MASTER AP EURO FLASHCARDS
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What is Feudalism?
A hierarchical structure where landowning nobles (lords) provided land (fiefs) to vassals in exchange for loyalty and service, such as military support

What is Scholasticism?
A way of learning and thinking that emphasizes using logic and reason to analyze and understand philosophical and theological ideas
Italian Renaissance vs. Northern Renaissance art
Both developed humanism and used realism to present differing subjects. The Italian Renaissance used science to achieve perfection in symmetry and anatomy. The Northern Renaissance did not represent the idealized human form; instead, they focused on scenes of daily life.
What caused the rise of totalitarianism in the 20th century?
Widespread social and economic instability (Great Depression), disappointment with the post-war settlement, and the rise of strong leadership in the face of political chaos
Where did the Renaissance start?
Florence, Italy
Why was the printing press important?
Made books less expensive and more accessible, increased literacy rates
What was the 100 years war?
England v. France, caused by a succession crisis in France
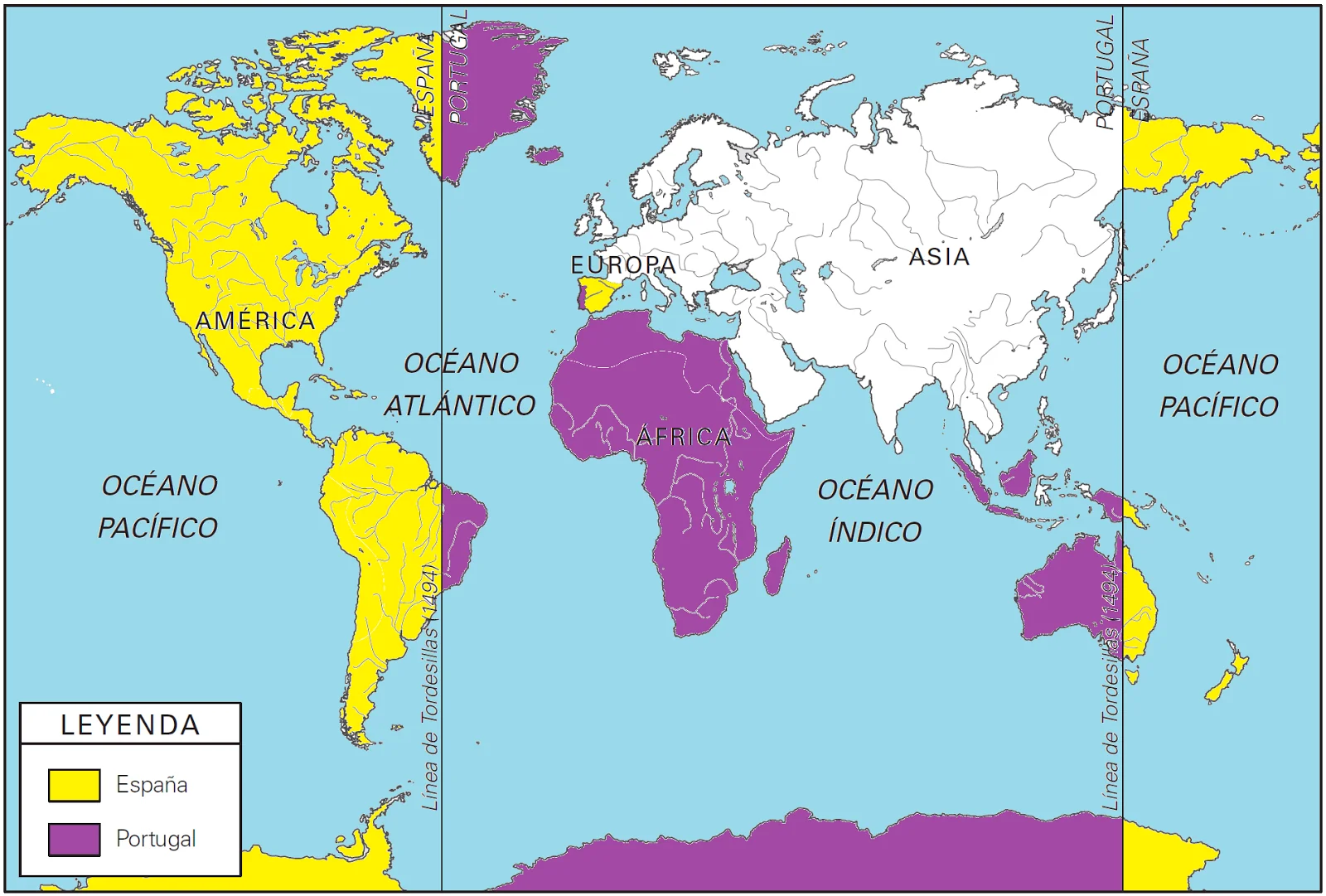
What was the Treaty of Tordesillas?
