Bio unit 2 test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
Last updated 3:51 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
1
New cards
what are cells mostly made up of
water
2
New cards
what is one of the most important element in cells
carbon
3
New cards
what organic molecules is carbon a "backbone" for
proteins
lipids
carbohydrates
nucleic acids
lipids
carbohydrates
nucleic acids
4
New cards
what are hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
5
New cards
what are functional groups
certain groups of atoms attached to carbon skeletons of different molecules that give the molecules their properties
6
New cards
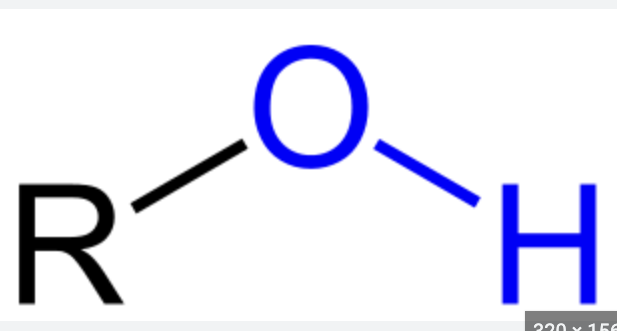
hydrogen and oxygen bonded
makes molecules alcohols
are polar
attract water molecules and dissolves organic compounds
makes molecules alcohols
are polar
attract water molecules and dissolves organic compounds
hydroxyl
7
New cards
what are organic compounds made of/ have
carbon
8
New cards
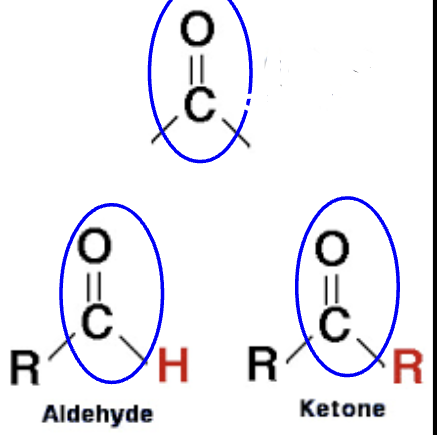
carbon and oxygen double bonded
has two types: aldehydes and ketones
determine overall structure of molecules and make molecules polar
has two types: aldehydes and ketones
determine overall structure of molecules and make molecules polar
carbonyl
9
New cards
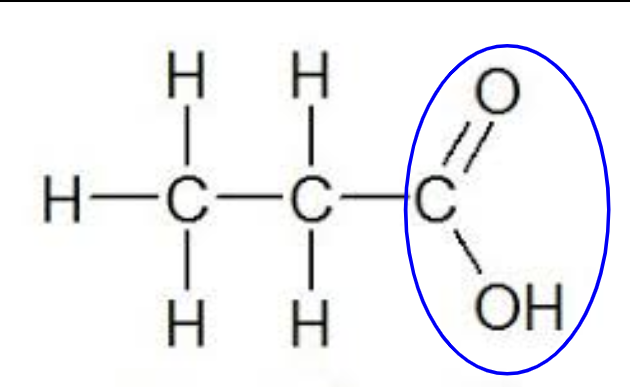
makes a substance acidic
critical in creating bonds between molecules
critical in creating bonds between molecules
carboxyl
10
New cards
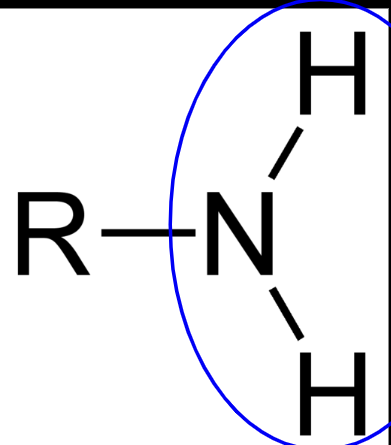
NH2
gives molecules a slightly positive charge
gives molecules a slightly positive charge
amino functional groups
11
New cards
what are amino acids made of
a central carbon attached to an amino group, hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, variant r
12
New cards
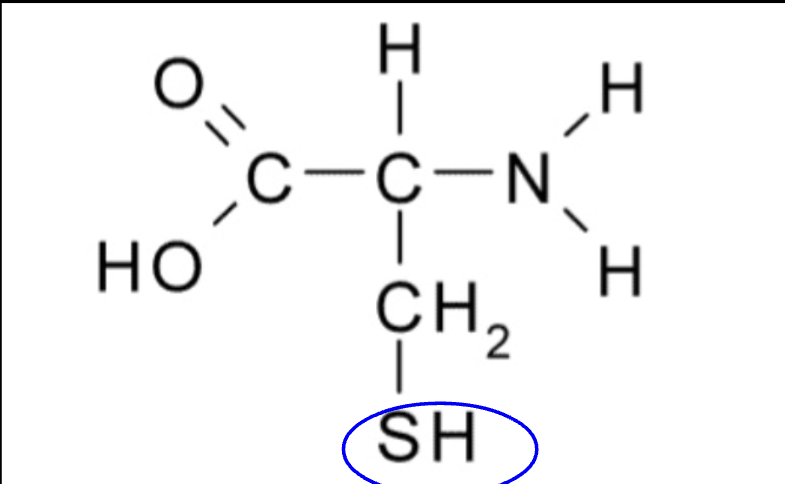
SH
critical in binding to other groups in amino acid chains
help determine the structure of 3D proteins
critical in binding to other groups in amino acid chains
help determine the structure of 3D proteins
