Endo 6 - Analgesics, Antibiotics, Anesthesia in Endo (Dr. Chen)
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Define the following:
A multifactorial noxious experience that involves not only the sensory response but also modification by cognitive, emotional and motivational influences related to past experience?
pain
What type of pain?
- Sharp, stabbing, short duration
acute
What type of pain?
- Dull, aching, long duration
chronic
What is an increased pain sensation or lowered pain threshold?
hyperalgesia
Patient experiences severe/prolonged pain to a cold test that is only mildly painful on the control tooth. What are they experiencing?
hyperalgesia
What type of pain?
A stimulus that is usually painful is even more painful
hyperalgesia
What is pain resulting from a non-noxious stimulus?
allodynia
What type of pain?
A stimulus that is usually NOT painful becomes painful
allodynia
Patient experiences pain on percussion that is not painful on control tooth. What are they experiencing ?
allodynia
What is absence of sensibility to pain, particularly to the relief of pain without loss of consciousness?
analgesia
What are the 3 D's of treating endo pain?
Diagnosis
Definitive dental treatment
Drugs
Which D?
- Pre-op pain control
- Accurate diagnosis
- Anxiety reduction
Diagnosis
Which D?
- Intra-op pain control
- Effective local anesthetic and operative techniques
- Completing the procedure
Definitive dental treatment
Which D?
- Post-op pain control
- Pharmacologic agents
Drugs
When diagnosing odontogenic pain, which principle is most important for identifying the source of the patient's chief complaint?
Reproduce the chief complaint
T/F: Research states that patients are only accurate 60-70% of the time on which tooth associates with pain but 90% accurate when the pain is periapical
True (estimated %s)
What should you do if a diagnosis cannot be made?
Consider referral to specialist
- Only proceed to treatment if there is a clear diagnosis
Odontogenic pain can be caused by what?
inflammation
Define the following:
- Pulpal inflammatory pain due to stimulation of nociceptors on afferent nerve fibers (A-delta and C- fibers) in dental pulp
- Periodontal inflammation
Odontogenic pain
Pulpal inflammation is the release of inflammatory mediators that stimulate receptors on nociceptive afferent nerve fibers. What are the nerve fibers that are stimulated?
A) A-delta
B) B-delta
C) C-fibers
D) A + C
E) all of the above
D) A-delta and C-fibers
T/F: Antibiotics can reduce pain in a patient with irreversible pulpitis
false (DO NOT REDUCE PAIN)
6 types of non-odontogenic pain
Musculoskeletal: myofascial pain, TMD
Neuropathic: trigeminal neuralgia, herpes infection, atypical odontalgia (phantom tooth pain)
Neurovascular: migraine, cluster headache
Inflammatory: sinusitis
Systemic disorders: cardiac pain, herpesvirus infections, tumors
Psychogenic pain: somatic symptom disorder
Inflammatory mediators sensitize nociceptive neurons leading to spontaneous pain and ______ pain threshold (allodynia)
reduce
effective dental tx decreases which 3 tissue level inflammatory mediators
Bradykinin "BK”
Prostaglandin "PG”
Cytokines
In Pak & White's 2011 study, it showed patients reported 90% reduction in pain within ________ of RCT
1 week
Pre-operative pain increases the chances for failing anesthesia by ___ fold!
8
Local anesthesia works by blocking what from entering cells?
sodium
What ion needs to be attached to the LA drug in order to block sodium from entering the cell?
hydrogen
T/F: Hydrogen must be attached to allow the drug to cross the cell membrane
false (cannot cross with hydrogen, reattaches when in cytoplasm)
How do you numb a highly sensitive tooth?
