chapter 1: neuroanatomy
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
neurons
nerve cells, human nervous system contains over 100 billion neurons, information processing unit of the nervous
system, specialized for precise
communication throughout the body
glial cells
support cells in the nervous system in which different types of glial cells perform distinct
roles in the nervous system
nucleus
contains DNA, the genetic code that
makes you, you, DNA is translated to
RNA, which leaves the nucleus through a process called transcription
ribosomes
makes proteins through translation, reads mRNA and translates into proteins, essential structures for cellular function
mitochondria
the powerhouse of the cell." ATP
(cellular energy) is produced through
cellular respiration
transcription
the process by which DNA is copied into RNA
translation
the process by which mRNA is used to create proteins
DNA
genetic information stored in every cell, cells differ because they express different genes and thus create different proteins
dendrites
neural input region that receives information
from other neurons, branch-like structures
soma (cell body)
integrates information coming from dendrites; houses basic cellular architecture (nucleus, etc.), big role in electrical communication, regulates cell function, integrates information from all dendrites by summing the electrical signals generated there
axon
long projection leading away from the soma,
information integrated by the soma is relayed down the axon, primary output communication that carries action potential
axon terminals
the very end of the axon, contacts
the dendrites of other neurons to pass information along, electrical to chemical communication
neuron communication
all about energy transfer between neurons, electrical potential energy is stored in the neuron via an ion concentration gradient (negative) and chemical potential energy is stored in the neuron in the form of
neurotransmitters
dendritic spines
short outgrowths on dendrites that increase the surface area available for synapses which leads to more input from other neurons
axon hillock or initial segment
site of action potential initiation, beginning of the axon
myelin sheath
a fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hop from one node to the next
nodes of ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath, action potential can jump between
axon collaterals
side branches of the axon
synapses
tiny gaps between dentrites and axon terminals of different neurons, neurotransmitters are released here, synapses detect calcium which triggers synaptic vesicles to move toward presynaptic membrane