sulfhydryl
13
New cards
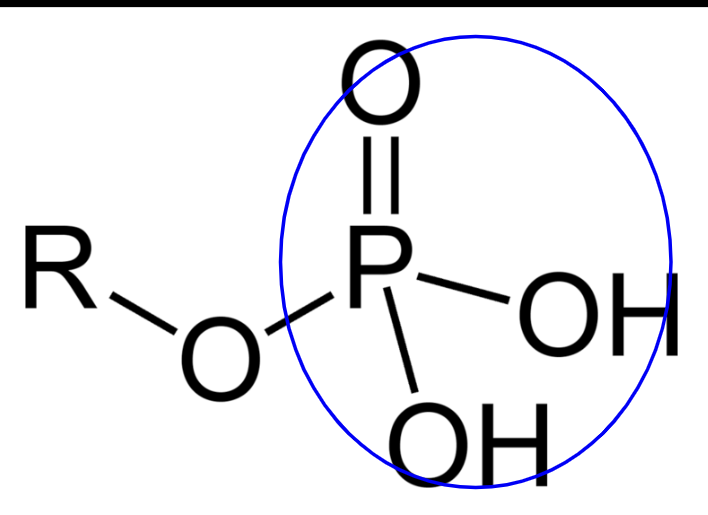
PO
critical in binding to other groups and saving energy in the chemical bonds formed
critical in the structure of ATP
critical in binding to other groups and saving energy in the chemical bonds formed
critical in the structure of ATP
phosphate groups
14
New cards
macromolecules
large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms
15
New cards
monomer
single "building block" of organic molecules
16
New cards
polymer
many monomers bonded together
17
New cards
which of life's organic molecules are polymers?
carbohydrates
proteins
nucleic acids
proteins
nucleic acids
18
New cards
how do monomers connect together?
dehydration synthesis
19
New cards
how are polymers disassembled into monomers?
hydrolysis
20
New cards
what is a product of dehydration synthesis?
water
21
New cards
what is needed to perform hydrolysis?
water
22
New cards
sugars and the polymers of sugars
carbohydrates
23
New cards
simplest carbohydrates
monosaccharides
24
New cards
carbohydrate macromolecules are...
polysaccharides
25
New cards
what are polysaccharides important for?
energy carrying
structure
structure
26
New cards
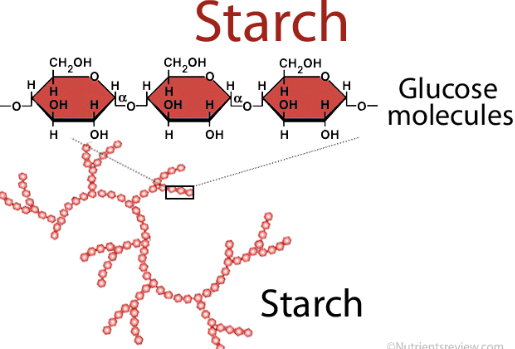
starch
energy storage polysaccharide of plants
consists entirely of glucose monomers
consists entirely of glucose monomers
27
New cards
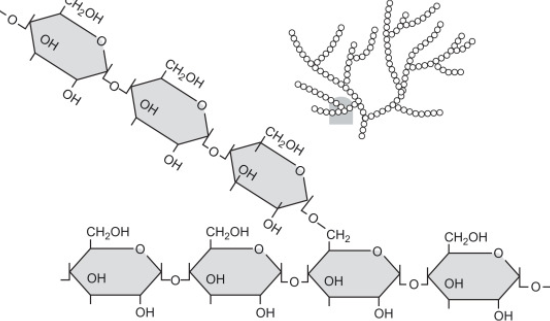
glycogen
energy storage polysaccharide in animals
mainly in liver and muscle cells
mainly in liver and muscle cells
28
New cards
cellulose
structural polysaccharide forming the tough wall of plant cells
29
New cards
polymers with alpha glucose
helical
30
New cards
polymers with beta glucose
straight
31
New cards
mammals can digest
alpha linkages but not beta linkages
32
New cards
structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of arthropods and cell walls of fungi
chitin
33
New cards
the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers
lipids
34
New cards
all lipids are...