Initial LA
Maxilla: buccal + palatal infiltration
Mandible: IAN block and infiltration
Supplemental techniques
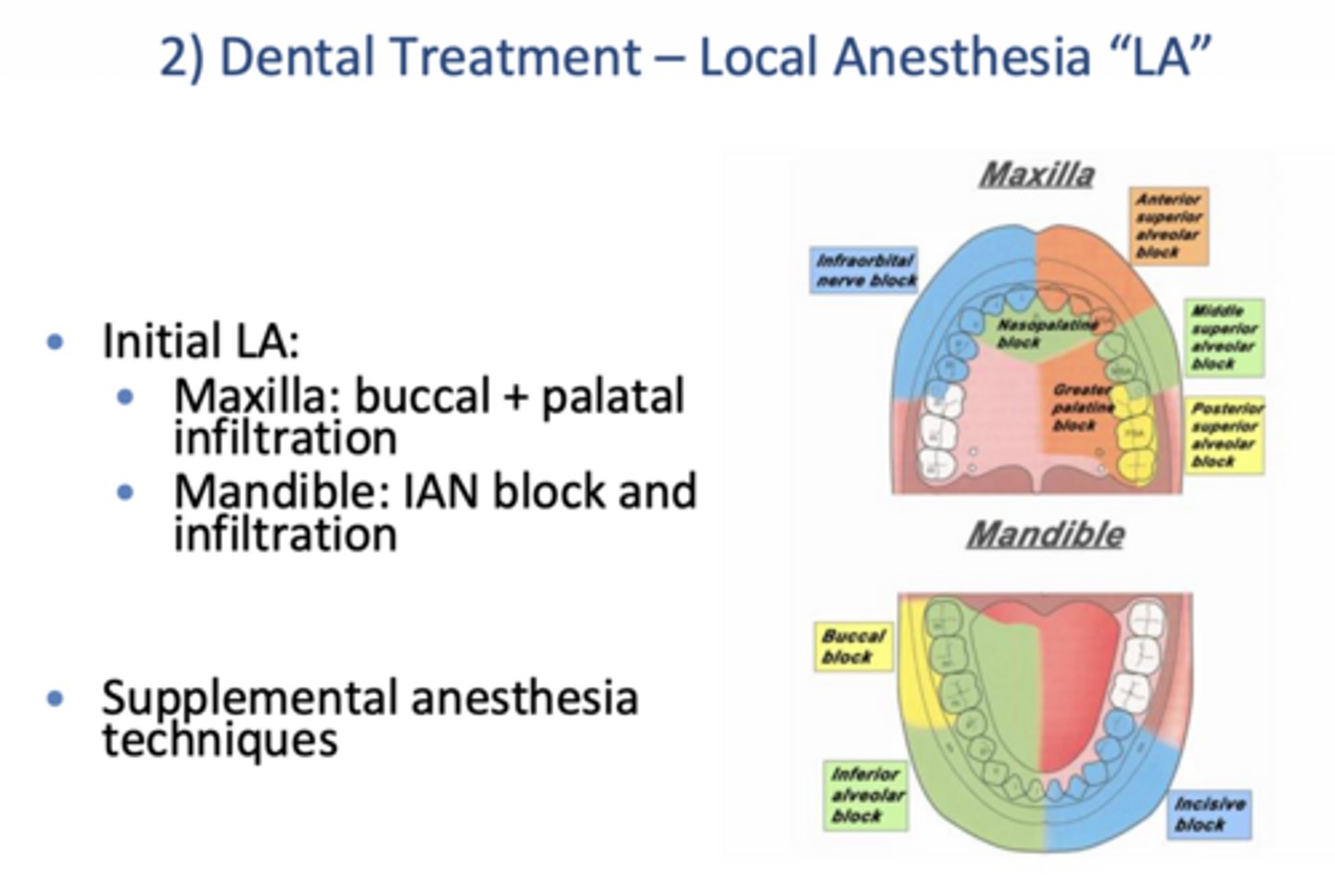
What are some ways to improve LA in a highly symptomatic patient?
Initial IAN block(s) and infiltration
Multiple IAN blocks
Supplemental anesthetic (intraligamental/PDL, intra-pulpal, intraosseous)
Pre-op NSAIDS
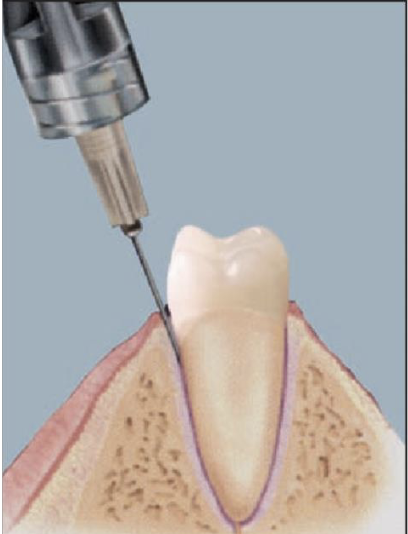
Which type of anesthesia technique?
- The needle is wedged between the root and crestal bone with heavy pressure slowly applied for 10-20 seconds
- Need significant resistance to deposition of solution
- Only a small volume is necessary (0.2 mL)
- Onset is immediate and lasts about 10 min
Intra-ligamental/PDL
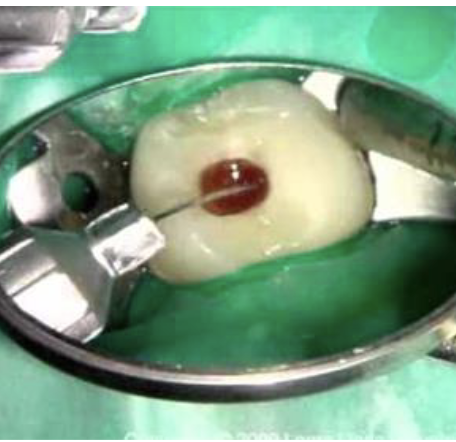
Which type of anesthesia technique?
- 2 options:
- - Inject into pulp chamber through hole in the roof
- - Inject into each root individually if chamber has already been unroofed
- Wedge the needle into the chamber or canal
- Apply pressure on the syringe handle for 5-10 s
Intra-pulpal
What is CRUCIAL when giving an intra-pulpal injection?
