Bio9 lab - skeletal muscle
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
One motor neuron's action potential causes
all the muscle fibers it connects to contract
NMJ is made of
axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and motor endplate of the muscle fiber.
At regular points along the muscle fiber, the sarcolemma extends deep into the center of the fiber to form structures called
t tubules
Local depolarization of the motor endplate initiates a ? that travels along the ? and down t-tubules
Ap, sarcolemma
Sarcomeres are joined together by
z lines
what happens at the Z lines
actin/myosin are joined
actin =
myosin =
thin
thick
The process of progressive activation of motor units is called
recruitment
the number of action potentials delivered to a muscle within a set period of time
frequency
tetanus
sustained maximal muscle contraction
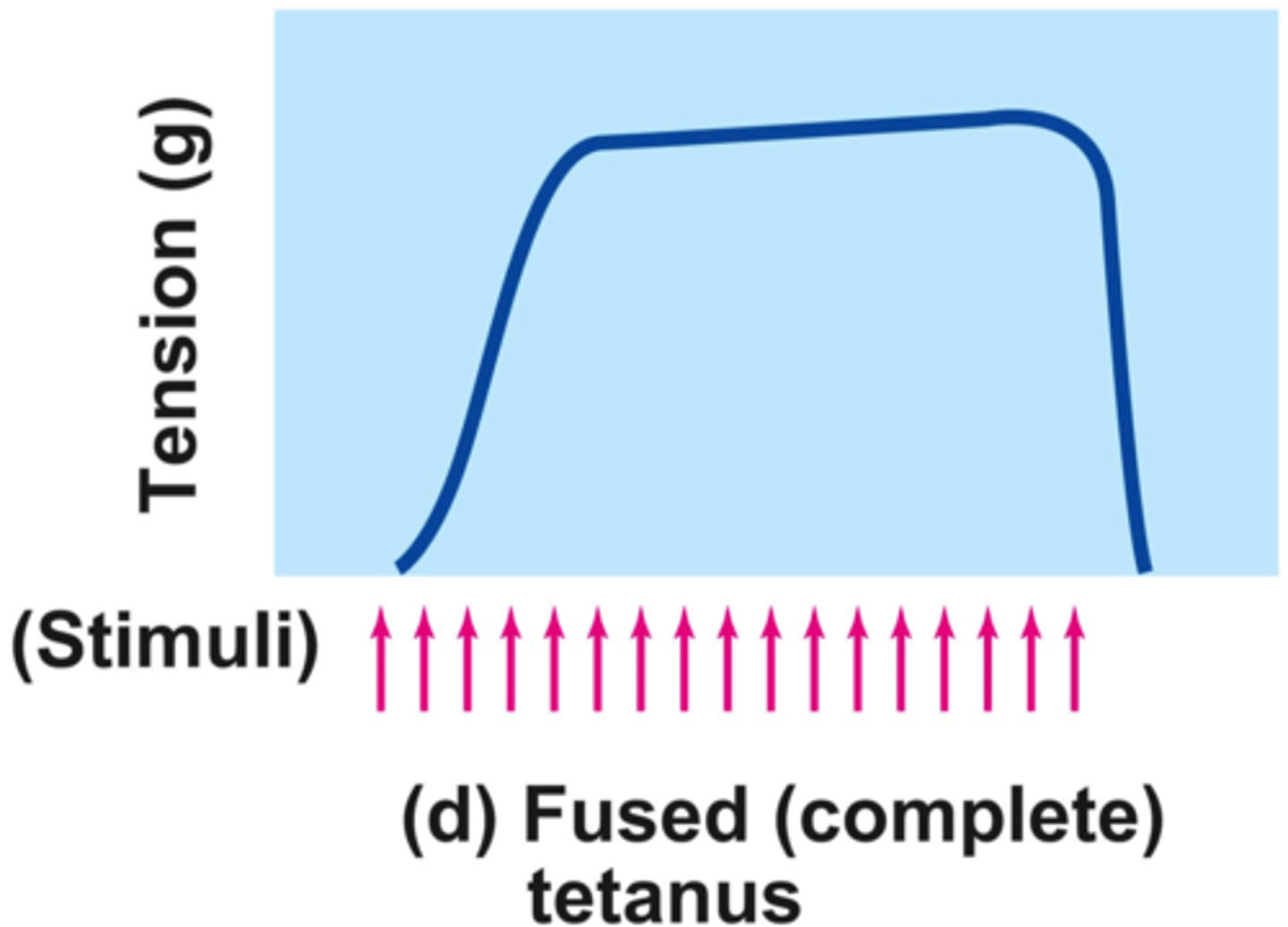
twitch
a quick cycle of contract/relax
Summation
accumulation of contraction
isometric
