unit 5 econ final review
1/23
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
perfectly competitive labor market
- many small firms hiring workers
- workers with identical skills
- constant wage
- firms hire at a wage set by the industry (workers are wage takers)
derived demand
the demand for resources is determined (derived) by the products they help produce
marginal resource cost (MRC)
- additional cost of an additional resource (worker)
- MRC = wage set by market and is constant in perfectly competitive labor markets
- Δtotal cost/ Δinputs
marginal revenue product (MRP)
- additional revenue generated by an additional worker (resource)
- MRP = marginal product of resource x price of product
- Δtotal revenue/ Δinputs
MRP = MRC
continue to hire until
demand for labor
different quantities of workers that firms will hire at different wages
law of demand for labor
inverse relationship between wage and quantity of labor demanded
supply for labor
different quantities of workers that are willing to work at different wages
law of supply for labor
direct relationship between wage and quantity of labor supplied
tradeoff
work and leisure for workers
firms
demanders of labor
individuals
suppliers of labor
higher wages
gives workers incentives to leave other industries or give up leisure activities
wage/ price of labor
set by the market
demand for product increases
MRP increases causing demand to shift right
shifters of resource demand
- changes in demand for product
- changes in productivity
- changes in price of other resources (substitutes, complements)
shifters for supply of labor
- number of qualified workers
- gov regulation/licensing
- personal values (leisure, societal roles)
labor market imperfections/ reasons for wage differences
- misleading job information
- geographical immobility
- unions
- wage discrimination
minimum wage
- gov sets up wage floor to help workers bc the equilibrium wage is too low
- result: Qd ↓, Qs↑
least cost rule
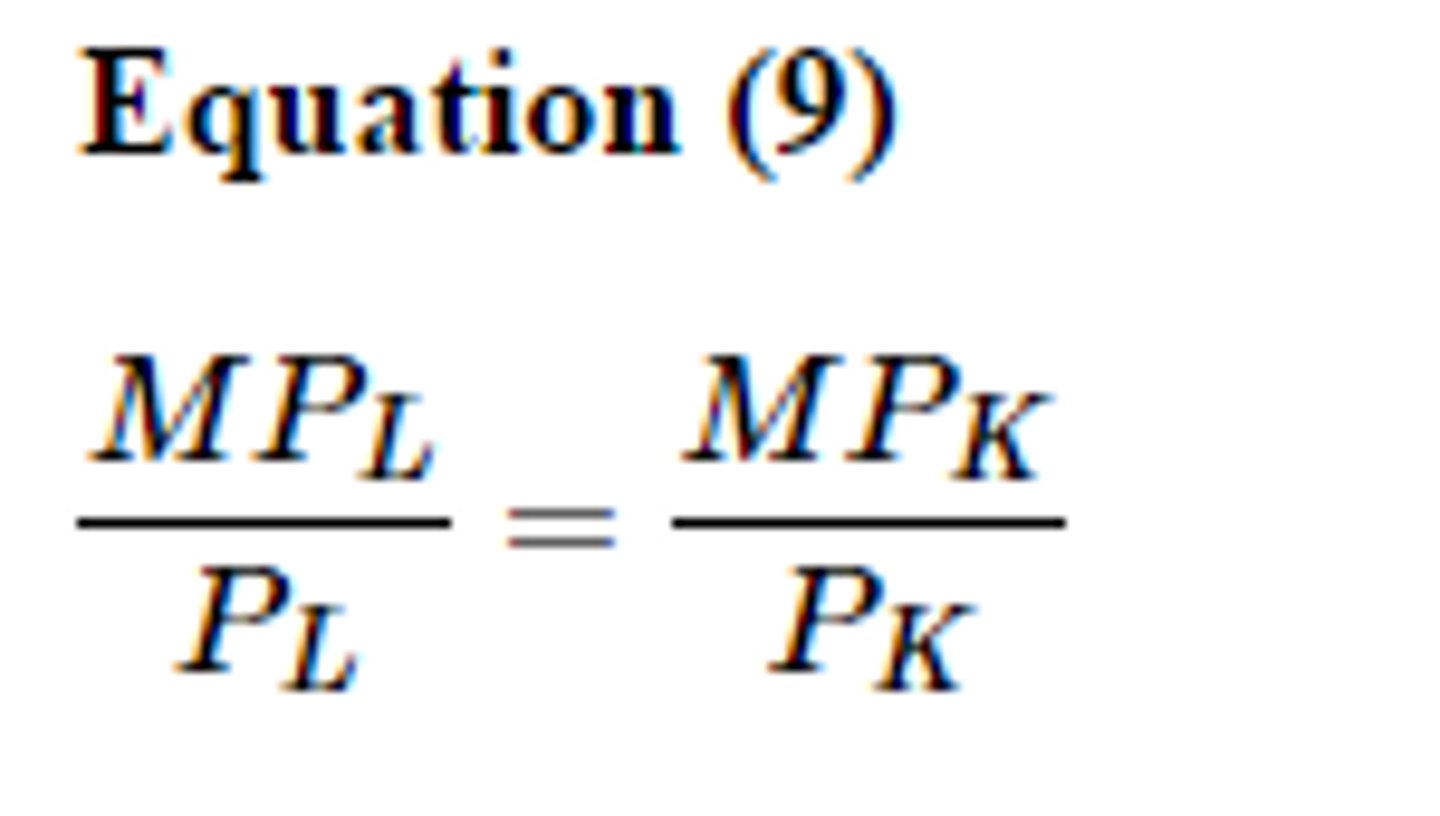
monopsony
- one firm hiring workers
- workers relatively immobile
- wage maker: increase wage to hire additional workers
how unions increase wage
- convince consumers to buy only union products
- lobbying gov officials to increase demand
- increase price of substitute resources
nondiscriminating monopsony
employer who must increase the wage offered to all workers in order to attract more workers (MCL > wage)
discriminating monopsony
- pays the higher wage only to the extra worker (MCL = wage)
- illegal if based on gender, age, religion, or race
- tends to be cheaper