigraphy
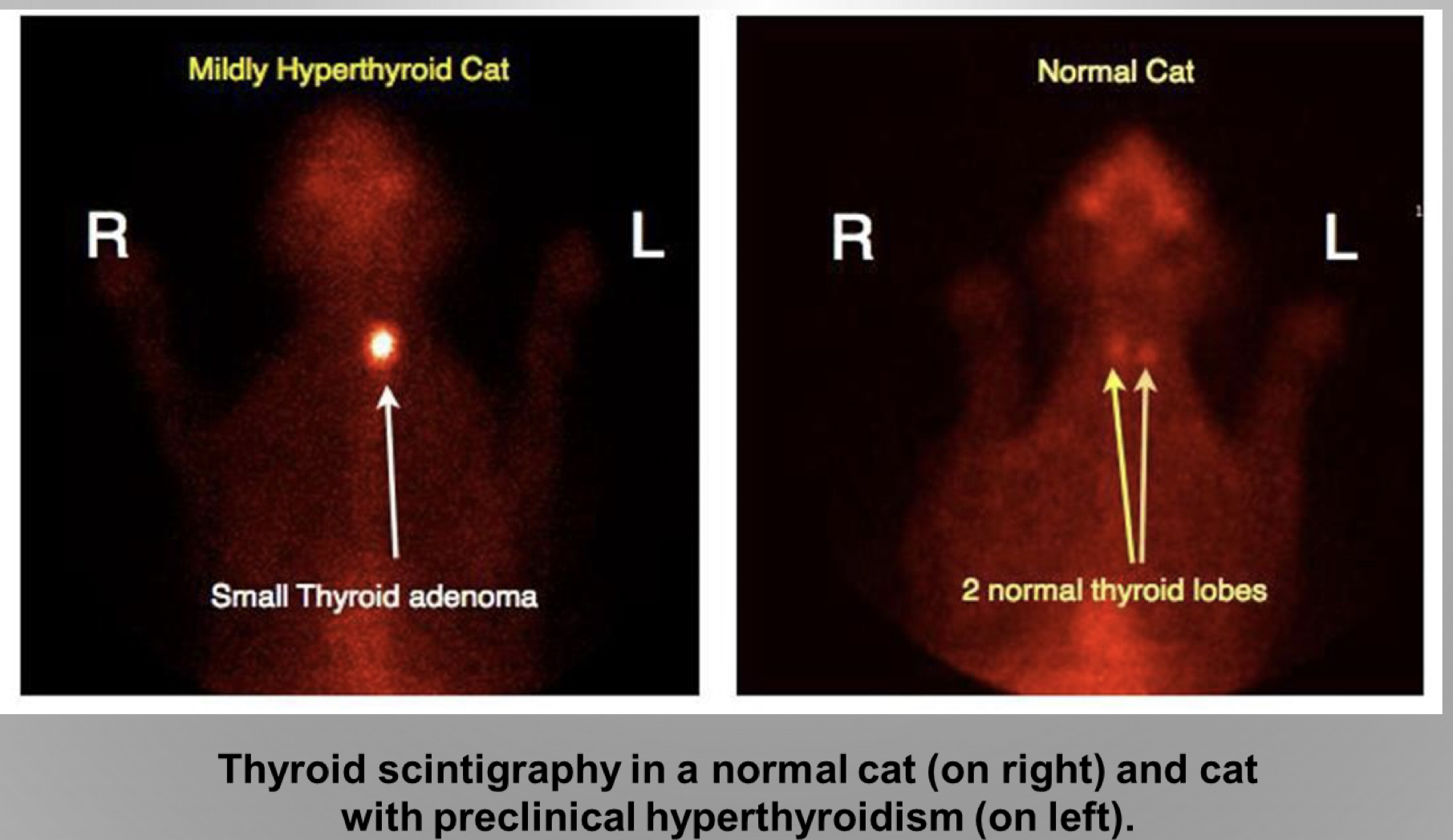
38
New cards
what thyroid tumors do cats get
thyroid adenoma
easier to treat than what a dog would have
easier to treat than what a dog would have
39
New cards
what thyroid tumors do dogs get
thyroid carcinoma
maglinent tumor
maglinent tumor
40
New cards
whats in the cartoid sheath
vagosympathetic trunk and common carotid artery
41
New cards
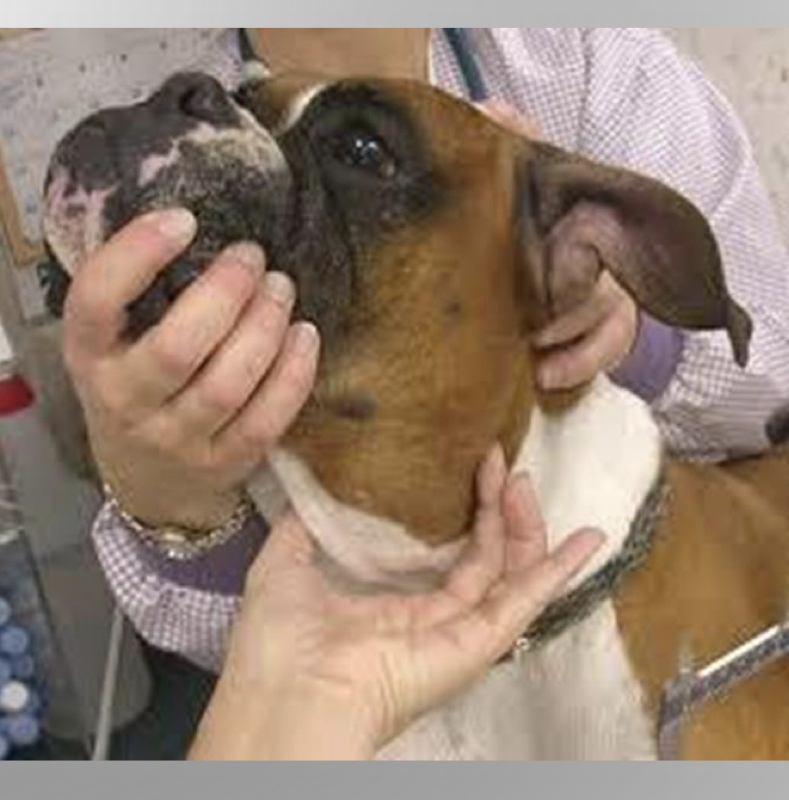

CASE
* 6yr old MN Boxer
* 1 week of persistent drooling with some blood present
* acutely swollen left side of face
* FNA of mass large volume of viscous clear fluid
* 6yr old MN Boxer
* 1 week of persistent drooling with some blood present
* acutely swollen left side of face
* FNA of mass large volume of viscous clear fluid
mandibular
\-sialocele
\-sialocele
42
New cards
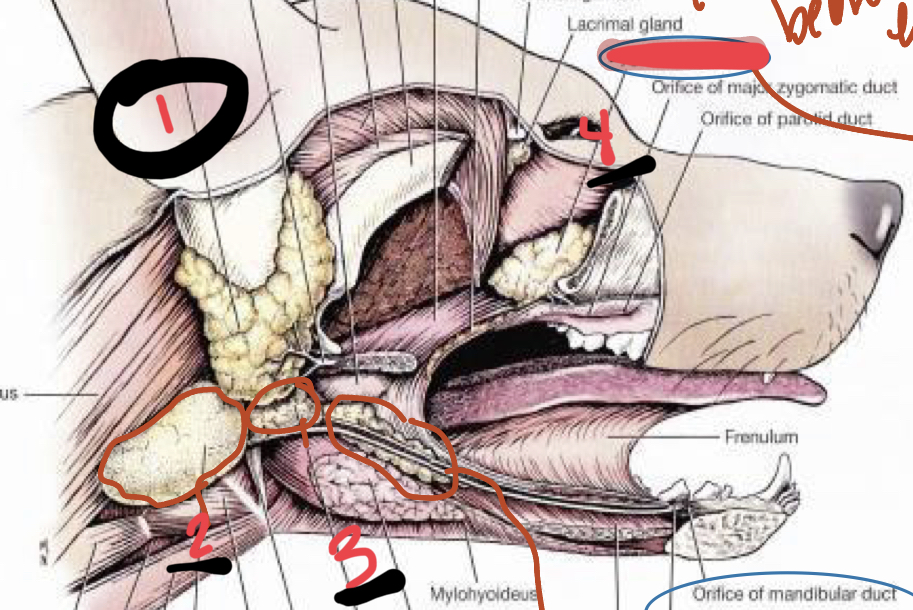
identify the glands
sublingual
mandibular
parotid
zygomatic
sublingual
mandibular
parotid
zygomatic
1. parotid
