BME211 Week 2
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
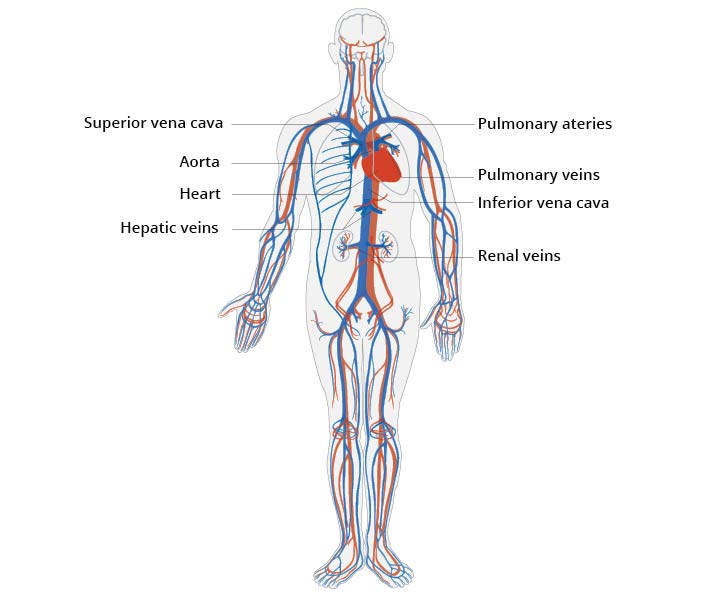
Function of the Cardiovascular System
Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste throughout the body and maintains blood circulation.
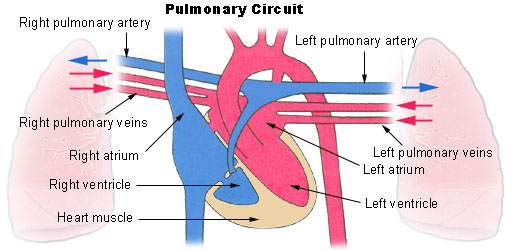
Pulmonary Circulation
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and back.
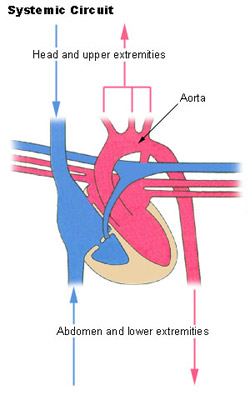
Systemic Circulation
Carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body and returns deoxygenated blood.
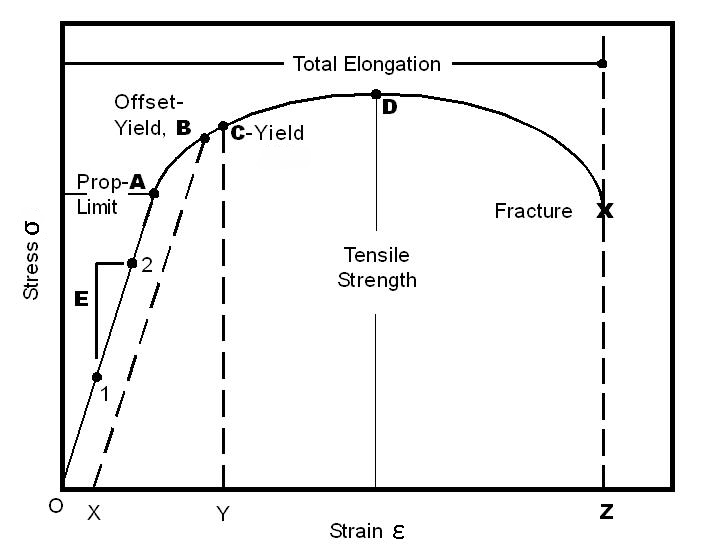
Stress
Force applied per unit area.
Strain
Deformation or change in shape in response to stress.
1D Deformation
Deformation in a single dimension, such as stretching or compressing along one axis.
Stress-Strain Curve
Shows the relationship between stress and strain; includes elastic region, yield point, plastic region, and failure point.
