Bonding and Isomerism
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Angstrom
Is used to measure the size of atoms
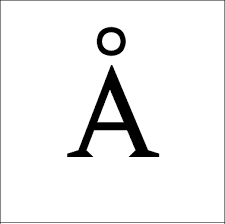
-10-4 Å
Size of the atom’s nucleus
1-5 Å
Size of the atom’s electron cloud
10-10 m
1 Å is equivalent to how many meters?
1.0073 amu
Atomic mass unit of protons
1.0087 amu
Atomic mass unit of neutrons
5.468 × 10-4 amu
Atomic mass unit of electrons
1+
Proton’s charge
0
Neutron’s charge
-1
Electron’s charge
Nucleus
Where are protons and neutrons located?
Electron cloud
Where are electrons located?
Protons and Neutrons
Contributes most to the mass of the atom
Electrons
Contributes most to the volume of the atom
Mass number/A
Protons + Neutrons = ?
Atomic number/Z
Number of protons or electrons
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass number due to the different number of neutrons
Carbon isotopes
Isotopes of a certain element have the same chemical properties but different nuclear decay process, a good example is this element
Orbitals
Region of space surrounding the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding and electron
two electrons
Each orbital can contain a maximum of this many electrons
s and p orbitals
Most important orbitals in organic compounds
Electron configuration
The distribution of electrons of an atom in different shells and orbitals
Shells (1, 2, 3, 4)
Orbitals are grouped in
Lewis Symbol
Shows the valence electrons of an atom as dots
Octet Rule
Chemical bonding results in an atom having eight valence electrons in order to achieve stability
Ionic and Covalent bonding
2 possible ways of chemical bonding to achieve stability
Ionic bonding
Transferring of valence electrons from one metal and nonmetal atom
Electropositive
Tend to release or give electrons during ionic bonding
Electronegative
Tends to attract or receive an electron