Chapter 5: The Organic Molecules of Life
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What do we consider Organic Molecule?
Molecule that contains CARBON
Typically associated with living organism
Inorganic Molecules
Does NOT contain CARBON
Mineral or gases
What are other common element found in organic molecules?
H
N
O
Why is Carbon selected as Organic Compound?
Stable
Almost always shares e- with other C making long chain
C-H (hydrocarbon) form stable ring structure
What type of bond would be used in a Carbon Bond?
Covalent Bond
4 classes of Organic compound
Carbohydrates
Protein
Lipid
Nucleic Acid
Composition: Carbohydrates
C
H
O
Ration of 1:2:1
Very Common Carbohydrate used in all organism is
Glucose
C6H12O6
Plants make glucose through
Photosynthesis
Main function of Carbohydrates is
Immediate SHORT TERM ENERGY STORAGE in animals and plants
Carbohydrates: single sugar
Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates: Two sugar
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates: Many sugars
Polysaccharides
Other form of Carbohydrates include
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Long chain of Carbohydrates bonded together
Glycogen importance
For the animals: Energy storage in the liver
Cellulose importance
Cell wall of the plant
Starch importance
Plant energy storage
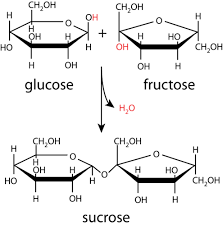
Bond between carbohydrate is though which chemical reaction?
Condensation: dehydration
Releases water
OH+OH→ release water and O bonds 2 ring together
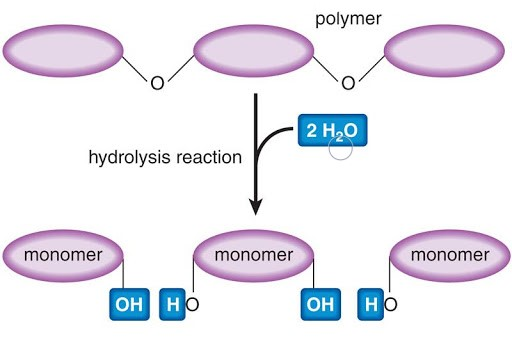
Breaking polymer of Carbohydrates is through which Chemical reaction?
Hydrolysis: add H2O
Lipids are made of
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Is lipid hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic, They do not mix with water
Example of lipids
Butter
Oil
Wax
Lipids are made of
Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Function of lipid
Long term Energy Storage
Structural support of Cell Membrane
Cell signaling (hormones)
Special lipid of cell membrane is called
Phopholipids
Types of FATS
Saturated Fat
Unsaturated Fat
Trans Fat
Characteristics of Saturated Fat
Single bond only
Solid at room temperature
Example: Wax
Characteristics of Unsaturated Fat
One or more double bond or triple bond
Liquid at room temperature
Example: Oil
Characteristics of Unsaturated Trans Fat
Contain double bond between two carbons with hydrogen on the opposite side
Harder to break down
Example: dounut
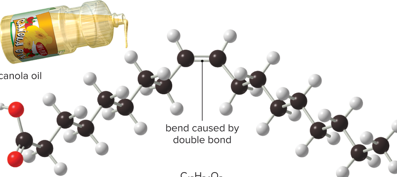
Name of fat
Unsaturated Fat
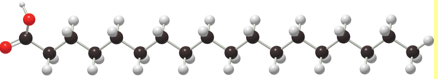
Name of Fat
Saturated Fat
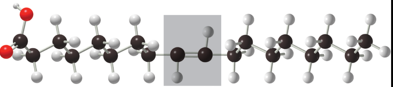
Name of Fat
Unsaturated Trans Fat
What are Steroids?
Lipids that possess a Carbon Ring
Function of steroid
It depends on the compound (functional group) at the end of each carbon skeleton:
Cell signaling
Hormone
Cell membrane structure
Which of the following correctly matches an organic compound with its example?
Carbohydrates-Fructose
The sex hormone such as Testosterone and Estrogen at the 6 weeks or less of Fetal development will
Determine the sex of the fetus and its characteristics
Protein is composed of
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Smaller SUBUNIT of protein is called
Amino Acids (AA)
Amino acids are linked together with which bond?
peptide bond
How many AA to build proteins in living organism?
20 AA
Peptide bond is a covalent bond, The e - are
Not shared equally allowing H-bond between C=0 and N-H
How to determine the function of the protein?
The order of AA will determine the function of the protein
Function of Proteins
Structural support: Muscle, hair
Cell transport: Channel and carrier protein
Metabolism: Enzyme
Expression of the Traits
Defense: Antibody
Regulation: Intercellular Messenger (hGh)
Motion: actin and myosin
Level of structure of the Protein
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
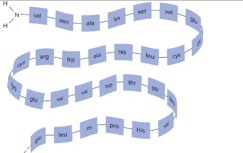
Primary structure of protein
Linear: sequence of Amino Acid
Secondary structure of protein
Alpha helix
Beta sheet
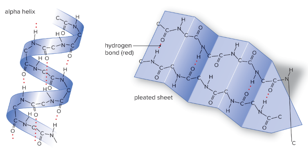
Tertiary structure of protein
Globular Shape: Folding helix will determine the function of protein

Quaternary structure of protein
Two or more polypeptide interacting

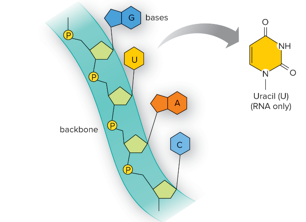
What is Nucleic Acid?
Long chain of repeating subunits of NUCLEOTIDES
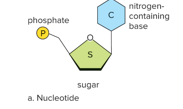
Nucleotide is composed of
5 ring sugar
Phosphate group
Nitrogen base
Two types of Nucleic Acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
DNA Nitrogen Base
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Double strand
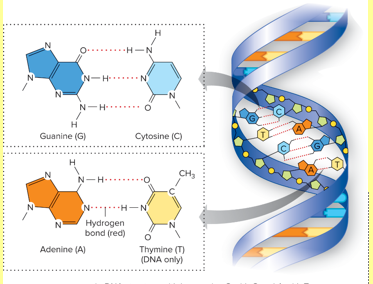
RNA Nitrogen Base
Adenine (A)
Uracil (U)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Single strand
Purines are
Double ring
A, G
Pyrimidine
Single ring
C,T,U
Function of Nucleic Acid
Storage of Genetic Material
Responsible for heredity