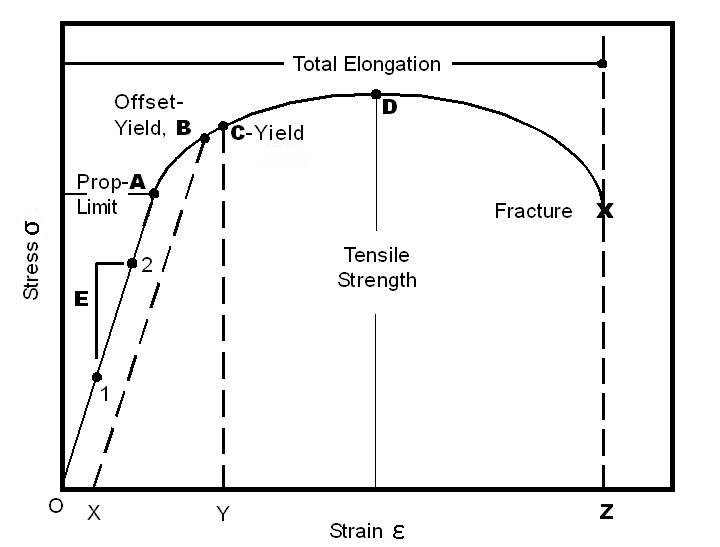
Viscoelastic Behavior
Materials that exhibit both elastic (spring-like) and viscous (fluid-like) properties, such as biological tissues.
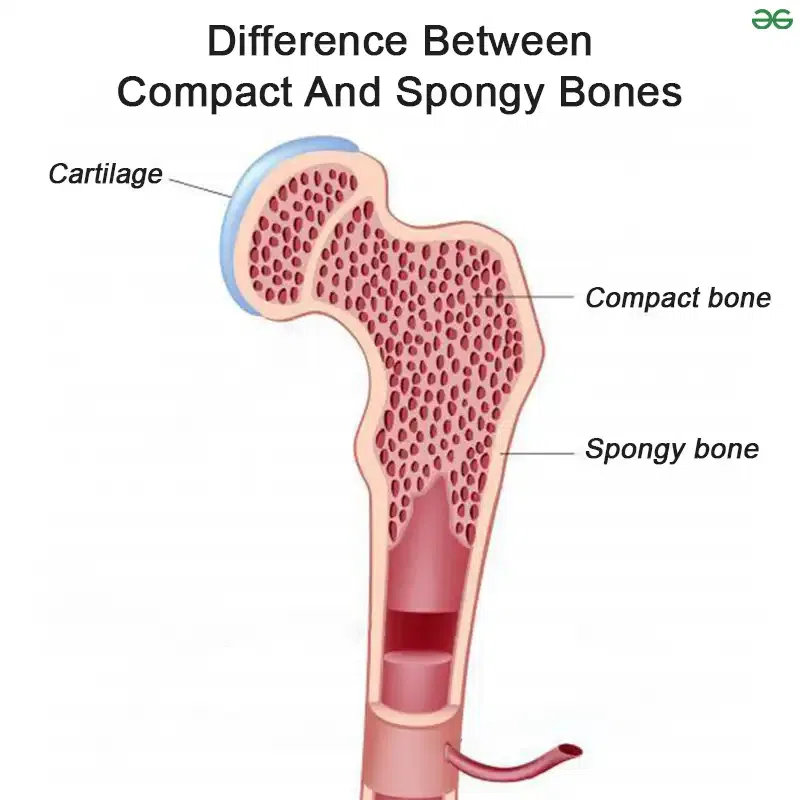
Compact Bone
Dense and strong, supports and protects.
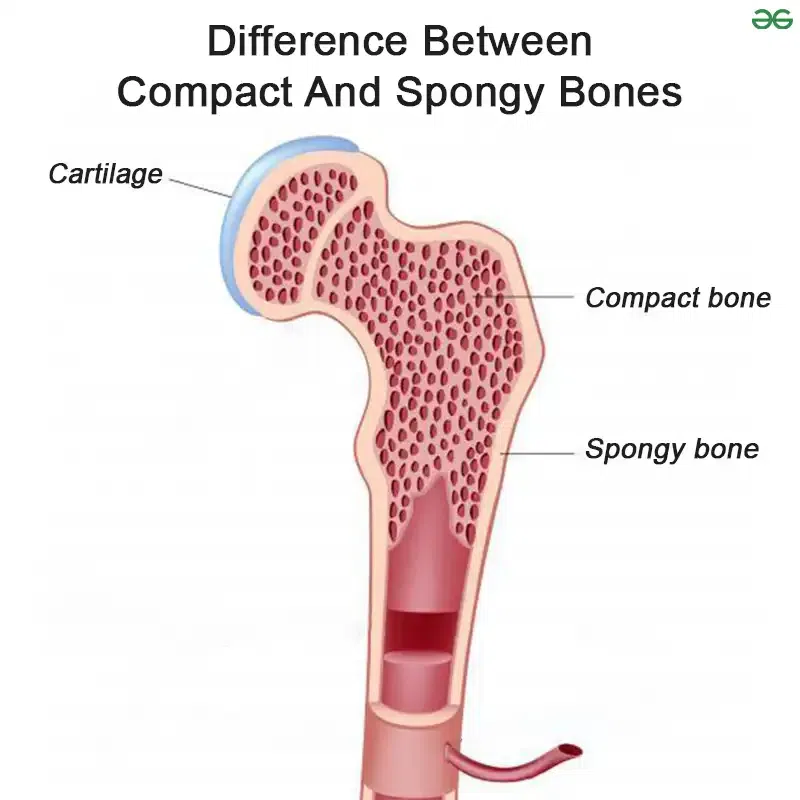
Spongy Bone
Porous and lightweight, found at bone ends, helps absorb impact.