2. mandibular
3. sublingual
4. zygomatic
43
New cards
what happens if the sublingual gland tears
saliva goes anywhere under the tongue
44
New cards
what happens if the mandibular gland tears
saliva goes anywhere in the neck
45
New cards
what happens if the parotid and zygomatic gland tears
it will leak saliva under the ear
46
New cards
where do the mandubular and sublingland glands empty out
at the sublingual papilla
47
New cards
which glands of the most diseases
mandibular and sublingual
48
New cards
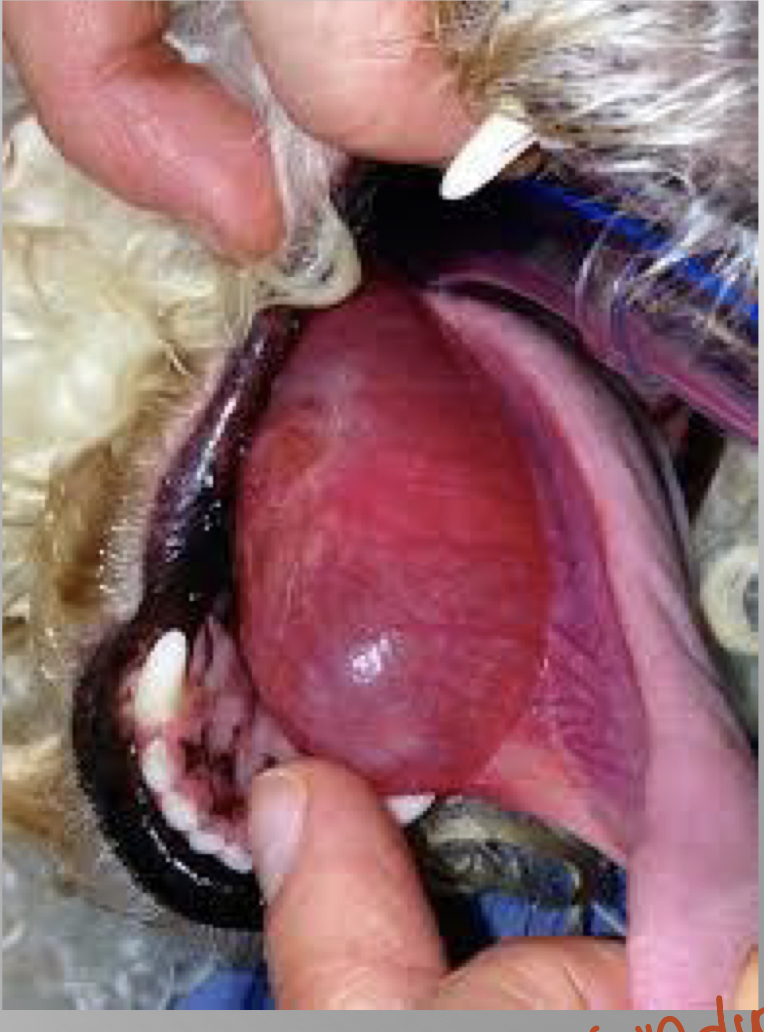
what is this called
ranula
sublingual tear
sublingual tear
49
New cards
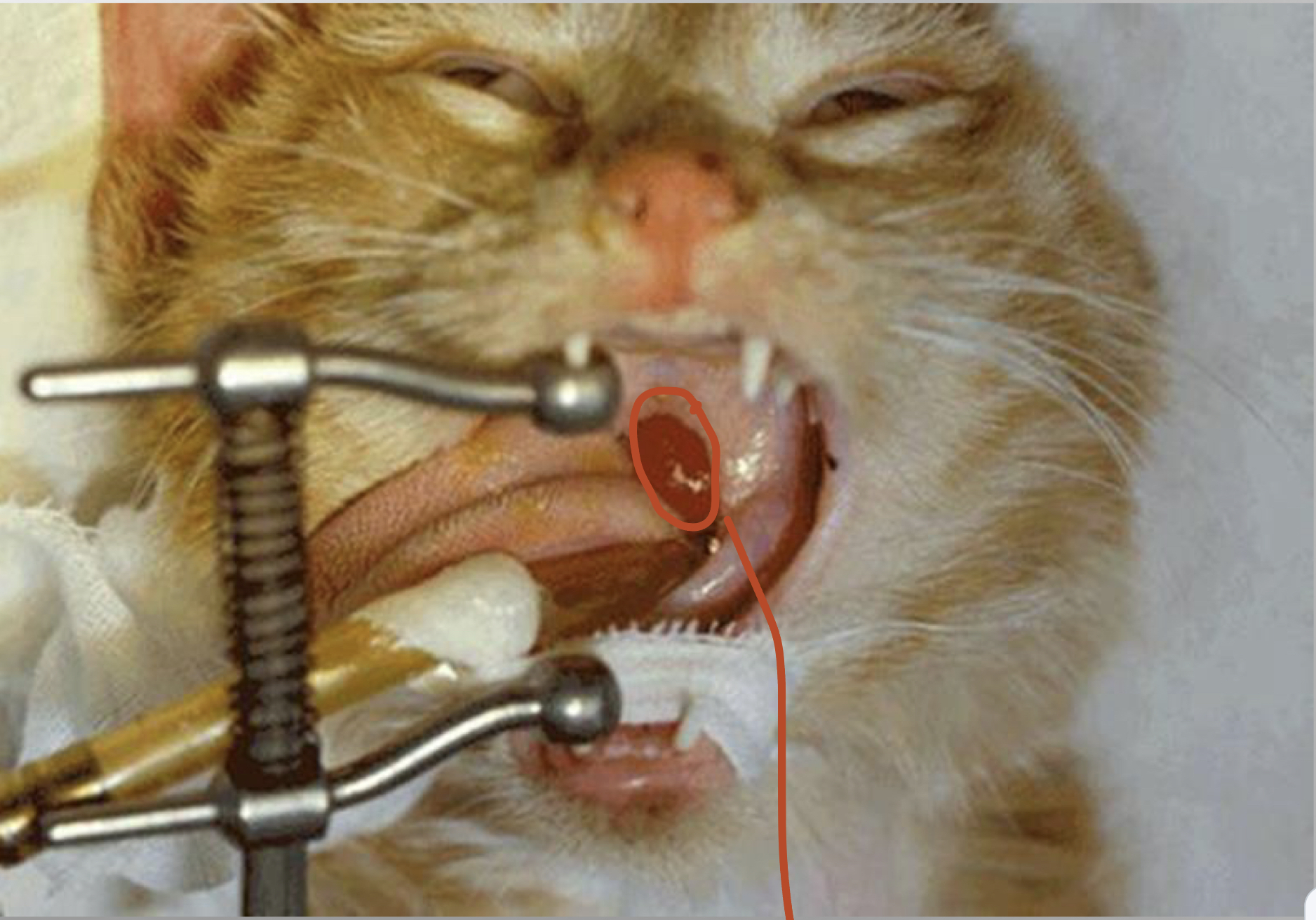
CASE
* 1yr old mc tabby
* mild dyspnea
* noisy breathing
* nasal discharge
* 1yr old mc tabby
* mild dyspnea
* noisy breathing
* nasal discharge
nasopharyngeal polyps
* benign inflammatory in nature
* grow out of the middle ear
* young cats
* benign inflammatory in nature
* grow out of the middle ear