hydrophobic
35
New cards
three important lipids
fats (triglycerides)
phospholipids
steroids
phospholipids
steroids
36
New cards
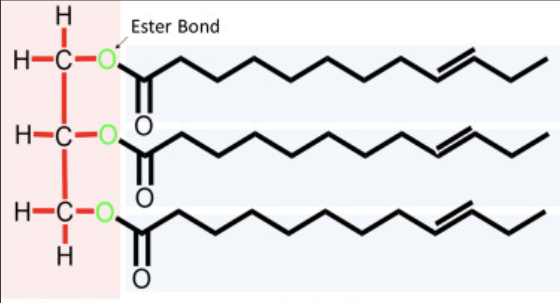
constructed of two types of smaller molecules: glycerol (tree carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon) and fatty acids (carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton)
fats
37
New cards
fatty acids vary by
length
number and locations of double bonds
number and locations of double bonds
38
New cards
most animal fats are... which are solid at room temperature
saturated fats
39
New cards
plant and fish fats are usually... and liquid at room temperature
unsaturated
40
New cards
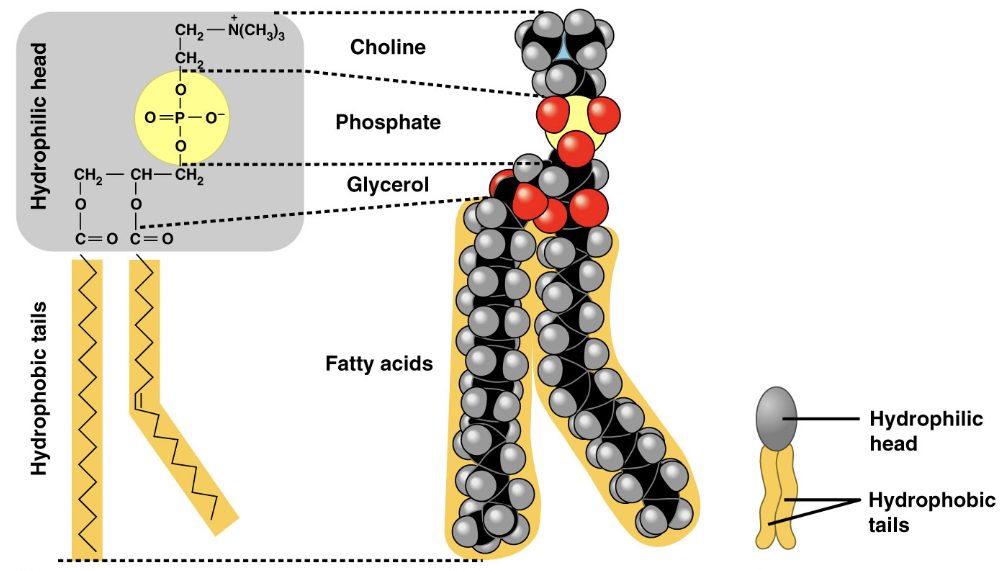
two fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol
phospholipids
41
New cards
fatty acid tails are...
hydrophobic
42
New cards
head is...
