Organic - Chapter 5: Carboxylic Acid & Esters
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1
New cards
Carboxyl Group
The COOH functional group.
2
New cards
Carboxylic Acid
Group of molecules containing the carboxyl functional group.
3
New cards
abundantly
Carboxyl-containing compounds are found _______ in nature. Ex.) Lactic acid
4
New cards
tart
The ____ flavor of foods that taste sour is usually caused by the presence of one or more carboxylic acids.
5
New cards
-oxo
Ending of ketone branches.
6
New cards
priority
Carboxylic acids are the top _______ when naming organic molecules.
7
New cards
True
T or F: Carboxylic acids were among the first organic compounds to be studied due to their abundance in nature.
8
New cards
familiar source
Carboxylic acids were usually named after some _____________.
Ex.) Acetic acid was named after Latin word for vinegar, acetum.
Ex.) Acetic acid was named after Latin word for vinegar, acetum.
9
New cards
Formic Acid
(IUPAC = Methanoic Acid) Stinging agent of certain ants and beetles, used in food preservation.
10
New cards
Acetic Acid
(IUPAC = Ethanoic Acid) Active ingredient in vinegar, used in food preservation.
11
New cards
Propionic Acid
(IUPAC = Propanoic Acid) Salts used as mold inhibitors.
12
New cards
Butyric Acid
(IUPAC = Butanoic Acid) Odor-causing agent in rancid butter.
13
New cards
Caproic Acid
(IUPAC = Hexanoic Acid) Characteristic odor of Limburger cheese.
14
New cards
Oxalic Acid
(IUPAC = Ethanedioic Acid) Present in leaves of some plants such as rhubarb and spinach, used as a cleaning agent for rust stains on fabric and porcelain.
15
New cards
Citric Acid
(IUPAC = 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-PropaneTriCarboxylic Acid) Present in citrus fruits, used as a flavoring agent in foods, present in cells.
16
New cards
Lactic Acid
(IUPAC = 2-HydroxyPropanoic Acid) Found in sour milk and sauerkraut, formed in muscles during exercise.
17
New cards
liquid
Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are ______ at room temperature.
18
New cards
unpleasant
Carboxylic acids have characteristically sharp or ______ odors.
19
New cards
increases
The boiling point of carboxylic acids ________ as the molecular weight increases.
20
New cards
waxlike
Heavier carboxylic acids (greater than ten carbons) are ________ solids.
21
New cards
highest
Carboxylic acids have the ________ boiling points when compared to compounds with similar molecular weights.
22
New cards
polar
The -COOH group is very ______ and has the ability to hydrogen bond with other -COOH groups.
23
New cards
alcohols
Carboxylic acids have stronger intermolecular forces (higher boiling points) than ______, because they can form dimers.
24
New cards
Dimer
Two identical molecules bonded together by two hydrogen bonds.
25
New cards
soluble
Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are very _______ in water due to the hydrophilic carboxyl group. The
-COOH groups can hydrogen bond with water.
-COOH groups can hydrogen bond with water.
26
New cards
hydrophobic
As the length of the ________ hydrocarbon portion increases, the water solubility decreases.
27
New cards
True
T or F: Carboxylic acids containing eight or more carbon atoms are considered to be insoluble in water.
28
New cards
False
T or F: The same trend found in BP is found in solubility.
hydrocarbons < ethers < aldehydes & ketones < carboxylic acids < alcohols
hydrocarbons < ethers < aldehydes & ketones < carboxylic acids < alcohols
29
New cards
acidic behavior
The most important chemical property of carboxylic acids is their ___________.
30
New cards
hydrogen
The acidic character of carboxylic acid is caused by the ________ attached to the oxygen of the carboxyl group.
31
New cards
Carboxylate Ion
Formed when the H+ leaves the carboxylic acid in water.
32
New cards
weak acids
Carboxylic acids behave as ________ having a low dissociation.
33
New cards
reversible
The acidic reactions are _________.
34
New cards
Le Chatelier's Principle
The addition of H3O+ (low pH) favors the formation of the carboxylic acid where the removal of H3O+ (high pH) favors the formation of the carboxylate ion.
35
New cards
7.4
At pH ____ (the pH of blood/body fluids), the carboxylate form predominates.
36
New cards
salts
Even though carboxylic acids are weak, they can still readily react with strong bases (NaOH & KOH) to form _______.
37
New cards
Pyruvic Acid
(Pyruvate) An important intermediate in the energy conversion reactions in living organisms.
