MBIO 2700 / Topic 4a: Amino Acids
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are proteins polymers of? On that note, if we want to understand the properties of proteins, what do we need to study specifically?
Proteins are made of their monomer units amino acids. Thus, if we want to study protein properties, we have to study amino acid properties.
We get amino acids (AAs) from our own body as they are produced (non-essential AAs) and from consumed nutrients that we can’t make (essential AAs).
Show me the structure of your generic AA. Name the five parts of the AA.
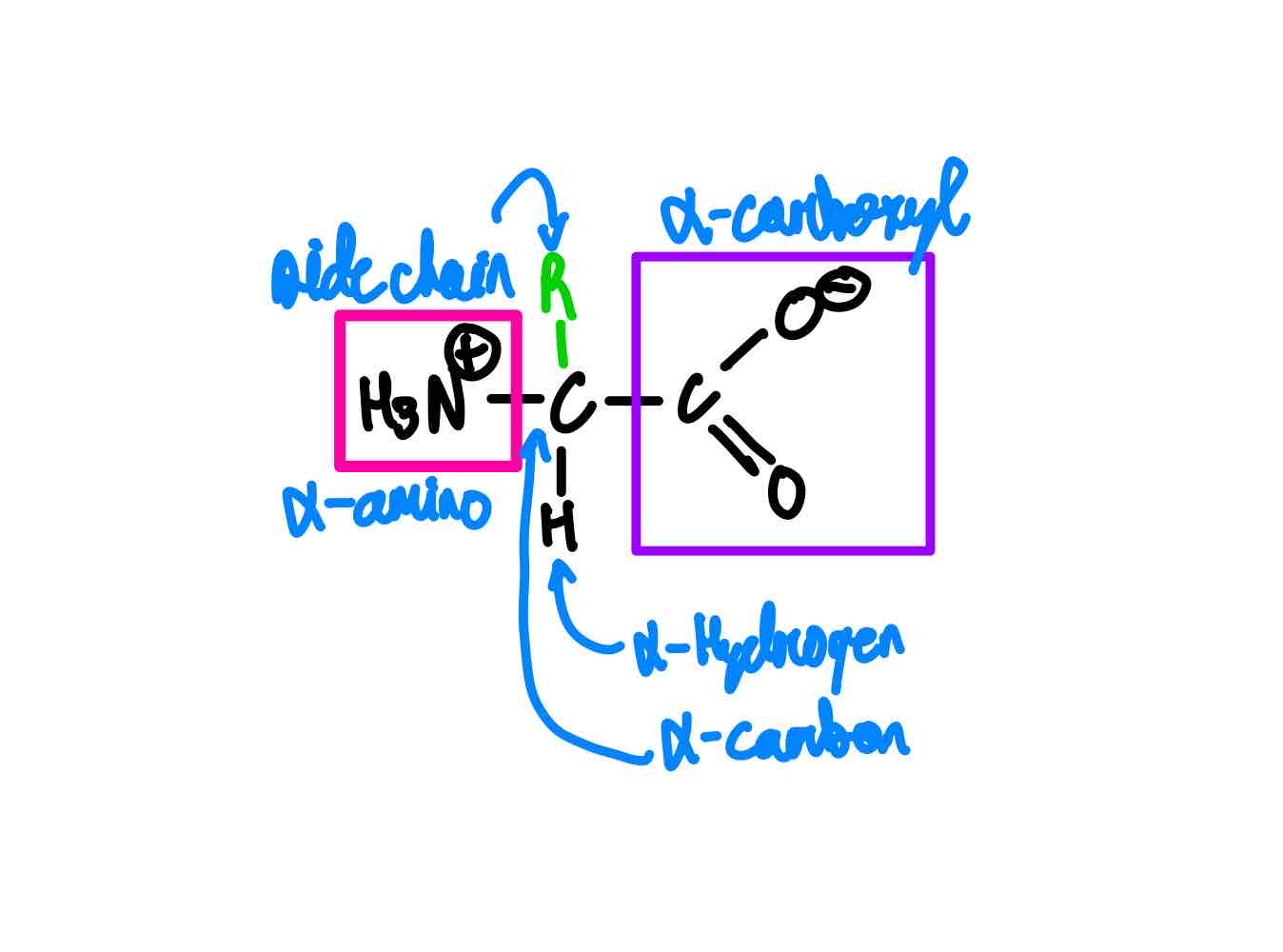
You can categorize the 20 AAs into five categories. What are these categories? How many AAs will you find in each?
Non-polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic. (7 AAs)
Aromatic. (3 AAs)
Polar, uncharged, hydrophilic. (5 AAs)
Negative, acidic at pH of 7. (2 AAs)
Positive, basic at pH of 7. (3 AAs)
What are the seven non-polar amino acids?
Glycine (Gly, G).
Alanine (Ala, A).
Valine (Val, V)
Leucine (Leu, L).
Isoleucine (Ile, I).
Proline (Pro, P).
Methionine (Met, M).
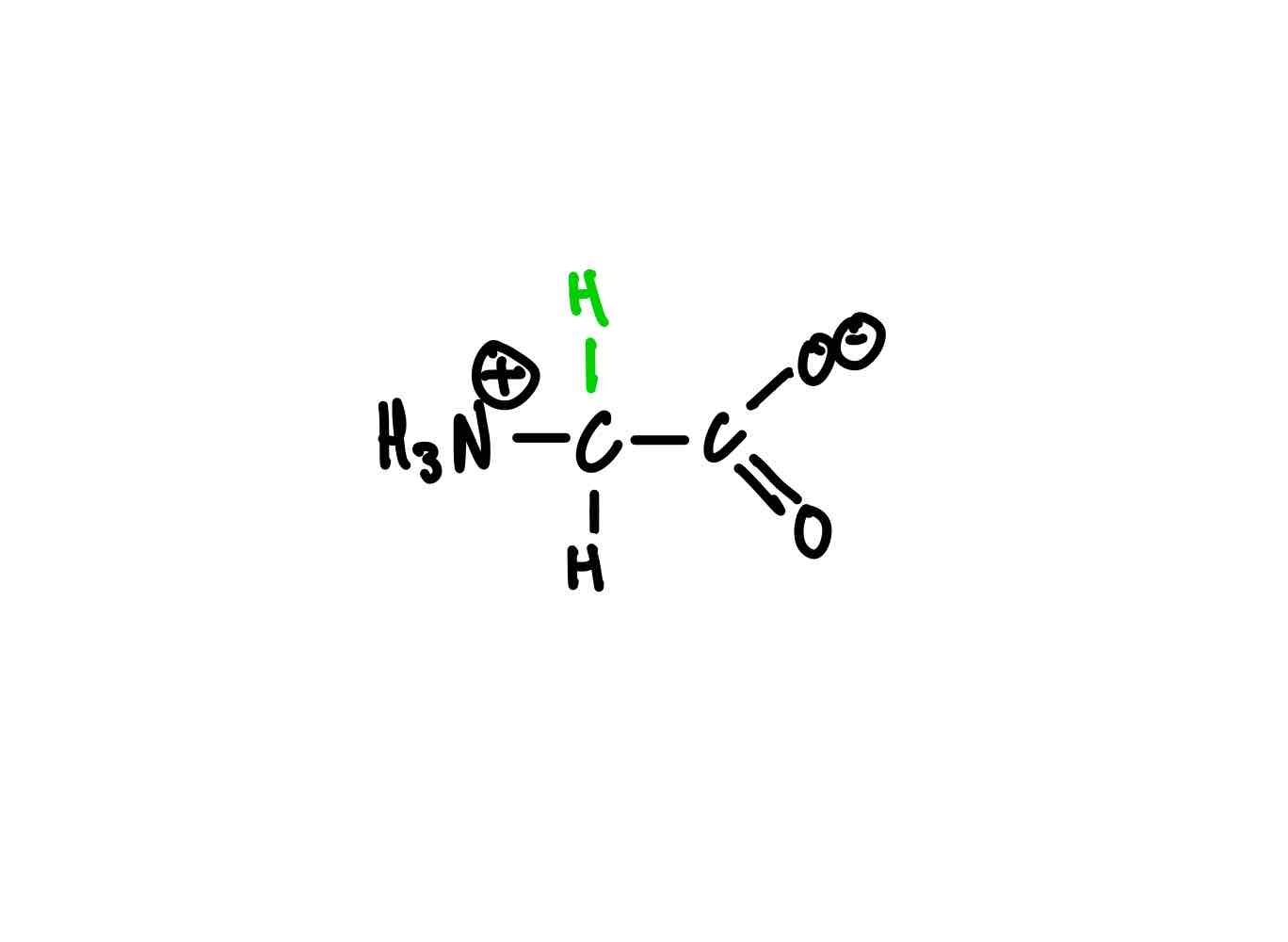
What’s the structure for glycine?