Back pressure (Walton 1997, Rosenberg 1975)
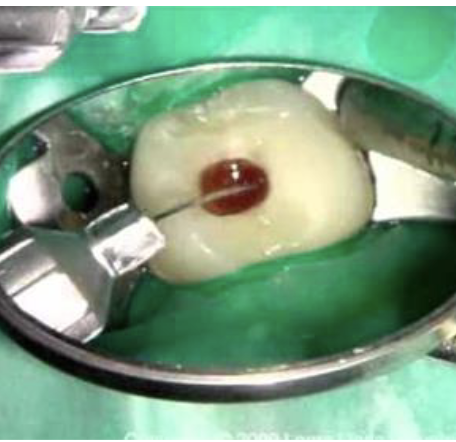
Do the types of anesthetics have any influence on the intra-pulpal effectiveness?
No - even saline works!
(In intrapulpal anesthesia, pain control comes from the pressure of the injection, not the pharmacologic action of the anesthetic so any solution, even saline, is effective as long as adequate back pressure is achieved)
Which type of anesthesia technique?
- Injection of solution directly into cancellous bone spaces around tooth
- Quick onset (30 seconds)
- Avoid mental foramen and IAN area
- Avoid perforating into the maxillary sinus
intraosseous
Do lip numbness and soft tissue anesthesia = pulpal anesthesia?
NO
If treating mandibular tooth, consider _________, check for lip numbness, then perform additional infiltrations
IAN block
For vital cases, how should you always test the tooth before beginning treatment?
Cold test
Opioid or non-opiod?
- NSAIDs
- Acetaminophen
Non-opioid
3 common opioids
Codeine
Hydrocodone (Vicodin)
Oxycodone (Percocet)
4 advantages of non-opioids
Can be effective for pain of inflammatory origin
Fewer side effects than opioids
No addiction potential
Readily available (OTC)
For Post-Op instructions, we recommend that patients should take ___ tablets of Ibuprofen (____ mg) every 4-6 hours
2, 400
For Post-Op instructions, we recommend that patients should take ___ tablets of Acetaminophen (____ mg) every 6 hours
2, 650
What is the max amount of Ibuprofen vs. acetaminophen a pt should take post-op per day?
ibuprofen: 3200 mg
acetaminophen: 3000 mg
What 3 effects do NSAIDS have? (hint: all As)
Anti-inflammatory
Analgesic
Antipyretic
Aspirin and NSAIDS block which pharmalogical pathway?
Cyclo-oxygenase (COX)
NSAIDS and aspirin target the COX pathway which also blocks what?
prostaglandins → depresses inflammatory response
What pain pathways do NSAIDS work on?
Peripheral pain pathways
Decrease in PG concentration has what 2 effects?
Raise threshold for pain-conducting nerves to discharge
Reduce fever
What are 3 adverse effects of NSAIDs?
Causes reversible effects on platelet aggregation (TXA2) → increase bleeding time
Long term use may cause changes in renal + liver functions and may require monitoring
