Physics- Longitudinal and Transverse waves
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
In mechanical waves, particles _______ about a fixed point
oscillate
oscillate definition
Rapidly moving back and forth between two points
What is a progressive wave?
Oscillations that transfer E and info
Transverse wave definition
A wave in which particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave of travel (and E transfer)
e.g. of transverse waves
electromagnetic waves (radio, visible light, UV)
Can transverse waves be polarised
yes
polarised in waves defintion
When waves are polarized, their oscillations occur in a single plane. This means that the waves vibrate in a specific direction, perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
Longitudinal waves definition
A wave in which particles oscillate parallel to direction of wave travel (+ E transfer)
e.g. of longitudinal waves
sound and ultrasound waves
Can longitudinal waves be polarised?
No
What is displacement in waves and what axis is it usually on?
Distance of point on wave from equilibrium position
Y-axis
Wavelength definition and symbol
Distance between points on successive oscillation of wave in phase
Greek letter lambda (λ).
amplitude definition
max displacement of particle in wave from equilibrium position
how to measure wavelength is longitudinal waves
distance between 2 compressions/ rarefactions
what is period/ time period ?
time taken for one complete oscillation or cycle of wave
what is frequency ?
n. of complete oscillations/ wavelengths passing a point her unit time
what is wave speed?
distance travelled by wave per unit time
Phase definition
how far the cycle of one point is compared to another point on the same wave
what does phase tell us
how much a point/ wave is in front/ behind another
When are waves in phase?
when relative crests/ troughs are aligned
Is 360
When are waves in antiphase?
when crest of one wave allinges with trough of another
is 180
how to convert λ to degrees and radian
X by 360 / 2π
What is a CRO and its full name?
Cathode- Ray Oscilloscope
Lab instrument used to display, measure and analyse wavefront of electrical circuits
Using wave speed equation for wave of constant speed if:
Wavelength increases = frequency decreases
Wavelength decrease= frequency increase
What are compresssions?
Areas of high pressure due to particles being close together
What are rarefractions?