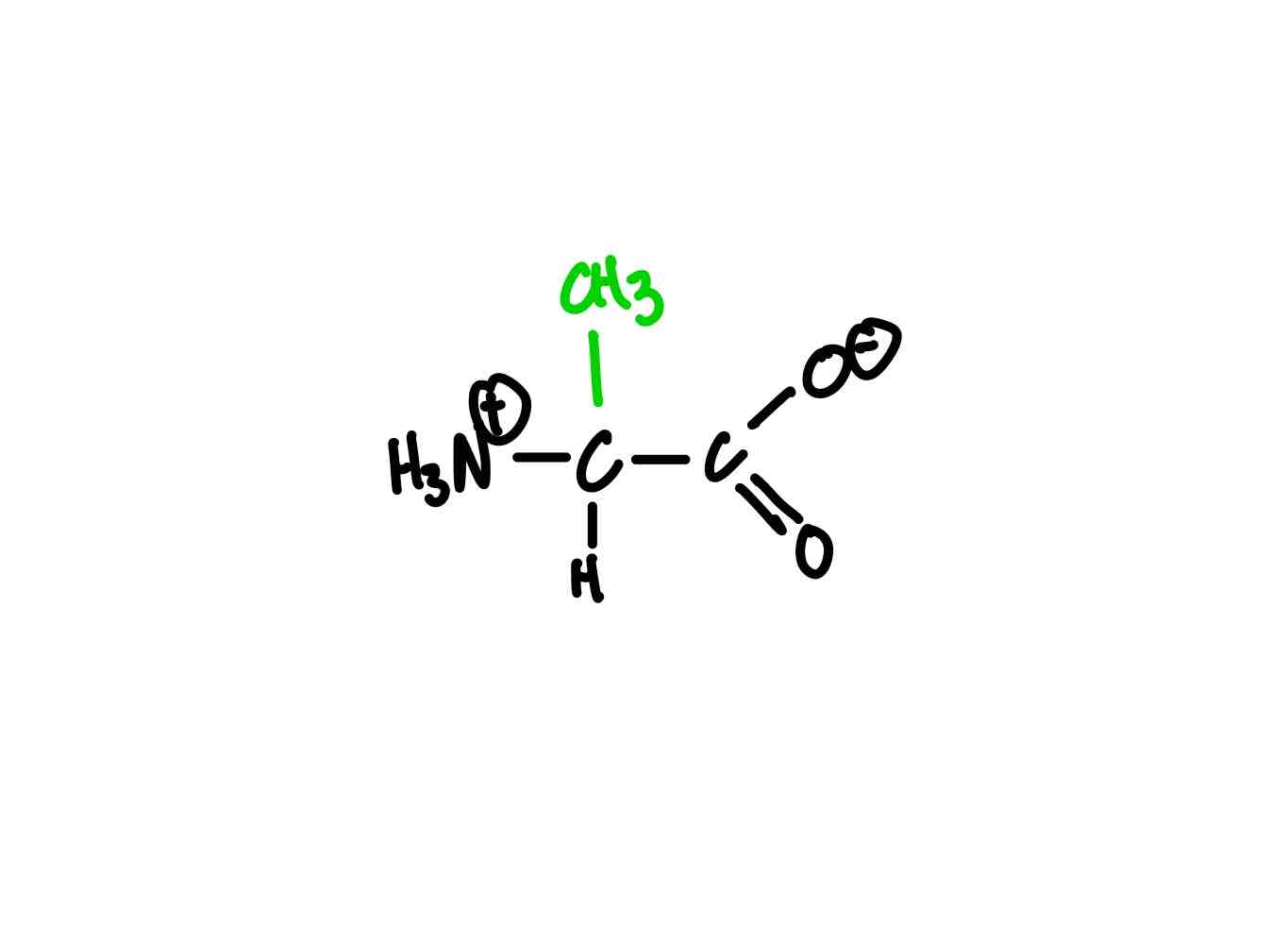
What’s the structure for alanine?
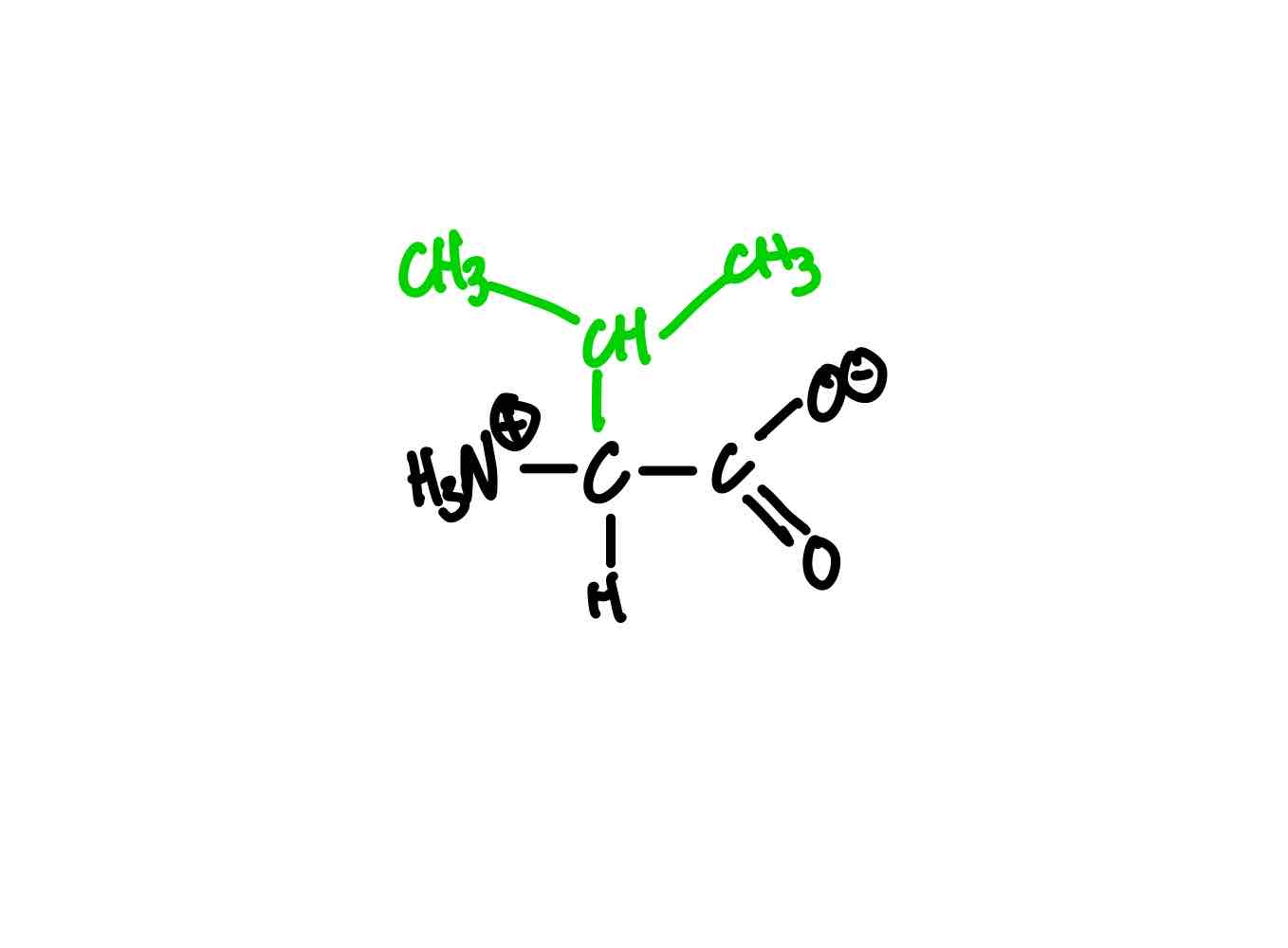
What’s the structure for valine?
What’s the structure for leucine?
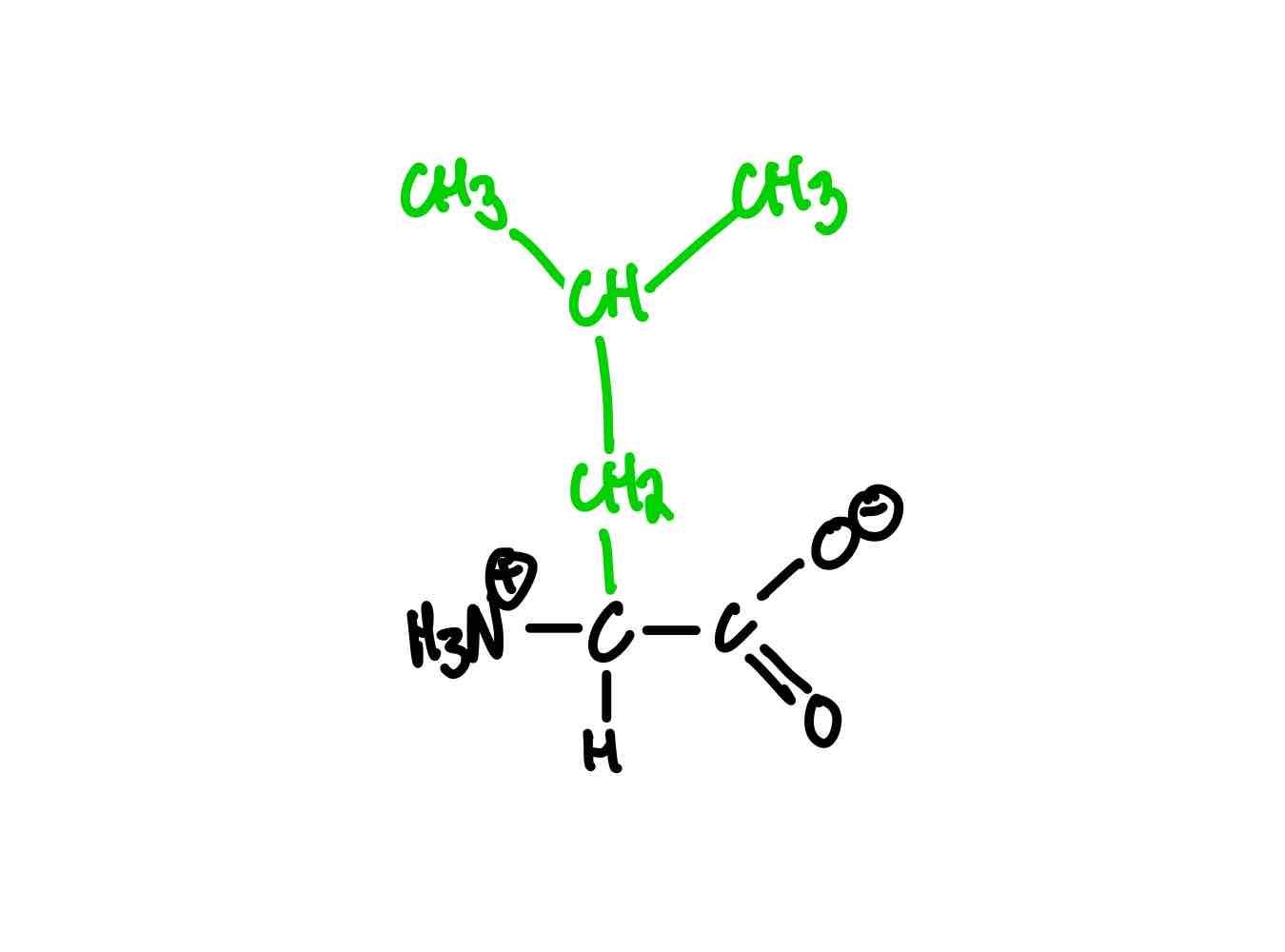
What’s the structure for isoleucine?