GI side effects
What is 1 NSAID contraindication that was emphasized?
Pregnant/nursing women (use acetaminophen)
6 additional contraindications of NSAIDs
Cardiovascular disease with fluid retention
Coagulopathies
Peptic ulcer
Ulcerative colitis
History of Aspirin hypersensitivity
Use caution with some ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, cyclosporine, hydantoins, lithium, methotrexate, sympathomimetics, anticoagulants
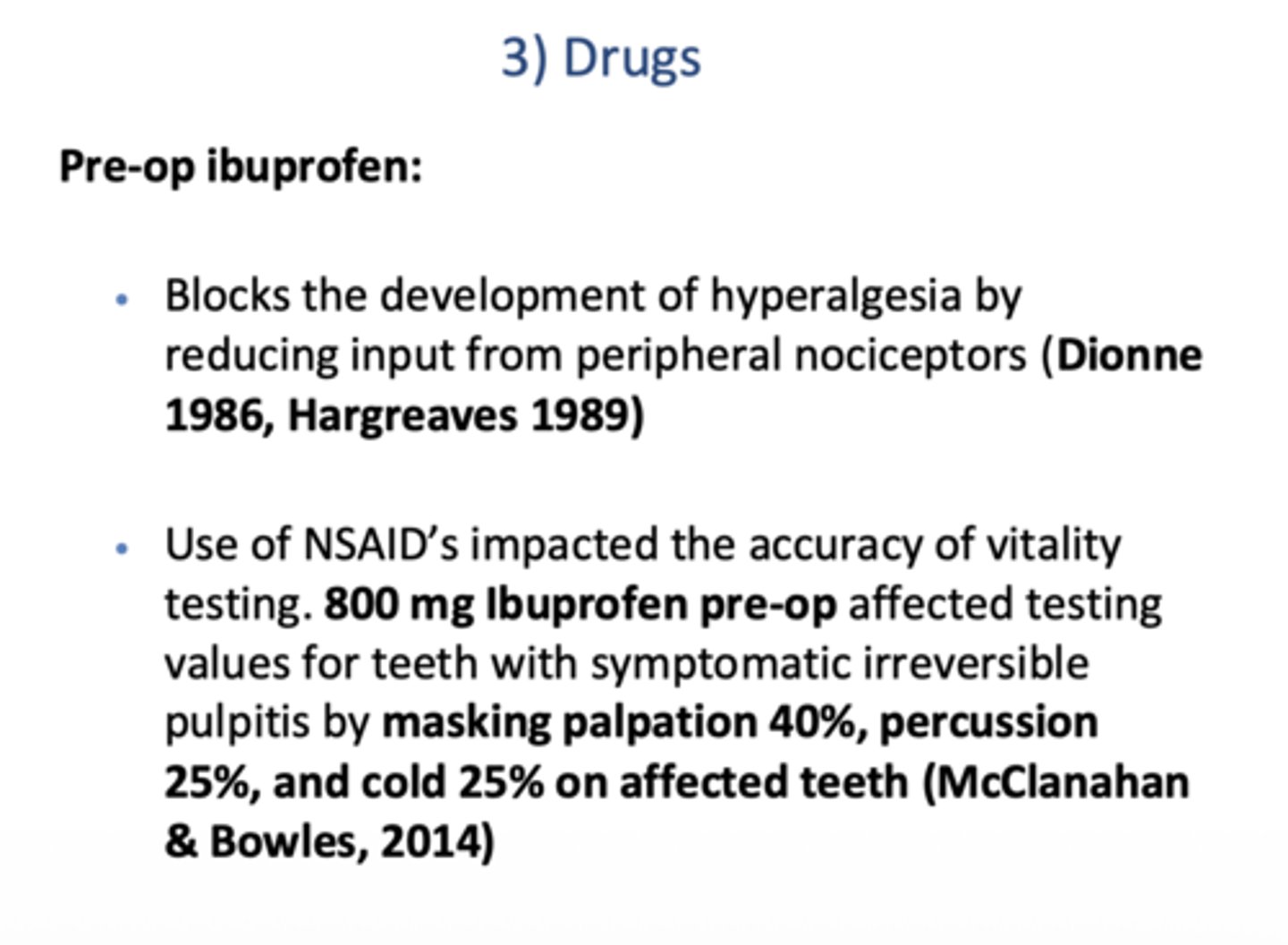
Pre-op ibuprofen blocks the development of hyperalgesia by reducing input from peripheral ____________
nociceptors (Dionne 1986, Hargreaves 1989)
Using NSAID's pre-op can mask testing of vital teeth by what 3 ways?
Mask palpation 40%
Mask percussion 25%
Mask cold 25%
McClanahan & Bowles, 2014)
What drug?
- Analgesic and antipyretic (only WEAK anti-inflammatory action)
- Weak COX inhibitor
- - Decrease PG production → depresses inflammatory response
- Acts primarily on CNS but also has peripheral action
Acetaminophen (Paracetamol/"APAP")
What are 4 acetaminophen contraindications/adverse effects?
G6PD-deficient patients
Do not use with alcohol
Drugs that interfere w/ hepatic P450 enzyme may increase toxic metabolites as acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver
Little to no effect on platelets or GI system
how do opioids block pain
blocks CNS mechanisms of pain + hyperalgesia by interfering with pain transmission, integration, and interpretation in cerebral cortex via activation of Mu and/or kappa receptors
7 adverse effect of opioids
Nausea
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Constipation
Potential for respiratory depression
Potential for abuse, tolerance, and addiction
Increased CNS depression when taken with alcohol
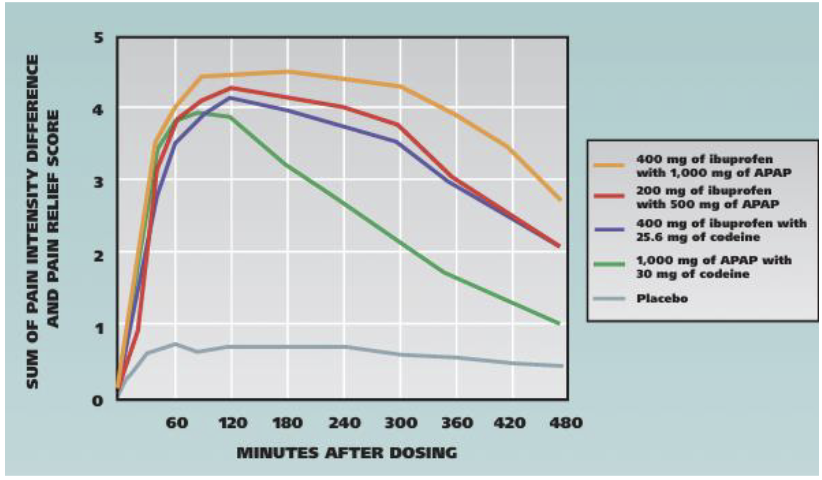
According to Moore & Hersh (2013), what analgesic regimen provides the greatest postop pain relief after 3rd molar extraction + fewer adverse effects than opioids?
Ibuprofen-APAP combination
T/F routine endo has mild anticipated post-procedural pain
true
T/F surgical endo has severe anticipated post-procedural pain
false, moderate
This is the ADA recommendation for which type of pain?
