Topic 3 - Energy
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What is energy?
The ability to do work.
What is the unit for energy?
Joules
Give examples of energy stores
Kinetic
Thermal
Chemical
Gravitational Potential
Elastic Potential
Electrostatic
Magnetic
Nuclear
Sound
Heat
Define: Kinetic energy
The store of energy in a moving object.
Which energy store stores energy when an object is moving?
Kinetic energy store.
Calculate: Kinetic Energy
Kinetic = 0.5 x mass x velocity2
State the symbols for kinetic energy, mass and velocity.
Kinetic Energy = KE
Velocity = v
Mass = m
State the units for kinetic energy, mass and velocity.
Kinetic Energy = J
Mass = Kg
Velocity = m/s
What is Gravitation Potential Energy?
The energy an object has because of its position above the ground.
Calculate: Gravitational Field Strength
Mass x gravitational field strength x height.
State the symbols for gravitational potential energy, mass, gravitational field strength and height.
Gravitational Potential Energy = GPE
Mass = m
Gravitational Field Strength = g
Height = h
State the units for gravitational potential energy, mass, gravitational field strength and height.
Gravitational Potential Energy = J
Mass = kg
Gravitational Field Strength = N / kg
Height = m
What is the gravitational field strength on Earth?
9.81 N/kg
Can energy be created?
No
What does the law of Conservation of Energy state?
Always conserved.
Cannot be created or destroyed.
Can be stored, transferred or dissipated.
Can energy be destroyed?
No
Can energy be created?
Can energy be transferred?
Yes
Can energy be stored?
Yes
Can energy be dissipated?
Yes
What is a system in Physics?
An object or group of objects.
What is a closed system?
Total energy has no net energy as no energy can be transferred to or from the surroundings.
Can energy be transferred to the surroundings in a closed system?
No
Can energy be transferred to the surroundings in a open system?
Yes
Calculate: Total input energy
Total input energy = Useful output + Wasted output
What is efficiency?
How good a machine is at transferring energy to useful stores.
How can efficiency be expressed?
As a decimal, fraction or percentage.
Calculate: Efficiency
Useful output energy / total input energy
Is a device more or less efficient if it changes more input energy to useful output energy?
More efficient
Is a device more or less efficient if it changes more input energy to wasted output energy?
Less efficient
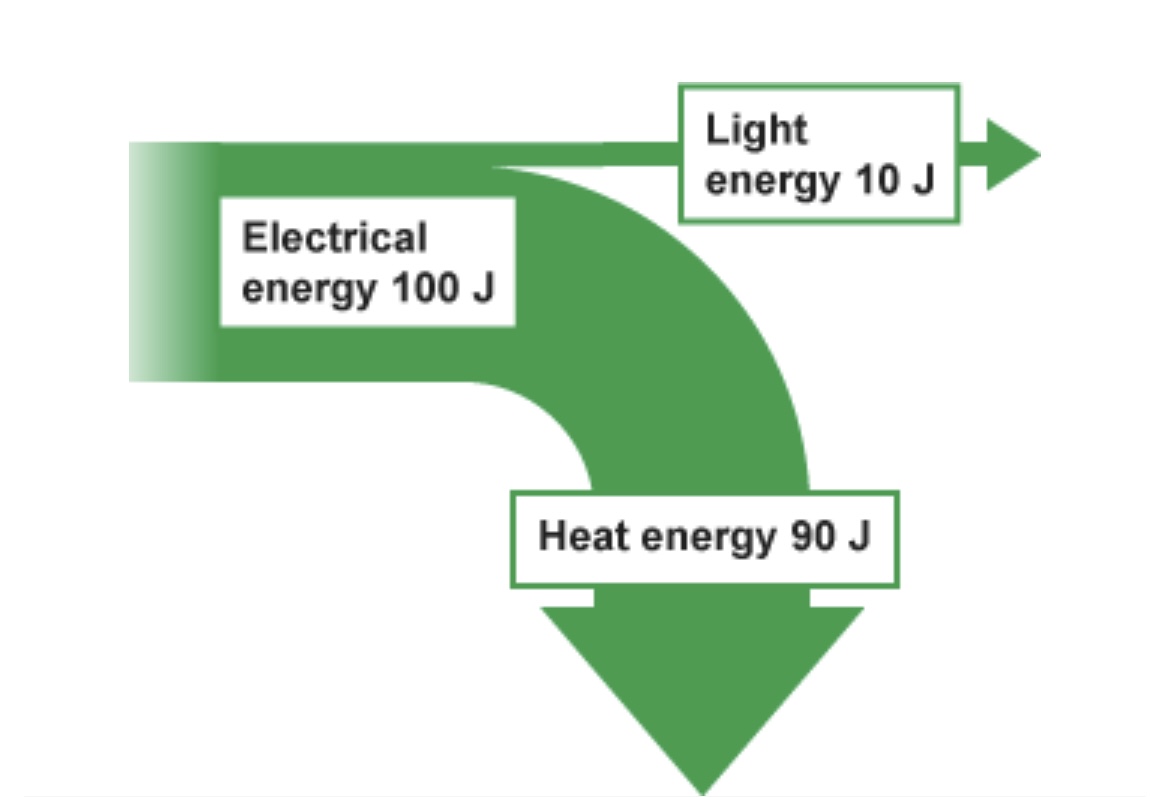
Is the light or heat energy wasted output energy?