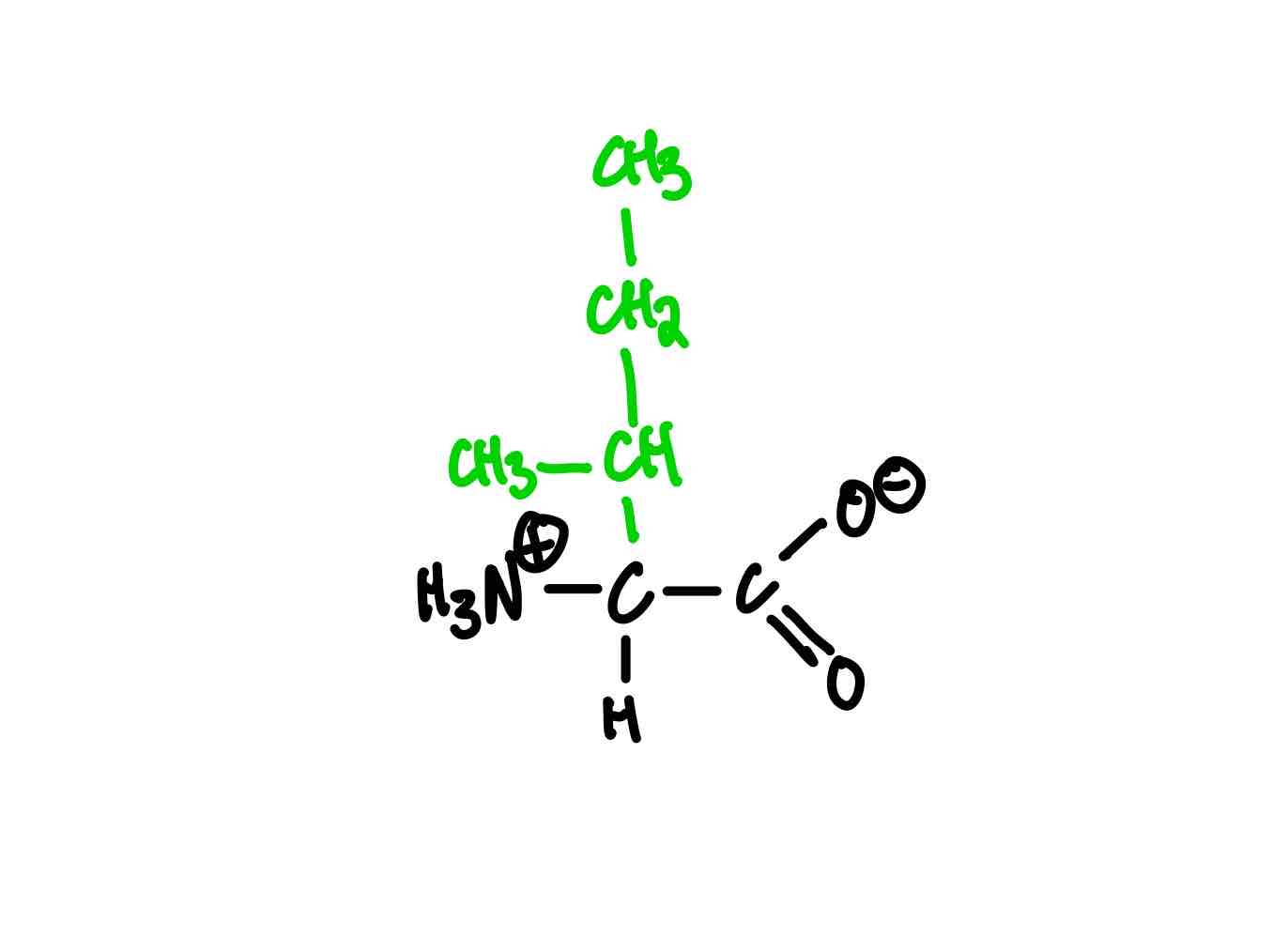
What’s the structure of proline?
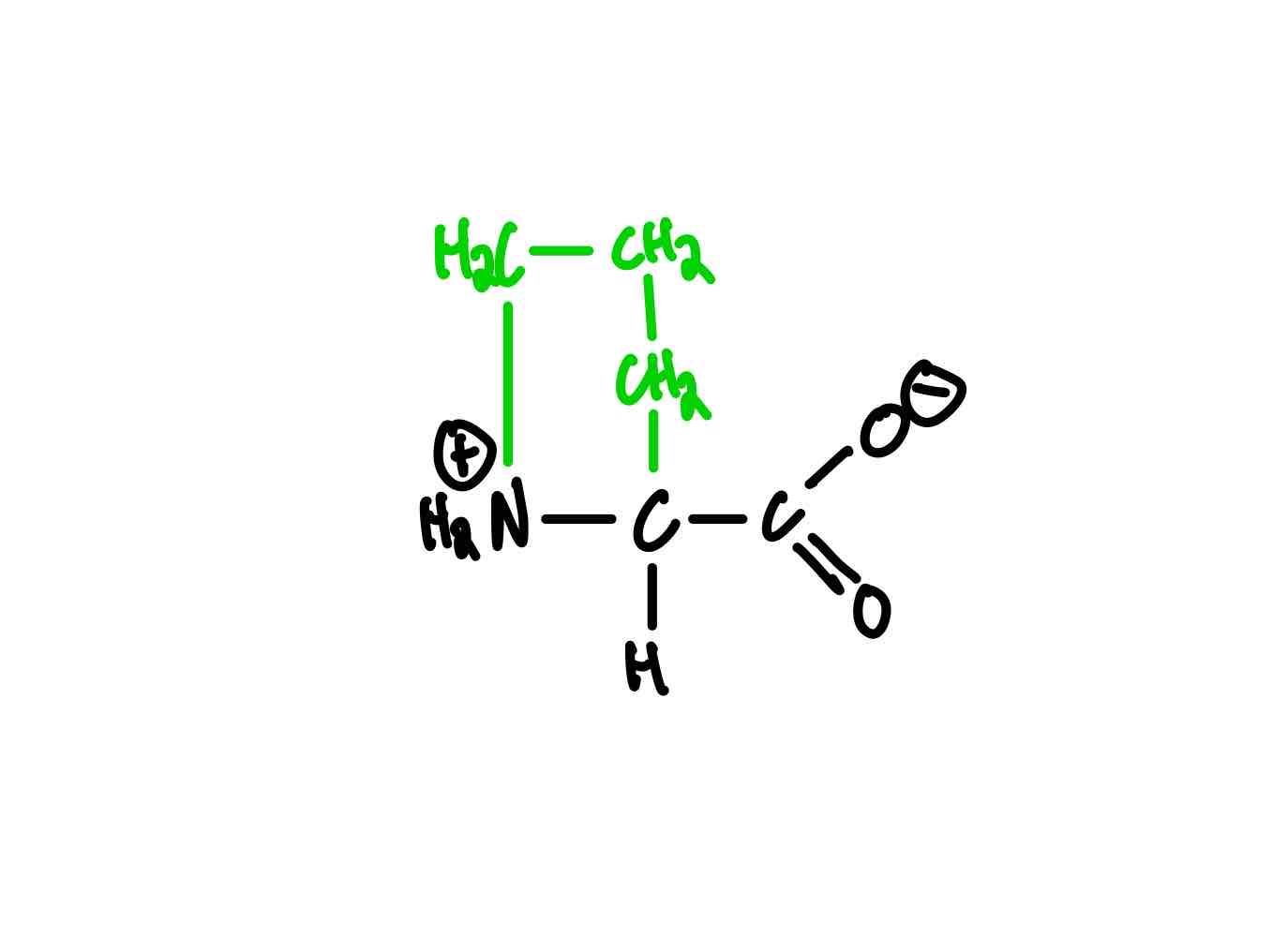
What’s the structure of methionine?
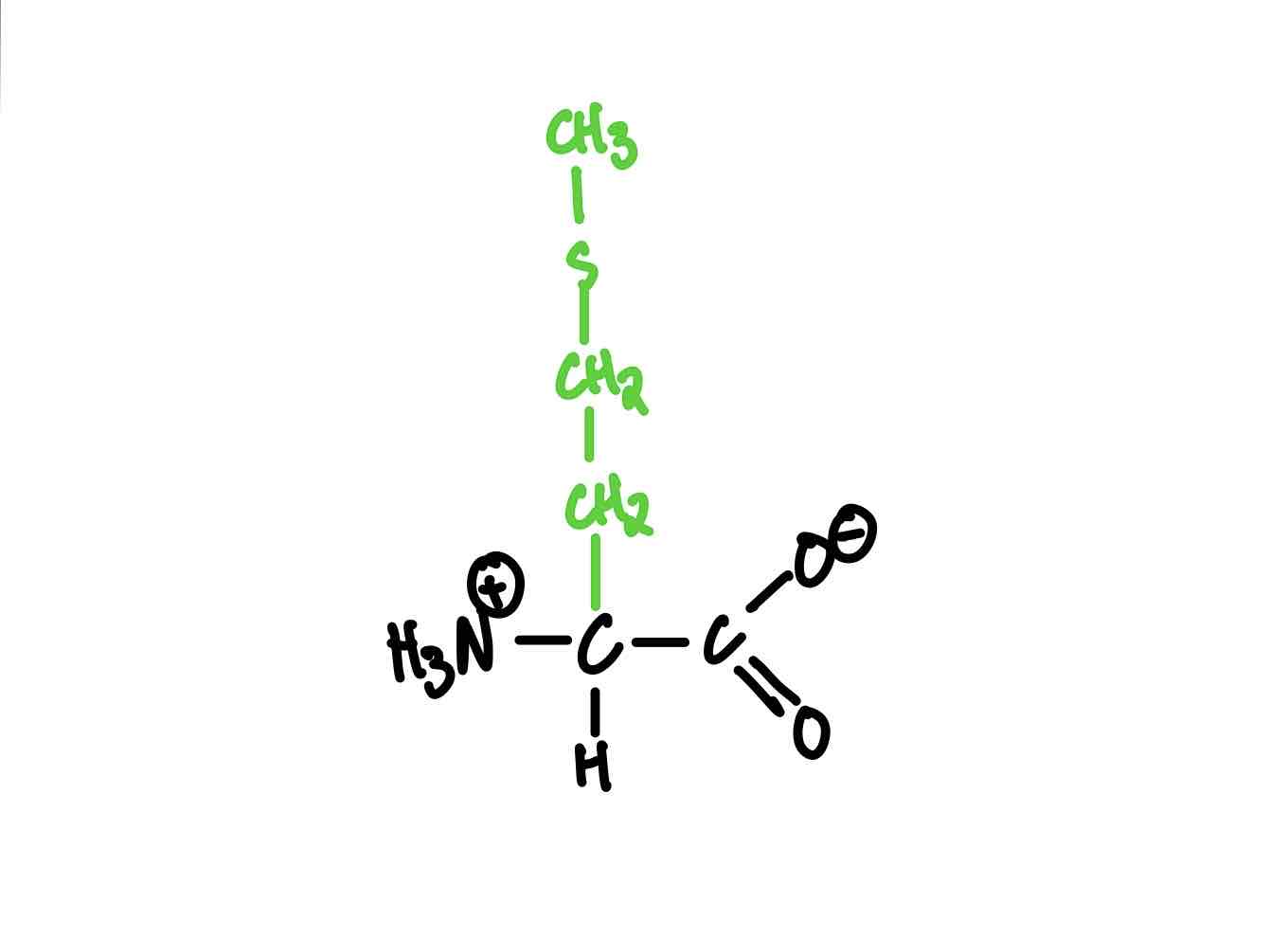
What are the three aromatic amino acids? Provide the full name, 3-letter abbreviation, 1-letter abbreviation, and pKa whenever applicable.