Areas of low pressure due to particles spread further apart
What is intensity in waves?
Amount of energy passing thru a unit of area per unit time / power per unit area
Intensity unit
Watts per metre squared, Wm-2
What is Intensity proportional to?
Amplitude squared and frequency squared
What are spherical waves?
Wave from a point source which spreads out equally in all directions
What is the area spherical waves move through?
Surface area of a sphere: 4πr2
Does intensity increase or decrease as spherical wave through increasing distance from source?
Decreases (assuming there is no absorption)
Intensity is also proportional to _____ in spherical wave
1/r2
distance travelled by a wave in 1 oscillation is = to
wavelength
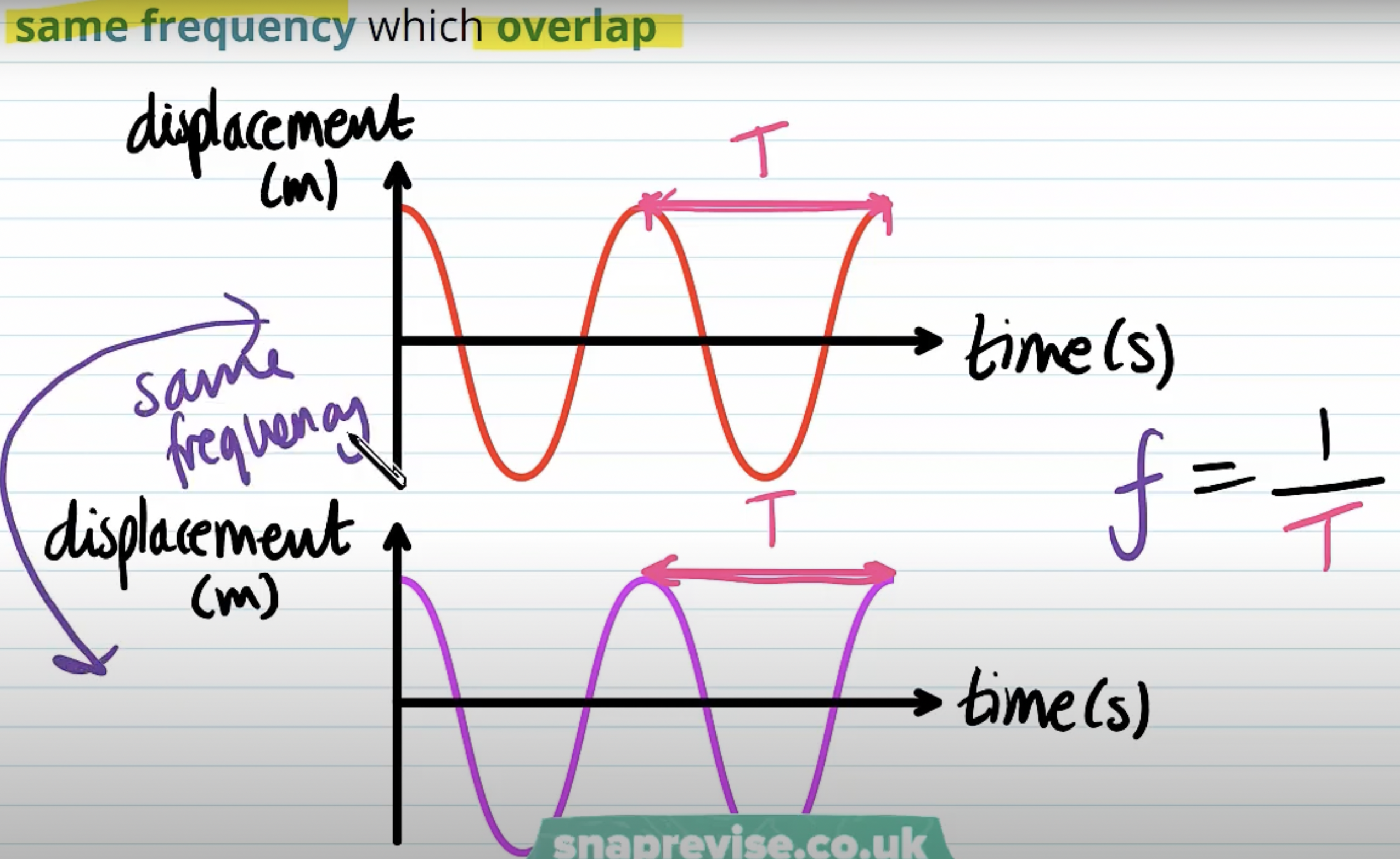
If two waves have same frequency they also have same ____
time period
how to find phase difference in degrress
360 x d/λ
d=- distance between two points
ever ___ of a n osculation in standing waves they have 0 displacement
1/4
stationary waves need to hace the same ___ to form
frequency
stationary waves are in a constant _____ _____
phase relationship
coherent waves are waves with:
constant phase relationship
same frequency
coherent waves produce a _____ interference pattern
stable
what is a stable interference pattern
contain fixed positions of constructive and destructive interference
way to create stable interference pattern
stationary wave
coherent waves travelling in opposite directions or they cross at a point
monochromatic light
continuous stream of oscillations of the electromagnetic field at a single frequency
how to find distance between slits in a diffraction grating
d= L/ n
d= distance
L= length along the grating
n= the n. of lines
amplitude is inversely proportional to what
distance
what does an oscilloscope show and what can this be used to work out?
time period
frequency
how can you find refractive index using the critical angle method
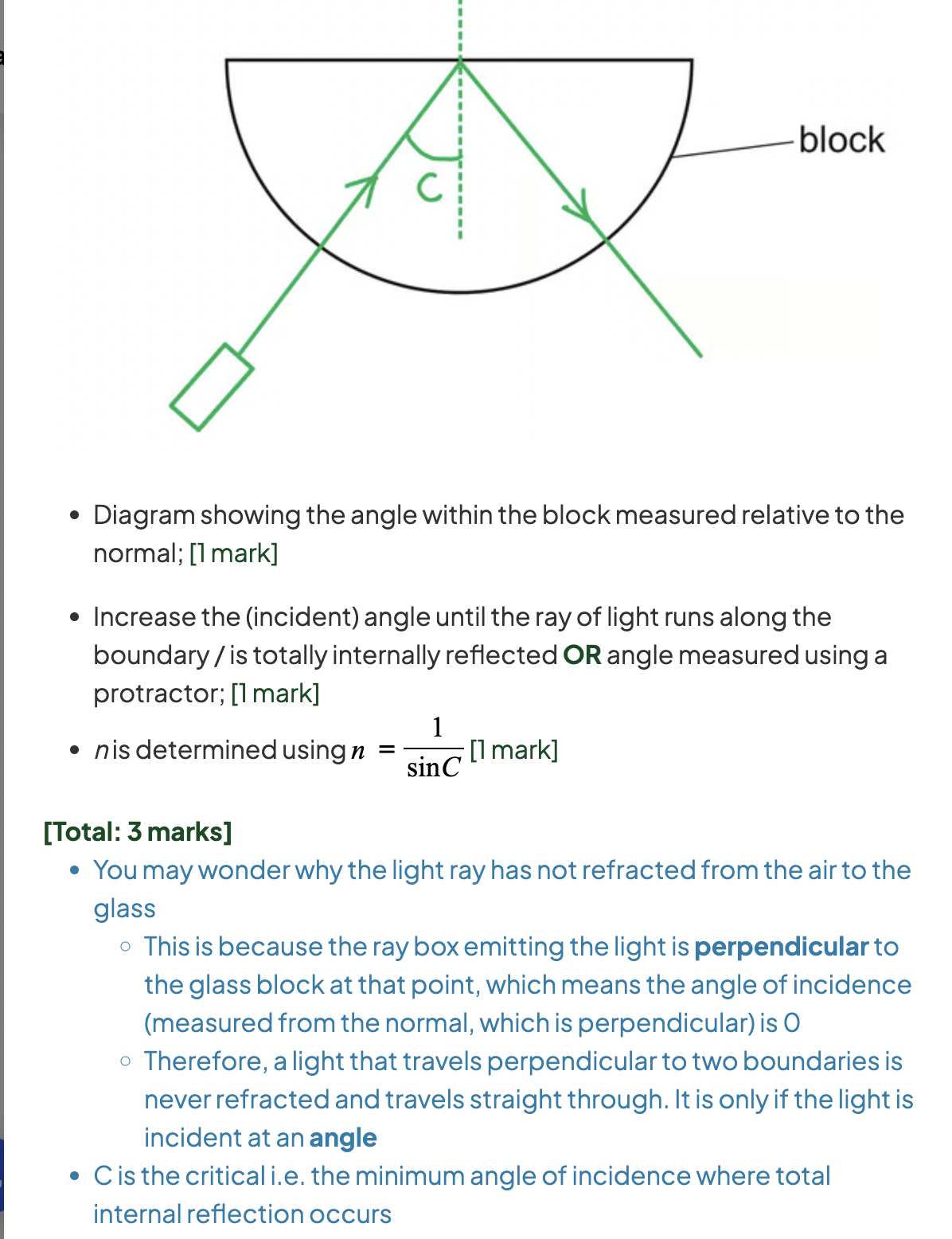
Another critical angle equation
SinC= n2/n1
how can you demonstrate in lab that light is plane polarised
Use a polaroid / polarising filter
Rotation of this will change the intensity (of the light)
if working out distance of refracted wave from depth use
work out it with trig using angle
show that the speed v of the wave is given by the equation v = fλ
v=s/t
Since distance is and time is : v=λ/ T
as T=1/f
