BIO101 Unit 1 Chapter 4
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Why is carbon the backbone of biological molecules?
Because it can form four covalent bonds, allowing diverse and stable structures like chains, rings, and branching molecules.
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
4
Why can carbon form complex molecules?
Its tetravalence allows bonding in multiple directions and with many elements.
What are hydrocarbons?
Molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen.
Why are hydrocarbons important?
They store large amounts of energy and are found in fats and fuels.
Are hydrocarbons hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic due to nonpolar C–H bonds.
What are carbon skeletons?
The chain of carbon atoms forming a molecule’s backbone.
What variations can carbon skeletons have?
Length, branching, double bonds, and ring structures.
What effect do double bonds have on structure?
They make the molecule planar and restrict rotation.
What are isomers?
Molecules with same formula but different structures.
What are structural isomers?
Molecules with different covalent arrangements of atoms.
What are cis-trans isomers?
Molecules with same bonds but different spatial arrangement around a double bond.
What is required for cis-trans isomers to occur?
A double bond.
What are enantiomers?
Mirror-image isomers that differ in 3D arrangement.
What makes a carbon asymmetric?
Being bonded to four different groups.
What is chirality?
Property of a molecule that is not superimposable on its mirror image.
What is the difference between chiral and achiral?
Chiral = non-superimposable; achiral = superimposable.
What is a functional group?
Specific chemical groups attached to carbon skeletons responsible for molecular behavior.