An agreement between Spain and Portugal that divided newly discovered lands outside of Europe (moved the line of demarcation)
Who was John Wycliffe?
(1328-1384), rejects papal authority, teacher at Oxford
Who was John Calvin?
a French theologian, pastor, and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation, created Calvin’s “Geneva” where protestantism was created
What was the Council of Trent?
(1545-1563) a council to address the Protestant Reformation by clarifying Catholic doctrines, reforming church practices, and condemning Protestant beliefs.
What was the Edict of Nantes?
Issued by Henry IV 1598, granted religious tolerance and equality to the Huguenots (French Protestants) and ended the French Wars of Religion
What was The Peace of Westphalia?
A series of treaties that ended the 30 years war
What caused the French Wars of Religion?
Religious persecution and political mistreatment of Huguenots
What was Tulipmania?
a period of extreme financial speculation in the Dutch Golden Age, where the prices of tulip bulbs soared to unprecedented levels, then collapsed
Who was Lousi XIV?
King of France from 1638-1715, absolute ruler, ordered construction of Versailles
What was the Enlightenment?
a philosophical, intellectual, and cultural movement that dominated European thought in the 17th and 18th centuries
What is Empiricism?
Knowledge is gained by senses
Who was Voltaire?
Enlightenment thinker who wrote the Treatise on Tolerance
What where salons and coffeehouses used for during the French Enlightenment?
French philosophers such as Voltaire, Montesquieu and Rousseau met to discuss
What is a nuclear family?
a household composed of two parents and their children, often viewed as the traditional family unit
Agricultural revolution
16th-17th century, includes open field system, and crop rotations
What did John Locke think?
all persons are endowed with natural rights to life, liberty, and property and that rulers who fail to protect those rights may be removed by the people, by force if necessary
What is the Bourgeoisie?
the middle class, typically with reference to its perceived materialistic values or conventional attitudes.
What was the Ancient Régime (the Estates General)?
Corrupt French government system that led to the French Revolution
What was the Thermidorian Reaction?
Period of several months between Robespierre and the Directory following the French Revolution, highly conservative
Reign of Terror
Maximilien Robespierre came to dominate the Committee of Public Safety during the Reign of Terror. The Reign of Terror took place between September 5, 1793, and July 27, 1794
What was Napoleonic code?
(1804), offices based on merit and efficiency, deprived women of rights
What was the Cottage Industry?
“early factory”, goods produced in home
Why did the Industrial Rev start in GB?
Coal, Iron, Rivers, Ports
What was the Crystal Palace?
(1851), massive building made from glass that hosted industrial fair
What was the Congress of Vienna?
A series of meetings to decide European order after the fall of Napoleon
What were the effects of the Concert of Europe?
Creates a period of 50 years that Europe is eaceful and very conservative
What is Marxism?
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels suggests that history is an unending class struggle
Why did Germany unify?