hydrophillic
43
New cards
when phospholipids are added to water, they form a ... with hydrophobic tails pointing toward the ... which can be found in cell membranes
bilayer/ interior
44
New cards
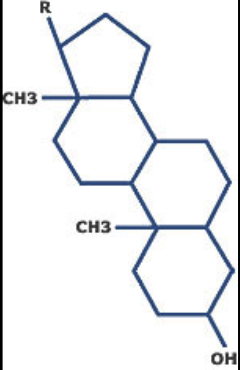
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings (3 6-carbon and 1 5-carbon)
steroids
45
New cards
an important steroid that is a component in animal cell membranes
cholesterol
46
New cards
account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells and do everything
proteins
47
New cards
polymers of amino acids
polypeptides
48
New cards
one or more polypeptides
protein
49
New cards
amino acids are...
proteins
50
New cards
amino acids are linked together into a polypeptide by
peptide bonds
51
New cards
the sequence of amino acids determines its ... and therefore its ...
shape/function
52
New cards
primary structure
unique sequence of amino acids
53
New cards
secondary struture
coils and folds in the polypeptide chain
54
New cards
tertiary structure
interactions between various side chains (r groups)
55
New cards
quaternary structure
when a protein consists of multiple polypeptide chains
56
New cards
typical secondary structures
alpha helix coil
beta pleated sheet
beta pleated sheet
57
New cards
a slight change in primary structure can affect...
a protein's conformation and ability to function
58
New cards
enzymes
proteins that act as catalysts that speeds up chemical reactions and perform their function repeatedly
59
New cards
when a protein has lost its 3D confirmation it becomes ... (can be affected by changes in pH, salt concentration, and temp)
denatured
60
New cards
two types of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
61
New cards
provides directions for its own replicatin
DNA
62
New cards
DNA directs synthesis of ... and controls protein synthesis
mRNA
63
New cards
protein synthesis occurs in...
ribosomes
64
New cards
made of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group
nucleotide monomers
65
New cards
portion of nucleotide without the phosphate group
nucleoside
66
New cards
polynucleotide
nucleotide polymers are linked together
67
New cards
2 polynucleotides form a double helix in
DNA
68
New cards
elements essential to life
carbon
oxygen
hydrogen
nitrogen
(CHON)
oxygen
hydrogen
nitrogen
(CHON)
69
New cards
when does a hydrogen bond form?
when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom
70
New cards
van der walls interactions
molecules or atoms that are very close together can be attracted by fleeting charge differences
71
New cards
the main reason earth is habitable
water
72
New cards
water is a ... molecule (opposite ends have opposite charges)
polar
73
New cards
cohesion
hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together
74
New cards
high specific heat
water can absorb or release a lot of energy without large changes in its temperature
75
New cards
when bonds break heat is ...
absorbed
76
New cards
when bonds form heat is...
released
77
New cards
evaporative cooling
as liquid evaporates, the remaining surface cools
78
New cards
water has a ... heat of vaporization
high
79
New cards
why does ice float in liquid water
hydrogen bonds in ice are more "ordered", making it less dense
80
New cards
universal solvent
can dissolve many substances due to its polarity
makes aqueous solutions
makes aqueous solutions
81
New cards
why is water an effective solvent?
it readily forms hydrogen bonds
82
New cards
t/f water can dissolve compounds made of nonionic polar molecules
true
83
New cards
free energy
the portion of a system's energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout
84
New cards
catalyst
chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by it
85
New cards
an enzyme is a ...
protein
86
New cards
enzymes end in
-ase
87
New cards
activation energy
the amount of energy a chemical reaction needs to get started (usually in the form of heat)
88
New cards
how do enzymes catalyze reactions?
they lower the activation energy needed
89
New cards
do/do not affect to change in energy
do not (hasten reactions that would occur eventually)
90
New cards
substrate
the reactant that the enzyme acts on
91
New cards
what is formed when the enzyme bonds to its substrate?
the enzyme-substrate complex
92
New cards
active site
where the substrate binds to the enzyme
93
New cards
induced fit
how the enzyme folds around the substrate (like a handshake)
94
New cards
how do enzymes lower activation energy?
orienting substrates correctly
straining substrate bonds
providing favorable microenvironment
covalently bonding to the substrate
straining substrate bonds
providing favorable microenvironment
covalently bonding to the substrate
95
New cards
enzyme activity can be affected by...
environmental factors (pH and temp)
chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme
chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme
96
New cards
each enzyme has...
an optimal temp/pH
97
New cards
enzymes at high temperatures are...
denatured
98
New cards
enzymes at low temperatures are...
inactive
99
New cards
inhibitors
can slow enzyme activity
100
New cards
competitive inhibitors
bond to active site of the enzyme