Phenylalanine (Phe, F).
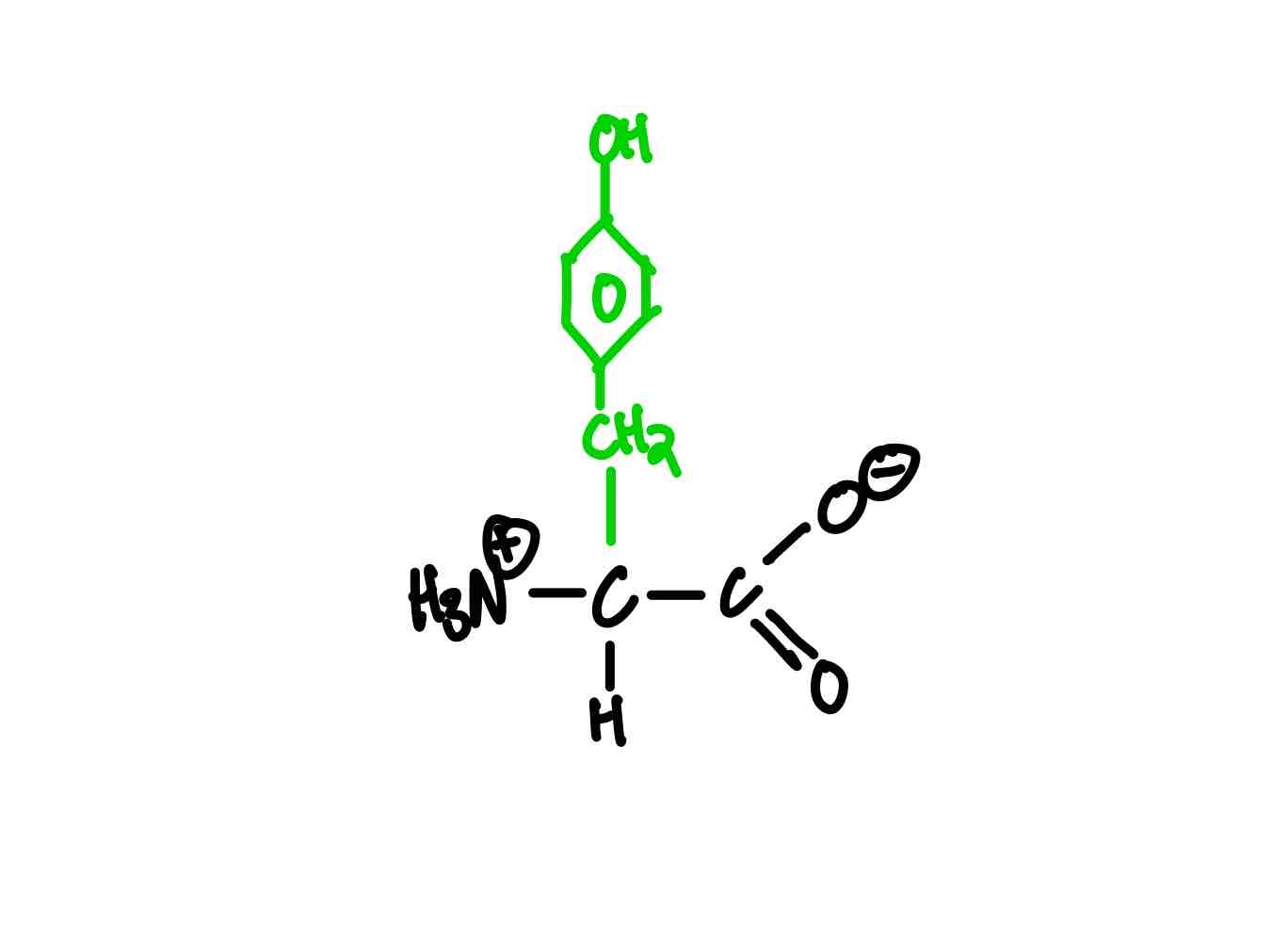
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y). pKa = 10.1.
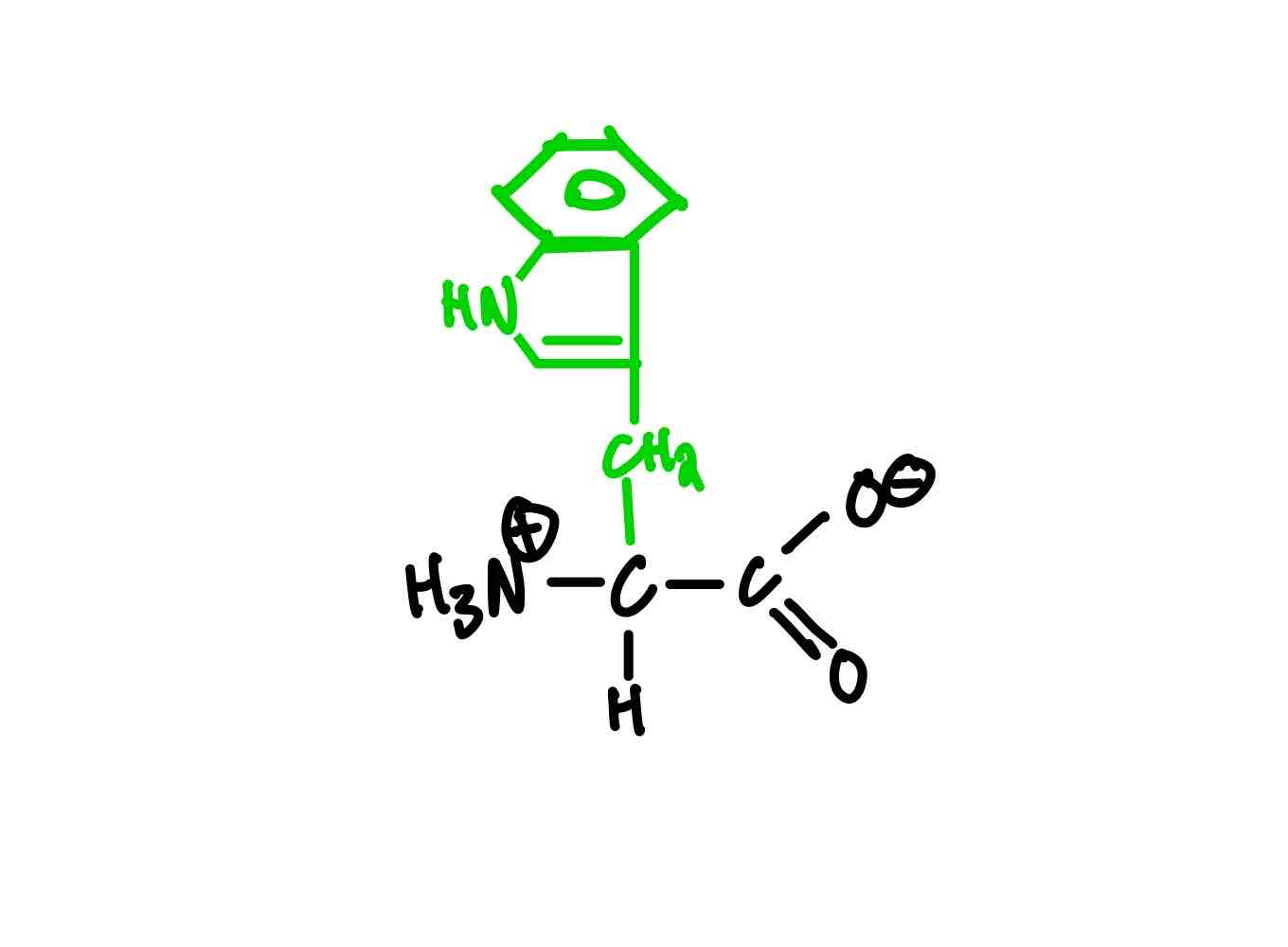
Tryptophan (Trp, W).
What’s the structure of phenylalanine?
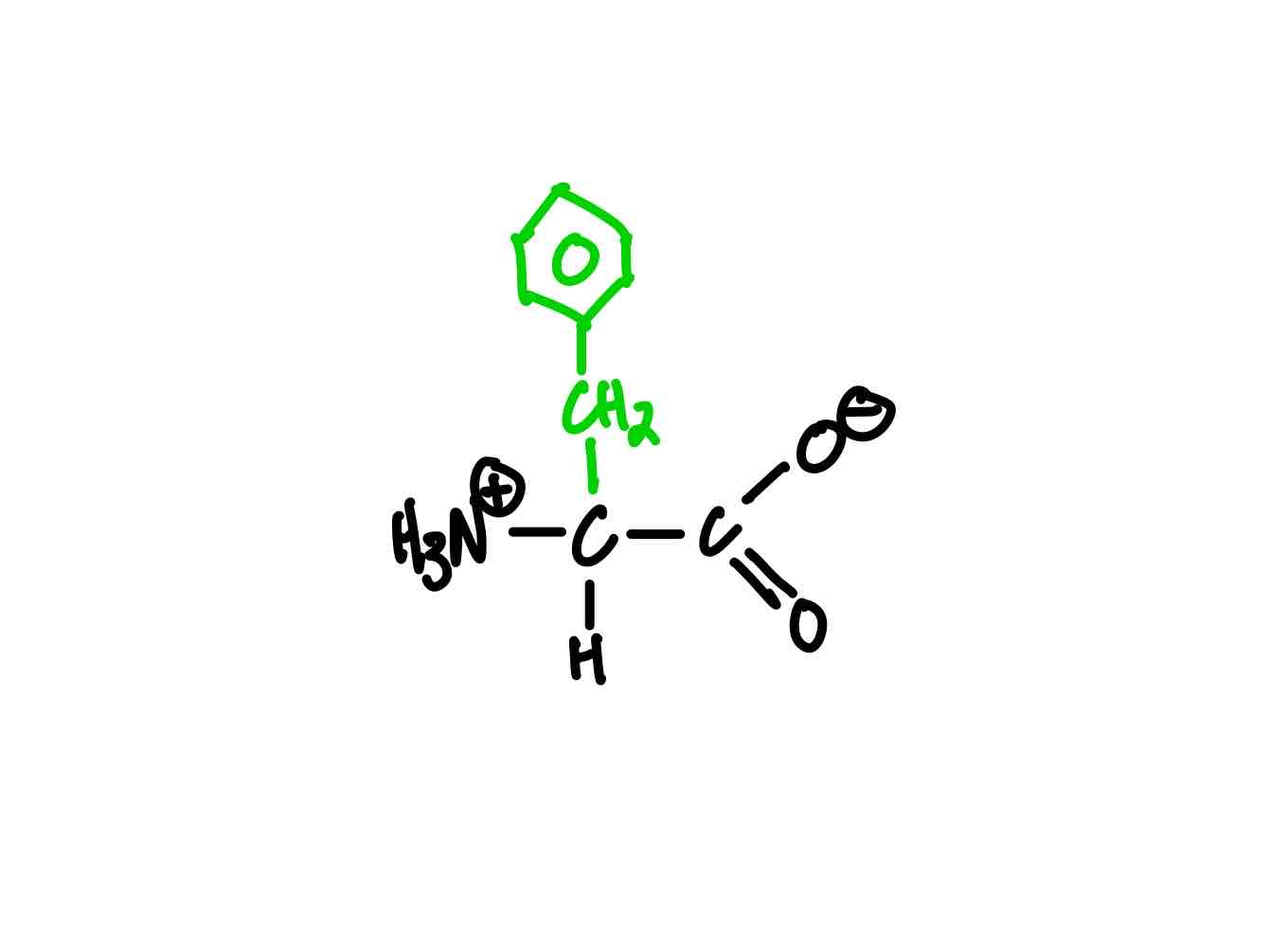
What’s the structure of tyrosine?
