Nervous system
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Nerve net (hydra)
Have no CNS
ganglion cells provide connections in all direction
axons non myelinated
slow conduction speed
What does the nervous system do
Detect changes in body and local environment
Produce a response
2 types of nervous system + structure
CNS - Brain + Spinal cord
Protected by meninges (protective membrane)
PNS - other neurones
2 divisions of the PNS + function
Somatic nervous system - voluntary actions
Autonomic nervous system (heart rate + breathing)
Sensory neurone
Carries impulse form receptor cells to co-ordinator
Relay neurone
Receive form sensory and relay to motor
Motor neurone
From coordinator to effector to bring a response
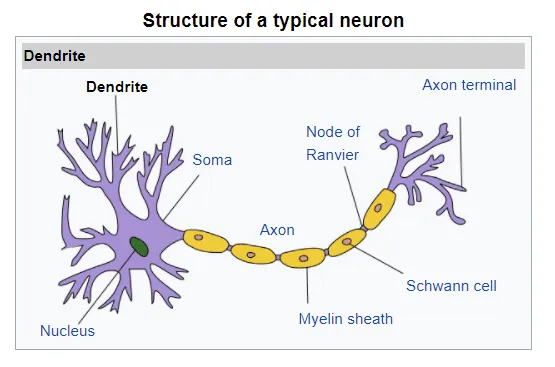
Dendrite
Carry impulse towards cell body
Axon
Transmits away from cell body
Schwann cells
Surround neurones and insulate
Myelin sheath
Made of many Schwann cells - acts as electrical insulator
Nodes of Ranvier
Areas on axon where myelin sheath is missing
Cell body
Contains nucleus + other cell organelles
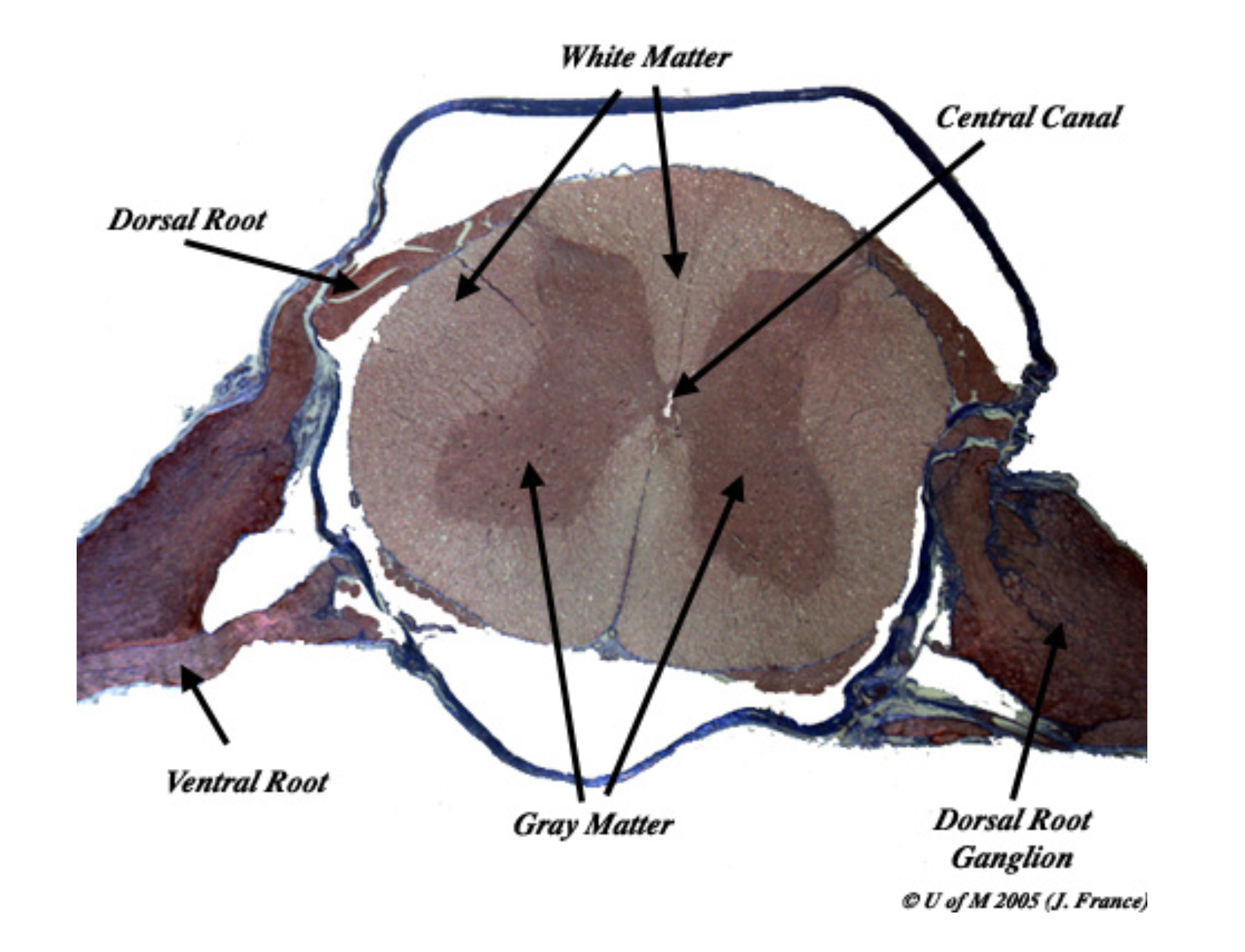
Describe a reflex arc
Sensory neurone enter spinal cord by dorsal root (back)