Heat
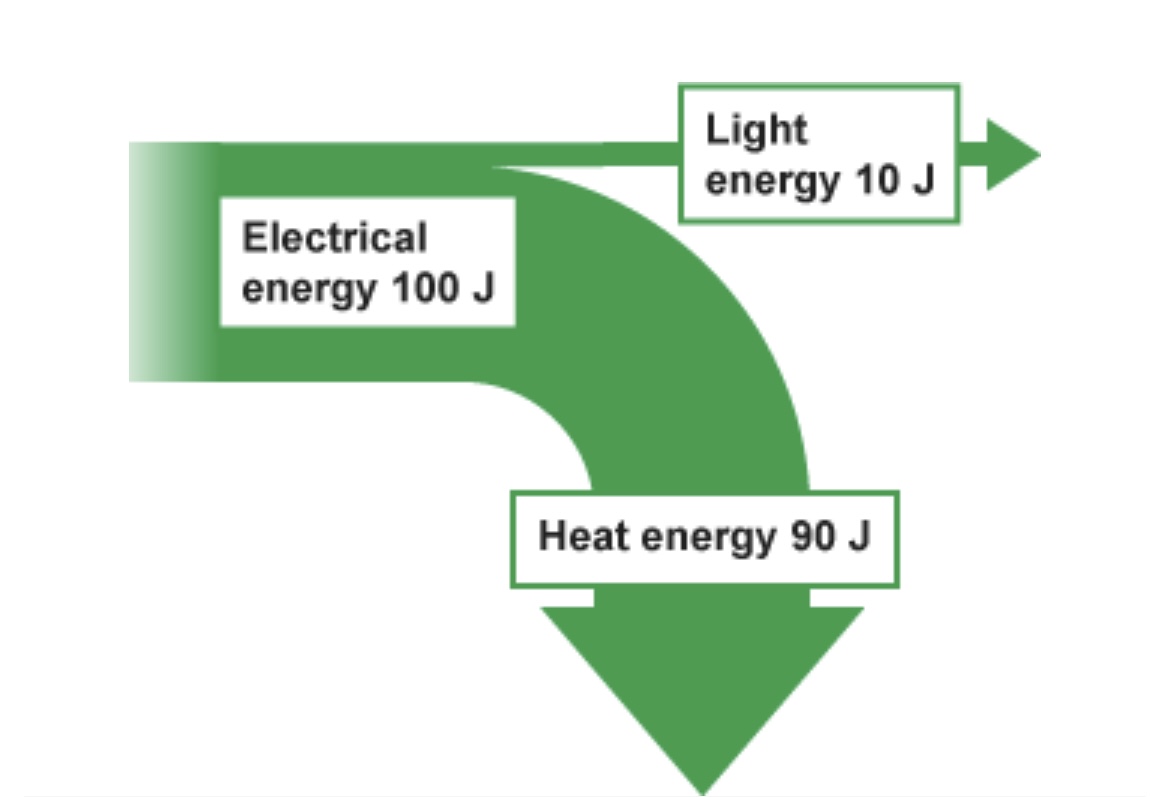
Is the light or heat energy useful output energy?