What’s the structure of tryptophan?
What are the five polar amino acids? Provide the full name, 3-letter abbreviation, 1-letter abbreviation, and pKa whenever applicable.
Serine (Ser, S). pKa = 13.6.
Threonine (Thr, T). pKa = 13.6.
Cysteine (Cys, C). pKa ≈ 8.3.
Asparagine (Asn, N).
Glutamine (Gln, Q).
What’s the structure of serine?
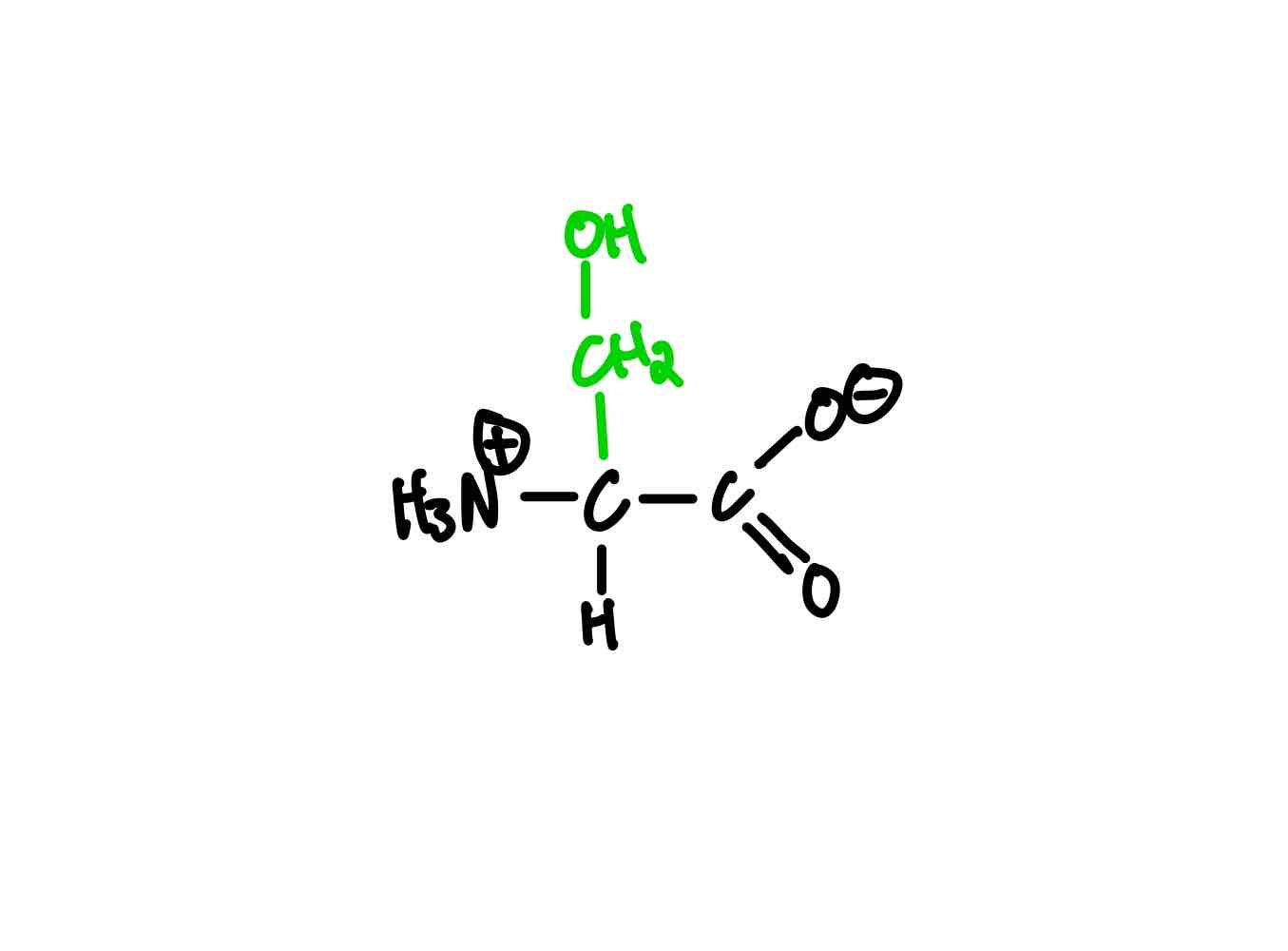
What’s the structure of threonine?
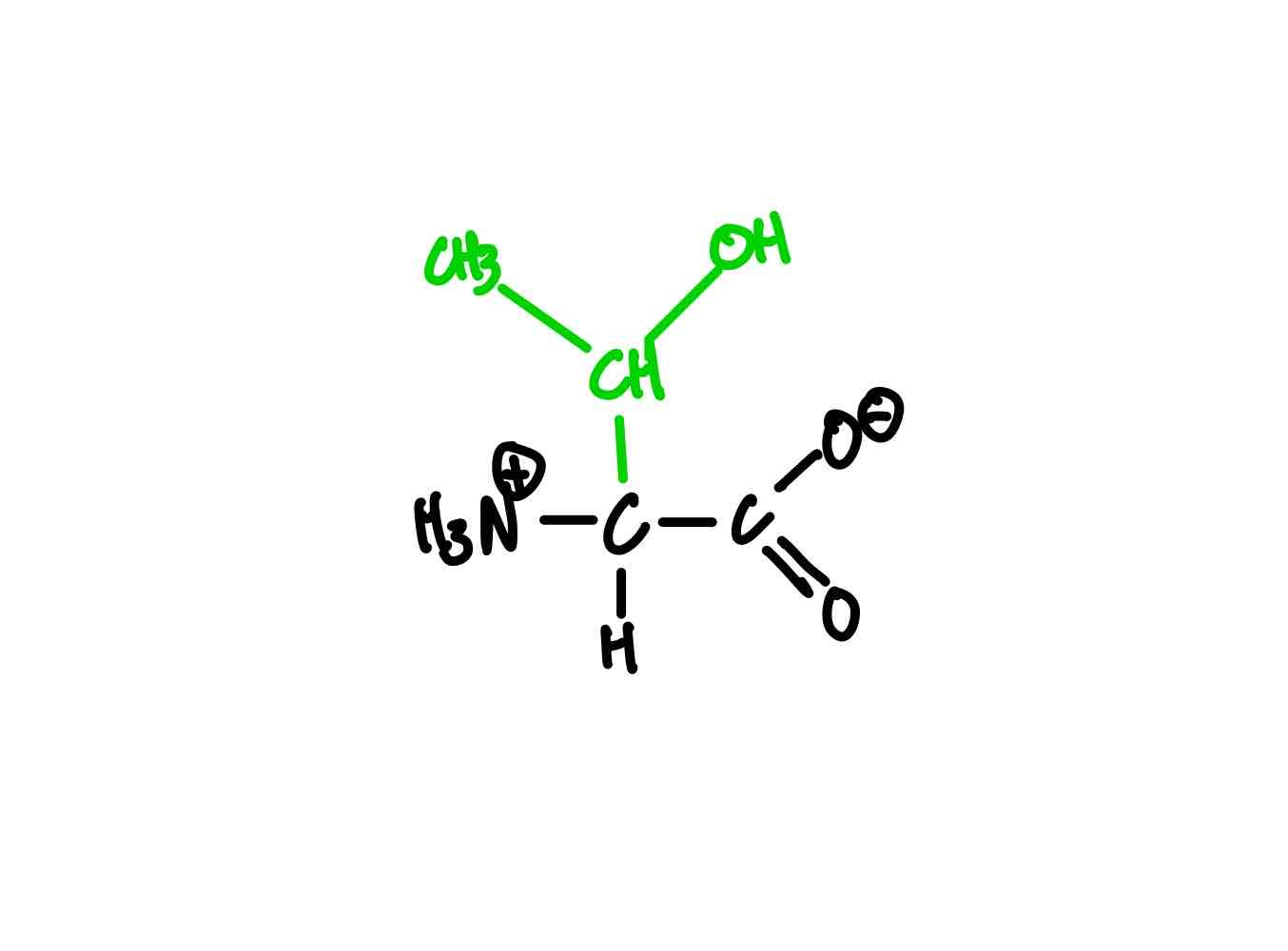
What’s the structure of cysteine?