* young cats
50
New cards
if you put florescent in the nasolacrimal duct where would it leak out of
nose
51
New cards
what can u do to unblock the nasolacrimal duct
put a cannula in there
52
New cards
what is a cherry eye
when the 3rd eyelid is prolapsed
* doesnt cause any problems
* cosmetic to fix
* doesnt cause any problems
* cosmetic to fix
53
New cards
how would you test for olfactory nerve
you would test for smell but its very subjective
54
New cards
how would you test for the optic nerve
you would throw a cotton ball or something that doesnt make noise and see if there is a response
test can be subjective
test can be subjective
55
New cards
how do you test for oculomotor nerve
you would shine a light on its eye and pupil should constrict
56
New cards
how do you test for trochlear nerve
eye would be deviated laterally if something was wrong and would lose function of its dorsal oblique muscle
* known as lazy eye
* to strength the muscle you could patch the good eye to strength the eye muscles
* known as lazy eye
* to strength the muscle you could patch the good eye to strength the eye muscles
57
New cards
how to test for trigeminal nerve
its pretty hard to do
* you want and eye blink but without putting air by the eye
* also there jaw wont be able to shut and be salivating everywhere
* you want and eye blink but without putting air by the eye
* also there jaw wont be able to shut and be salivating everywhere
58
New cards
how to test for abducens
* eye will be deviated medially
59
New cards
how to test for facial nerve
sensory
poking their face
* would have facial paralysis and drooling
poking their face
* would have facial paralysis and drooling
60
New cards
what would happen if vestibulocochlear nerve was damaged
* balance would be off
* eyes would be moving back and fourth
* testing for hearing is hard
* eyes would be moving back and fourth
* testing for hearing is hard