Light
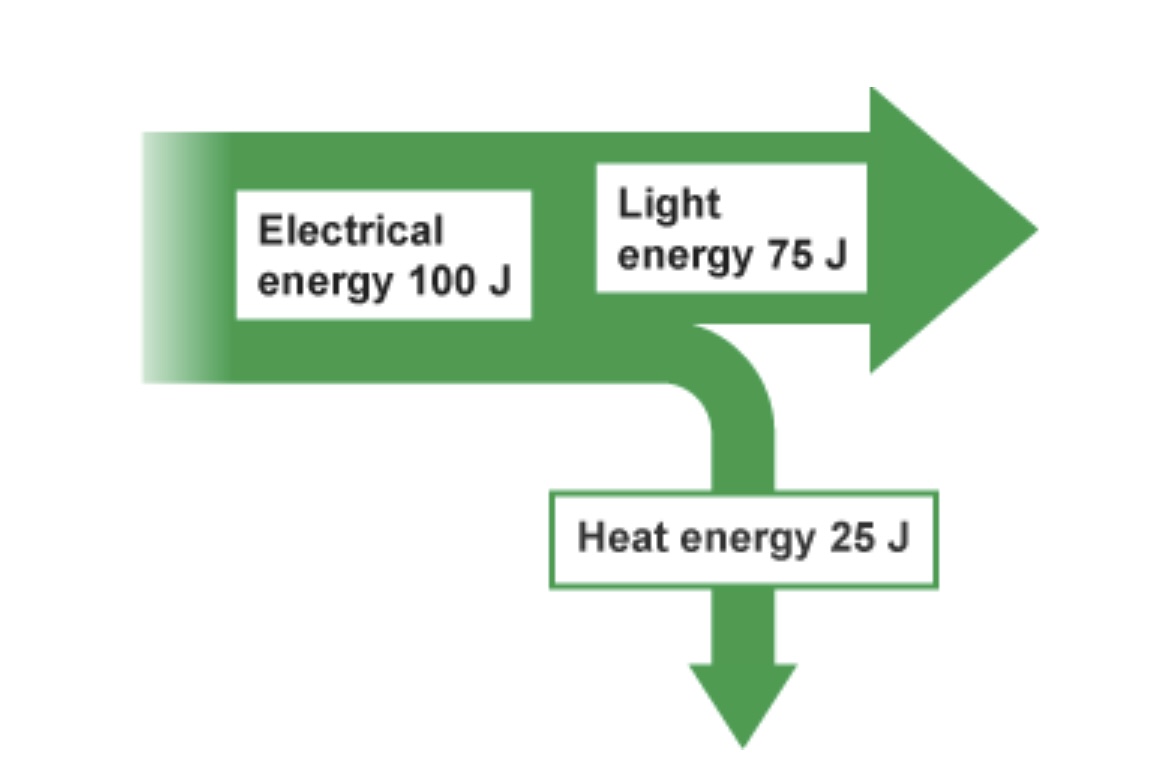
Is the light or heat energy wasted output energy?
Heat
Is the light or heat energy useful output energy?
Light
Does conduction or convection typically occur in solids?
Conduction
Does conduction or convection typically occur in fluids?
Fluids
What is insulation?
Wrapping an object with a material of low thermal conductivity to reduce the rate of energy transferred via heat.
What does it mean if a material has low thermal conductivity?
A material resists heat flow, transferring/conducting heat energy slowly.
Is a material of low or high thermal conductor a better insulator?
Low thermal conductivity.
What does the rate of heat transfer depend on?
Thickness of the material
Thermal conductivity of material
Temperature difference
What can we use to detect how much a home is insulated?
An infrared camera.
How can we reduce conduction in our homes?
Thick walls
Cavity walls
Carpets
Double glazing
Loft insulation
What is a cavity wall?
Inner and outer walls have a gap between, sometimes filled with insulating foam.
How can we reduce convection?
Place a lid on a hot drink or saucepan.
What can be used to reduce friction?
Lubricants such as oil or grease.
Is black or white a better absorber of heat?
Black
Is black or white a better reflector of heat?
White
Can renewable or non renewable be replenished at a faster rate than it is being used?
