unit 4 econ final review
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
imperfect competition
- monopolies
- oligopolies
- monopolistic competition
- monopsonies
monopoly
- single seller
- unique good, no substitutes
- price maker
- high barriers to entry
- ads
price maker
firm can manipulate the price by changing the quantity it produces
natural monopoly
natural for only one firm to produce because they can produce at the lowest cost
imperfectly competitive firms graph
- downward sloping demand curve (to sell more, prices must be lowered)
- MR ≠ P
TR at peak
MR = 0
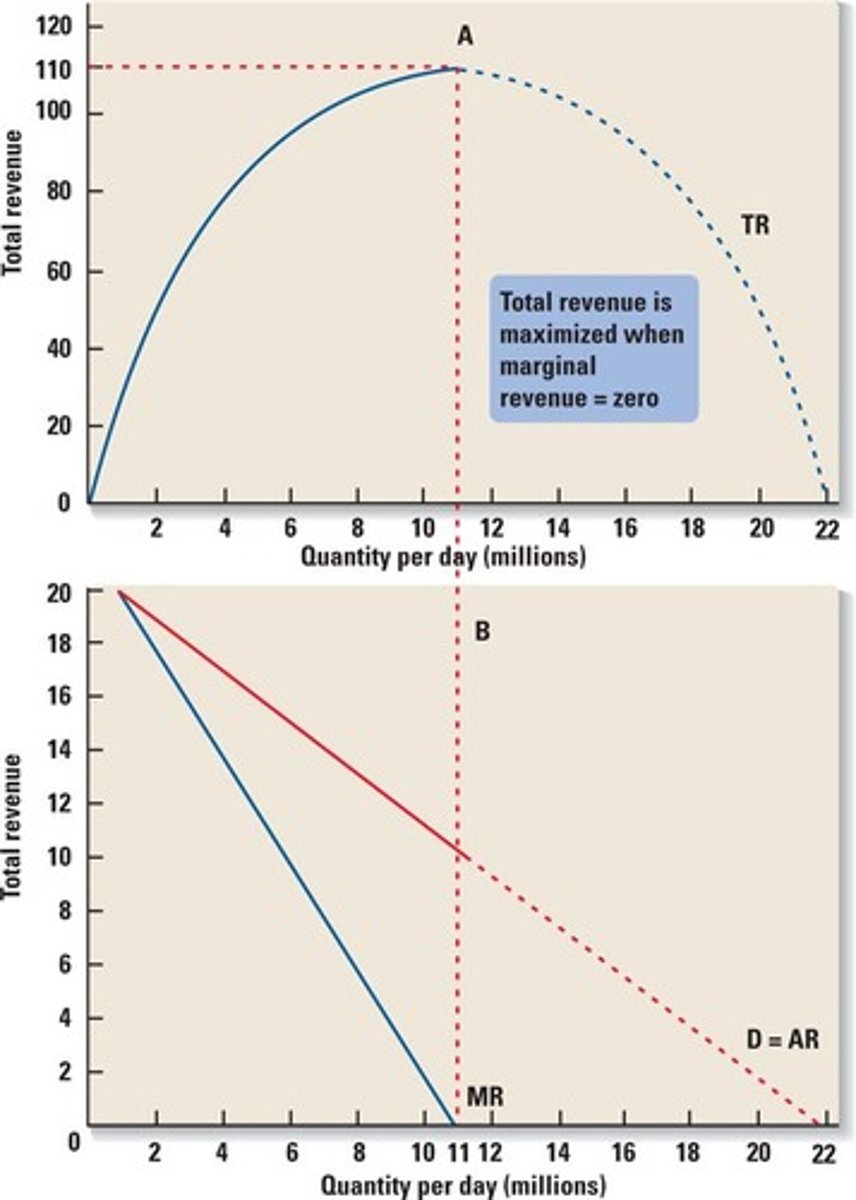
elastic range
monopoly only produces in what range of elasticity
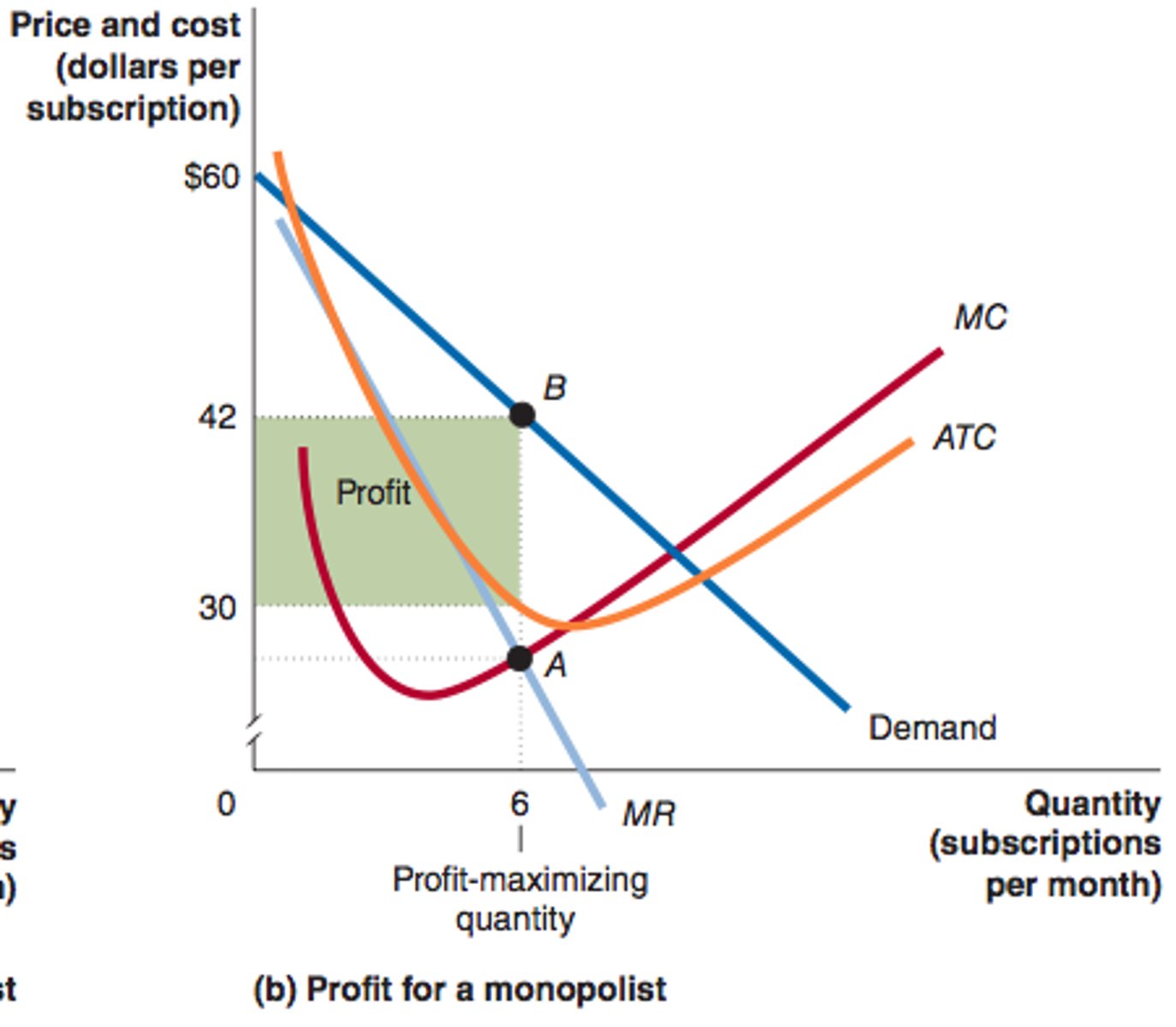
monopolists production