Elastic Arteries
Large, elastic fibers, absorb pressure from heartbeats.
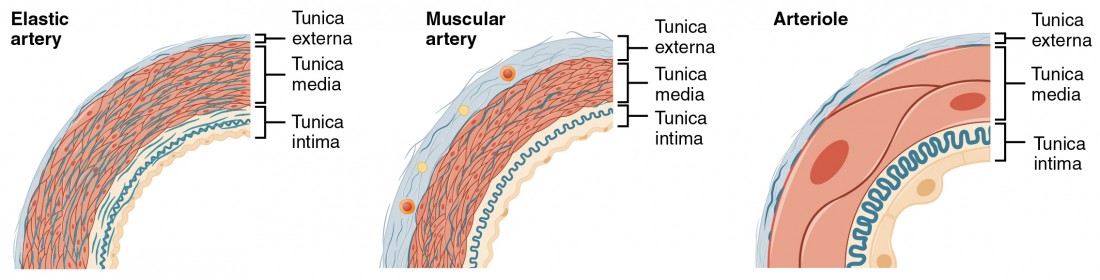
Muscular Arteries
Distribute blood, control flow with smooth muscle.
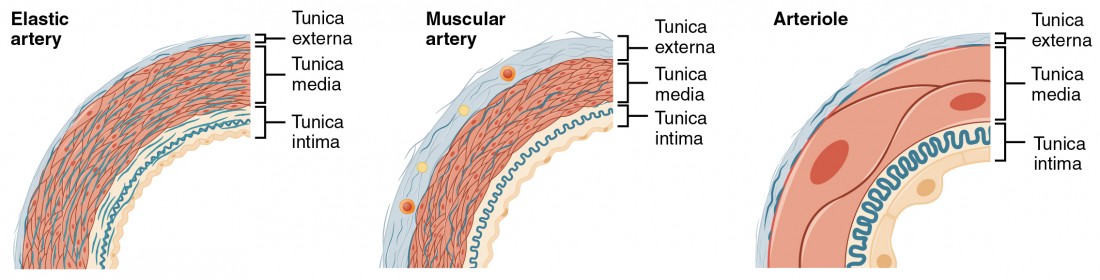
Arterioles
Small, regulate blood flow into capillaries.
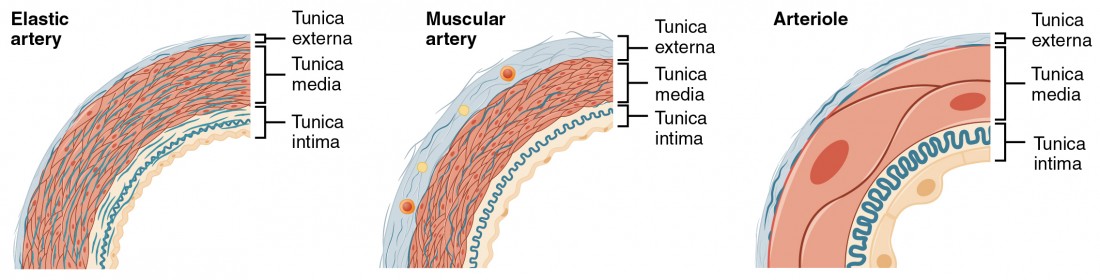
Hydrostatic Pressure
Pressure exerted by a fluid due to gravity.
Hydrostatic Pressure Equation
\( P = \rho g h \) (where \( \rho \) = fluid density, \( g \) = gravity, \( h \) = height).

Viscosity
Measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow.
Shear Rate
Rate at which layers of fluid move past each other.
Newtonian Fluid
Constant viscosity, regardless of stress (e.g., water).
Non-Newtonian Fluid
Viscosity changes with stress (e.g., blood).
Poiseuille’s Equation
Describes laminar flow of fluids in a tube; dependent on tube radius, length, and fluid viscosity.