neurones synapses signal through relay neurone in grey matter
Motor neurone travels via ventral root (front)
What are the 4 types of axon transport proteins
Na+ / K+ pump
Voltage gated Na+ and K+ channels
K+ always open channels
Sodium / potassium pump
Uses active transport to move 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ in
Movement of ions at resting potential
-70 due to 3Na+ out and 2K+ in actively
K+ always open channel allows some out
Resting potential + charge
Potential difference between inside and out of membrane when impulse is not being conducted
Due to the movement of ions the membrane is polarised and rests at -70mV
Action potential part 1 - Depolarisation
Stimulus causes opening of Na+ channel
Ions diffuse in across electrochemical + concentration gradient
If enough diffuse in and raise to -55mV all Na+ channels open and rapid diffusion of ions cause an action potential of +40mV
Action potential part 2 - Repolarisation
When PD reaches 40mV - Na+ close and K+ open
K+ rapidly diffuse out down concentration and electrochemical gradient
Action potential part 3 - Hyperpolarisation
Due to rapid diffusion out of K+ ions - axon becomes more negative at 90mV
K+ channels then close and Na+/K+ pump restarts and membrane become polarised again
All or nothing law
To cause depolarisation, stimulus must exceed threshold value
The action potential size is constant (40mV)
Refractory period
After action potential, Na+ voltage-gated Chanels are inactivated for a short time
Benefits of the refractory period
Prevents action potential being generated in opposite direction - second being generated too close to first
Why does an action potential travel further in a mylenated axon
Saltatory conduction
Depolarisation only happens at the nodes of ranvier rather than the whole axon
Why is saltatory conduction more efficient
Less places to depolarise / reprise requiring less ATP for active transport
Factors affecting speed of impulse
Mylenation
Diameter of axon - less resistance
Temperature movement of substances is quicker + ATP production quicker
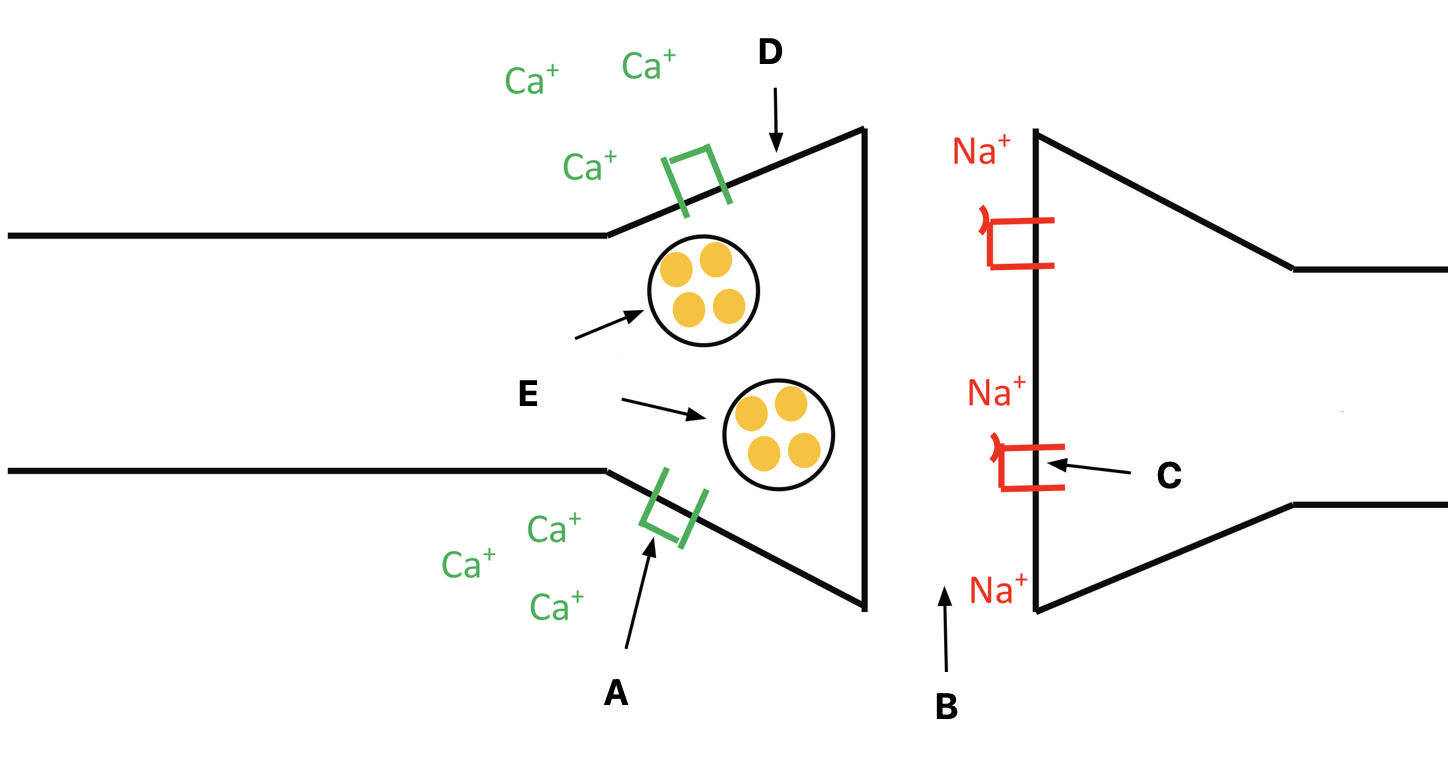
Label A-E
A - Voltage gated Ca2+ channel
B - synaptic cleft
C - Ligand gated Na+ channel
D - Pre-synaptic bulb
E - Neurotransmitter vesicles contining acetylcholine
Describe the process that happens when an impulse reaches a synapse
Ca2+ channels open
Causes vesicles to move and fuse with membrane
Releases neurotransmitter to diffuse across the cleft