therefore v=fλ
phase difference
phase difference = time t for the two rays to travel between the dashed lines X and Y x 360/ period T of the light wave
Constructive interference is only possible when the phase difference is __
a whole n. of wavelengths
tubes closed at one end only have _____-numbered harmonics
odd i.e. 1st, 3rd, 5th etc
SHM Equation:
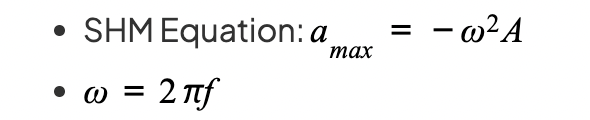
equation used in diffraction grating equation (learn)
nλ= dSinθ
n=order of diffraction pattern (use heights n.)
d= distane between slits (m)
θ= normal to maxima angle
How to work out distance between slits, d
d=1/N
N= n. of slits per m
What do each “axes” on an oscilloscope measure?
Vertical divisions= voltage/ amplitude of wave
Horizontal divisions= time
Can a wave be both refracted and reflected at a boundary?
Yes, at low angle of incidence most will be refracted, but some will reflect
Superpose definition
2 waves in the same place combining
Coherence definition:
Coherent waves have same frequency and wavelength and a fixed phase difference
Path difference v phase difference
Path difference: difference in distance that two waves have travelled in terms of wavelength ( units of length)
Phase difference: difference in the point in the cycle of two waves as a proportion of a full wave cycle ( units of degrees/ radians)
What is youngs double slit experiment?
A single source of light directed towards a double slit, which creates 2 coherent beams of light. This intereferes as it hits the screen and creates an intereference pattern
What is the impact of increasing slit width?
Increases width of the central diffraction maximum
units of λ=ax/D
λ- wavelength
a- slit spacing
x- fringe
d- distance to screen
What 2 properties can be explained if light is a wave?
Diffraction
Interference
What is a stationary wave?
Consists of alternating fixed pattern of nodes (0 amplitude + no vibrations ) and antinodes (points of max amplitude). No energy is transferred across the wave
Similarity and difference between stationary and progessive waves
S: Both have wavelength, frequency and amplitude
D: stationary waves don’t transmit energy from one place to another
What is meant by harmonics ?
Points where stationary wave form doesn’t change beacuse the waves in each direction are reinforce each other
How many nodes and antinodes does 1st harmonic have?
Nodes- 2 (1 at either end)
Antinodes- 1 (in the middle)