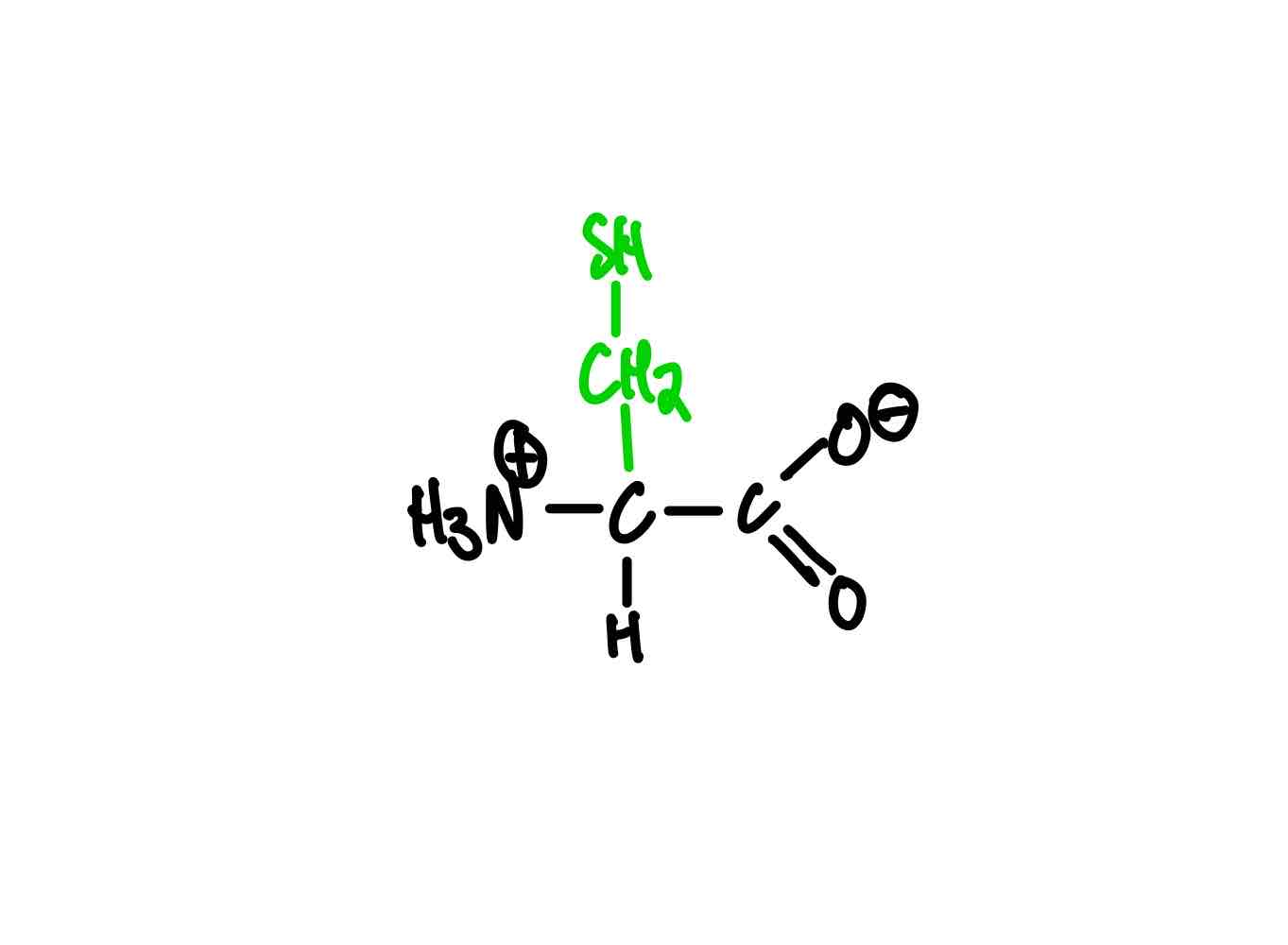
What’s the structure of asparagine?
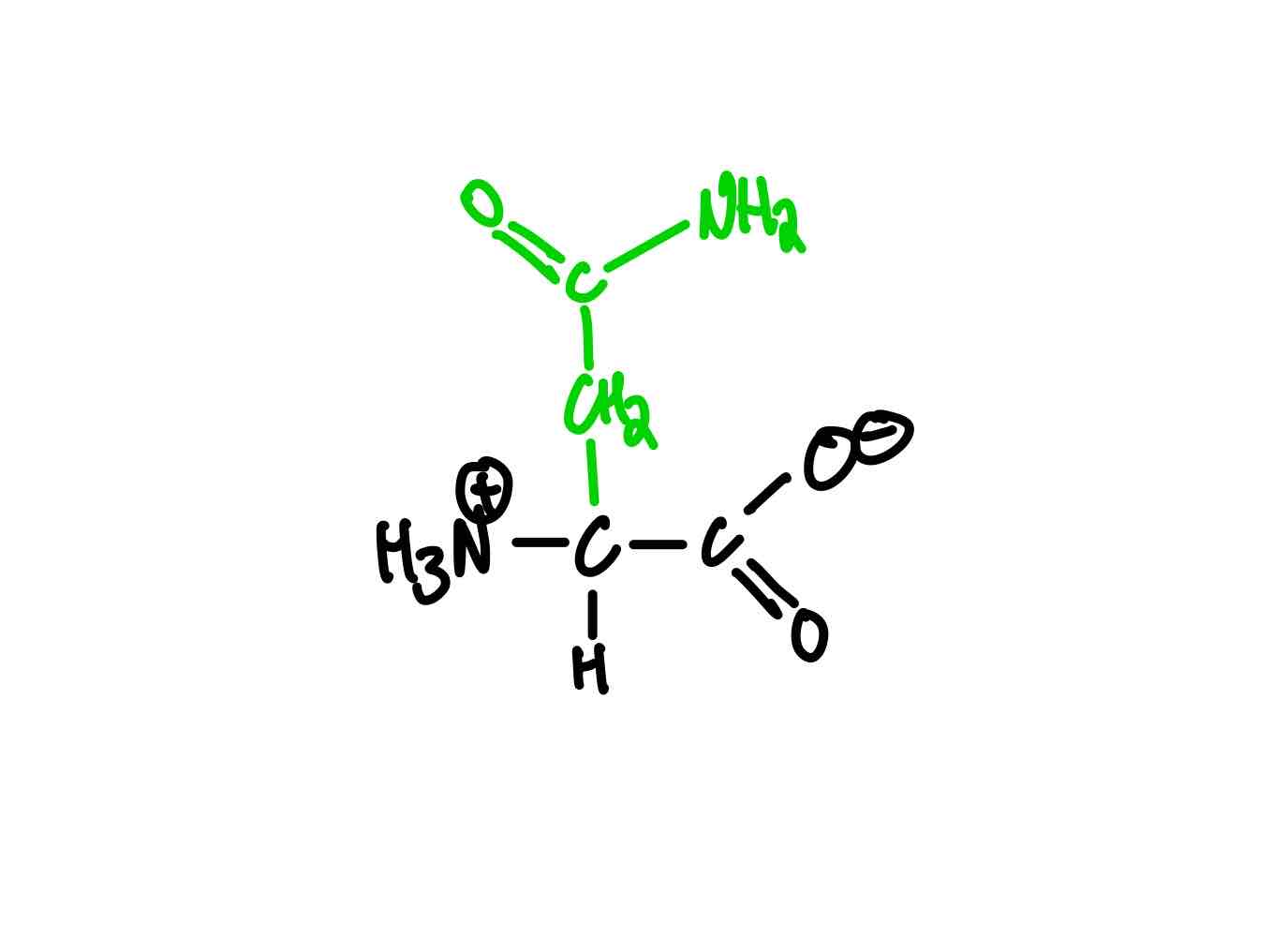
What’s the structure of glutamine?
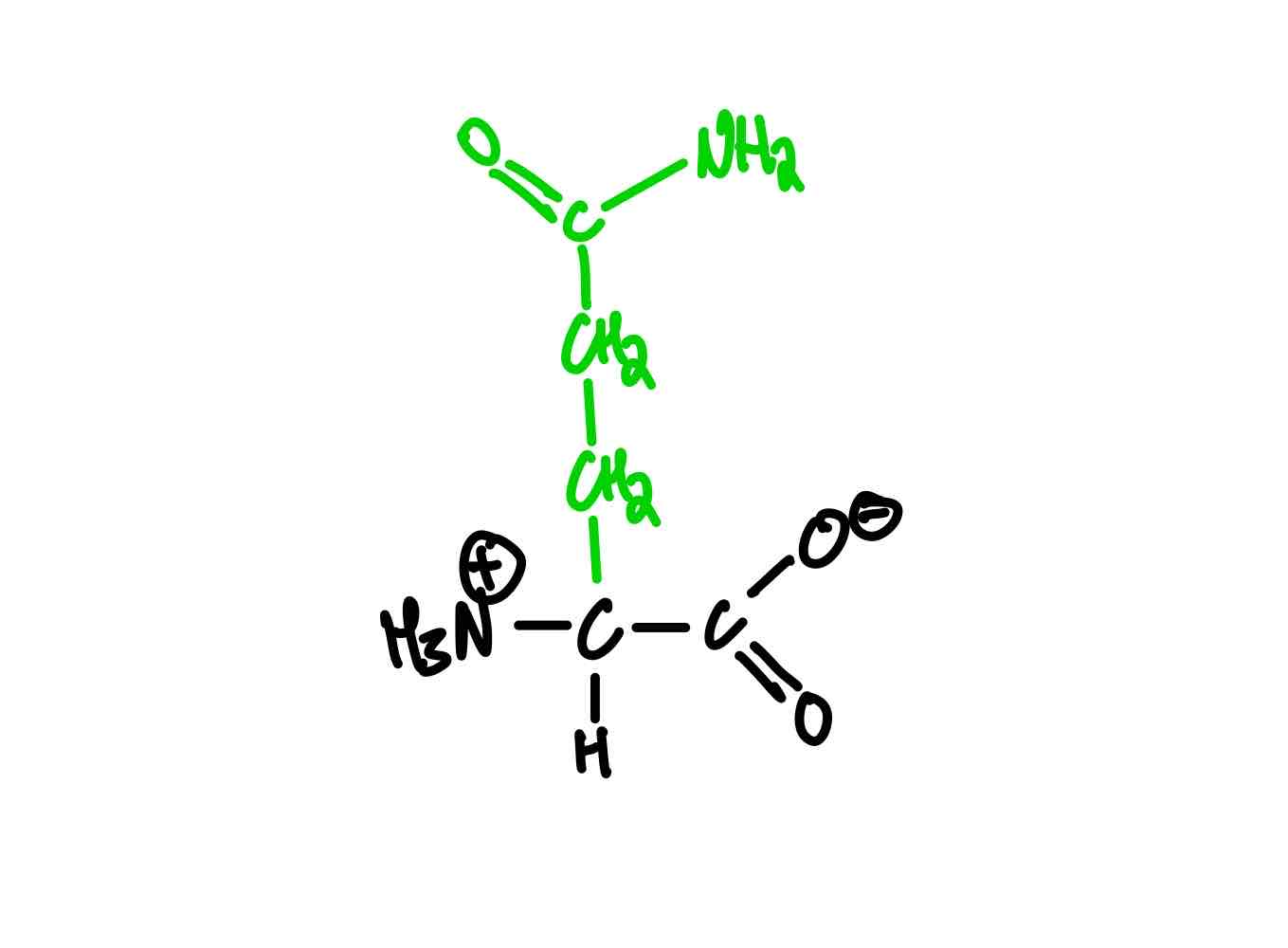
What are the two amino acids negative at pH of 7? Provide the full name, 3-letter abbreviation, 1-letter abbreviation, and pKa.