Ibuprofen 200-400mg every 4-6 hours for 24 hours
A) mild pain
B) mild to moderate pain
C) moderate to severe pain
D) severe pain
A) mild pain
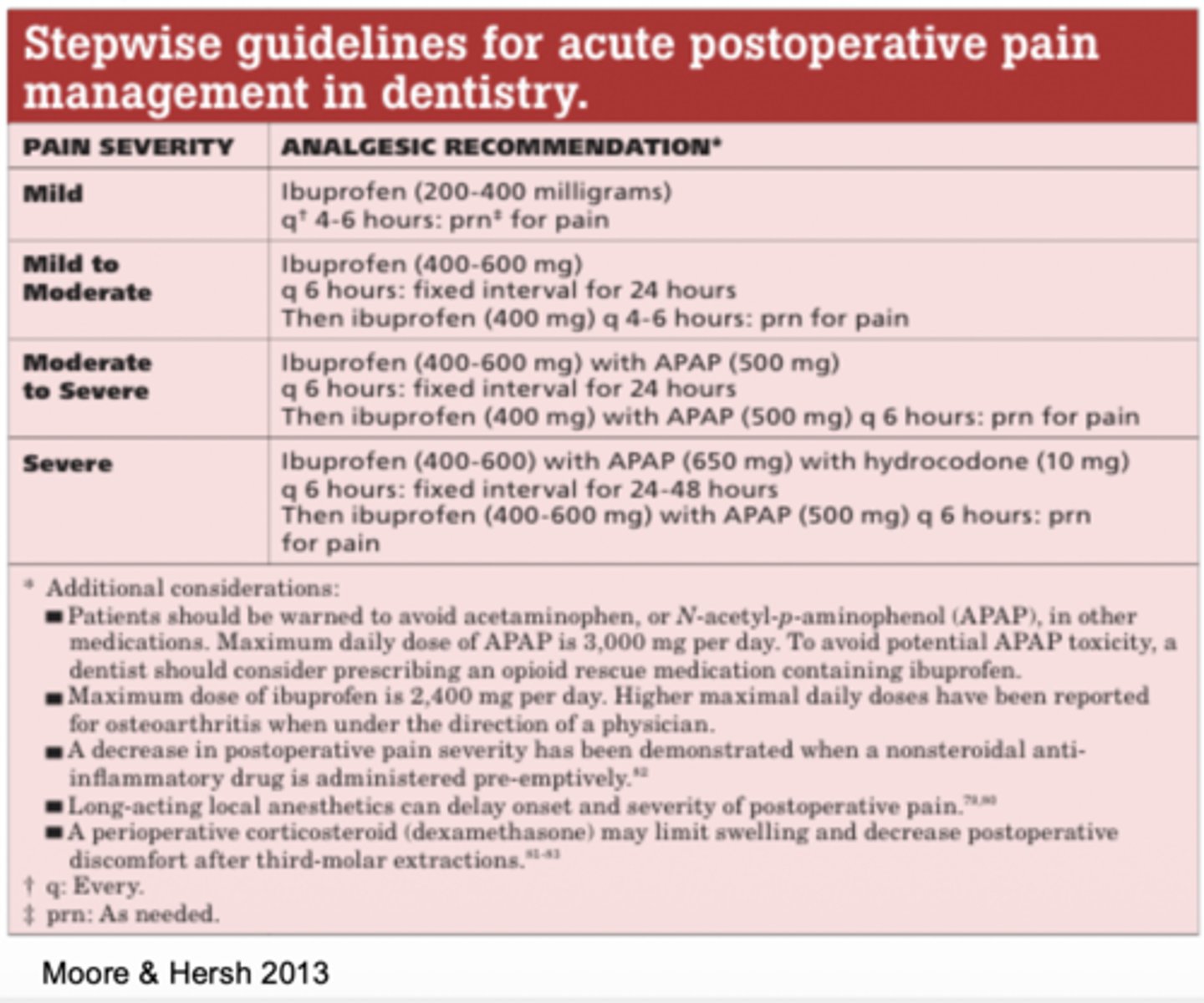
This is the ADA recommendation for which type of pain?
