unit 7 developmental psychology
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
11th ap psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
developmental psychology methods
- biological/retrospective
- cross-sectional
- longitudinal
- cross-sequential
biological/retrospective study method
- participant's past is reconstructed through interviews and other research about their life
- advantages: in-depth and detailed study of one person
- disadvantage: personal recall may not be accurate
cross-sectional
- participants of various ages are compared at one point in time to determine age-related differences
- advantages: inexpensive, quickly completed, low attrition rate
- disadvantages: based on observations, differences may be attributed to group differences as opposed to age differences
longitudinal
- same participants are studied at various ages to determine age-related changes
- advantages: in-depth study revealing more detail, eliminates cohort differences
- disadvantages: expensive, time consuming, potentially high attrition rate
cross-sequential
- participants of various ages are compared at several points in time to determine both age-related differences and age-related changes (combination of cross-sectional and longitudinal)
- benefits: shortens length of research, easier to examine cohort effects beyond age
prenatal development
- period that extends from conception to birth, usually encompassing 9 months of pregnancy
- germinal → embryonic → fetal
germinal stage
- time period: 2 weeks
- zygote moves towards uterus; begins to implant in the lining
- placenta and umbilical cord begin to form
- cells begin to differentiate
embryonic stage
- time period: 6 weeks
- critical period
- major organs and structures begin to develop
fetal stage
- time period: week 8-40
- the fetus experiences tremendous growth
- muscles begin contract
- the baby moves into position
ctitical periods
- times during which certain environmental influences can have an impact on the development of the infant
- embryonic stage and imprinting
teratogens
- agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
- ex: alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, mercury
alcohol (teratogen)
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)- intellectual disability, delayed growth, facial malformations, smaller than normal head size
nicotine (teratogen)
miscarriage, low birth of weigh, still birth, short stature, intellectual disability
rooting reflex
a newborn's tendency when touched on the cheek, to turn toward the touch, open the mouth and search for the "nipple"
grasping reflex
a newborn's tendency to close fist around anything placed in their hand
startle/ moro reflex
a newborn's tendency to throw head back, extend arms, legs, cry and bring arms/legs back in when startled
sucking reflex
a newborn's tendency to suck on objects that are placed in mouth
babinski reflex
- stroke sole of foot from heel toes
- big toe lifts while others spread
stepping reflex
newborn's tendency to make stepping motions when held upright
how brain development unfolds
according to genetic instructions, causing various bodily and mental functions to occur in sequence
2-4 months (motor/movement milestones)
raising head and chest
2-5 months (motor/movement milestones)
rolling over
4-6 months (motor/movement milestones)
sitting up with support
6-7 months (motor/movement milestones)
sitting up without support
7-8 months (motor/movement milestones)
crawling
8-18 months (motor/movement milestones)
walking
schema
- concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
- mental molds of our experiences so the brain can build upon concepts
- ex: pointing to an apple and the child forms a concept for it
assimilation
- interpreting a new experience in terms of an existing schema
- ex: a child might see a cherry and say apple because both objects are red, round, and sweet
accomodation
- the process of adjusting/modifying a schema
- ex: how to correct the child, so they can alter the schema for cherry to differentiate between cherries and other fruits
piaget
- stages of cognitive development (thinking)
1. sensorimotor
2. preoperational
3. concrete operational
4. formal operational
piaget sensorimotor
- birth to 2 years
- use of senses and motor abilities to learn about the world/interact with objects in the environment
- object permanence
- habituation
- stranger anxiety
- separation anxiety
object permanence
- piaget sensorimotor
- awareness that objects continue to exist when not perceived
habituation
- piaget sensorimotor
- decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation
- ex: babies opening presents because they pay more attention to new objects than "habituated" ones
stranger anxiety
- piaget sensorimotor
- ex: a baby crying when taking photos with santa because he is unfamiliar
separation anxiety
- piaget sensorimotor
- ex: being upset when someone close to the baby leaves them
piaget preoperational
- 2 to 7 years
- children learn to use language as a means of exploring the world
- pretend play
- animism
- centration
- transductive reasoning
- egocentrism
- theory of mind
pretend play
- piaget preoperational
- make-believe activities
- ex: i used to pretend i was working at a store by merging two desks as a checkout counter
animism
- piaget preoperational
- giving inanimate objects characteristics of living things
centration
- piaget preoperational
- focusing on only one aspect of a situation at a time
transductive reasoning
- piaget preoperational
- belief that connection/similarities between two things are cause and effeect
egocentrism
- piaget preoperational
- inability to see another's perspective
theory of mind
- piaget preoperational
- children's ideas about their own and others' mental states; they come to understand views of others
piaget concrete operational
- 7 to 11 years
- children become capable of logical thinking processes
- conservation
- classification
- reversible thinking
- mathematical transformations
conservation
- piaget concrete operational
- knowing there's the same amount water when poured from one cup to another, even if one "looks" more full
classification
- piaget concrete operational
- grouping and organizing
reversible thinking
- piaget concrete operational
- things can be fixed
- ex: deflated balloon can be inflated (it is not broken)
mathematical transformations
- piaget concrete operational
- learning basic math
piaget formal operational
- 12 years to adult
- the adolescent becomes capable of abstract thinking
- abstract logic
- hypothetical thinking
- potential for mature moral reasoning
abstract logic
- piaget formal operational
- ability to understand theories (things that aren't right in front of you)
- ex: concept of numbers
hypothetical thinking
- piaget formal operational
- question rules
- ex: considering how long it will take to finish project
potential for mature moral reasoning
- piaget formal operational
- ex: is this fair?