(Asp, D) Aspartic acid (protonated) / aspartate (deprotonated). pKa = 3.9.
(Glu, E) Glutamic acid (protonated) / glutamate (deprotonated). pKa = 4.2.
It is acidic, therefore it donated a proton already at pH of 7, and therefore bears a negative charge.
What’s the structure of aspartate?
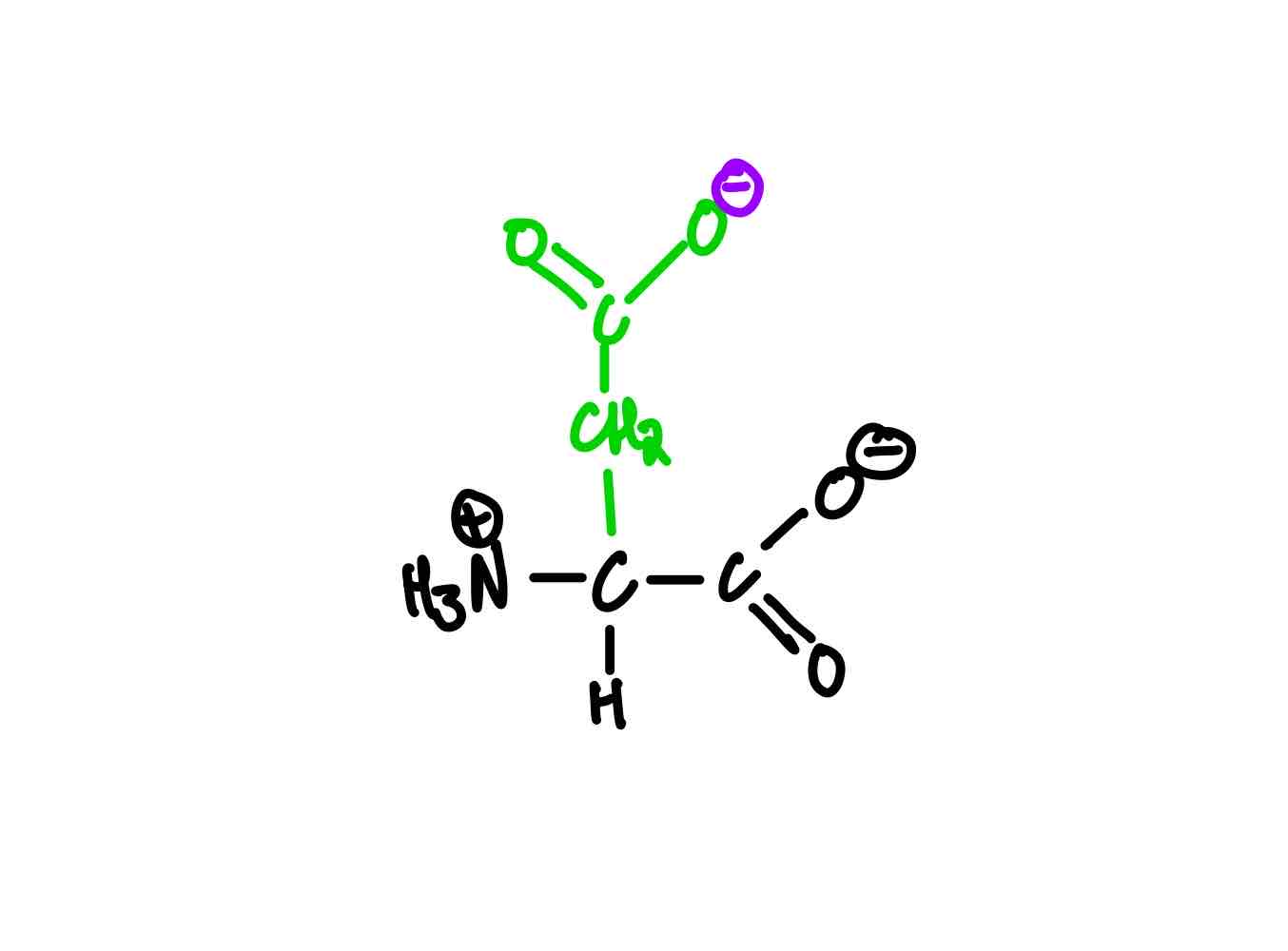
What’s the structure of glutamate?
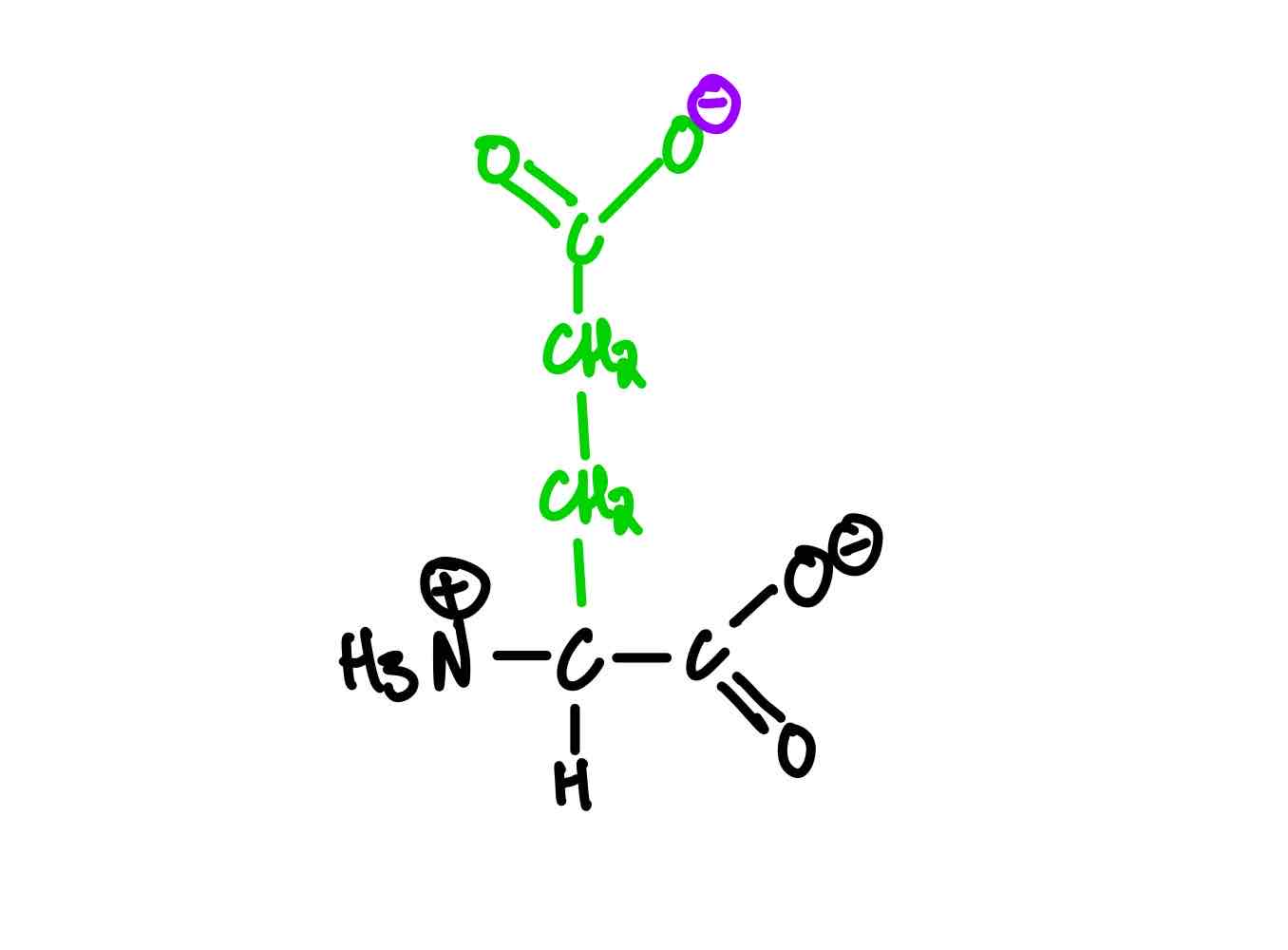
What are the three amino acids positive at pH of 7? Provide the full name, 3-letter abbreviation, 1-letter abbreviation, and pKa.
Lysine (Lys, K). pKa, = 10.5.
Arginine (Arg, R). pKa = 12.5.
Histidine (His, H). pKa = 6.0.
It is basic, therefore it accepted a proton already at pH of 7, and therefore bears a positive charge.
What’s the structure of lysine?
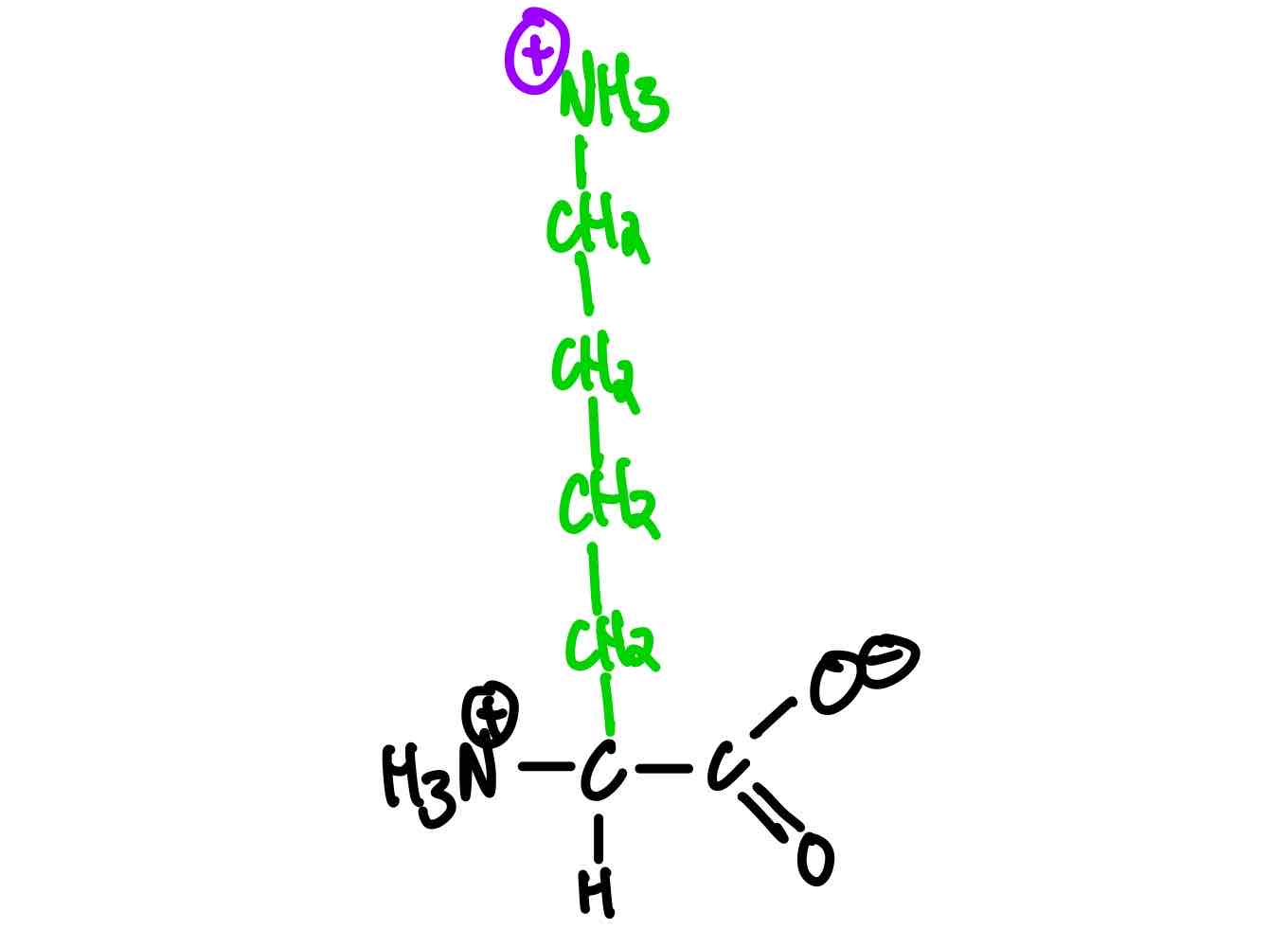
What’s the structure of arginine?