produces where MR = MC (quantity) but charges the price consumers are willing to pay, identified by the demand curve
why monopolies are inefficient
- charge higher price
- don't produce enough (not allocatively efficient)
- produce at higher costs (not productively efficient)
- little incentive to innovate
- they have little external pressure to be efficient
at MR = MC
- monopolist produce less and charge a higher price
- decreases CS and increases PS
reasons to regulate monopolies
- keep prices low
- makes monopolies efficient
how to regulate monopolies
- price controls: price ceilings
- taxes don't work bc taxes limit supply
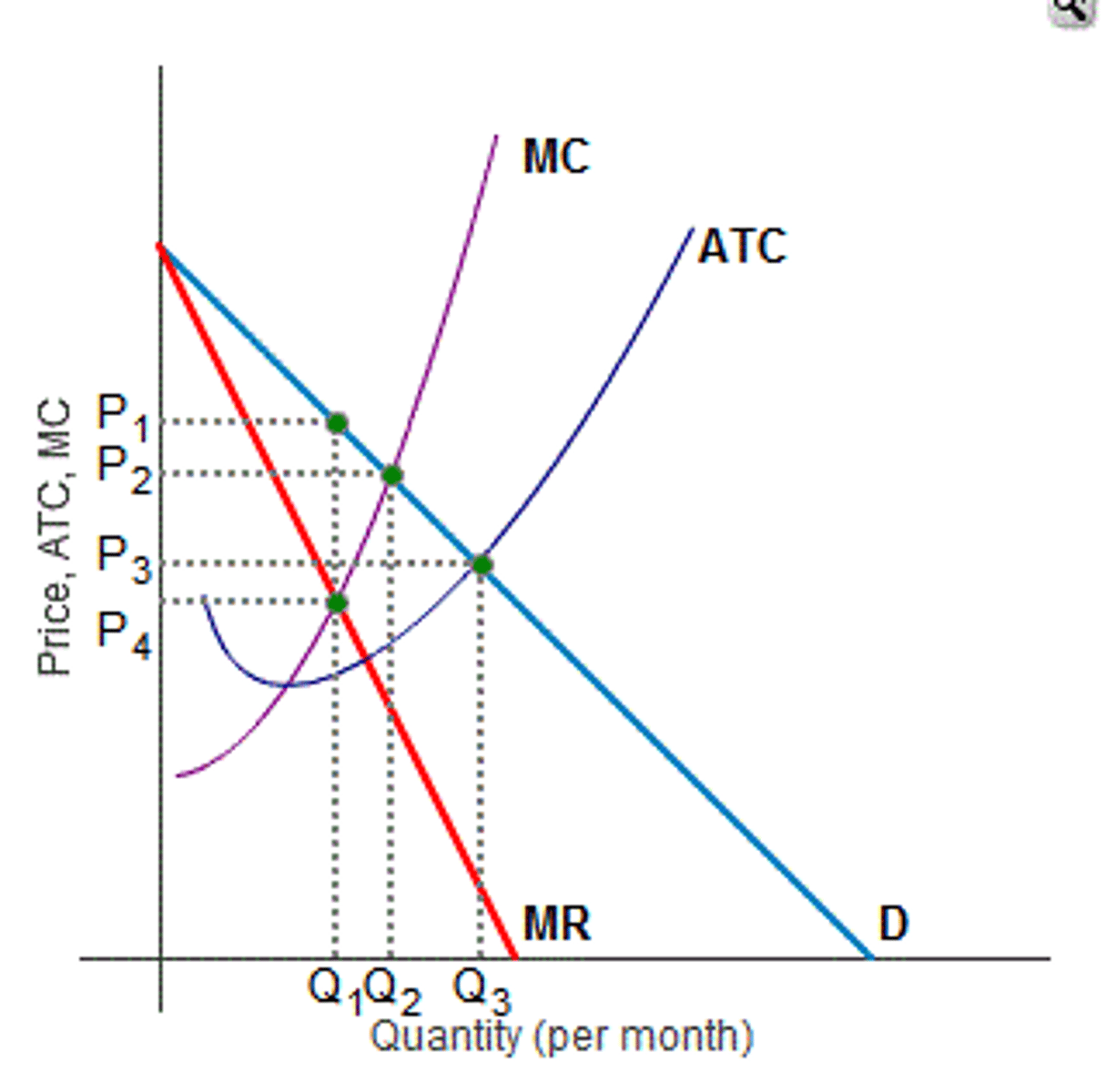
where to put price ceiling
- socially optimal price
- fair return price/ break even
unregulated monopoly production