fluid intelligence
- basic reasoning, memory capacity, and speed of information processing
- decreases as you age
- ex: grandparents can't work phone
crystallized intelligence
- accumulated knowledge
- increases as you age (because more experiences)
- ex: grandparents know more wisdom
lev vygotsky
- sociocultural theory
- stressed the importance of social interactions with other people, especially highly skilled children or adults, in the child's cognitive development
- scaffolding
- zone of proximal development
scaffolding
process in which a more skilled learn gives help to a less skilled learn, reducing the amount of help as the less skilled learner becomes more capable
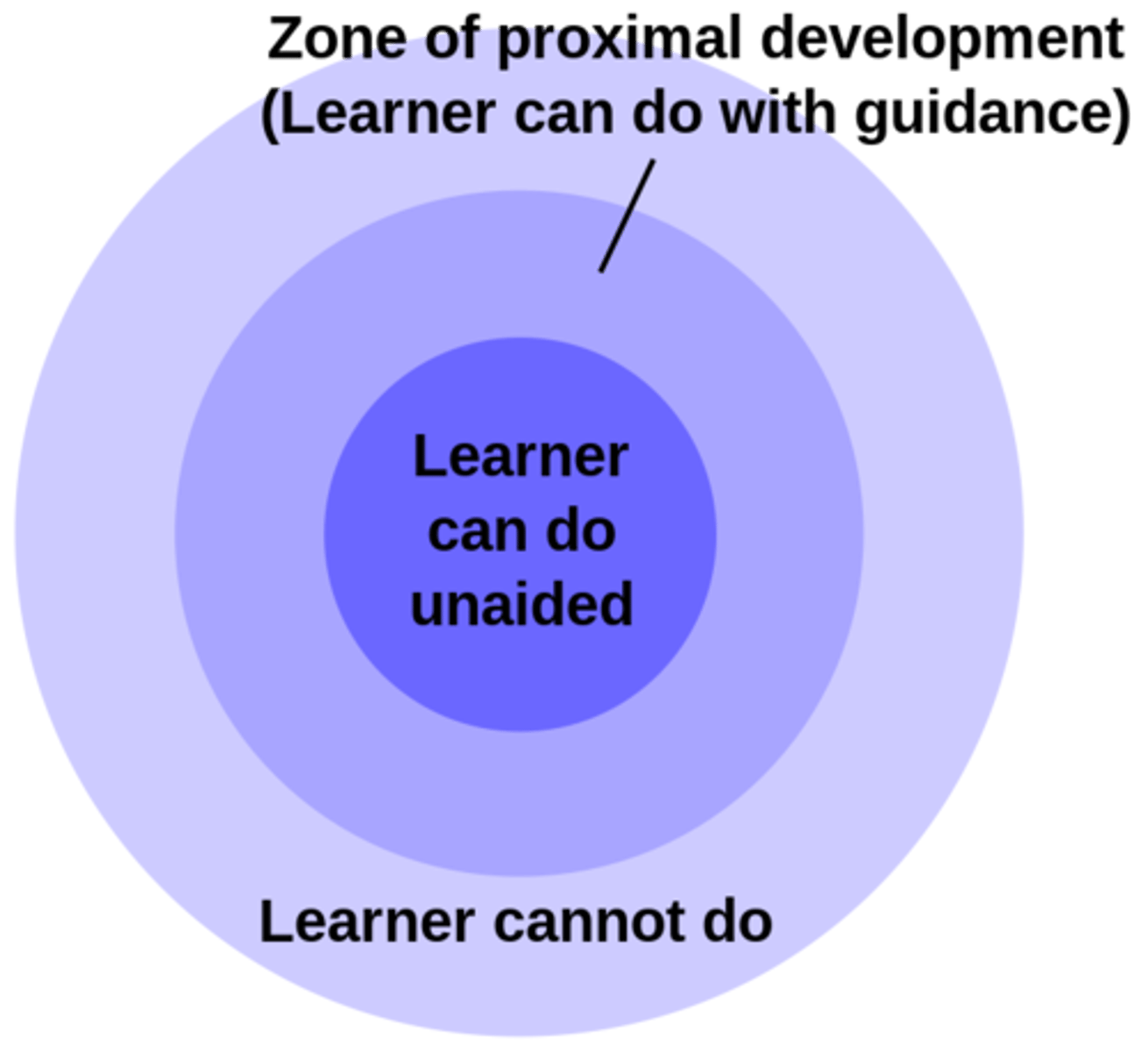
zone of proximal development
what kids can do alone vs what kids can do with help
kohlberg
- stages of morality
1. pre-conventional
2. conventional
3. post-conventional
kohlberg pre-conventional
- 3 to 7 years
1. punishment avoidance and obedience
2. exchange of favors
punishment avoidance and obedience
- kohlberg pre-conventional
- children focused on self-interest; consequences determine morality
- obey rules to avoid punishment or gain concrete awards
- ex: child who steals toy from another child does not see actions wrong unless punished
exchange of favors
- kohlberg pre-conventional
- child recognizes interests and needs of others but behaves morally to receive moral behavior
- self-interest remains
- ex: child shares with peers with understanding that peer will then share with him/her
kohlberg conventional
- 8 to 13 years
3. good boy/girl
4. law and order
good boy/girl
- kohlberg conventional
- child behaves morally to live up to expectations ("golden-rule thinking")
- maintain trust and loyalty
- overcome egocentric thinking (concerned about feelings and perspectives of others)
- ex: child arrives on time to class to avoid upsetting the teacher
law and order
- kohlberg conventional
- recognition and respect for law and order (importance of being a good citizen)
- understand large social system (need for social order)
- ex: child criticizes parents for speeding because it is against the law
kohlberg post-conventional
- adulthood
5. social contract
6. universal ethical principles
social contract
- kohlberg post-conventional
- morality vs legality: some laws are better than others
- what's moral might not be legal
- recognizes laws should still be followed (societal respect for individual values and beliefs)
- ex: county tax is excessive and the law needs to be changed but you would still pay the tax
universal ethical principles
- kohlberg post-conventional
- individual's judgements based on belief in universal ethical principles (person holds to ethical principles regardless of law)
- morality determined by individual's own consciousness
- ex: individual helping a runaway slave in pre-civil war america
carol gilligan
- criticized kohlberg's theory of being only males
- proposed men and women have different perspectives on morality
- men's actions lead to a fair or just end
- women's actions are nonviolent and hurt the fewest people
attachment
- the emotional bond between an infant and the primary caregiver
- demonstrated by a child's "closeness-seeking" and distress upon separation
- develops within the first six months of life
- two types: contact and familiarity
attachment through contact
- humans form a bond with those who care for them in infancy; based upon interaction with caregiver
- harry harlow
harry harlow