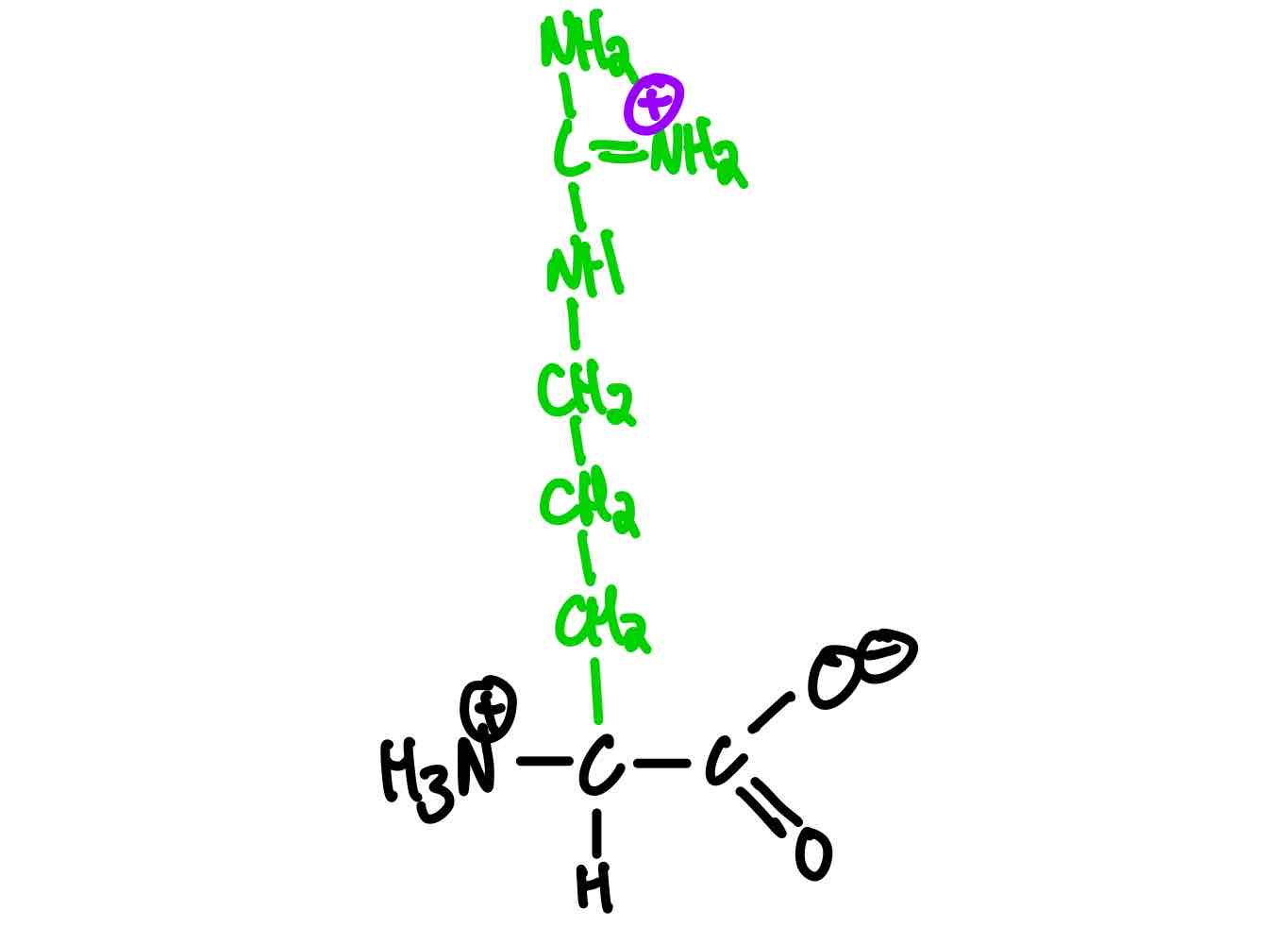
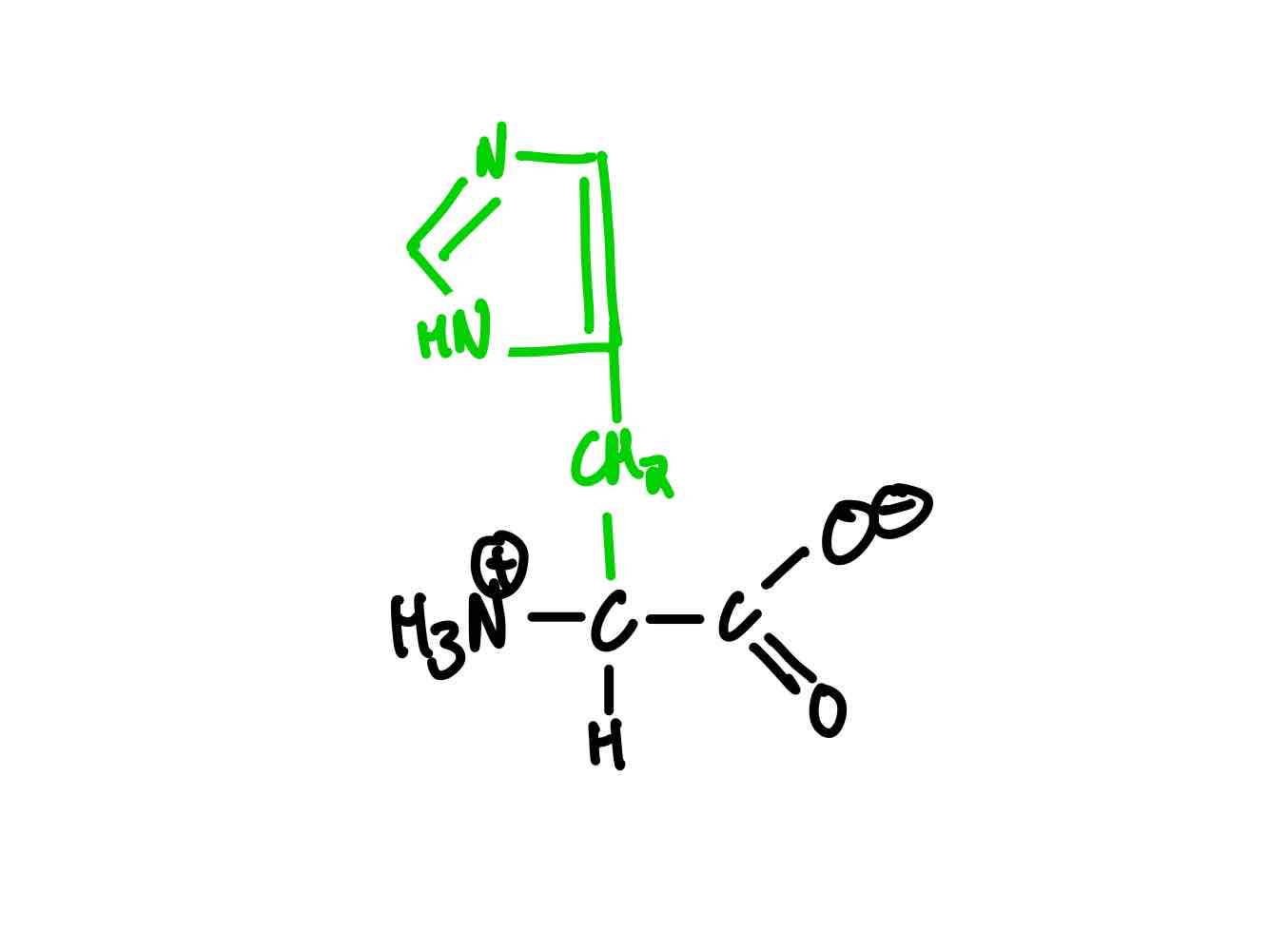
What’s the structure of histidine?
What’s the difference between molecular conformation and molecular configuration?
Molecular conformation = arrangement via bond rotation.
Molecular configuration = arrangement via connectivity.
Differentiate the two kinds of isomers: constitutional isomers and stereoisomers.
Constitutional isomers: same molecular formula, different constitution.
Stereoisomers: same molecular formula, same constitution, different arrangement in space.
Differentiate the three types of stereoisomers: conformational isomers, enantiomers, and diastereomers.
Conformational isomers, a.k.a. conformers, are stereoisomers that interconvert by low energy processes like bond rotations and chair flips.
Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images.
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable non-mirror images.
How do we use the “D” and “L” to assign molecular configuration?
D is when the amino group is on the right, opposite to hydrogen, which would be on the left.
L is when the amino group is on the left, opposite to hydrogen, which would be on the right.
How can you relate stereochemistry to biochemical processes via enzymatic activity?
> Enzyme has active site.
> Active site is specfic to one of two stereoisomers = enzyme specificity.
> Enzyme wants same molecule but w/ specific arrangement.
What is the formula to calculate the number of stereoisomers for one molecule?
2n = x, wherein n = # of chiral centres, and x is the # of stereoisomers.
In what configuration do amino acids naturally occur?
Amino acids naturally occur in the L configuration.