Structure of hydroxyl group?
–OH
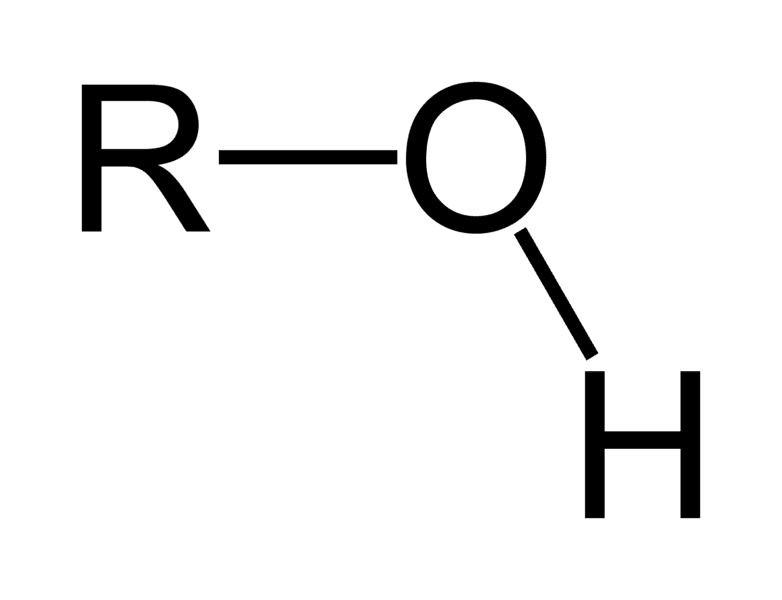
Properties of hydroxyl group
Polar, forms hydrogen bonds, increases solubility
Carbonyl group structure
C=O
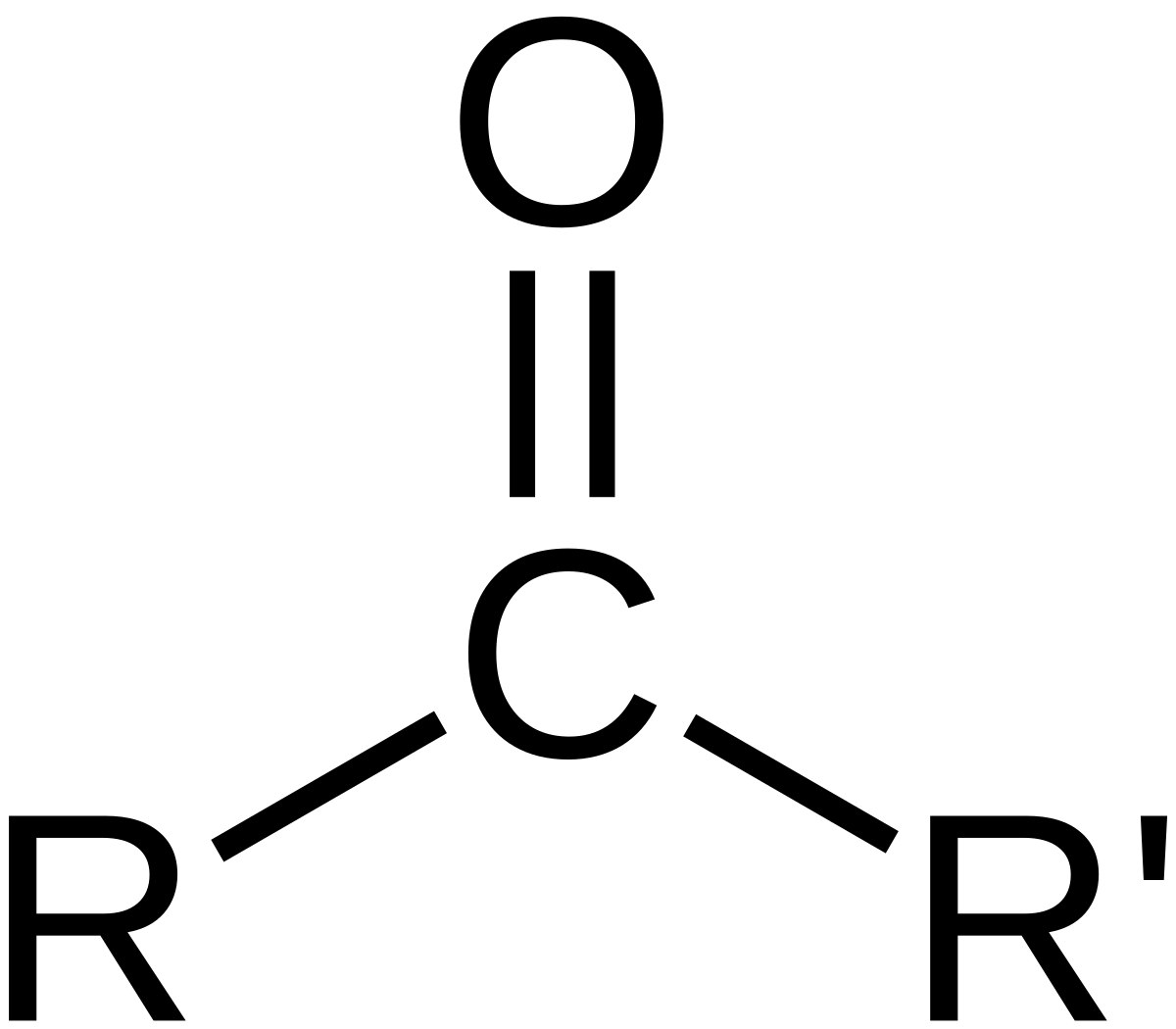
Carbonyl groups are found in
Aldehydes (at end) and ketones (within carbon skeleton)
Carboxyl group structure
–COOH
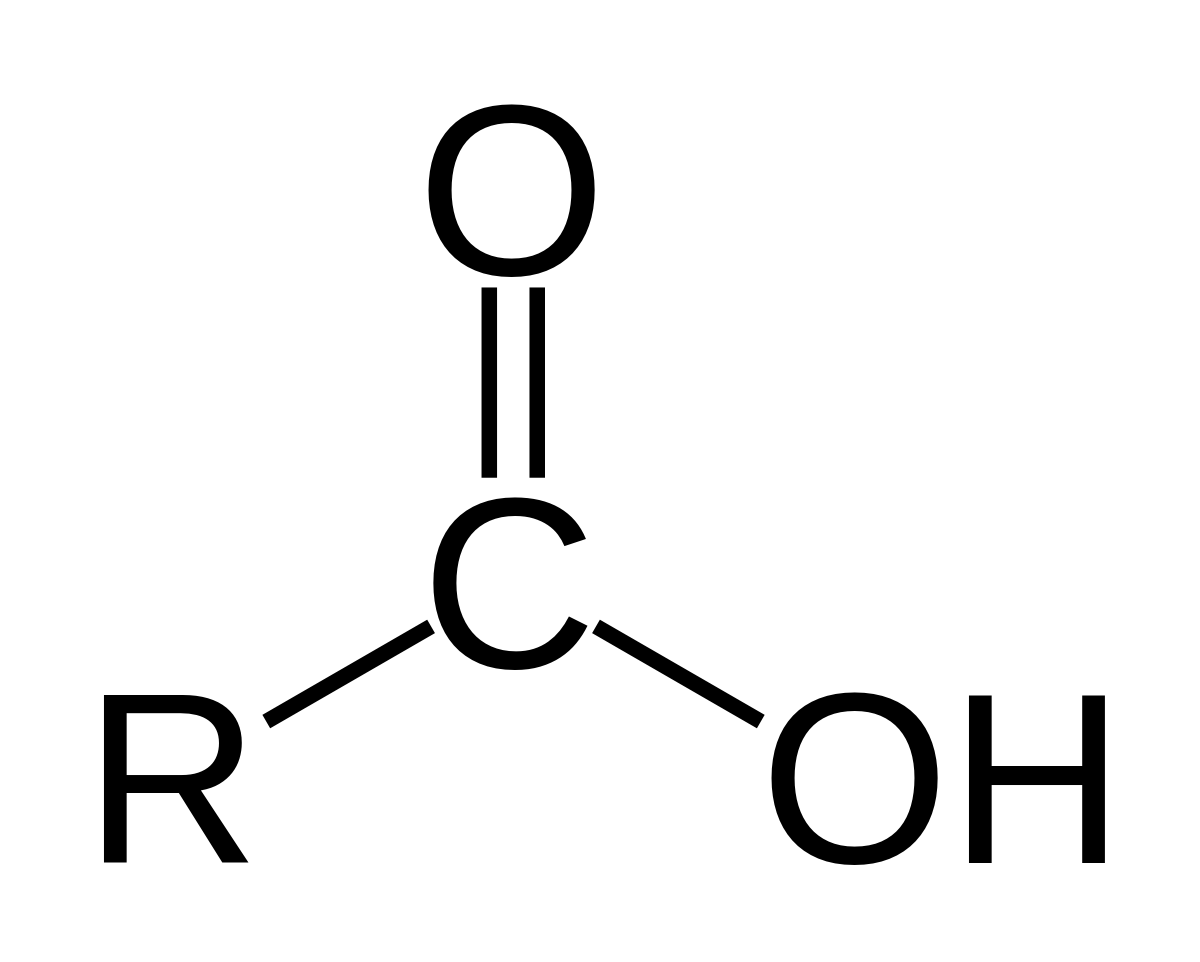
Function of carboxyl group
Acts as an acid (donates H⁺)
Amino group structure
–NH₂
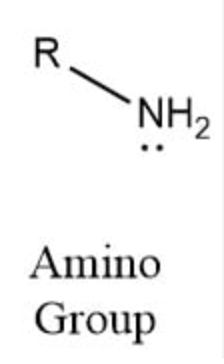
Function of amino group
Acts as a base (accepts H⁺)
Sulfhydryl group structure
–SH
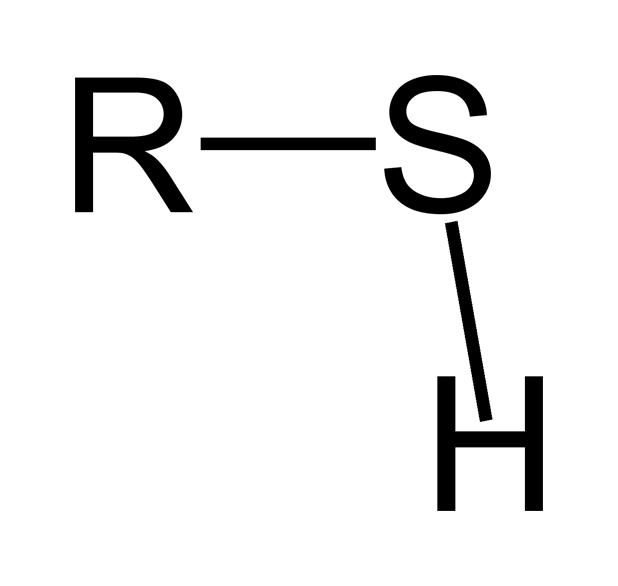
Sulfhydryl group function
Forms disulfide bridges in proteins
Phosphate group structure
–OPO₃²⁻
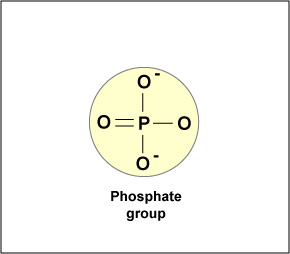
Phosphate group function
Adds negative charge, involved in ATP and nucleic acids.
Methyl group structure
–CH₃