Ibuprofen 400-600mg every 4-6 hours for 24 hours
Then Ibuprofen 400mg as needed every 4-6 hours
A) mild pain
B) mild to moderate pain
C) moderate to severe pain
D) severe pain
B) mild to moderate pain
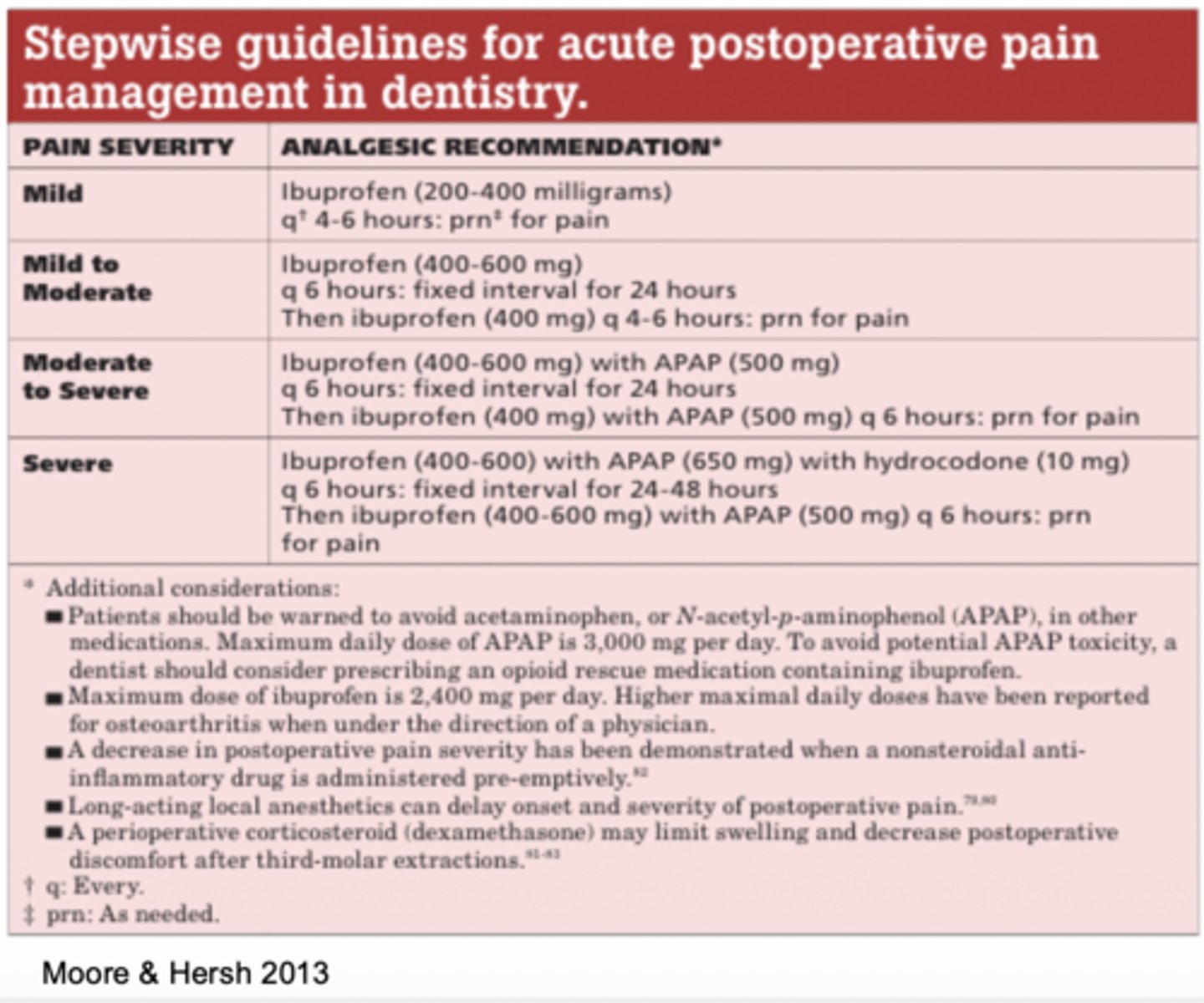
This is the ADA recommendation for which type of pain?
Ibuprofen 400-600mg every 4-6 hours plus acetaminophen 500mg fixed internal every 6 hours for for 24 hours
Ibuprofen 400mg and acetaminophen 500mg as needed every 4-6 hours
A) mild pain
B) mild to moderate pain
C) moderate to severe pain
D) severe pain
C) moderate to severe pain
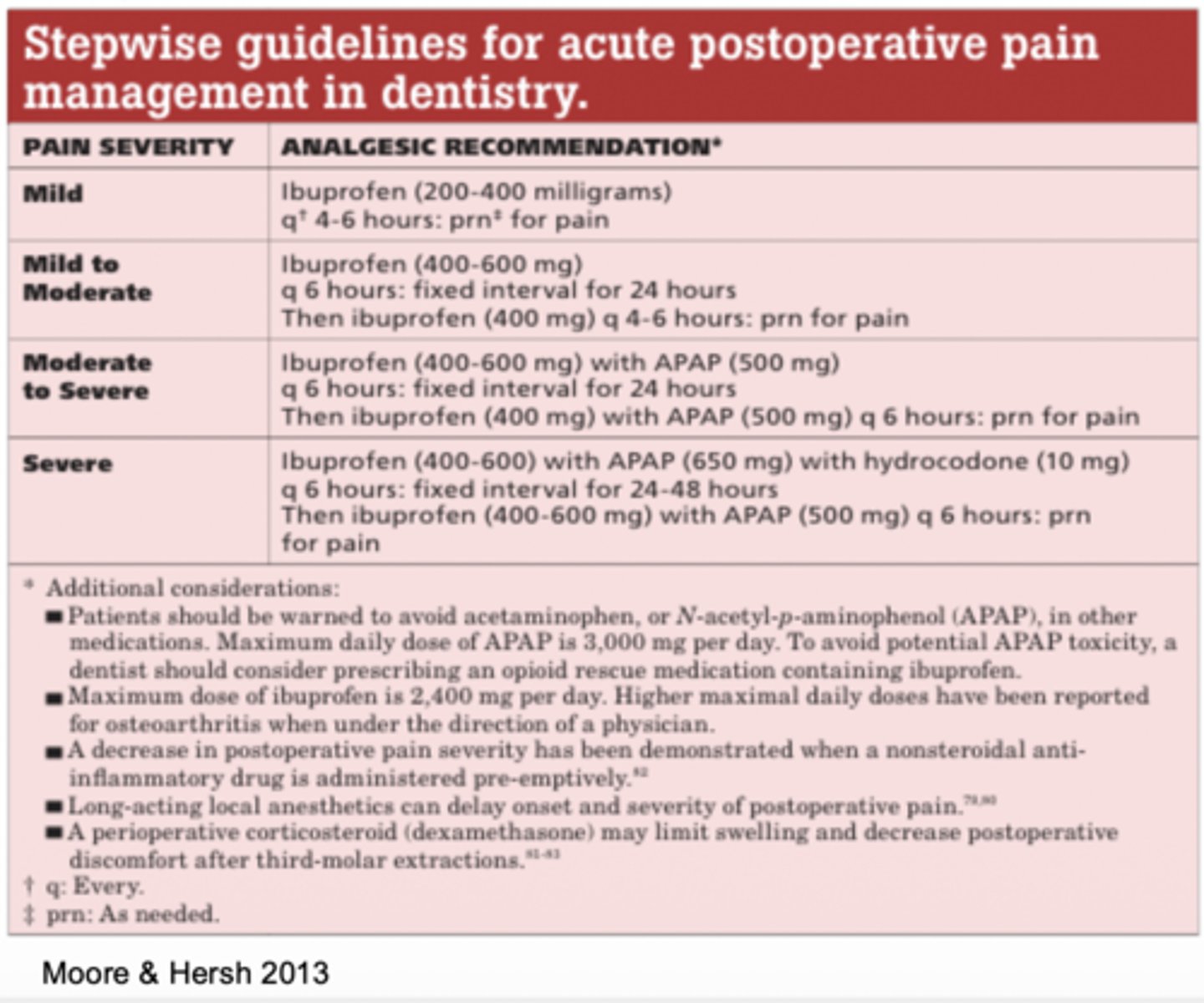
This is the ADA recommendation for which type of pain?
Ibuprofen 400-600mg plus acetaminophen 650mg with hydrocodone 10mg fixed interval every 6 hours for 24-48 hours.
Ibuprofen 400-600mg plus acetaminophen 500mg as needed every 6 hours
A) mild pain
B) mild to moderate pain
C) moderate to severe pain
D) severe pain
D) severe pain
Codeine is what schedule drug?
III
Codeine can be taken with which non-opioid drug?
Tylenol
Oxycodone is what schedule drug?
II
What is post-op pain that requires an unscheduled visit and treatment?
flare up
What is the biggest indicator of flare ups?
pre-op pain
2 types of antibiotics
bactericidal
bacteriostatic
Which type of antibiotic?
- Causes microbial cell death
- Interferes with cell wall synthesis
bactericidal
2 common bactericidal antibiotics
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Which type of antibiotic?
- Inhibits the growth, reproduction, or pathogenicity of the bacteria
- Depends on the host immune system to eradicate the bacteria
bacteriostatic
2 common bacteriostatic antibiotics
Macrolides
Tetracycline
Can you give a bactericidal with bacteriostatic antibiotics?
NO
What are 5 targets of antibiotics?
Metabolic enzymes
Cell wall synthesis
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
DNA synthesis
5 indications for antibiotics in endo
Acute apical abscess w/ systemic involvement or in a medically compromised pt
Rapidly progressing infections w/ cellulitis or osteomyelitis
Persistent infection despite intervention
Soft tissue trauma requiring tx
Replantation of avulsed teeth
Should you prescribe antibiotics?
•Chronic apical abscess
no
Should you prescribe antibiotics?
•Acute apical abscess without systemic involvement (localized fluctuant swelling)
no
Should you prescribe antibiotics?
•Stand-alone treatment for endodontic pain/infections
no
Should you prescribe antibiotics?
•Irreversible pulpitis
no
When prescribing antibiotics in endo for an active infection, do you want a broad or narrow spectrum?