- studied attachment through contract by looking at baby monkeys and wired mother monkeys
- role of physical contact, "comfort contact" in attachment
attachment through familiarity
- occurs in many species of animals during a critical period
- konrad lorenz and imprinting
konrad lorenz
studied attachment through familiarity by imprinting
imprinting
- attachment through familiarity
- tendency to follow the first moving object seen as the basis for attachment
- ex: baby ducks following a nearby dog
mary ainsworth
- the "strange situation"
- studied attachment styles
characteristics of attachment
- proximity maintenance
- safe haven
- secure base
- separation distress
proximity maintenance
desire to be near those which we are "attached"
safe haven
returning to attachment figure for comfort and safety
secure base
attachment figure acts as base of security
separation distress
anxiety in absence of attachment figure
secure attachment
- most common
- willing to explore ("touched base")
- wary of strangers: calm so long as mom is nearby
- ex: when mom leaves, infant is noticeably upset until mom returns
- possible issues in adulthood: secure attachment
avoidant attachment
- only somewhat willing to explore
- did not "touch base"
- did not look at strangers
- reacted very little to mothers absence or to her return
- possible issues in adulthood: dismissive-avoidance attachment (not interested in pursuing relationships)
ambivalent attachment
- unwilling to explore (clingy)
- very upset by strangers regardless of mother's presence
- very upset by mother's departure and not easily soothed upon return (may push mother away upon return)
- possible issues in adulthood: preoccupied attachment
disorganized-disoriented attachment
- generally fearful, dazed, and depressed expression
- unable to decide how they should react to mother's return (little to no eye contact)
- child's caregiver, a source of safety, become a source of fear (inconsistent behavior of parent creates confusion for child)
- possible issues in adulthood: fearful-avoidant attachment
deprivation of attachment
- impact on denying monkeys physical comfort from their mothers
- genie (girl trapped in room and missed her critical period)
- physical development: smaller
- cognitive development: not forming neural connections
- language production: can learn words but not sentences/grammar
baumrind
- parenting styles
- authoritarian
- permissive
- authoritative
authoritarian
- strict parenting style
- impose clear set of rules and expect obedience; controls most of decision-making
- sets family goals, give rewards, and handles punishment
- more directive; provides greater structure
- can be confrontational
- can be effective if used with loving/caring approach
- researching finding: leads to fewer social skills and lower self-esteem issues
permissive
- lenient parenting style
- more submissive to children's desires
- make few demands and use little punishment
- broad boundaries (encourage freedom of expression)
- promotes more maturity and self-responsibility
- more trail and error, more discussion
- research finding: leads to more aggressive and immature behavior in younger children
authoritative
- mixture of the other parenting styles
- parent is both demanding and responsive
- attentive and sensitive to child's needs
- family operates like team and decision-making is more democratic
- set and enforce rules, but explains reasoning
- encourages discussion
- discipline is opportunity for teachable moments