B (point on demand curve that's above MR = MC point)
socially optimal
- allocative efficiency
- where MC = D on graph
fair return
- no economic profit
- where ATC = D on graph
regulating natural monopoly
price ceiling to get socially optimal quantity would cause the firm to make a loss and require a subsidy
price discrimination
selling the same products to different buyers at different prices
price discrimination conditions
- have monopoly power
- segregate market
- consumers can't resell product
price discrimination results
- several prices
- more profit
- no CS
- higher socially optimal quantity
monopolistic competition
- large number of sellers
- differentiated products
- some control over price
- low barriers to entry
- ADVERTISING
- not efficient
- D > MR
nonprice competition
- branding
- service
- location
- advertising: increase demand and make it inelastic
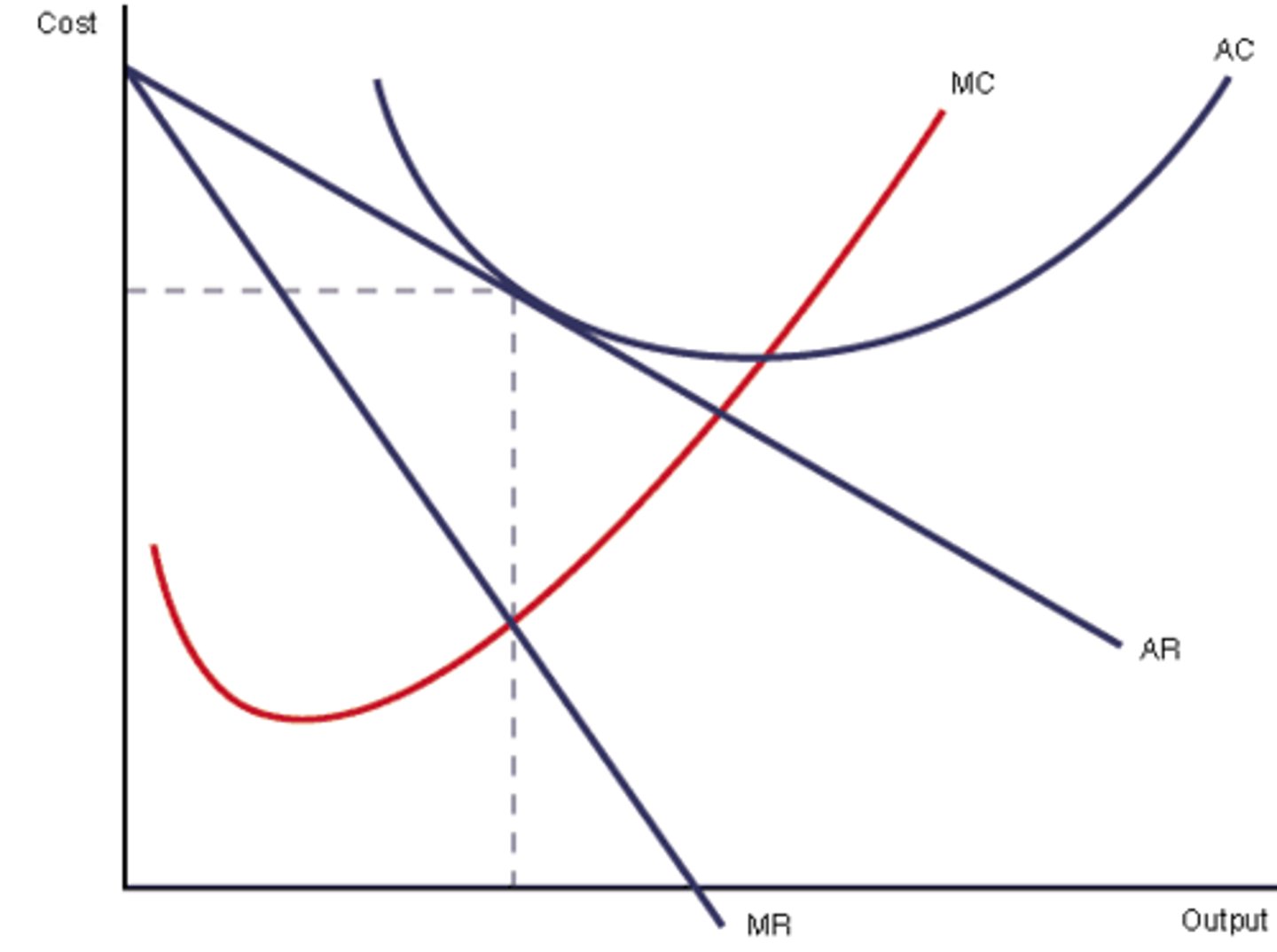
long run monopolistic competition
- new firms will enter, driving down the demand for firms already in the market
- firms enter until there is no economic profit
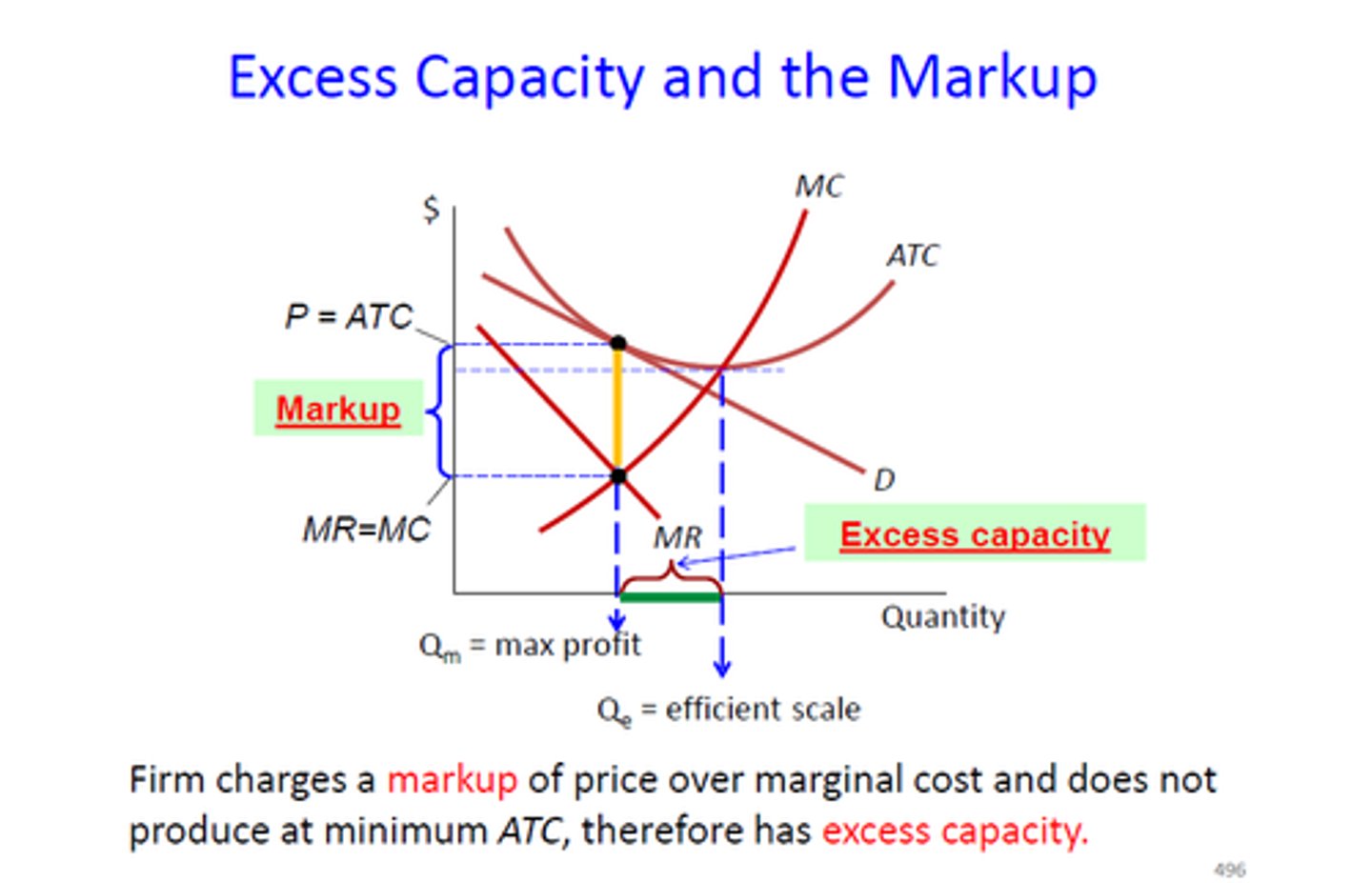
- equilibrium: quantity where MR = MC up to P = ATC
- excess capacity
short run profits
- new firms enter = more substitutes, less market shares for existing firms
- demand for each firm falls
short run losses
- firms exit = less substitutes, more market shares for remaining firms
- demand for each firm rises
monopolistically competitive efficiency
- not allocatively efficient (P ≠ MC)
- not productively efficient (production ≠ minimum ATC)
excess capacity
- firm can produce at the lowest costs (minimum ATC) but they decide not to
- gap between minimum ATC output and profit maximizing output
oligopoly
- few large producers
- identical or differentiated products
- high barriers to entry
- price maker
- interdependence (strategic pricing)
- collude to gain profit
oligopoly barriers to entry
- economies of scale
- high start up costs
- ownership of raw materials
game theory
- study of how people behave in strategic situations
- helps firms in an oligopoly maximize profit
dominant strategy
best move to make regardless of what your opponent does
collusion
- act of cooperating with rivals in order to "rig" a situation
- results in the incentive to cheat
- gains profit
- firms act as a monopoly and share the profit