38
New cards
metal
Both common names and IUPAC names are assigned to carboxylic acid salts by naming the _____ first and changing the ending the -ic ending of the acid name to -ate.
39
New cards
solid
Carboxylic acid salts are _______ at room temperature.
40
New cards
ionic
Carboxylic acid salts are usually soluble in water because they are _______.
41
New cards
Fatty Acids
Carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains (12-20 carbon atoms), first isolated from natural fats.
42
New cards
True
T or F: Even long chain acids with an extensive nonpolar hydrocarbon portion can be solubilized by converting them into salts.
43
New cards
soaps
Na+ and K+ salts of long-chain acids are used as ______.
44
New cards
preservatives
Calcium and sodium propanoate are used commercially as ____________ in bread and cheese (prevent mold growth).
45
New cards
Sodium Benzoate
Another preservative that occurs naturally in foods such as cranberries and prunes, it is also used in products such as ketchup and carbonated beverages.
46
New cards
Zinc 10-undecylenate
Used to treat athlete's foot.
47
New cards
buffer
A mixture of sodium citrate and citric acid is widely used as a _______ to control pH.
48
New cards
anticoagulant
In blood, the buffer (citrate/citric acid) functions as an __________.
49
New cards
maintain
Products sold as foams or gels (jelly, ice cream, whipped cream) ________ their desirable characteristics at certain pHs which can be controlled by the citrate/citric acid buffer.
50
New cards
Ester
Group of molecules containing the -COOR functional group (a carbonyl next to an alkoxy group).
51
New cards
acid catalyst
When carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an ___________, carboxylic esters are formed.
52
New cards
Esterification
The process of forming an ester linkage between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
53
New cards
ester linkage
The ester functional group has an ___________ between the carbonyl carbon and the oxygen atom.
54
New cards
structural
The ester functional group is a key _________ feature in fats, oils, and other lipids.
55
New cards
fragrances
Esters are found in many fruits and flowers, giving them their __________.
56
New cards
flavoring agents
Because of esters being found in fruits and flowers, they are commonly used as ___________ in foods and as scents in personal products.
57
New cards
Polyesters
Polymers made by esterification reaction.
58
New cards
Condensation Polymerization
When monomers combine to form polymers and a small molecule (usually water).
59
New cards
contrast
Condensation polymerization is in _______ to addition polymerization where all atoms of the alkene monomer are incorporated into the polymer.
60
New cards
False
T or F: In many polymerization reactions each monomer has only one functional group so the chain only grows at one end.
61
New cards
True
T or F: You must have the same number of monomers and alcohols for a polyester to form.
62
New cards
monomers
Molecules of product from these reactions continue to react with available __________ until the polyester is formed.
63
New cards
three
Over ______ billion pounds of polyester (PET) are produced annually.
64
New cards
spinnerettes
Polyester fibers are formed by melting the polymer and forcing the liquid through tiny holes in devices called _____________. The resulting fibers are spun into thread or yarn.
65
New cards
PET Uses
Automobile tire cords, permanent-press clothing, sutures for blood vessels & the esophagus, and sheets/films for manufacturing magnetic tapes for tape recorders.
66
New cards
good yields
The reversible nature of the esterification reaction does not always allow for ____________ of product.
67
New cards
Carboxylic Acid Chlorides
More reactive than carboxylic acids thus they are used instead to obtain higher product (ester) yields.
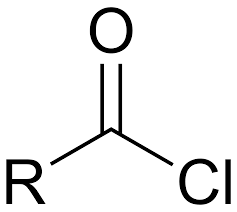
68
New cards
Carboxylic Acid Anhydrides
More reactive than carboxylic acids thus they are used instead to obtain higher product (ester) yields.