narrowest possible
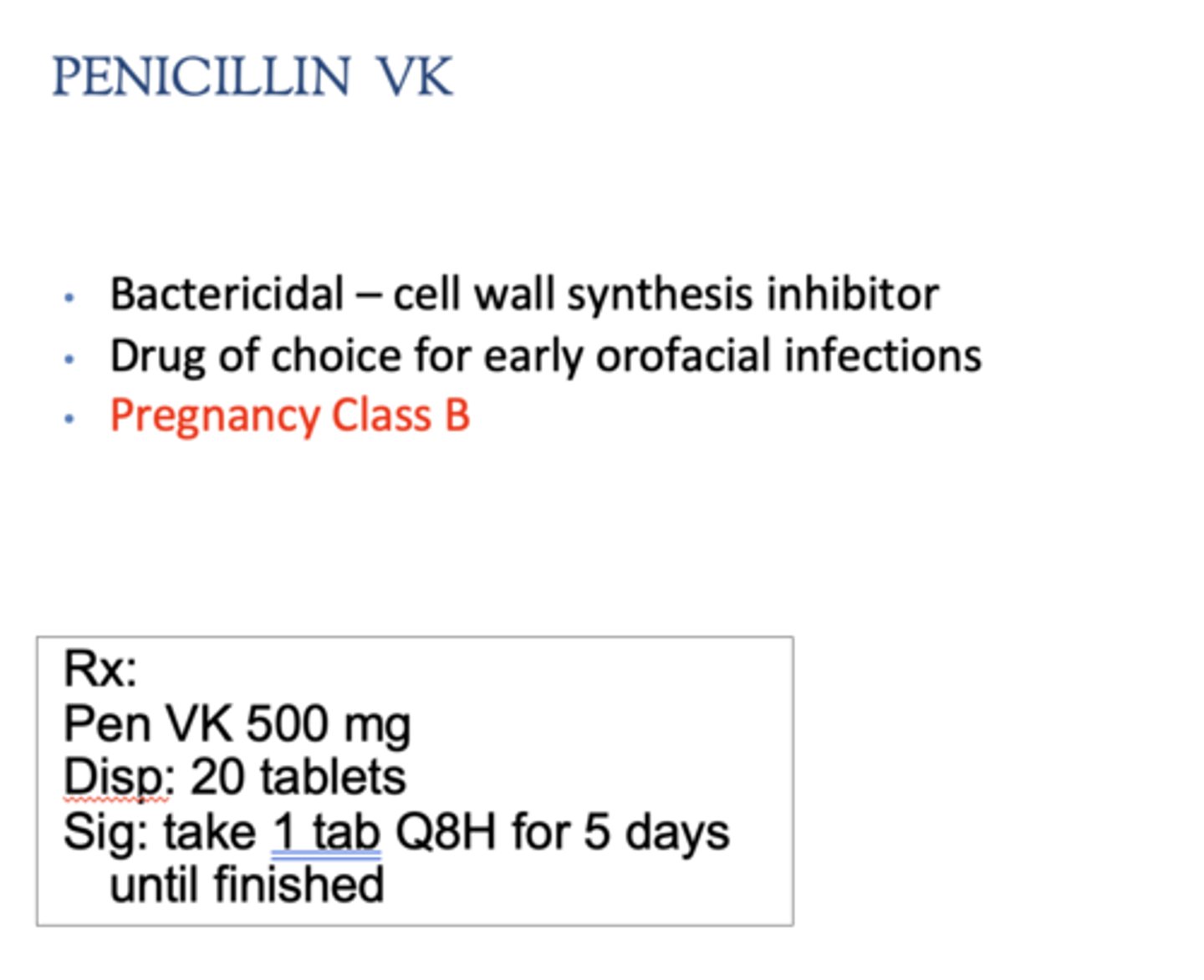
What is the drug of choice for early orofacial infections + pregnant pts?
penicillin VK
Which drug rx?
- 500 mg
- Disp: 20 tablets
- Sig: take 1 tab QID for 5 days until finished
Penicillin VK
Does penicillin or amoxicillin have a broader spectrum?
amoxicillin
Where is amoxicillin absorbed?
Rapidly in the gut
What pregnancy class does amoxicillin have?
Class B
What is your "go-to" if a patient needs antibiotics + has no allergies?
amoxicillin
What dose is amoxicillin prescribed at?
500 mg
How many pills are given with an amoxicillin rx?
21 tabs
What is the instructions for an amoxicillin 500 mg rx?
take 1 tab Q8H for 7 days
Which antibiotic?
Amoxicillin + clavulanate potassium
Augmentin
Which antibiotic?
- Bactericidal - cell wall synthesis inhibitor + beta lactamase inhibitor
- For more severe infections
- Expensive! --> cheaper option = 2 Rxs
- Common doses - 500 mg/125 mg or 875 mg/125 mg
Augmentin
Which antibiotic rx?
875 mg/125 mg
Disp: 14 tabs
Sig: take 1 tab TID for 7 days
Augmentin
Which antibiotic?
- Bactericidal - cell wall synthesis inhibitor
- Classified into 5 generations based on spectrum
- Allergic cross reaction possible between penicillin and cephalosporin due to side chain similarity
Cephalosporins
Which antibiotic rx?
Cephalexin (Keflex) 500mg
Disp: 21 capsules
Sig: take 1 tab Q8H for 7 days
Cephalosporins
These are examples of commonly used ________:
- Cephalexin (Keflex) - 1st gen
- Cefuroxime (Ceftin) - 2nd gen
Cephalosporins
T/F:
- True penicillin allergy is much less common than reported.
- Most childhood rashes are delayed, non-IgE reactions often related to viral infections, not a true allergy.
- True penicillin allergy is IgE-mediated, occurs within minutes to hours, and only a small subset of patients truly need to avoid penicillins (and select cephalosporins with similar side chains)
True