presynaptic membrane
part of the axon terminal that releases the neurotransmitter
postsynaptic membrane
part of the target cell (often in the dendrites) that detects neurotransmitters
synaptic vesicles
membrane-bounded compartments in which synthesized neurotransmitters are kept
receptors
parts of the cell membrane that receive the neurotransmitter and initiate or prevent a new electric signal, specific proteins that control electrical state of postsynaptic membrane
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
established neuron doctrine which is the idea that the brain is comprised of neurons, made possible by the Golgi Stain
reticulum theory
idea that the brain was not
made up of cells, but was more like a giant net (no synapses or space between cells) advanced by Golgi himself
astrocytes
help form semi-permeable Blood Brain Barrier by contacting blood vessels, convey nutrients from the blood to neurons, help maintain homeostasis in the extracellular environment, minor role in cleaning up some extracellular debris
oligodendrocytes
create myelin that wraps around axon inside the brain and spinal cord, central nervous system
schwann cells
create myelin that wraps around axon outside the brain and spinal cord, peripheral nervous system
microglia
protect the brain by scavenging for pathogens, damaged cells, and other debris, acts as brain's mini immune system
resting state
cell bodies remain still while the branches move around, surveying the area
reactive state
once a threat is detected, they change their shape to engulf and destroy the danger
ependymal cells
form the barrier around ventricles and
channels containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), contain Cilia, hairlike projections that can move to help CSF flow
anterior
front side of the body
posterior
back side of the body
superior
top, toward the head
inferior
bottom, away from the head
medial
toward the midline, center
lateral
away from the midline, more towards outside
ipsilateral
same side, same side as thing being studied
contralateral
opposite side, opposite side as thing being studied
dorsal
toward the back
ventral
toward the stomach
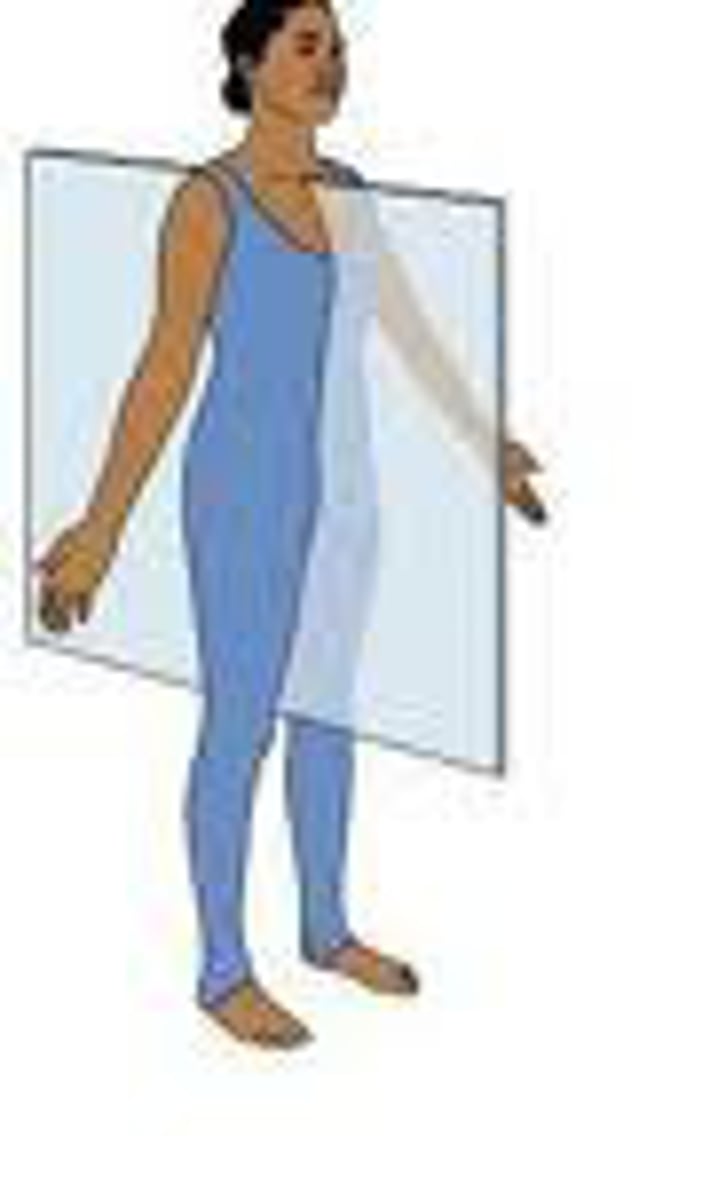
coronal
divides the body into slices from front to back
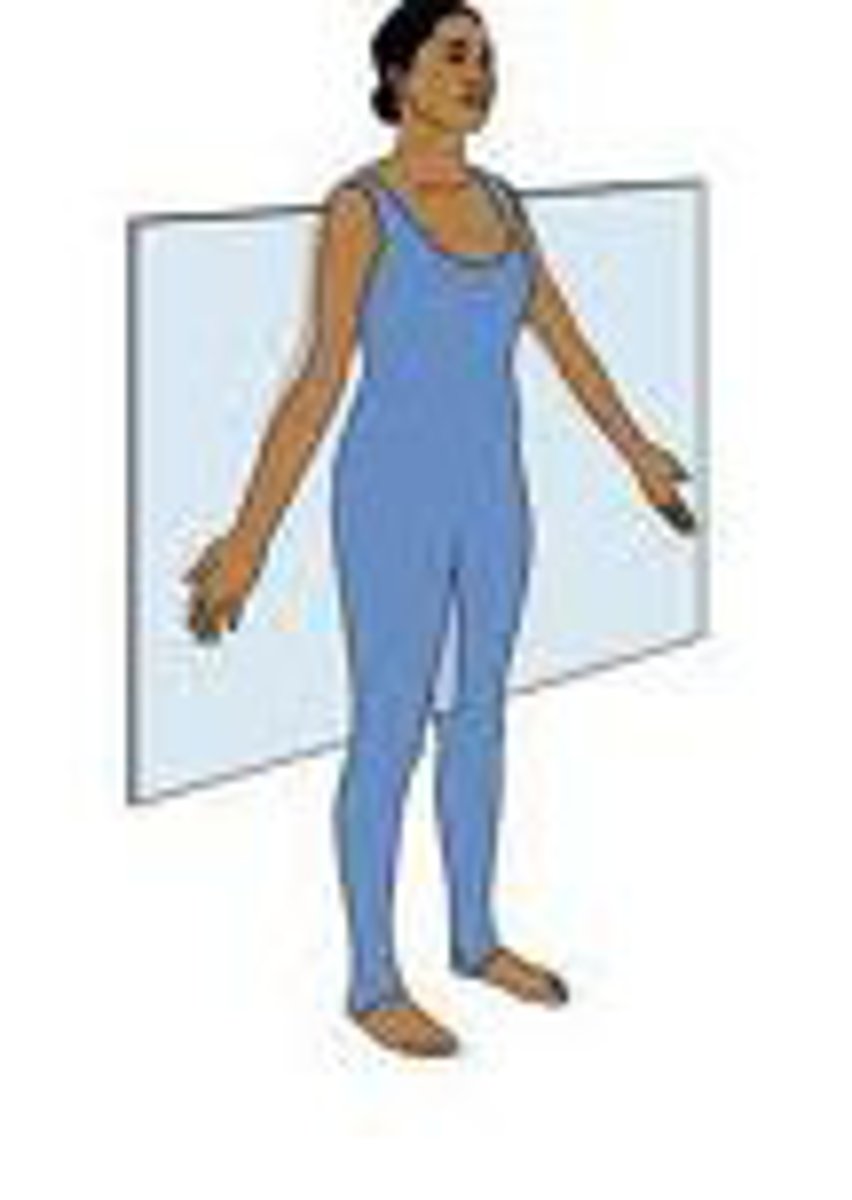

sagittal
divides body into left and right
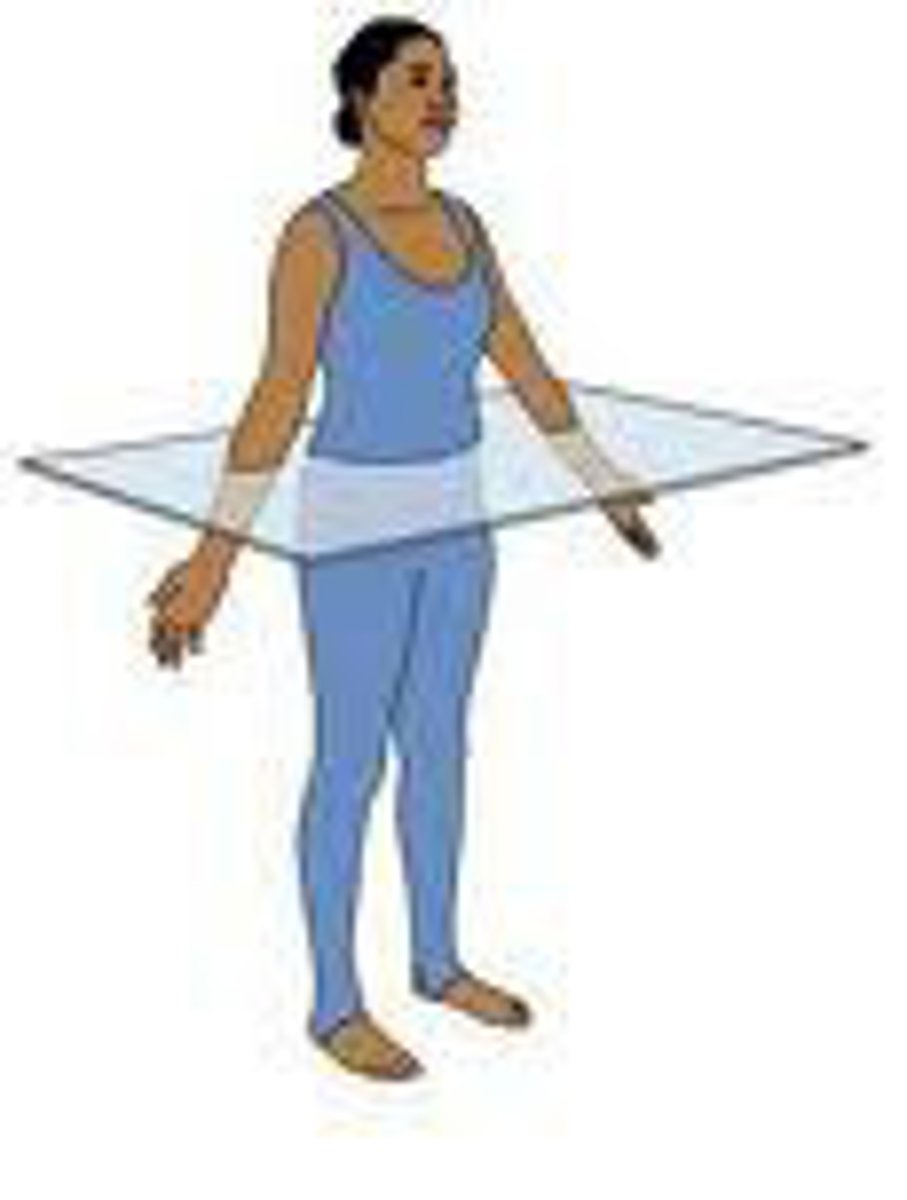
horizontal
side to side, top to bottom
central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
nerves