Binds to complimentary receptors and causes ligand-gated Na+ channels to open
This depolarises the post synaptic membrane and causes an action potential
Acetylcholinesterase
Hydrolyses acetylcholine into choline and ethanoic acid
ATP is then used to reform the into neurotransmitter in vesicles
Function of synapses
Transmit impulses between neurones
Make sure impulse travels in one direction only
Filter out low level stimuli
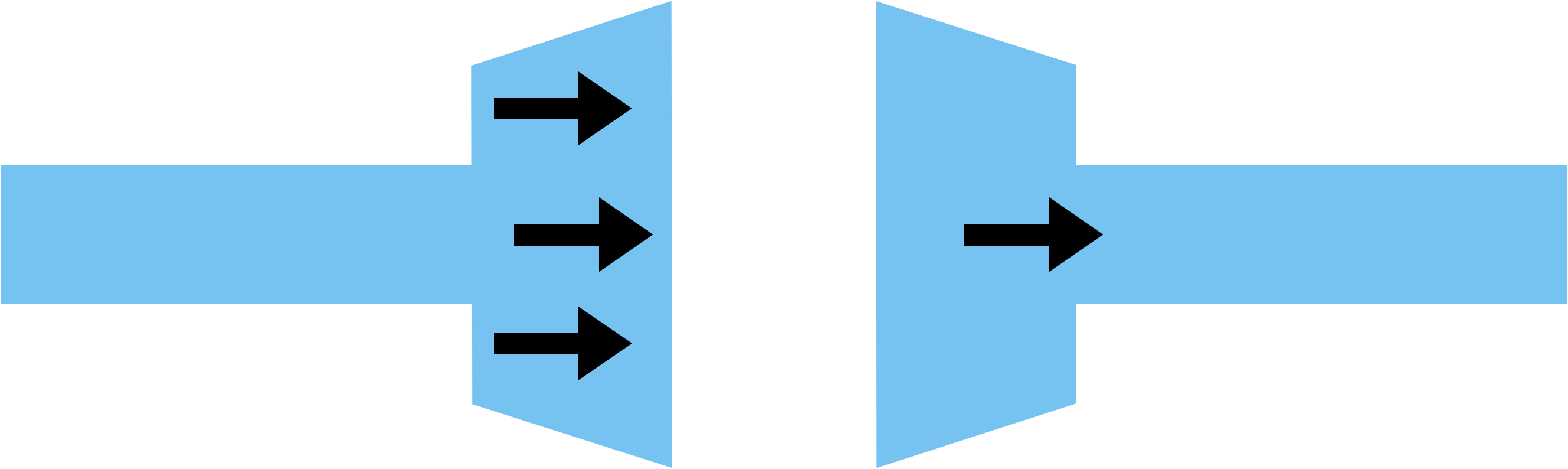
Temporal summation
Only be stimulated if there are frequent action potentials
Spatial summaiton
Only stimulated if multiple presynaptic neurones are present
Agonist - Synapse drugs
Binds to receptor and activates it
Antagonist - synapse drugs
Binds to receptor but doesn’t activate (similar to competitive inhibitor)
Organphosphorous insecticides
Inhibit acetylcholinesterase
Causes repeated firing of action potentials across posy synaptic membrane
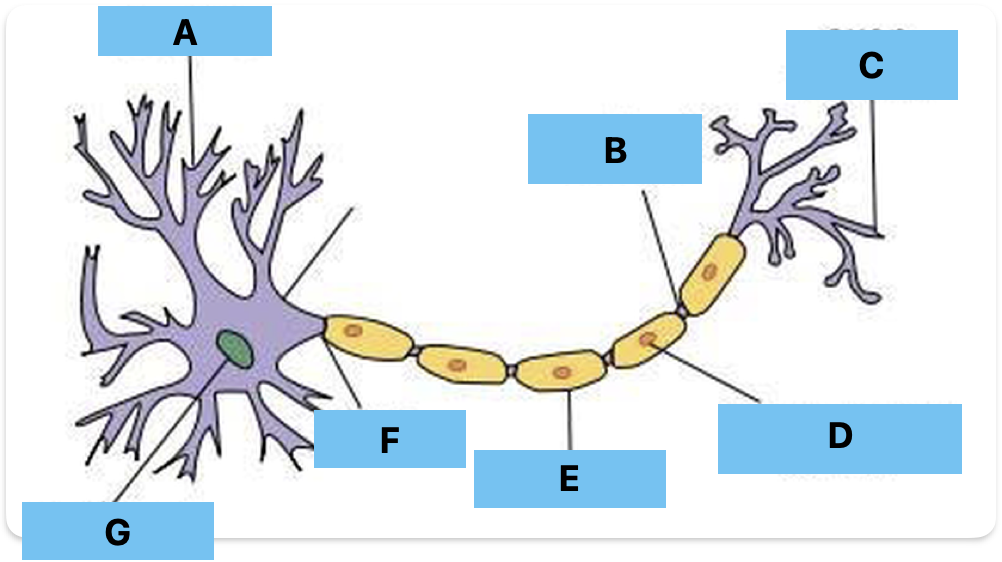
Label A-G
Dendrite
Node of ranvier
Axon terminal
Schwann cell - insulation
myelin sheath - insulation
axon - transmits impulse away form cell body
Nucleus in cell body
Local circuits
When the channels adjacent are stimulated to depolarise the next part of the axon