SCIENCE - 2nd Quarter: Finals
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Respiratory system
Passageway of gas into and out of the body.
Brings oxygen into the body and gets rid of the carbon dioxide
▪In humans, it is divided into two: Upper Respiratory Tract and Lower Respiratory Tract
MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE
Integumentary ▪
Gills ▪T
Tracheal system ▪
Lungs
RESPIRATION
Confused with breathing
▪Overall exchange of gases among the atmosphere, blood and cells
▪BREATHING
act of taking air in and out
▪EXTERNAL RESPIRATION
exchange of O2 and CO2 between the air and blood within the lungs
INTERNAL RESPIRATION
exchange of O2 and CO2 between blood and the cell
▪CELLULAR RESPIRATION
process of using O2 to use and produce energy
Nose or Nasal Cavity ▪
Pharynx
▪Larynx
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT (3)
Nose or Nasal Cavity
▪Primary organ for smell
▪Main entrance for airflow
▪Pharynx
Throat ▪
Pathway for air and food ▪
Nasopharynx – oropharynx – laryngopharynx
▪Tonsils(Pharyngeal tonsil ▪Palatine tonsil ▪Lingual tonsil)
Voice box
Trachea
▪Bronchi -
▪Lungs ▪
Bronchioles ▪
Alveoli
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT
▪Trachea
Windpipe
▪Consists of ciliated mucosa
▪Bronchi
Passageway of air into lungs
▪Left- narrower, longer and less straight
▪Lungs
▪Main organ of respiratory system
▪Divided into several lobes
▪Alveoli
Where gas exchange occurs
BRONCHITIS
Coughs out mucopurulent sputum – mucus and pus ▪
Caused by virus, and bacteria. ▪
Also associated with cigarette smoking, emphysema, and air pollution
PNEUMONIA
▪Inflammation of the lungs ▪
May be bacterial or viral
SARS-COV-2 – Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome COronaVirus 2
is the virus that causes the COVID-19
▪ Transmission of SARS-CoV is primarily from person to perso
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
Hypertension
▪140/90 mm Hg ▪
“silent killer”
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Arteries become narrowed and hardened due to buildup of plaque around the wall ▪
(?) vascular disease
▪Disrupts the flow of blood
STROKE
When blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted.
▪ Within minutes, brain cells starts to die.
▪ Prompt treatment is crucial. Early actions can minimize brain damage.
HEART ATTACK, 1 MYO, 2 cardial, INFRACTION
▪Myocardial infarction (MI)
(1) – muscle ,
(2) – heart ,
(3) – death of tissue due to lack of blood supply
MYO
60 – 100pm
How fast does your heart beat?
how many ml of blood per min
60 – 100ml
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Deliver Oxygen
Deliver Nutrients
Remove Carbon Dioxide
Remove Waste
Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood
Parts of circulatory System
Red= Erythrocytes
White=Leukocytes
Platelets=Thrombocytes
Scientific names of red, white and platelets
Deliver Oxygen
Deliver Nutrients
Remove Carbon Dioxide
Remove Waste
Role of erythrocytes (red)
Hemoglobin
Iron-containing Protein that gives the rbc a RED color
White Blood Cell (Leukocytes)
Protect the Body from Bacteria, Viruses, and Foreign Substance
White Blood Cell (Leukocytes)
It is Colorless Bigger than RBC 1
: 700 RBC
There are multiple types of (?)
They only live for a several days
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Main role is to Clot the Blood
Trapped by fibrin made by Fibrinogen(pRotein)
Not True cells
plasma (55%)
Wbc and platelets (4%)
rbc (41%)
Percentages of red,white, and platelets in the blood
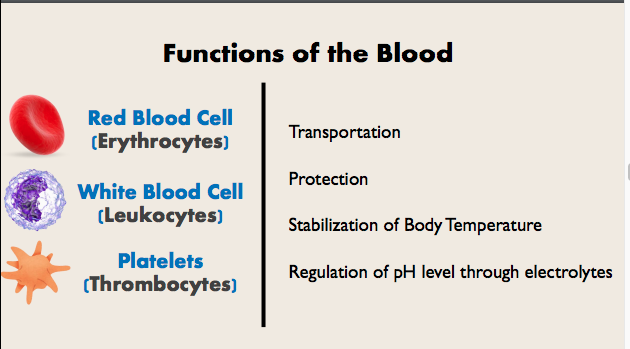
Function of the blood
Blood Vessels
A network of tubular structure that acts as passageway for blood through the tissues and organs
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Parts of blood vessels
Arteries
Carries oxygenated blood AWAY from the heart
Veins
Carries deoxygenated blood TOWARDS the heart
Capillaries
Carries blood from VESSEL to ORGAN / TISSUE
The main function of the heart is to deliver a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients to the body by pumping blood
Main function of the Heart
Atria
Are the receiving chambers of the heart.