bundles of axons in the PNS
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain, control sensory and motor factors for your face
motor nerves
control muscles, information flow is efferent (away from the CNS)
sensory nerves
convey sensation to the CNS, information flow is afferent (toward the CNS)
dorsal root ganglia
contain the somas of specialized neurons that conduct sensory info from PNS to CNS, send information toward spinal cord
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles, sensory and motor information
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs
sympathetic nervous system
controls "fight-or-flight" response, tells organs & tissue to burn metabolic
energy, high adrenaline, requires action
parasympathetic nervous system
controls "Rest & Digest" response, tells organs and tissue to conserve metabolic energy, maintains essential life functions
enteric nervous system
nervous system regulating the gut microbiome, good gut health = good nervous system health
meninges
multilayered, fluid-filled sack which has protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord, consists of dura mater, arachnoid mater, subarachanoid space, and pia mater
subarachnoid space
contains cerebrospinal fluid, allows the brain to float
ventricles of the brain
open spaces/canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
lateral ventricles
ventricles located in each cerebral hemisphere that produce CSF
third and fourth ventricles
CSF flows through and circulates here to the spinal cord
theory of localization
Franz Joseph Gall proposed that different parts of the brain carry out distinct functions
phrenology
belief that the shape of the skull reflected the shape of the brain, believed that by measuring the skull, one could understand things about a person's psychology
neural system
a population of neurons that communicate
across the boundaries between brain regions, communication between different lobes
neural circuit
a population of neurons that communicate within a brain region or between immediately
adjacent brain regions
forebrain
largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, and the limbic system, among other structures
cortex
plays a crucial role in many cognitive processes, including perception & decision making, wrinkly exterior of the human brain
gyri (gyrus)
ridges of the cortex (hills)
sulci (sulcus)
shallow grooves of the cortex (valleys)
gray matter
made up primarily of cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons
white matter
made of myelinated axons
corpus collasum
connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain and allows information to pass between them
frontal lobe
region of the brain responsible for executive function & motor control like attention, decision making, etc.
parietal lobe
region of the brain responsible for touch, proprioception (position of limbs in space), somatosensory etc.
occipital lobe
region of the brain responsible for vision, etc.
temporal lobe
region of the brain responsible for hearing, some cortical structures in learning and memory, etc.
neocortex
90% of human cortical surface area, made up of 6 distinct cell layers, differentiated by size, shape, density, and connections of the neurons in each, layer I is the most superficial, layer VI is the deepest
allocortex
10% of human cortical surface area, made up of 3 or 4 layers of cells, depending on region
lissencephalic
brains have a smooth cortex
gyrencephalic
brains have a wrinkly cortex
basal ganglia
technically nuclei, not ganglia, located deep within the forebrain, beneath the cortex,
critical for initiating voluntary movement, dopamine reading center (processing)
limbic system
highly interconnected group of structures is important for functions such as emotion & memory, includes hippocampus and amygdala
hippocampus
limbic region crucial for remembering the events of your life, integration of new memories
amygdala
an area crucial for emotion & emotional memory, attachment of feelings and emotions to certain memories
thalamus
a cluster of nuclei at the center of the
forebrain, directs sensory information of all types to cortex, smell does not get directed
hypothalamus
cluster of nuclei with many functions,
including regulating energy intake and control of the endocrine (hormonal) system via the pituitary gland, so-called master gland of the endocrine system, regulating homeostasis/bodily functions
midbrain
relatively small region in humans, but still plays a key role, made up of tegmentum & tectum
tegmentum
contains neurons that produce
the neurotransmitter dopamine, sending
projections to the basal ganglia and cortex
tectum
processes audio/visual information
& controls orientation responses
hindbrain
division of the brain located at the base of the brain containing the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing, outgrowth of the spinal cord containing nuclei that give rise to the cranial nerves, life-support systems
pons
connects the rest of the brain to the cerebellum; also contains nuclei that give rise to cranial nerves
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include precise control of motion