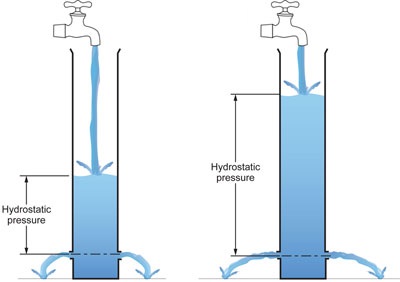
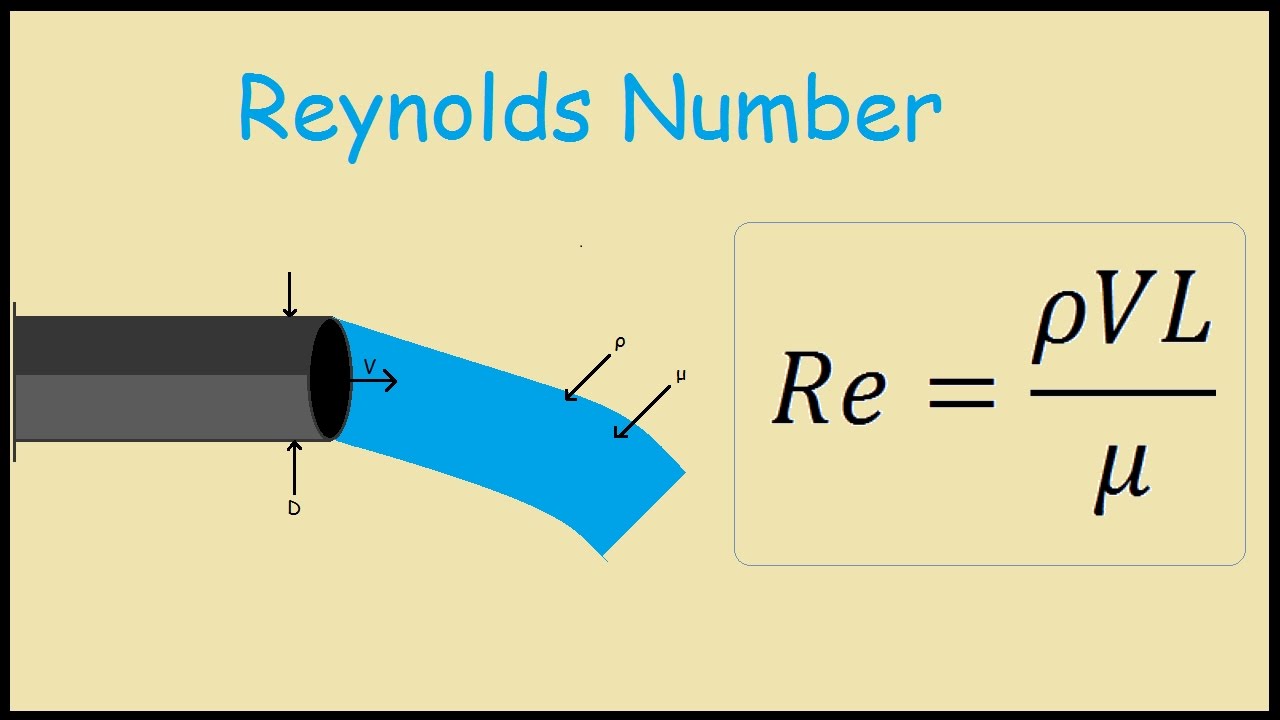
Reynolds Number
Predicts flow type (laminar vs. turbulent).
Reynolds Number Equation
\( Re = \frac{\rho v D}{\mu} \) (where \( \rho \) = density, \( v \) = velocity, \( D \) = diameter, \( \mu \) = viscosity).
Blood Function
Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste; flow is regulated by heart and vessel dynamics.
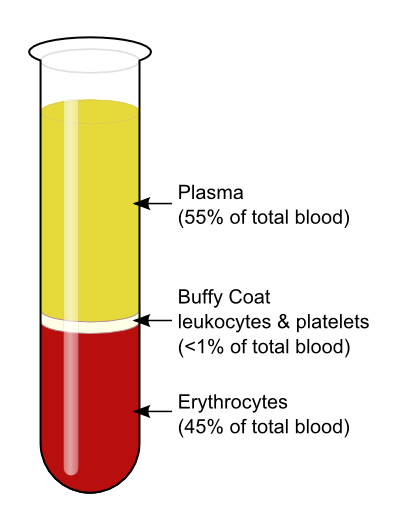
Constituents of Blood
Red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma, each serving specific functions like oxygen transport and immune response.
Viscous Behavior of Blood
Blood behaves as a non-Newtonian fluid due to red blood cell interactions, altering flow characteristics.
Vortex Formation
Abnormal blood flow patterns, like vortices, can occur in diseased arteries, leading to plaque formation and increased disease risk.