Crimean war breaks up Concert of Europe, 1849 revolutions fail
What is Realpolitik?
politics based on practical, pragmatic considerations rather than ideological belief, created by Otto Von Bismarck
What was the Dreyfus Affair?
Alfred Dreyfus wrongfully accused of high treason, he was jewish, example of antisemitism
What is Zionism?
Jewish nationalism
What was the Crimean War?
Ends Concert of Europe, increases nationalism and first war with photography and medical sanitization
What was the Berlin Conference?
A 1884-1885 meeting of European powers in Berlin, Germany, to regulate colonial possessions and trade in Africa
What was the Russian Revolution?
Ends Romanov dysnasty and starts the USSR
What was the Five Year Plan?
Stalin’s economic plan to make the USSR a global power
What was the Yalta and Potsdam Conferences?
Conferences that planed the D-Day invasion and discussed plans for post WWII Europe
What is COMECON and COMIFORM?
The USSR’s version of the Marshall Plan (to aid eastern European countries in recovering from WWII)
What is Imperialism?
A nation extending its rule/control over another country
Who was Otto Von Bismark?
Chancellor of Germany from 1871-1890, who united Germany in 3 wars, coined the term ‘realpolitik’
What was the Renaissance?
A period of cultural, artistic and political “rebirth” following the Middle Ages
What was the 100 year war?
A war between France and England over territorial disputes an the issue of succession to the French throne
Who was Napoleon Bonaparte?
Absolute ruler of France, attempted to conquer the US and Haiti and established Napoleonice code
Who was Karl Marx?
A German philosopher who wrote the Communist Manifesto, known as the ‘father of communism’
Who was Adam Smith?
A Scottish professor who wrote The Wealth of Nations in 1776 and produced the idea of Laissez Faire Economics
Who was Adolf Hitler?
A German political leader who was in charge of the Nazi party and who was responsible for the death of 16 million people during the Holocaust
Who was Vladimir Lenin?
Leader of the Bloshevik Revolution and first president of the USSR
Who was Rasputin?
Spiritual healer and advisor to the Russian royal family (the Romanovs)
Why did Russian drop out of WWI?
Because of the Russian Revolution
What is a total war?
A war in which participants use all of the resources in order to wage a war and the laws of war are typically disregarded
Who was Franz Ferdinand?
The archduke of Austria-Hungary who was assassinated by Gavrilo Princip (a member of the Black Hand {a Serbian Nationalist Group})
What was the Paris Peace Conference?
A Conference that decided the terms of peace after WWI, created the Treaty of Versailles and formed the League of Nations
What were the MAIN causes of WWI?
Militarism, Allainces, Imperialism and Nationalism
What is Fascism?
A political ideology that stresses the glory of the state, unquestioning obedience to its leader and harsh suppression of dissent
What were the causes of WWII?
The fail of the Treaty of Versailles and the rise of the Nazi Party
What were the Nuremberg Laws?
Antisemetic and racist laws that where enacting in Nazi Germany
What was Kristallnacht?
The night of the broken glass when 30,000 Jews where arrested
What was the Munich Agreement?
Hitler promised that he would not take more territory after taking Rhineland and the Sudentenland
Who was Peter the 1st?
Absolute ruler of Russia who had the Peterhof Palace constructed
What is Keynesian Economics?
An economic system created during the Great Depression that promotes economic involvement in the economy
Who was Benito Mussolini?
An Italian nationlist and the founder of Itilan Fascim who ruler during WWII
What is Humanism?
a philosophical and ethical stance that emphasizes the value, dignity, and potential of individuals and society, often without supernatural or religious beliefs. It focuses on human agency, reason, and the pursuit of a meaningful life through personal fulfillment and contributing to the greater good.
Who was Raphel?
A renaissance painter who painted the School of Athens
Who was Desiderius Erasmus?
A Dutch humanist, theologian, and scholar during the early Protestant Reformation. He was a prolific writer and editor who published critical editions of classical and early Christian works, including the Greek New Testament
Who was Martin Luther?
