Antibiotic and its Action against Bacteria
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are antimicrobials
An agent that kills microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, protozoas, fungi) or stops their growth
What are antibiotics
Agents with biological activities to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria
What is antimicrobial resistance?
The ability of bacteria to resist the effects of an antibiotic
when the bacteria change in a way that reduces the effectiveness of antibiotics
What are antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) methods?
Methods used to determine how sensitive or resistant a bacteria is to a specific antibiotic
What are the 2 main types of AST (antimicrobial susceptibility test)?
Disc diffusion
Minimum inhibitory concentration
AST: What is minimum inhibitory concentration and what can it be divided into?
What: Determine of the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight incubation
Agar dilution
Broth dilution
E-test
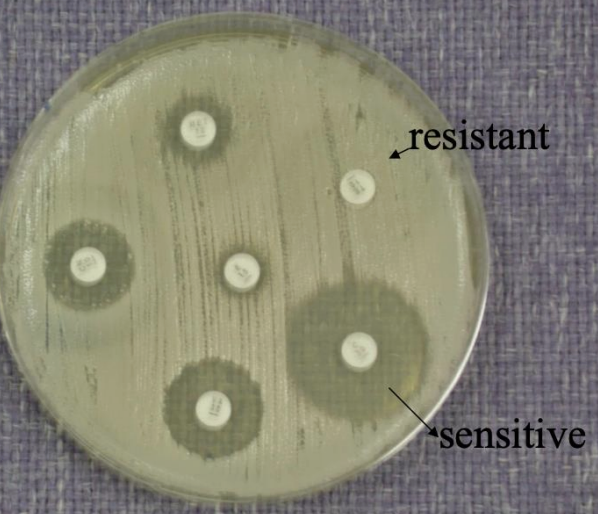
AST: Disc Diffusion
Name of method
Principle
Interpretation
Name of method: Kirby-Bauer Method
Principal:
Paper discs containing known concentrations of antibiotics are placed on the surface of an agar plate (usually Mueller–Hinton agar) that has been inoculated evenly with the test bacteria.
The antibiotic diffuses outward from the disc into the agar.
After incubation, bacteria grow everywhere except where the antibiotic concentration is high enough to inhibit them.
This clear area around each disc is called the zone of inhibition.
Interpretation:
Measure the diameter of the inhibition zone (in mm).
Compare with standard reference charts (CLSI or EUCAST) to classify the bacterium as:
Sensitive (S)
Intermediate (I)
Resistant (R)
AST: MIC: Broth Dilution Method
Serial dilutions of an antibiotic are prepared in liquid (broth) medium.
Each tube (or well) is inoculated with a standard bacterial amount and incubated.
The lowest concentration that shows no visible turbidity (no growth) is the MIC.
Can be done as:
Macrobroth (in test tubes)
Microbroth (in microtiter plates — automated systems often use this)
AST: MC: Agar Dilution Method
Serial concentrations of antibiotic are mixed into solid agar plates.
Each plate is spot-inoculated with the test bacterium.
After incubation, the lowest antibiotic concentration plate with no visible growth indicates the MIC
AST: MC: E test
A plastic strip impregnated with a gradient of antibiotic concentration is placed on an agar plate inoculated with the test bacterium.
After incubation, an elliptical zone of inhibition forms around the strip.
The point where the ellipse edge meets the scale on the strip gives the MIC value directly.
What are the properties of antimicrobial agents?
Selective toxicity
Bacteriacidal (bacteria killing) instead of bacteriostatic (inhibit growth)
Stable, low cost
Microbe should not become readily resistant
Have activity broad (act against both G+ and G-) or narrow spectrum (act against G+ OR G-)
What is the mechanism of antibiotic?
Cell wall and cell membrane synthesis inhibitors
Nucleic acid inhibitors
Protein synthesis inhibitors
Folic acid metabolism inhibitors
Cell wall inhibitors
Active against
How it works
Inhibits
Spectrum of activity
Examples
Active against: Growing bacteria
How it works:
Reacts with enzymes required in peptidoglycan synthesis
So cells develop weak points
And become osmotically fragile (cell lyse)
Inhibits: Peptidoglycan synthesis
Spectrum of activity:
Bacteriacidal
Aerobic and anaerobic G
Examples: Bacitracin, Cephalosporin, Cycloserine, Penicillins, Vancomycin
Cell Membrane Inhibitors
Active against
Examples
Active against: Gram negative bacteria and fungi
Examples:
Polymixins - effective against G -ve bacteria
Polyenes - effective against fungi
Protein synthesis inhibitors
Inhibits
Examples
Inhibits: Protein synthesis
Examples: Aminoglycosides, tetracyling
Nucleic Acid inhibitors
How it works
Examples
How it works: Targets molecules involved in nucleic acid synthesis and replication
Examples: Quinolones
Folic acid metabolism inhibitors
Inhibits folic acids which are enzymes that are necessary for bacterial protein synthesis and synthesis of amino acids
What are the ways that microorganisms exhibit resistance to drugs
Produce enzymes that destroy active drug (Staphylococci resistant to penicillin produce B-lactamase that destroys penicillin)
Change their permeability to the drug
Develop an altered structure target for the drug
Develop an altered enzyme that can still perform its metabolic function but less affected by drug
How bacteria resist the antibiotics
Antibiotic inactiviation
Alteration of the target site
Descreased acess to site of action
Enzymatic Inactivation of Antimicrobial Agents
What
Example
What: When bacteria produces specific enzymes that inactivate or modify the drug
Example: B-lactamases
Enzyme cleave the beta lactam ring of susceptible antibiotics
In gram positive
Modificiation of Cell Wall permeabiltiy
What
Cause
What: Decrease access to site of action
Cause: Change in lipopolysacharide