Ventricles
Are the pumping chambers of the heart
Vena Cava
It is the largest vein, carrying deoxygenated blood back to the heart. There are two branches: the superior vena cava, which carries blood from the head and neck region to the right atrium, and the inferior vena cava, which carries blood from the lower parts of the body to the right atrium. (
Pulmonary Artery
Whereas the (?) veins transport oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium. (
Aorta
It is known as the largest artery, carrying oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to every part of the body. Its branches are the coronary arteries which are responsible for supplying blood to the heart.
Arteries
Are thick-walled to cope with the high pressure of the blood flowing through them. They transport oxygen-rich blood that moves away from the heart
Veins
Have thinner walls than arteries. This is because they easily collapse when cut. Functionally, They convey blood coming from all parts of the body, back to the heart.
Capillaries
Are the smallest blood vessels that are just one cell thick. This is because the exchange of materials, such as gases and nutrients, can easily take place between the blood and the cells. They are located between the arterioles and venules. (1
Lub- DUb
The normal heart sound is typically described as_
Blood pressure
It is a fundamental physiological parameter that measures the force of blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it throughout the circulatory system. (
Sphygmomanometer
Blood pressure can be measured using a
Blood pressure
it is the force exerted by the circulating blood against the walls of the blood vessels. (
Cardiac Cycle
The (?) refers to the series that occur during one complete heartbeat
Karl Landsteiner
an Austrian scientist, discovered four blood groups in 1900: A, B, AB, and O. The combination of these components determines an individual's blood type. Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1930 for his work.
Anemia
Consistent lack of red blood cells
Genetics
study of how traits are passed from parent to offspring
Gene
a unit of heredity; a section of DNA sequence encoding a single protein
Genome
the entire set of genes in an organism
Alleles
two genes that occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes and that cover the same trait (like ‘flavors’ of a trait).
Locus
– a fixed location on a strand of DNA where a gene or one of its alleles is located
Homozygous
having identical genes (one from each parent) for a particular characteristic
Heterozygous
having two different genes for a particular characteristic.
Dominant
the allele of a gene that masks or suppresses the expression of an alternate allele; the trait appears in the heterozygous condition.
Recessive
an allele that is masked by a dominant allele; does not appear in the heterozygous condition, only in homozygous.
Genotype
the genetic makeup of an organisms
Phenotype
– the physical appearance of an organism (Genotype + environment)
▪ Monohybrid cross
a genetic cross involving a single pair of genes (one trait); parents differ by a single trait.
Genetics
deals with the study of heredity and variation
Heredity
is the transfer of traits from parent to offspring
Variation
means similarities and differences among organisms.
HEREDITY
IT IS THE TRANSMISSION OF GENES FROM PARENTS TO THE OFFSPRING( children)
chromosomes, gene
TRAITS are determined by the genes on the (?). A (?) is a segment of DNA that determines a trait.
chromosomes
characteristics are passed on in the (?) that offspring inherit from their parents including human characteristics, gender and etc
Body
is made up of different orangs, which are made of tissue
Skin
is one of many different types of tissues in the body
Cells
are the building blocks of tissues
Different tissues are made of different cells that cary out different roles
Nucleus
is the control centre of a cell
each (?) contains long strands of genetic info
Chromosomes
cary the genetic info located in the nuclei of cells
in most (?) are matched in pairs
“strands”
Chromosomes
They are made from chromatic or a material consisting of DNA and associated with proteins
A long stringy aggregate of genes that carries hereditary information
gene
each (?) is a sepertae section of a chromosome and controls a separate characteristic
gene
is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes, which are made up of DNA, act as instructions to make molecules called proteins.
Homologous chromosomes
Matching pairs of chromosomes are called (?)
46 chromosomes
In human body cells there are a total of (?) chromosomes, u inherit half (23) your chromosomes from you rmother and from ur father
genotype
the full set of genes of an organism is called its
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism; The gene (or allele) combination an organism has. –
Example: Tt, ss, GG, Ww
Phenotype
The physical characteristics of an organism; The way an organism looks –
Example: Curly hair, straight hair, blue eyes,
u= dominant
Lower= recessive
A gene can be represented using a letter
dominant= ?
Recessive= ?
Gregor Mendel
was the first biologist to use Mathematics – to explain his results quantitatively
deoxyribonnucleic
dna stands for
DNA molecule
chromosomes and the genes they carry are made a molecule called
Punnett Squares
is the standard way of working out what the possible offspring of two parents will be. –
It is a helpful tool to show allelic combinations and predict offspring ratios.
scientific name of red
erythrocytes
scientific name of white
Leukocytes
scientific name of platelets
Thrombocytes