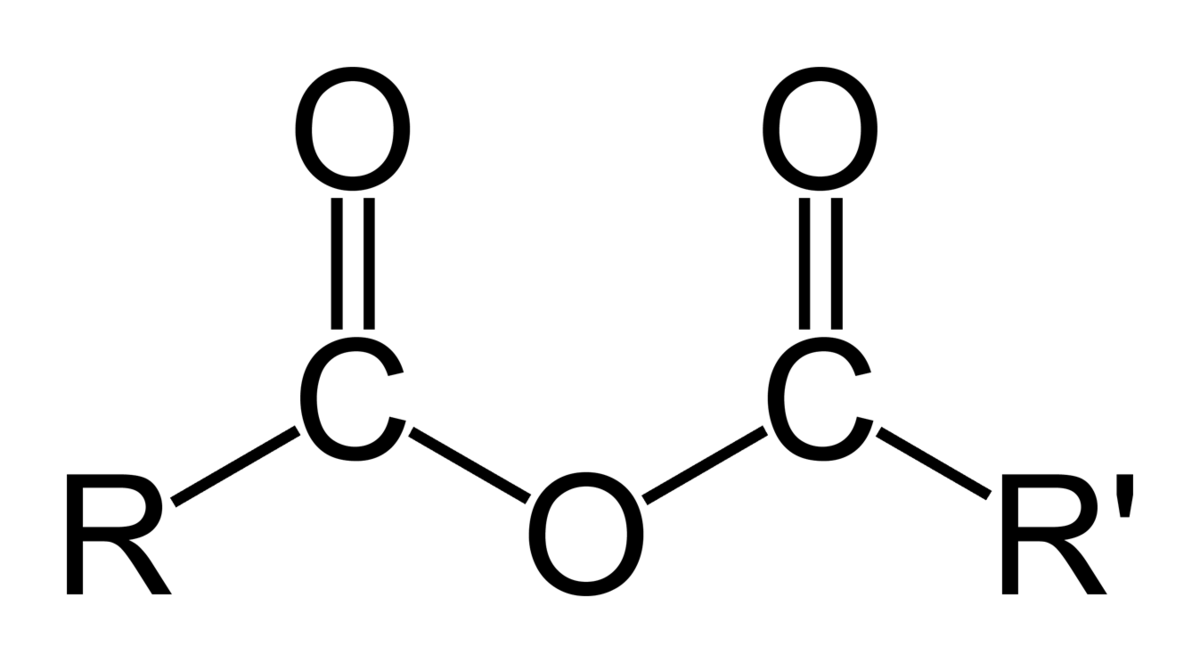
69
New cards
breaking
The most important reaction of esters (commercially and biologically) involve the ________ of the ester linkage. Ex.) Hydrolysis & Saponification
70
New cards
Ester Hydrolysis
Reaction of an ester with water to break the ester linkage and produce an alcohol and a carboxylic acid (reverse of esterification).
71
New cards
Strong acids
___________ are used as the catalyst of Ester hydrolysis and the reaction is reversible.
72
New cards
digested
Ester formation and hydrolysis are very important in biological processes (esters such as animal fats and vegetable oil are hydrolyzed when ________).
73
New cards
Saponification
Reaction of an ester with a strong base (KOH or NaOH) to break the ester linkage and produce an alcohol and a carboxylate salt.
74
New cards
fats, oils
Saponification of _____ and _____ is important in the production of soaps.
75
New cards
inorganic acids
Alcohols can form esters by reacting with ____________ such as sulfuric, nitric, and phosphoric acids.
76
New cards
biochemistry
The most important inorganic acid in ___________ are the esters of phosphoric acids (H3PO4).
Ex.) phospholipids and nucleic acids (diesters)
Ex.) phospholipids and nucleic acids (diesters)
77
New cards
Phosphoric acid
Because _____________ has three -OH groups, it can form monoesters, diesters, and triesters.
78
New cards
life
Monoesters and diesters are essential to _____ and represent some of the most important biological molecules.
79
New cards
body pH
At _________, the two -OH groups of phosphoric acid are ionized and the phosphate group has a charge of -2.
80
New cards
chemical energy
Phosphate esters are key compounds in the storage and transfer of ___________ in living systems.
81
New cards
Phosphoric Anhydrides
Compounds that contain multiple phosphate groups linked together. The most important are diphosphate esters and triphosphate esters.
82
New cards
Adenosine Diphosphate
(ADP) Phosphoric anhydride of great biological importance.
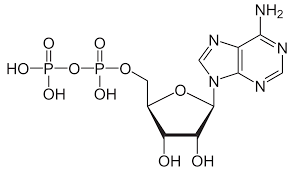
83
New cards
Adenosine Triphosphate
(ATP) Phosphoric anhydride of great biological importance.
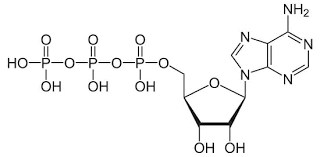
84
New cards
Aspirin
An ester prepared from salicylic acid used as a pain reliever, anti-inflammatory agent, and anticoagulant.
85
New cards
Nitroglycerin
A nitrate ester resulting from the reaction of nitric acid and glycerol used as an explosive.