- research finding: leads to higher self-esteem, self-reliance, and social competence
erikson
- stages of psychosocial development
1. infancy: trust vs mistrust
2. toddlerhood: autonomy vs shame and doubt
3. preschool: initiative vs guilt
4. elementary school: industry vs inferiority
5. adolescence: identity vs role confusion
6. young adulthood: intimacy vs isolation
7. middle adulthood: generativity vs stagnation
8. late adulthood: integrity vs despair
infancy (erikson)
- birth to 1 year
- children learn ability to trust others (based on caregiver)
- trust develops = confidence and security
- unsuccessful completion = inability to trust (sense of fear, anxiety, insecurity)
- trust: needs dependably met through reliability, care, and affection
- mistrust: needs not being met
toddlerhood (erikson)
- 1 to 3 years
- children begin to asset independence
- encouragement and support leads to confidence
- children criticized, or overly controlled, feel inadequate and may become overly dependent on others
- autonomy: personal control and sense of independence
- shame and doubt: failure leads to doubt in abilities and experience of shame
preschool (erikson)
- 3 to 6 years
- children asset control, or power, over surrounding environment (mimic/help parents)
- initiative: given opportunities, feels secure in abilities, success equals sense of purpose
- guilt: children criticized/controlled, disapproval
elementary school (erikson)
- 6 years to puberty
- coping with new social settings and demands
- children develop pride in accomplishments
- industry: if children are encourage and reinforced, they develop confidence and sense of competence
- inferiority: failure to meet demands of new social situation leads to feelings of inferiority, its efforts are restricted, child doubts ability
adolescence (erikson)
- teen years to 20
- premier challenge of adolescence is the struggle to form a clear sense of identity
- identity: development of sense of self and personal identity
- role confusion: confusion about self-concept and sense of belonging
young adulthood (erikson)
- 20 to early 40s
- share ourselves more intimately with others (long term commitments)
- intimacy: success leads to sense of comfort, commitment, safety, and security
- isolation: feelings of loneliness and isolation
middle adulthood (erikson)
- 40s to 60s
- establish careers, settle down in relationships, and begin families
- generativity: sense of contribution and usefulness through family/children, work/career, and community involvement
- stagnation: failure to achieve creates feeling of stagnation, lack of purpose, shallow involvement in society
late adulthood (erikson)
- late 60s and up
- our productivity slows in late adulthood and we contemplate accomplishments
- integrity: sense of satisfaction and fulfillment in looking back at accomplishments
- despair: feeling of regret and bitterness due to failure or goals not accomplished, can lead to depression and hopelessness
freud
- psychosexual stages of development
1. oral
2. anal
3. phallic
4. latency
5. genital
oral (freud)
- birth to 2 years
- children derive pleasure from oral activities (chewing, sucking)
- developmental issues: delayed process = child resist growing up and becomes manipulative, interrupted process = oral fixation (eating, smoking) and dependence on things
anal (freud)
- 2 to 3 years
- toilet training
- developmental issues: parents too demanding = children obsessed with order (anal retentive), parents not demanding enough = child is messy or careless (anal expulsive)