same length, joint doesn't move, develops tension (gravity)

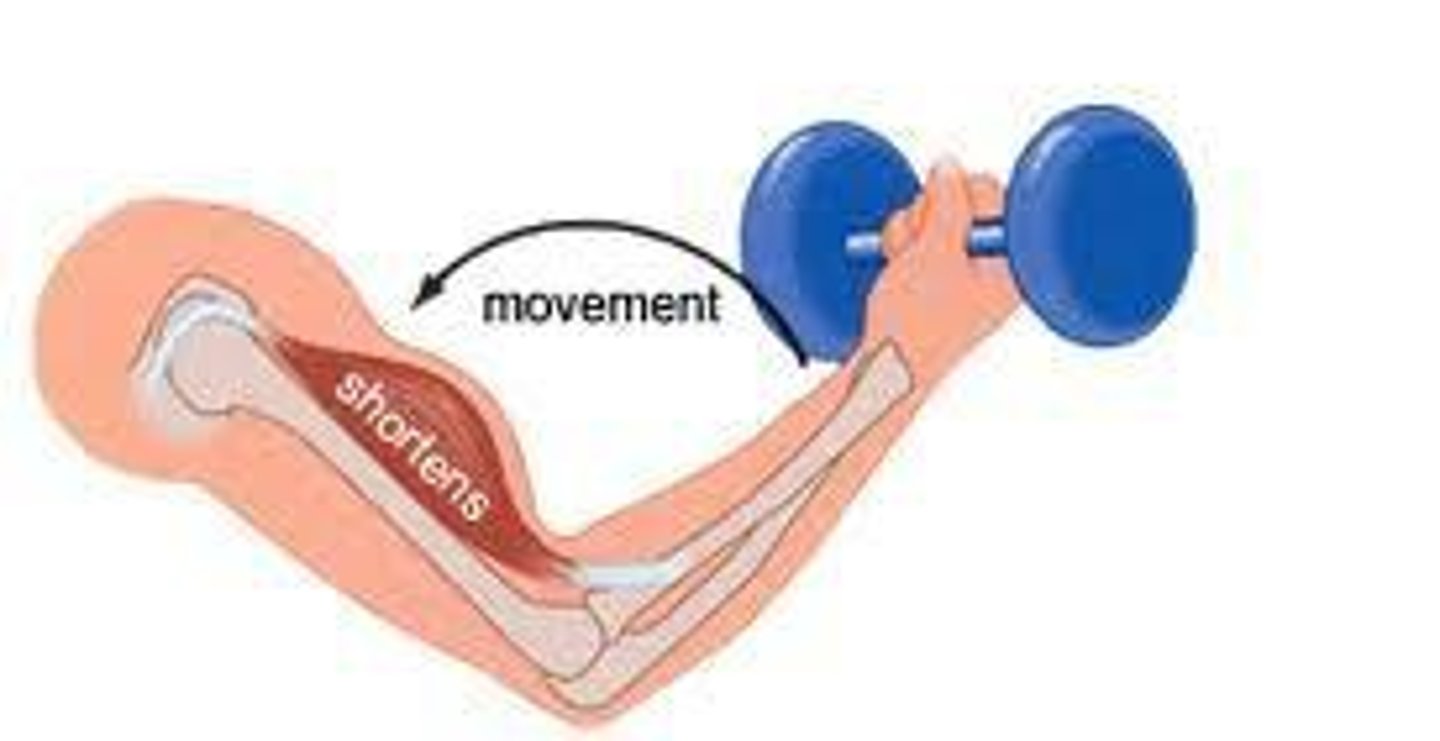
isotonic
muscle shortens,tension stays same, concentric,ecentric

Eccentric
muscle lengthens
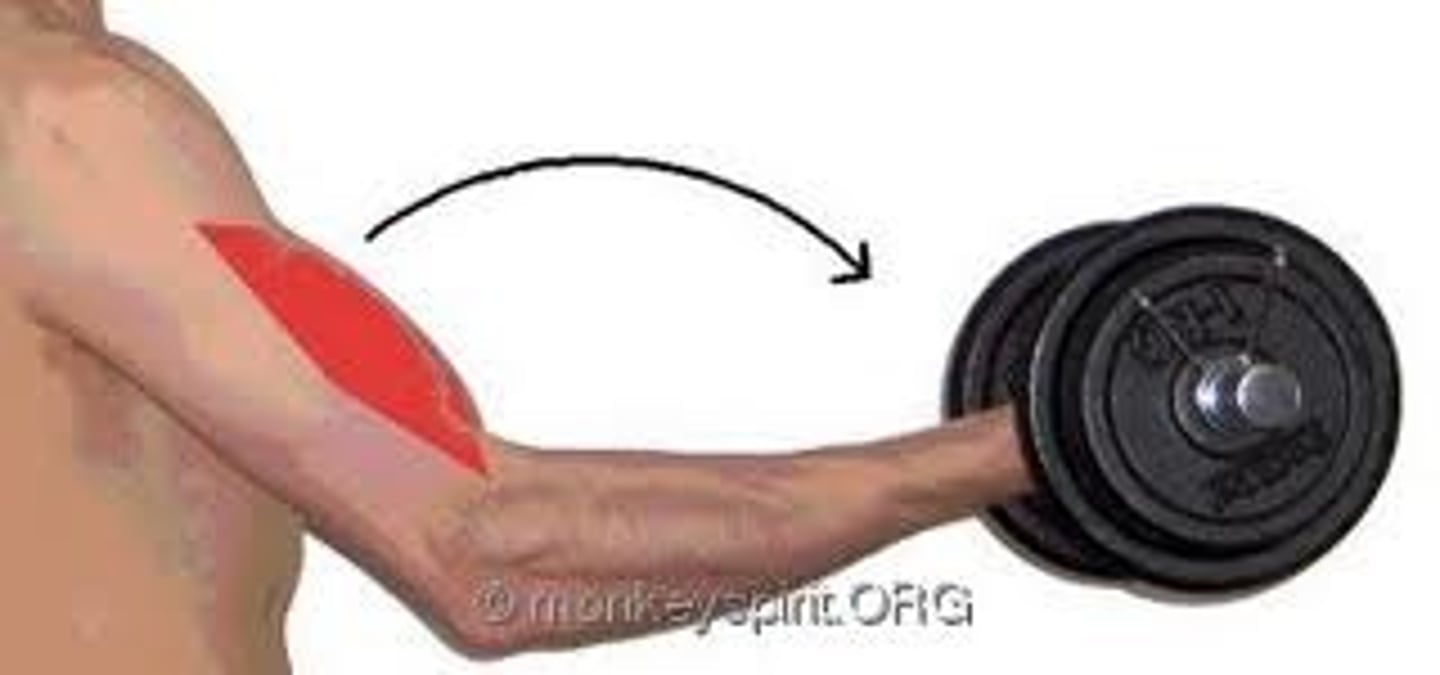
concentric
muscle shortens
proportion of fibers in the muscle contracting
- threshold
few
proportion of fibers in the muscle contracting
- maximal stimulus
100%/all
proportion of fibers in the muscle contracting
- above max status
100%/all
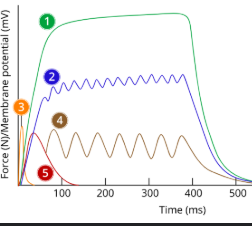
1
tetanus
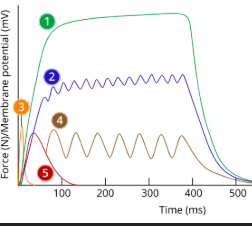
2
Incomplete tetanus
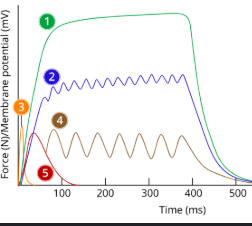
3
Action potential/ap
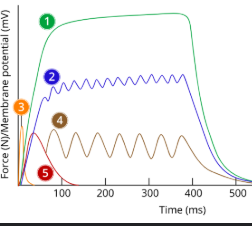
4
Summation
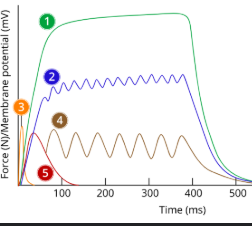
5
Twitch
Why do toxins like those from Clostridium tetani harm your muscles?
They stop nerves from letting muscles relax, causing painful spasms and stiffness
If breathing muscles are affected, it can be deadly.
How does latency differ between ulnar nerve stimulation at the wrist vs. the elbow
shorter at the wrist and longer at the elbow.
Why is latency longer when the ulnar nerve is stimulated at the elbow?
signal has to travel a longer distance to reach the muscle, so it takes more time.
Conduction velocity (signal)
50 meters/per second
In skeletal muscle, what is a minimum unit of contraction caused by a single action potential called?
twitch
myofibril, endomysium, muscle, muscle fiber, epimysium, sarcomere, fascicle, perimysium
order them small to big
Sarcomere, myofibril, muscle fiber, endomysium, fascicle, perimysium, muscle, epimysium
functions of skeletal muscle
locomotion, posture, heat, joint support
Motor units that control larger groups of muscles (like posture) are generally much ? in size
larger
to prevent constant muscle stimulation, how is ACh cleared quickly from the synaptic cleft?
broken down by enzyme and recycled back into vesicles
The removal of which ion causes the muscle to relax after contraction?
Ca2+
Excitation contraction coupling
converts electrical stim to motor stim