Renewable resources.
Can renewable or non renewable be used up at a faster rate than they can be replenished?
Non renewable resources.
What are renewable energy resources?
Resources that can be replenished at a faster rate than it is being used.
What are non renewable energy resources?
Resources that are used up faster than they can be replenished.
Give examples of renewable resources
Solar
Wind
Tidal
Biofuel
Wave
Hydroelectricity
Geothermal
Give examples of non renewable resources
Nuclear
Fossil fuels
Name the 3 fossil fuels
Oil, coal and natural gas.
What are fossil fuels used for?
Vehicles (Petrol/Diesel)
Heating homes
Cooking (Gas cookers)
Generating electricity
How do fossil fuels generate electricity?
Fossil fuels are burnt in the furnace to create heat. This generates steam which turns in a turbine for electricity.
Give advantages of using fossil fuels.
Cheap
Reliable
Found in large amounts/Abundant.
Can be stored/transferred.
Give disadvantages of using fossil fuels.
Slowly running out.
Pollution is harmful to the environment/human life.
Burning coal/gas can release sulfur dioxide, causing acidic rain.
When burnt, they release carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere and contributes to global warming.
How does nuclear power generate electricity?
Nuclear/Atomic fission produces heat which can create steam that drives the turbine to generate electricity.
Give advantages of using nuclear power.
Efficient
Not used up fast.
Clean energy source.
Give disadvantages of using fossil fuels.
Expensive
Highly radioactive waste must be disposed of safely.
How does biofuel generate electricity?
Biomass (plants/animal waste) are burnt to give off heat. This creates steam which turns turbines to generate electricity.
Give advantages of using fossil fuels.
Reliable
Readily available.
Short time to grow.
Grown all year around.
Carbon neutral; amount of carbon dioxide released when burnt equates to amount absorbed by the atmosphere whilst plants grow.
Give disadvantages of using fossil fuels.
Increased food prices.
Areas of the forest are cleared to grow crops for biofuel. This leads to an increase in deforestation + destruction of habitats.
When burnt, they release carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere and contributes to global warming.
How does hydroelectricity generate electricity?
Involves flooding a valley by building a dam. The GPE lost by water falling from the dam is converted to KE which is used in turbines to generate electricity.
Give advantages of using fossil fuels.
Reliable
No harmful emissions.
Immediately responds to increase in energy demands.
Give disadvantages of using fossil fuels.
Expensive
Must flood area to build dam which damages habitats.
How do geothermal sources generate electricity?
Hot water/Rocks underground become steam and generate electricity in a turbine.
Give advantages of using geothermal sources.
Reliable as rocks are always hot.
Geothermal stations only have a small environmental impact.
Give disadvantages of using fossil fuels.
Expensive
Difficult to set up.
Building geothermal power plants can trigger earthquakes.
Limited locations as rocks are only hot where there’s volcanic activity.
How do solar sources generate electricity?
Solar panels absorb light to create electricity.
Give advantages of using Solar sources.
No pollution.
Reliable in places with lots of light.
Give disadvantages of using Solar sources.
Cannot be used in cloudy countries or at night.
Lots of energy required to build solar panels.
Cannot increase production during extra demand.
How do wind sources generate electricity?
Wind turbines have generators inside that rotate when wind blow towards them, turning the generator to produce electricity.
Give advantages of using wind sources.
No pollution; sustainable.
Creates jobs.
Give disadvantages of using wind sources.
High initial cost.
Winds aren’t always strong/it’s not always windy.
People don’t like windmills and it can spoil the view.
How do tide sources generate electricity?
Tidal barrages are big dams with turbines in them. As the tide comes in, water is let out through the turbines to generate electricity.
Give advantages of using tide sources.
No pollution; sustainable.
Minimal environmental impact.
Give disadvantages of using tide sources.
Affect boat access.
Alter habitats for wildlife.
Can spoil the view.
Can block sewage that needs to go out to sea.
How do wave sources generate electricity?
Give advantages of using wave sources to generate electricity.
No pollution.
Unreliable; dependent of size of the wave.
Give disadvantages of using wave sources to generate electricity.
High initial cost.
Ugly on the coastline.
Turbines may disturb animals or destroy habitats.