A German theologian and a key figure in the Protestant Reformation. His challenge to the Catholic Church and its teachings led to a major schism within Christianity and the rise of Protestantism.

Who was “Bloody Mary”?
Queen of the United Kingdom from 1553-1558, her efforts to restore Roman Catholicism to England got her the nickname “Bloody Mary”
What was the Peace of Augsburg?
signed in 1555… a treaty that ended religious conflict in the Holy Roman Empire by allowing each prince to choose the religion of his territory, either Lutheranism or Roman Catholicism.
What is Mercantilism?
There is a fixed amount of wealth in the world, and the state with the most gold “wins”
What technology made exploration possible?
Caravel, lateen sail, astrolabe
What was the Columbian Exchange?
The global exchange of good, flora, fauna, cultural practices and disease between the Old World and the New World
What is Capitalism?
An economic system where private individuals or companies own and control the means of production (like factories, land, and resources) and where the production and distribution of goods and services are determined by market forces, driven by profit motives and competition
What was the Encomienda System?
The labor system established by Spanish colonizers in South America
What effects did the Columbian Exchange have on Europe?
Shifted the focus of exports and imports from the Mediterranean to northern countries
What was the Commercial Revolution?
Occurring primarily in Europe from the 16th to 18th centuries, refers to a period of significant economic expansion and transformation driven by increased trade, exploration, and innovation. It laid the groundwork for modern capitalism by expanding trade routes, establishing new economic practices, and fostering the growth of banking and finance.
What was the Dutch East India Company?
(VOC), founded in 1602, was a powerful Dutch trading company that dominated global trade for nearly two centuries
What caused the protestant reformation?
Corruption of the Catholic Church in the forms of simony (the buying and selling of church offices) nepotism (appointing family and friends to church offices) and indulgences (offering a way for people to buy their salvation)
What were the 95 Theses?
A list of statements written by Martin Luther in 1517 criticizing the Catholic Church's corrupt practices
Who were the Huguenots?
French Protestants, primarily Calvinists, who lived in France during the 16th and 17th centuries
What was the St. Bartholemus’s Day Massacre?
A targeted group of assassinations and a wave of Catholic mob violence directed against the Huguenots (French Calvinist Protestants) during the French Wars of Religion.
What was the War of the Three Henrys?
A period of conflict in France (1585-1589) during the French Wars of Religion, involving King Henry III, Henry of Navarre (future King Henry IV), and Duke Henry of Guise. It stemmed from the struggle for the French throne and involved religious and political factions vying for power
What was the Defenestration of Prague?
Two nobles thrown out a window, was the immediate catalyst for the Thirty Years' War
What was the Thirty Years War?
A major European conflict primarily fought in what is now Germany, with roots in religious and political tensions arising from the Reformation and the declining influence of the Holy Roman Empire
What caused the rise of absolutist states?
Weakened influence of the catholic church and merchant classes where expanding rapidly during a period of global trade
What major ideas came about during the Scientific Revolution?
In astronomy, the scientific revolution led to the Heliocentric model of Copernicus and the telescope of Galileo Galilei. In mathematics, it led to the development of calculus, probability and analytical geometry. In biology, it led to the development of human anatomy as a science.
What was the Seven Years War?
A far-reaching conflict between European powers that lasted from 1756 to 1763. France, Austria, Saxony, Sweden, and Russia were aligned on one side, and they fought Prussia, Hanover, and Great Britain on the other.
What caused the French Revolution?
The Enlightenment, the corrupt and extravagant French monarchy, severe economic hardship, and widespread discontent with the existing social and political structures.
What was Romanticism?
A broad intellectual and artistic movement that flourished in Europe and North America from roughly 1790 to 1850. It emphasized emotion, intuition, and individual experience, often in contrast to the emphasis on reason and logic that characterized the Enlightenment.
